12+13
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Problem
An obstacle between a current state and a goal, where the solution is not immediately clear.
Gestalt Approach to Problem Solving
Emphasizes problem-solving as perceiving the problem's structure correctly and restructuring mental representations.
Restructuring
The process of reorganizing mental representations to find a solution without the need for mathematical equations.
Insight
A sudden comprehension or realization leading to a solution, involving a reorganization of mental representations.
Fixation
A major obstacle in problem-solving where focus on specific characteristics hinders finding a solution.
Functional Fixedness
A type of fixation where familiar functions of objects impede problem-solving by limiting alternative uses.
Mental Set
A preconceived notion about problem-solving approaches based on past experiences.
Means-End Analysis
A strategy to reduce the difference between initial and goal states by setting subgoals.
Analogical Transfer
Using the solution to a similar problem to guide the solution of a new problem.
Expertise in Problem Solving
Experts invest time in deliberate practice, possess domain-specific knowledge, and organize information based on underlying principles.
Analytical Approach
Experts invest time in problem analysis before solving them, leading to more effective solutions.
Domain-Specific Expertise
Expertise is specialized and may not transfer to unrelated fields, hindering out-of-the-box thinking.
Cognitive Processes in Expert Problem Solving
Experts excel in pattern recognition, memory retrieval, and mental simulations for problem-solving.
Creative Problem Solving
Creativity involves originality, utility, and practicality in solutions, as exemplified by Niels Bohr's unconventional problem-solving approaches.
Defining Creativity
Divergent thinking generates unique solutions, emphasizing the usefulness of creative solutions.
Brain Networks and Creativity
Default Mode Network (DMN), Executive Control Network, and Salience Network play roles in creativity and idea generation.
Role of the Default Mode Network (DMN) in Creativity
The DMN contributes to creative thinking through mind wandering and incubation effects.
Understanding the ECN and DMN in Creative Thinking
The ECN directs attention, while the DMN is active during mind wandering, collaborating for creativity.
Collaboration Between Networks
The ECN and DMN collaborate during creative tasks, managing imagination and exploring complex ideas.
Mindfulness and Its Impact on Creativity
Mindfulness techniques like OM meditation enhance creativity by activating the DMN and fostering a free flow of thoughts.
Analogical Problem Solving
Using solutions from similar problems to solve new ones.
Duncker’s Radiation Problem
Destroying a tumor with rays without harming surrounding tissue. using low multiple low intensity rays surrounding the tumor
Steps in Analogical Problem Solving
Noticing, mapping, and applying analogous relationships to generate solutions.
Analogical Encoding
Identifying similarities between problems to aid in problem-solving.
Analogical Paradox
Discrepancy between real-world analogy use and lab research application difficulty.
Expertise
High skill or knowledge level in a specific field, gained through experience.
Divergent Thinking and Connectivity
Generating unique solutions and forming connections between ideas.
Factors in Generating Ideas
Role of knowledge, brainstorming, and creative cognition in idea generation.
problems are either —>
well defined or ill defined
well defined problems
initial state, goal state, and permissible operations completely specified —> we know almost everything about the question
ill defined problems
uncertainty in one or more components we don’t know everything about the question, more difficult to study.
problems of inducing structure
1) encoding: identify appropriate attributes
2) inference: relate 1st and 2nd elements
3) mapping: relate 1st and 3d elements
4) application: relate 3rd and 4th elements
these four steps allow us to see where people make error if they do
coherence
representation compromised of parts connected in a way that makes sense
correspondence
internal representation “maps well” onto elements of the problem
relationship to background knowledge
problem elements linked to existing knowledge
3 requirements for understanding a problem
coherence, correspondence, relationship to background knowledge,
algorithm
set of operations that systematically and exhaustively generates a solution
heuristic
strategy that often helps generate a solution, does not guarantee success (more difficult than algorithms)
problem space
collection of nodes each representing a state of knowledge or possible action, problem solving seen as search through problem space
problem space states
initial, intermediate, goal
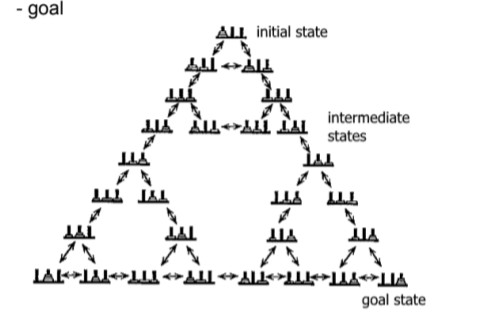
operators
links between nodes, consist of functions selected to solve problems. path constraints can rule out some possibilities.
mindlessness
thoughtless application of old ways of thinking to new situations without completely considering whether they are suitable
entrapment by categories
thinking of objects only in terms of the categories they fit into
incubation
problem solving facilitated by time away from it (effects not consistently found) but effect can be due to release from mental set/functional fixedness. retrieval of new information by changing context, recovery from fatigue, conscious problem solving, unconscious processing
reproductive thinking
based on existing associations involving what is already known (non creative thinking)
productive thinking
insights that go beyond the bounds of existing associations (creative thinking)
three process view
selective encoding insights (whats relevant and irreverent info), selective comparison insights (involve novel perception of how new info relates to old), selective combinations insights (combinding selectively encoded and compared info in a novel way.)
verbal overshadowing effect
verbal system processing interferes with insight problem solving ability
tactical learning
specific rules learned for specific problems
strategic learning
problem solving organized in an optimal way for problems in that domain (very broad)
what kind of problem is long division
problem of transformation
conjunctive rule
applies and operator —> has to satisfy all conditions. ex) child safety seat must be rear facing until child is 1 year old and weighs 10 kg
disjunctive rule
applies OR operator —> choose one. ex) you can adopt larry the cat or bob the cat
conditional rule
applies IF, THEN operator. ex) if a man is a bachelor THEN he is unmarried
biconditional rule
applies conditional rule in both directions, IF ( IF AND ONLY IF OR XNOR) an itiem is a member of the category and has both attributes or neither attribute. ex)
conditional reasoning
states relation between conditions antecedent (p) and a consequent (q) ( IF P,THEN Q). eg) if they play my favorite song at the bar I will dance & sing
propositional calculus
system for categorizing conditional reasoning statements
affirming the antecedent
produces a valid conclusion eg) they played my favorite song consequent = true. easiest to evaluate
affirming the consequent
“i am dancing & singing” —> produces invalid conclusion (you dont know why i am dancing & singing) antecedent = intermediate. next easiest to evaluate
denying the antecedent
produces invalid conclusion (consequent = intermediate) eg) they did not play my song. you don’t know if i’m dancing or not. most difficult to evaluate
normative model of decision-making
tells us how a decision should be made, given unlimited resources, (eg. memory time information) to devote to the decision.
economic human (homo economicus)
concept in neoclassical economics views humans as rational decision makers
descriptive model
how people really reach decisions, given limited Memorie abilities, time information etc. (humans do not always choose the best option) —> takes from experimental psychology
prospect theory (kahneman & tversky)
described how potential gains and losses are evaluated using heuristics and biases. tries to explain the decisions that we make. evaluation is made with reference to a neutral reference point (evaluate pros and cons to reference point)
representativeness heuristic
judging liklelihood by how well something matches the prototype (pattern or previous experience) mental shortcut that helps us make a decision by comparing information to our mental prototypes. if someone is described as quiet and introspective and enjoys reading, you might believe this person is more likely to be a librarian than a salesperson, based on the stereotype (or mental prototype) you have of librarians.
small sample fallacy
assuming small samples will be representative of population. If the sample size is not representative of the population, the conclusions drawn may be inaccurate.
base rate fallacy
people ignore or underweight the base rate information (general information or statistics) in favor of individual, specific information.
conjunction fallacy
reasoning based on expectation not probability.
gamblers fallacy
reasoning based on expectation not probability
availability heuristic
judging probability by how easily examples are retrieved (related to memory). caused by familiarity, recency, stimulation heuristic (ability to imagine)
anchoring and adjustment heuristic
initial approximation (anchor) may affect later judgment (adjustment)
hindsight bias
tendency to consistently exaggerate what could have been anticipated in foresight when looking in hindsight - hindsight groups 2/3 x more likely to agree with given diagnosis then foresight group
principles of unconscious thought
occurs outside of attention
capacity not limited by working memory
applies bottom up processing superior at weighting importance of choice attributes
uses associative thinking
divergent
illicit contrast
if one thing lacks a certain property any contrasting object must have the property or vise versa
argument by innuendo
directing one to a particular suggestive conclusion by choice of words
fallacy of the continuum
assuming small differences are always unimportant (latte factor)
fallacy of composition
assuming that what is true of the parts is true of the whole
intelligence
an inferred trait, representing the abilities to learn from experience, acquire knowledge, think abstractly, and adapt to changes
Francis Galton
first intelligence test (1822-1911), checked for a fee, perceptual tests. Contributed to the eugenics movement.
Alfred Binet & Theodore Simon (1905/1916)
developed test for slow learners, compare MA (mental age) w/ CA (chronological age). tested on vocabulary, comprehension, and verbal relations. purpose was to identify children who needed help and to provide them with special training.
Alfred Binet & Theodore Simon (1905/1916)
modified test for use in US (Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales)
based on Stern’s (1912) intelligence Quotient:
IQ = (MA / CA) × 100
easy to administer and score, hard to compare children of different chronological ages, not for adults.
David Wechsler (1939)
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) , Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI). more non verbal questions and tests were timed.
psychometric
dependent on number of correct answers
flynn effect
unstandardized intelligence scores have been increasing over time (intelligence creeping up over time)
▸ 14-point gain from 1932 to 1978
what causes the flynn effect?
the nature of intelligence has changed from practical to conceptual, due to social change. result of environment not genetics
social multiplier effect
virtuous cycle of skill improvement
factor analysis
determines minimum number of dimensions necessary to explain a pattern of correlations among subtests
Theory of Multiple Intelligences criteria includes ?
isolated by brain damage
• existence of prodigies, savants
• identifiable core operations (e.g., music: melody, harmony, rhythm, etc.)
• distinctive developmental history
• evolutionary plausibility
• support from experimental psychology
• psychometric support
• encodable in a symbol system
Gardners types of intelligence (multiple)
linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal/intrapersonal, naturalist - possibly existential
garnder’s theory of multiple intelligences —>
descriptive not prescriptive, discovered from real life/simulations not standardized tests. lacks empirical evidence and is based on subjective judgement
Triarchic Theory of Successful Intelligence (Robert Sternberg, 1985
consists of componential (analytical) intelligence, experiential (creative) intelligence, Contextual (practical) intelligence
metacomponents
recognizing a problem, selecting a procedure to solve it, checking the results - understanding you need to address something search memories to find steps to solve problem
performance components
planning, implementing the procedure - actually solving the problems and using the steps
knowledge Aquisition components
learning how to solve a problem - how did I learn to do this?
what is more a higher predictor of success, self-discipline or intelligence?
self discipline. Duckworth & Seligman self-discipline was more important than IQ in contributing to final grades
ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator in 1946
first electronic large scale general purpose digital computer
connectionism/PDP approach
emergent properties that arise from interconnected networks of processing units
ANN
artificial neural networks —> inspired by the functions of neurons
machine learning
applied by ANN, letting computers develop algorithms iteratively from its own data
supervised learning
ANNs with sophisticated neurons that use feedback to modify connection weights. able to learn from experience