ECON323
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the difference between positive and normative analysis? [L1]
Positive Analysis - how it works
Normative Analysis - how it should ideally work
What are the 4 functions of the state? [L1]
Production - in cases of natural monopolies (ex. electricity, water)
Regulation - intervention when private production creates market failure
Redistribution - transfer resources to citizens or firms
Taxation - raise revenues
What is the difference between efficiency and equity? [L1]
Efficiency: goal of reaching a Pareto efficient allocation of resource
Equity: goal of reaching a fair allocation of resources
What is the governments role in economic efficiency? [L1]
Government intervention need to restore efficient
Trade-off - solving market failures = government failures
What is an externality? [L2]
Def. - link between economic agents that lies outside the price system
Welfare that is directly affected by the actions of someone else without any transcation
What are some examples of negative externalities? [L2]
Driving a car = Generates congestion
Firm emits CO2 = Contributes to global warming
Drunk driving = Risks killing someone
Everyone studies economics = Lowers salary of economists
What are some examples of positive externalities? [L2]
Playing good music on street = Everyone can enjoy
Friend joins social network = Expand own social network
Clean shared kitchen = flatmates can enjoy
What are the effects of externalities in a market? [L2]
Negative production externality = market produces too much of the good
Positive production externality = market produces too little of the good
What are the assumptions of Coase Theorem? [L2]
Property rights are defined
Bargaining is costless
Few players involved
No wealth effect
![<p>What is the conclusion of Coase Theorem? (ex. Renauld’s Drums) [L2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ddb098f3-1875-4535-a09c-f88b5ddad166.png)
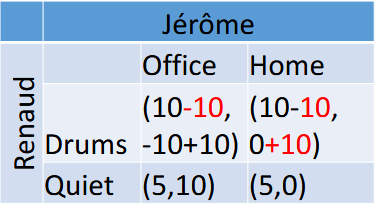
What is the conclusion of Coase Theorem? (ex. Renauld’s Drums) [L2]
Who owns the property right do not matter
Bargaining will restore efficiency
Property rights only determine who receives the payoff
What is an example of Coase Theorm in real life? [L2]
Carbon market
Firms can trade pollution allowances
Market distributes pollution in most efficient way
Government must determine how much pollution is allowed
What is the difference between Pigouvian taxation and externality markets? [L2]
Pigouvian taxation: taxing externalities
simple and direct
Government must guess marginal externality at the optimum
Markets
Decentralized and not direct
Government must guess quantities produced at the optimum
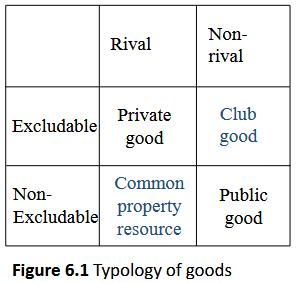
What is the difference between excludable, rival, and impure public goods?
Excludable Goods: consumers can be excluded from consuming it
Rival Goods: consumption by one consumer reduces the quantity available for others
Impure Public Goods: between private and public goods (ex. club goods, common property resources)
What is the problem with public goods? [L2]
Most public goods suffer from congestion
Pure public goods are an abstract idea (ex. highway for non-users)