Nuclear Fission
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
what is nuclear fission?
the breaking up of atomic nuclei
what is the process of nuclear fission
a slow-moving neutron is absorbed by an atom of uranium-235
the uranium-235 becomes uranium-236, an unstable isotope
The uranium splits into two daughter nuclei and three neutrons
This is known as nuclear fission
Each of the three neutrons can be absorbed ny another atom of uranium-235
Each of these uranium atoms undergoes fission, releasing even more neutrons
This is known as a chain reaction
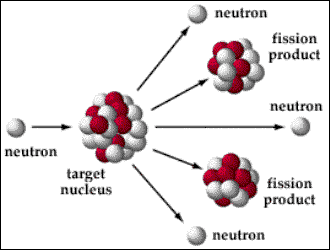
what is the equation for fission?
235^_92U + 1^_0n -> 236^_92U -> 141^_56Ba + 92^_36K + 3 1^_0n
what controls are in place to make nuclear fission safer?
Control rods
made of boron
absorbs unwanted neutrons
prevent out of control reactions
Moderator
water commonly used
slows down neutron so it can be absorbed
keeps chain reaction going
Fuel rods - contain enriched uranium-235 or plutonium-239
what are the pros and cons of nuclear fission
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|