ANs 230 E2 material Lecture11-16 proteins
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:07 AM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
Metabolic acidosis
If a cow owner increases the grain percentage in the feed, his cows will more likely be having:
2
New cards
cellulose
Which of the following dietary component has the slowest rate of digestion in the rumen:
3
New cards
ketone
In prolonged fasting, brain uses which of the following as energy source?
4
New cards
increase in propionate
feeding starch to ruminants typically results in
5
New cards
4\.5
Which of the PH value provided below is possibly representing a clinical rumen acidosis condition?
6
New cards
\n -More time spend eating
\-Prolonged digesta flow
\-Continuous gluconeogenesis
\-Prolonged digesta flow
\-Continuous gluconeogenesis
Which of the following factor helps ruminants keep glucose homeostasis?
7
New cards
propionate
In ruminants, this gluconeogenic compound serves as the main source of glucose:
8
New cards
microbes
Ruminants get metabolizable protein mainly through:
9
New cards
add buffers in feed
Which of the following is one of the possible preventions for rumen acidosis?
10
New cards
Chylomicrons
Which of the following lipoprotein has the highest lipid to protein ratio?
11
New cards
peptide bond
When a carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of another molecule it forms a:
12
New cards
amphoteric
When molecules can react both as an acid and base they are
13
New cards
chylomicrons
Fatty acids, other lipids and cholesterol are absorbed across the brush border of the small intestine, resynthesized into triglycerides and repackaged as:
14
New cards
\-acetone
\-acetoacetate
\-beta hydroxybutyrate
\-acetoacetate
\-beta hydroxybutyrate
Examples of ketones are
15
New cards
bile salts
The "right conditions" for pancreatic lipase to be highly efficient include:
16
New cards
micelles
During the process of lipid breakdown these molecules enable lipid digestion products to be transported to the epithelium for absorption into the small intestine:
17
New cards
biohydrogenation
Rumen microbes have a low tolerance for dietary unsaturated fatty acids which they convert to more saturated forms. This process is called:
18
New cards
cholesterol
This molecule plays a major role in cell membrane fluidity:
19
New cards
\n linolenic
example of omega 3 fatty acid
20
New cards
cholesterol
The parent compound of most sterols is:
21
New cards
sphingolipids
Which lipid is a poor conductor and critical part of the nervous system?
22
New cards
removal of amino group from amino acid creates ammonia and organic acid
\-ammonia is toxic and must be converted to urea (only ruminants can ingest)
\-ammonia is toxic and must be converted to urea (only ruminants can ingest)
Deamination
23
New cards
proteins are broke into amino acids by hydrolysis of their peptide bonds
Protein Catabolism
24
New cards
lipoproteins
These lipids are critical for transporting hydrophobic molecules in the body
25
New cards
lysine and leucine
only Ketogenic AA
26
New cards
Hydrolysis
What results in the breakdown of triglycerides into free fatty acids and monoacylglycerol?
27
New cards
Exocytosis
What is the process by which chylomicrons are transported into the lymphatic system?
28
New cards
amphipathic
Bile acids are?
29
New cards
triglycerides
The predominant form in which lipids are found in the body is:
30
New cards
Chylomicrons
Lipids are transported from the intestines into the bloodstream primarily as
31
New cards
A
Which of the following is a ketone body?
a. Acetoacetic acid
b. Pyruvic acid
c. Acetyl CoA
d. Propionic acid
a. Acetoacetic acid
b. Pyruvic acid
c. Acetyl CoA
d. Propionic acid
32
New cards
F
Lipids are directly absorbed across the gut epithelium similar to amino acids and glucose T/F
33
New cards
an amino acid
this structure describes?
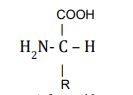
34
New cards
secondary protein structure
The chemical interactions between side groups causing folding of the alpha helix is an example of
35
New cards
Fibrins
These proteins have little nutritional value unless highly processed.
36
New cards
Flavoproteins
Heterocyclic compounds that transport hydrogen down the electron transport chain
37
New cards
Taurine
Which of the following compound is not an amino acid but essential for cats?
38
New cards
deamination
Digestion of protein results in the removal of amino groups by the process known as?
39
New cards
urea
A good source of dietary non-protein nitrogen (NPN) is:
40
New cards
Ammonia
What is a common intermediary formed during the breakdown of protein and is toxic to animals?
41
New cards
microbes can utilize it
Ruminants can handle higher levels of ammonia bc?
42
New cards
Amino acid composition and digestibility
Protein quality refers primarily to?
43
New cards
\-short shelf life
\-need lipids for absorption
\-sensitive to heat
\-need lipids for absorption
\-sensitive to heat
What is a common characteristic among Vitamins A, D, E and K?
44
New cards
\-Vitamin B 1, B2, and B6
When formulating diets for ruminants which of the following vitamin is typically not included in the diet?
45
New cards
Vitamin B12
This vitamin is synthesized by microbes and has a requirement for cobalt
46
New cards
Vitamin D
What has a profound influence on calcium and phosphorus metabolism?
47
New cards
\-is referred to as ash
\-makes up small % (1-3%) of total diet
\-cannot be synthesized or decomposed
\-makes up small % (1-3%) of total diet
\-cannot be synthesized or decomposed
The inorganic component of the diet
48
New cards
Hyponatremia
During vigorous exercise, the body can lose excess NaCl which is a condition referred to as?
49
New cards
camels
Which of the following animal might be best adapted for dealing with water shortage?
50
New cards
Cr (chromium)
This mineral is part of the glucose tolerance factor molecule and required for normal glucose entry into cells
51
New cards
zinc
Horses grazing grass pasture fed a supplement high in this mineral can see a decrease in calcium absorption
52
New cards
calcium absorption
zinc affects
53
New cards
calcitonin
What inhibits the activation of Vitamin D?
54
New cards
T
Increasing the amount of minerals in the diet can reduce the amount that is absorbed T/F
55
New cards
water in feeds
There are many sources of water for animals. This source of water in particular can be highly variable in terms of meeting water intake requirements of animals.
56
New cards
C
Which of the following feedstuffs has the greatest amount of water content?
a. hay
b. silage
c. lush fresh grass
d. whole corn
a. hay
b. silage
c. lush fresh grass
d. whole corn
57
New cards
fats
Oxidation of which of the following nutrient results in greatest amount of metabolic water?
58
New cards
F
At any given temperature water consumption of a dairy cow is negatively correlated with milk production T/F
59
New cards
F
The largest source of body water loss is feces. T/F
60
New cards
Hydremia
What is a condition of water intoxication seen commonly in puppies and exhibits symptoms similar to lack of Na, anorexia and lethargy.
61
New cards
\-it involves transfer of electrons
\-glucose is oxidized
\-O2 is reduced to H20
\-glucose is oxidized
\-O2 is reduced to H20
Why is the process of cellular respiration a redox reaction?
62
New cards
1000
One cell, on an average, can have _____mitochondria producing ATP molecules
63
New cards
acetyl CoA
The most basic compound in the overall process of cellular respiration and at the crossroads of ALL metabolism is?
64
New cards
C
the second law of thermodynamics states that?
a. energy can nether be created nor destroyed
b. energy transformation is 100% efficient
c. inefficiencies in transformation of energy are lost as heat
a. energy can nether be created nor destroyed
b. energy transformation is 100% efficient
c. inefficiencies in transformation of energy are lost as heat
65
New cards
T
Estimating GE of feeds alone is of little value in determining energy use of that feed for any specific animal. T/F
66
New cards
T
One can estimate the amount of heat produced in chemical reactions by measuring O2 and CO2 T/F
67
New cards
digestible energy
Subtracting fecal energy from feed energy will give us an estimate of
68
New cards
metabolizable energy
Subtracting energy in urine and gas from digestible energy will give us an estimate of
69
New cards
\-energy lost as heat during fermentation
\-energy lost as heat during nutrient metabolism
\-energy lost as heat during nutrient metabolism
In order to get an estimate of the NE content of a feed we need to know?
70
New cards
hay
which of the following feed will have lowest energy value?
71
New cards
T
When calculating maintenance energy it is assumed that all feed energy must be converted to heat T/F
72
New cards
\-heat increment
\-specific dynamic acti0on
\-dietary thermogeneis
\-specific dynamic acti0on
\-dietary thermogeneis
What represents the inefficiency of energy use?
73
New cards
lipogenic
acetate and butyrate are
74
New cards
gluconeogenic
propionate is
75
New cards
\-rapid fermentation
\-SCFA and lactic acid production
\-decrease in rumen PH
\-rumen acidosis
\-disruption in ruminal function
\-SCFA and lactic acid production
\-decrease in rumen PH
\-rumen acidosis
\-disruption in ruminal function
High starch diets in rumen SCFA profile
76
New cards
subclinical - ph 5.5 (decreased intake, gain, FE)
clinical- pH less than 5.0 (-increased lactic acid, metabolic acidosis, damage to papillae, microbial death and release of endotoxins)
clinical- pH less than 5.0 (-increased lactic acid, metabolic acidosis, damage to papillae, microbial death and release of endotoxins)
pH and rumen acidosis
77
New cards
\-parakeratosis
\-liver absccesses
\-laminitis
\-liver absccesses
\-laminitis
Rumen acidosis problems
78
New cards
\-buffers in feed or ionophores
\-reduce grain in feed
\-reduce grain in feed
rumen acidosis prevetion
79
New cards
\-more time spent eating and ruminating
\-prolonged digesta flow
\-steady VFA production
\-continuous gluconeogenesis
\-prolonged digesta flow
\-steady VFA production
\-continuous gluconeogenesis
glucose homeostasis in rumens have reduced fluctuation bc
80
New cards
glucose
What dont we typically feed ruminants to meet energy requirements
81
New cards
1\.) propionate
2\.) amino acids
3\.) lactic acid
4\.) glycerol
2\.) amino acids
3\.) lactic acid
4\.) glycerol
source of glucose precursors in ruminants
82
New cards
amphipathic
phospholipids, glycolipids, and sphingolipids are all
83
New cards
acetate which is used to make chemical energy
CHO,Fat,AA metabolism produce?
84
New cards
D
Which of the following can be found in a dipeptide
\
\\n
a. Basic amino group (-NH2)
b Peptide bond
c. Acidic carboxyl group (-COOH)
d. All of the above
\\n
\
\\n
a. Basic amino group (-NH2)
b Peptide bond
c. Acidic carboxyl group (-COOH)
d. All of the above
\\n
85
New cards
secondary structure
Alpha-helix is a key ____ of natural proteins:
86
New cards
20^300
Within natural living organisms, how many possible combination does a 300 AA middle-size protein have?
87
New cards
dipolar ions
In aqueous solution, amino acids exist as:
88
New cards
D
How do animals dispose excess amino acids?
a. Oxidation
b. Ureagenesis
c. Gluconeogenesis
d. All of the above
a. Oxidation
b. Ureagenesis
c. Gluconeogenesis
d. All of the above
89
New cards
most small intestine metabolize proteins are from microbial proteins
Regarding ruminants protein digestion what is true?
90
New cards
urea
In terrestrial vertebrates, nitrogen gets excreted as:
91
New cards
A
Which of the following is NOT true about "limiting AA"?
\
\
a. It's usually a dispensable AA
b. It prevents protein synthesis beyond the rate at which only that amino acid is available
c. Lysine and Methionine are "limiting AA" in poultry
d. It can not be sythesized in the body
\
\
a. It's usually a dispensable AA
b. It prevents protein synthesis beyond the rate at which only that amino acid is available
c. Lysine and Methionine are "limiting AA" in poultry
d. It can not be sythesized in the body
92
New cards
the side chain R group
Amino acids in living organisms differ from each at
93
New cards
\-pollution
\-digestive issues
\-hepatic abnormalities
\
\-digestive issues
\-hepatic abnormalities
\
Dietary protein is important for animals. However, an excessive protein supply in animal feed might result in:
94
New cards
cellulase
Microbes can help ruminants digest forage because they have:
95
New cards
a. Amino acid nitrogen
b. Non-protein nitrogen (NPN)
c. Ammonia nitrogen
d. All of the above
b. Non-protein nitrogen (NPN)
c. Ammonia nitrogen
d. All of the above
Crude protein can consist of:
96
New cards
H2N
example of amino group
97
New cards
COOH
group that is consider acidic
98
New cards
zwitter ions
In aqueous solutions amino acids exist as dipolar ions also known as
99
New cards
T
limiting amino acid is an essential amino acid that is available in the lowest concentration in relation to the body’s needs. T/F
100
New cards
C
Which of the following is not true about amino acids?
a. They synthesize glucose
b. They can be converted to fat
c. They are comprised of only three elements – carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
d. They are energy yielding.
a. They synthesize glucose
b. They can be converted to fat
c. They are comprised of only three elements – carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
d. They are energy yielding.