Psychoactive drugs
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
1
New cards
Recreational use
solely for enjoyment or effects
2
New cards
Therapeutic use
treat physical/ mental ailment
3
New cards
Psychoactive drug
A chemical substance that is natural or synthetic which alters brain and nervous system function, leading to changes in perception, affect/feelings, mood, consciousness, thoughts and behavior. Examples include caffeine, alcohol, marijuana, and cocaine.
4
New cards
What is a Chemical name?
A unique name given to a chemical substance for scientists based on its chemical composition and molecular structure. It is used to identify and differentiate between different chemical compounds.
5
New cards
What is a Generic name for a psychoactive drug?
A **generic name** is a name created by the drug developer and accepted by a scientific body that indicates the drug’s classification.
6
New cards
What is a Brand/ proprietary name for a psychoactive drug?
a **proprietary** or **brand name** is registered/patented by the manufacturer/company as a trademark and refers specifically to their drug product.
7
New cards
What is the chemical name for xanax?
8-Chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-s-triazolo \[4,3-α\] \[1,4\] benzodiazepine.
8
New cards
What is the generic name for Xanax?
alprazolam
9
New cards
what is the brand name for alprazolam?
xanax
10
New cards
Therapeutic use
**Therapeutic use** is the administration of a medication to treat a physical or mental ailment.
11
New cards
Recreational use
**recreational use** is the taking of a drug solely to enjoy or experience its pharmacological effects
12
New cards
Drug use
**drug use** means taking a drug properly in its correct dosage.
13
New cards
Drug misuse
Improper or excessive usage of a drug is **drug misuse. Misuse can be intentional or accidental.**
14
New cards
Example of drug use
Most people have used drugs this way such as by taking an aspirin to relieve a headache or drinking a beer.
15
New cards
Examples of drug misuse
* Injecting heroin to get high.
* Taking prescription opioids to experience relaxation instead of to relieve pain.
* Prematurely stopping a prescribed antibiotic treatment.
* stopping meds that should be tapered
* Taking twice the recommended dose because the regular amount isn’t effective enough. (taking a higher dose)
* Using someone else’s prescription medicine.
* Taking prescription opioids to experience relaxation instead of to relieve pain.
* Prematurely stopping a prescribed antibiotic treatment.
* stopping meds that should be tapered
* Taking twice the recommended dose because the regular amount isn’t effective enough. (taking a higher dose)
* Using someone else’s prescription medicine.
16
New cards
drug abuse
using a substance in a manner, amount or situation that causes problems socially, physically, psychologically, occupationally (totality of circumstances : if its one time not considered abuse)
17
New cards
drug dependence
drug use is so frequent and consistent it is difficult for your body to function without substance body adapts to the presence of drug can be physical/ psychological (body changes → dependence)
18
New cards
drug addiction
Compulsive drug use that continues despite awareness of its harmful consequences
19
New cards
drug addiction does not equal drug use does not equal drug abuse does not equal drug misuse does not equal drug dependence
true
20
New cards
Drugs are not good or bad
true
21
New cards
drugs have multiple effects and you can't choose which you get
true
22
New cards
Why is it a problem to blame the drug?
* Ignore factors that lead to abuse and addiction
* attempt to eliminate the substance
* attempt to eliminate the substance
23
New cards
What personality factors influence drug use?
Sensation seeking and impulsivity
24
New cards
Risk
Increased likelihood of drug use
25
New cards
Protective
Decreased the likelihood of drug use
26
New cards
Drug use has been around for thousands of years
true
27
New cards
What are the three main reasons for a drug use?
* Spiritual use
* Economic
* Treat illness
* Economic
* Treat illness
28
New cards
Why is understanding drug use difficult?
* Not having accurate & complete data ex: surveys in school miss a large population (those who do not attend school)
* Isolating root cause of drug use
* Isolating root cause of drug use
29
New cards
Two categories of problems
1. Actual drug use consumption of drug (OD’s, dependence)
2. Social Problems- indirect problems (jail, work & relationships.)
30
New cards
History of drugs
* Almost no regulations in the 1800s in the US
* Early 1900s brought regulations because the government was “protecting us- drugs were too dangerous”
* Early 1900s brought regulations because the government was “protecting us- drugs were too dangerous”
31
New cards
Three main concerns that lead to regulations of drugs
1. Toxicity- drug toxicity
2. Dependence and addiction
3. Crime
32
New cards
one main concern that led to regulations of drugs is crime what are some of the stats for crime?
* Criminal behavior precedes drug use
* Alcohol is linked to violent crime
* Over half of all homicides involve alcohol
* 1/3 of sexual assaults reported involves alcohol
* 2/3 of all domestic violence situation involves alcohol
* Alcohol is linked to violent crime
* Over half of all homicides involve alcohol
* 1/3 of sexual assaults reported involves alcohol
* 2/3 of all domestic violence situation involves alcohol
33
New cards
illicit drugs
illegal to sell, use, or possess
34
New cards
### 3 thing that shows that gove isnt “protecting us”
* Current laws don't represent rationally devise plans aren't based on research
* policies are reactive versus proactive
* Ineffective at addressing major concerns
* policies are reactive versus proactive
* Ineffective at addressing major concerns
35
New cards
War of drugs in 2023 how much did the US spend on the War of drugs
42\.5$ billion
36
New cards
what percentage does the DEA intercept illicit drugs?
10%
37
New cards
Drug OD rarely happen with a single drug it is most often a combo of sedatives/depressants
true
38
New cards
Drug illegal Prohibition
Criminalized sale used possession manufacture
39
New cards
Drug decriminalization
* Use, possession (of specific amount) acquisition not criminal (no Jail) but punishable by fines and citations
* Manufacture and sale still criminal
\
* Manufacture and sale still criminal
\
40
New cards
What does drug decriminalization not address
Drug purity or violence from drug trafficking
(not regulated not safe drug)
(not regulated not safe drug)
41
New cards
Drug legalization
Nothing criminal; sale, use, possession, manufacture legal
42
New cards
Nervous system is made of?
Central nervous system & peripheral nervous system
43
New cards
What is the central nervous system?
Brain + spinal cord
44
New cards
What is the peripheral nervous system?
Everything else besides brain and spinal cord
45
New cards
What parts does the peripheral nervous system have?
Automatic and somatic
46
New cards
What is the automatic part of the peripheral nervous system?
It is the involuntary system and it is made up of sympathetic and parasympathetic
47
New cards
What is sympathetic part of the peripheral nervous system's automatic (involuntary) part?
Increased elevates fighter flight (any threat)
48
New cards
What is parasympathetic part of the peripheral nervous system's automatic (involuntary) part?
Decreases brings us down
49
New cards
What is the somatic part of the peripheral nervous system?
voluntary muscle movement
50
New cards
What role does a nucleus accumbens play?
Plays a critical role in the word and development of addiction
51
New cards
Neuron
Analyze + transmit information a.k.a. communication
52
New cards
glia
Neuron support
* Firmness/structure
* Greek word for glue
* Common knowledge myth is 10 glia : 1 neuron ratio but it is actually closer to 1 glia to 1 neuron ratio
* Firmness/structure
* Greek word for glue
* Common knowledge myth is 10 glia : 1 neuron ratio but it is actually closer to 1 glia to 1 neuron ratio
53
New cards
nerve conduction
* Neuron are polarized (different charge inside of cell verses outside)
* Blocking the ion channels prevents action potential (neuron firing)
* Blocking the ion channels prevents action potential (neuron firing)
54
New cards
Action potential
Electrical signal that initiates the chain of events
55
New cards
Action potential
“All-or-firing” neuron fires then action potential neurotransmitters are released. Excitatory- makes it easier to fire inhibitory- makes it less likely to fire
56
New cards
Life of a neurotransmitter
1. Precursors in the blood
2. Uptake- select precursors taken from the bloodstream to cell
3. Synthesis- precursor synthesized (through enzyme action) into neurotransmitter
4. Storage- neurotransmitter stored in synaptic vesicle
5. Release- when action potential arrives at vesicle the neurotransmitter is released so the release happens from the presynaptic neuron
6. Binding neurotransmitter binds into receptor on postsynaptic cell
7. Metabolismo any of the the unbound neurotransmitters will either be
1. Reuptake- taking back into the presynaptic neuron
2. Cleared from synaptic gap (cleff)
57
New cards
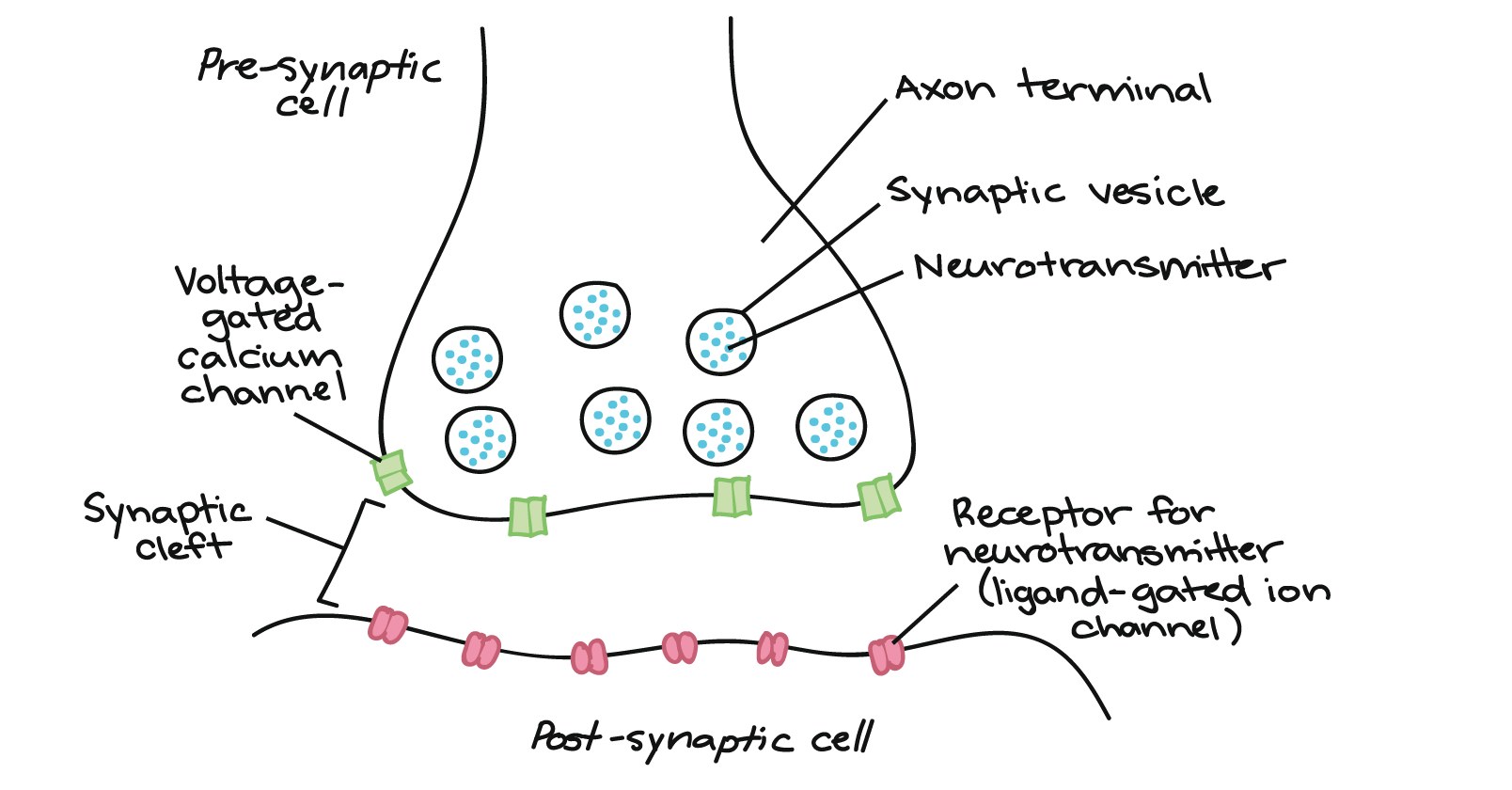
what does a post synaptic (dendrite) and presynaptic neuron (axon terminal) look like interacting?
this there is also antagonist Agnes receptors synaptic vesicles that you see in there. It's like a lock and key there's also a master key & a key that works in some places
58
New cards
What does Agonist do
Holds the door open
59
New cards
What does an antagonist do
Hold the door closed
60
New cards
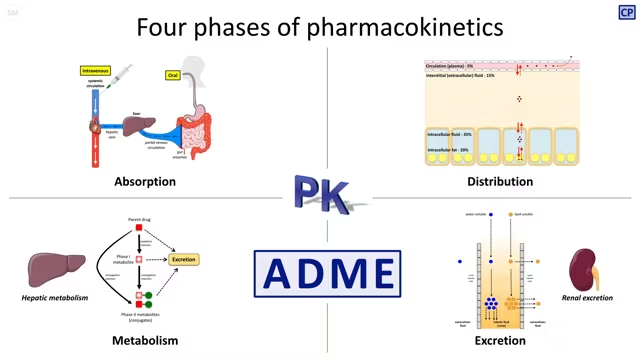
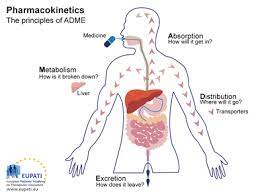
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion
61
New cards
First step of pharmacokinetics: Absorption
* Bioavailability= amount of drug that gets into bloodstream
* absorption rate varies by drug
* Both are impacted by route of admin (how do you get drug into body)
* absorption rate varies by drug
* Both are impacted by route of admin (how do you get drug into body)
62
New cards
Fastest routes
Fastest routes:
1. Smoking is the fastest method of administration (5-8 seconds)
2. Insufflation: 10-12 seconds
3. IV: around 15 seconds
1. Smoking is the fastest method of administration (5-8 seconds)
2. Insufflation: 10-12 seconds
3. IV: around 15 seconds
63
New cards
Bioavailability
The amount that does get absorbed is termed **bioavailability**, expressed as a percentage of the amount administered that enters the circulation.
64
New cards
Distribution
Drug bind to blood plasma protein and albumin
65
New cards
Distribution: what does higher affinity and low affinity mean?
High affinity equals more likely to bind
Low affinity equals less likely to bind
Low affinity equals less likely to bind
66
New cards
Binding helps with storage and balance
true
67
New cards
Binding of drugs: Higher amount bound to protein albumin equals less free molecules
True
68
New cards
Distribution: Binding of drugs: only free molecules have therapeutic effect because bound can't believe bloodstream
true
69
New cards
Drugs with high affinity will displace (pushoff) drugs with low affinity from the albumin
true
70
New cards
Does alcohol have low affinity or high affinity?
Low affinity
71
New cards
Does THC have low affinity or high affinity?
High affinity
72
New cards
Hi affinity needs higher effective dose
true
73
New cards
Bound drug molecules can't cross blood brain barrier
true
74
New cards
What is the blood brain barrier?
Filter that protects the brain
75
New cards
Small lipophilic molecules pass easier through the blood brain barrier
true
76
New cards
Cerebral trauma disrupts blood brain barrier and makes the barrier less effective
true
77
New cards
Effective dose → ED50
Dose that produces a meaningful effect and 50% of the population
78
New cards
Lethal dose → LD50
Dose that is lethal in 50% of the population
79
New cards
Toxic dose → TD50
Dose that is toxic but not lethal in 50% of the population
80
New cards
What is the therapeutic window?
Between the effective dose and the toxic/lethal dose
81
New cards
Therapeutic index
TD50/ED50 or LD50/ED50 this is used traditionally to determine drug safety and should always be greater than 1
82
New cards
Certain safety index
TD1 or LD 1 ÷ ED99 (near guaranteed response) (the one means what is the toxic dose and 1% what is the lethal dose in 1% and that's divided by the nearest guaranteed response of effective dose)
83
New cards
Time dependent factors
Onset, duration and termination of drug affects
* Route of admin
* How rapidly is drug absorbed and distributed
* How is drug eliminated from body
* Route of admin
* How rapidly is drug absorbed and distributed
* How is drug eliminated from body
84
New cards
Would taking additional doses before drug is fully out of system lead to compounding effects
yes
85
New cards
Metabolism (liver)
The drug form is changing in the liver,
* Enzyme breaks down drug molecules into metabolites (“mini-me”)
* metabolites are easier to remove from body through excretion
* active metabolites have physiological effects similar to parent drug.
* Enzyme breaks down drug molecules into metabolites (“mini-me”)
* metabolites are easier to remove from body through excretion
* active metabolites have physiological effects similar to parent drug.
86
New cards
Is it true that active metabolites have physiological effects similar to parent drug.
yes it is
87
New cards
is it true metabolites are easier to remove from body through excretion?
yes its “mini me” of drug molecules !!!
88
New cards
CYP50 enzyme are most important in?
drug metabolism (breaking things down)
89
New cards
Anytime foreign molecules (drug) are detected more CYP50 enzymes are produced to return to homeostasis
true
90
New cards
Excretion
drug molecules leaves body unchanged (most often kidneys) mostly through urine but can be through sweat feces tears breath bile saliva & mothers milk (semen)
91
New cards
MOA
Mechanism of action
92
New cards
Mechanism of action
Alters neurotransmission
93
New cards
Drug interactions
Additive effect and synergistic effect
94
New cards
Drug interaction additive effect
Drugs have similar effects to what you would expect DA1 plus DB1 equals D2
95
New cards
drug interactions synergistic effect
Drugs interact and multiply affects can't predict what you're gonna get DA1 + DB1 = D3
96
New cards
Specific effects
Only happen when chemical compound is present
97
New cards
Nonspecific effects
Placebo effects
98
New cards
Nonspecific (placebo) effects
Real effects but come from a unique combo of factors not the chemical compound (the drug itself) **Placebo effects**
99
New cards
What factors could affect your nonspecific placebo effects?
Perceptions/ expectations/ background are what affect your nonspecific placebo effects
100
New cards
Threshold
Lowest dose that produces a measurable response