IB HL Bio D 2.1-2.2, & 1.3: Cell Division & Reproduction
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
gene knockout
technique which targets gene for deactivation or removal from an organism
purpose: lets scientists study impact of a gene on an organism
Cytokinesis
the splitting of the cytoplasm of a parent cell to form 2 daughter cells
Cytokinesis in plants vs animals
Plants: cell plate
Animals: cleavage furrow using contractile ring
The cytoplasm ________ splits equally during cytokinesis.
(Always, sometimes, or never)
sometimes
Budding
form of asexual reproduction where a small daughter cell buds off a larger cell
example of unequal division in yeast
Oogenesis
unequal division of cells during meiosis to form one large egg cell
example of unequal division in females
Mitosis is required for...
growth and development
tissue repair
asexual reproduction
Meiosis is required for...
the production of gametes in sexual reproduction
Meiosis produces ____ daughter cells, each with ____ the number of chromosomes in the parent cell.
4, half
What stages does DNA progress through during cell division?
Chromatin coils around histones to form nucleosomes
nucleosomes coil around each other to form chromosomes (w/ sister chromatids)
Spindle Fibers function
attach to centromeres and aid in movement of a chromosome
Stages of the Cell Cycle
interphase
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
cytokinesis
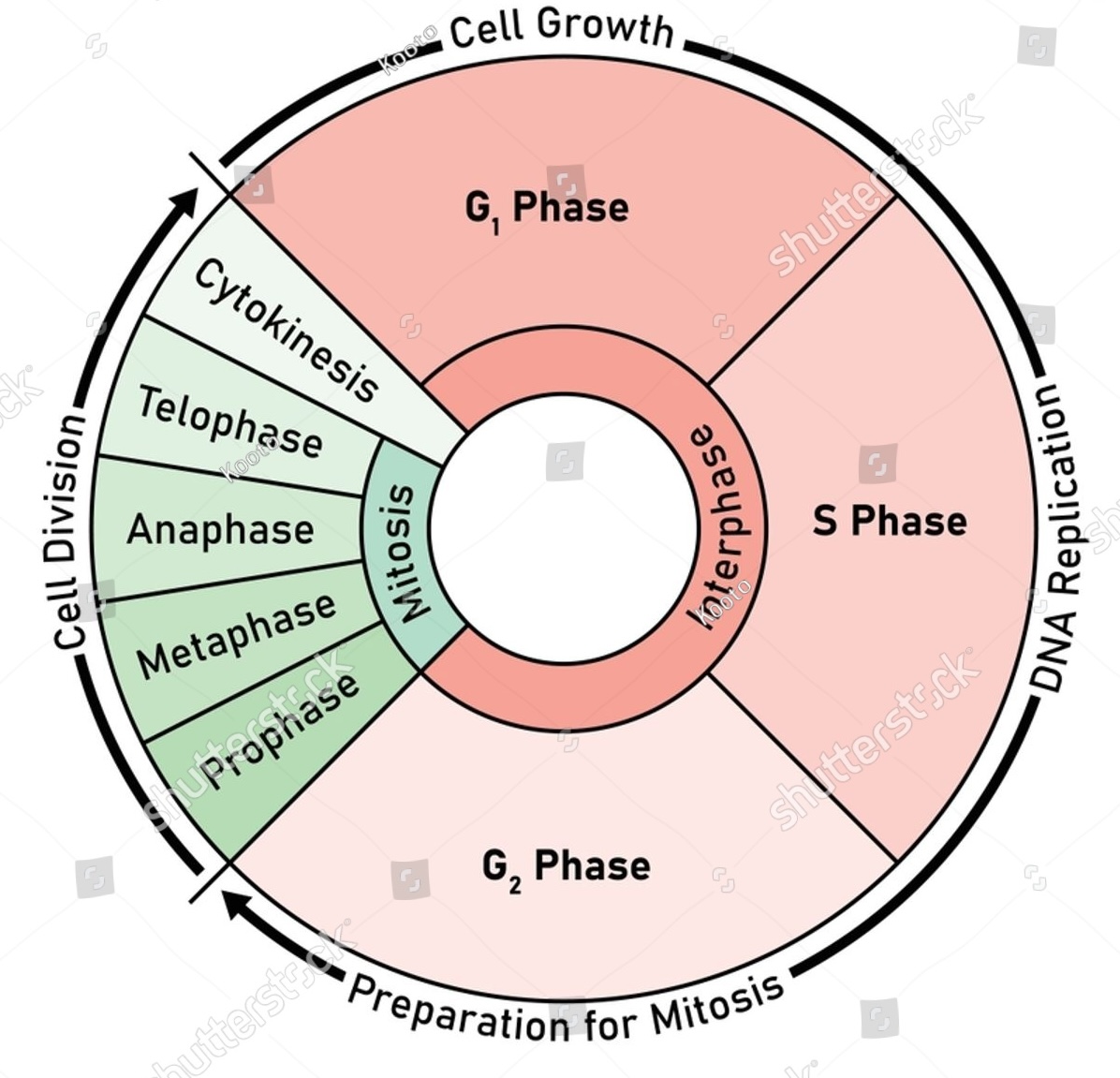
Interphase
G1: cell grows, protein synthesis occurs, allows cells to build new organelles
S: DNA replication
G2: cell grows, cell prepares for mitosis by growing/replicating organelles
Prophase
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes (2 sister chromatids & a centromere)
nuclear envelope breaks down
spindle fibers produced
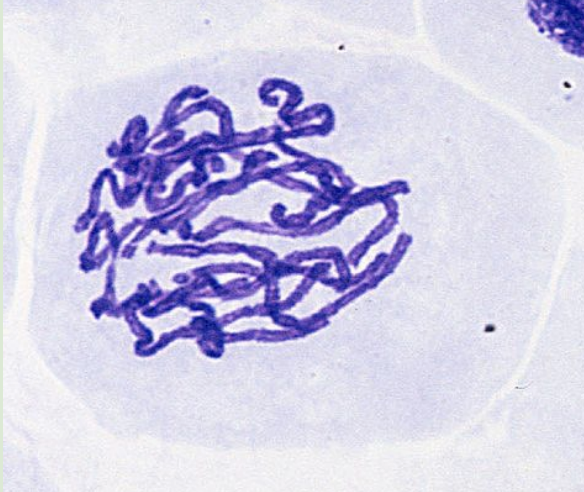
Metaphase
chromosomes line along equator of cell
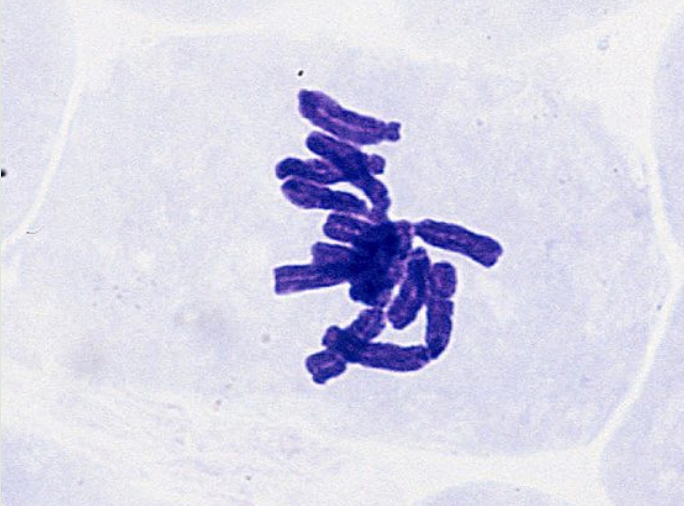
Anaphase
spindle fibers separate sister chromatids & move them to opposite poles
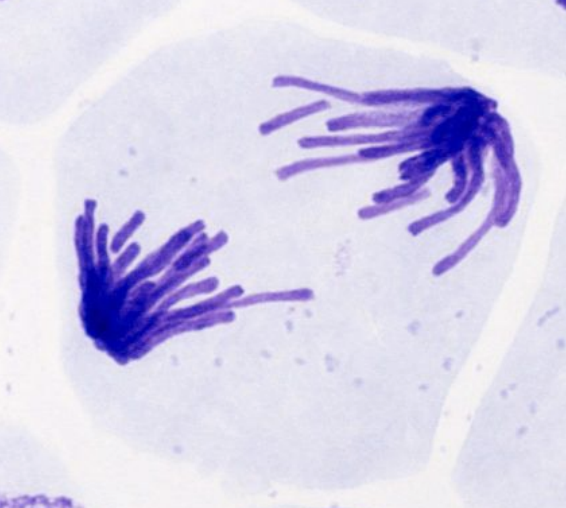
Telophase
nuclear membrane forms around set of chromosomes @ each pole
i.e.) 2 genetically identical nuclei are produced
chromosomes uncoil back into chromatin
Purpose of Condensation of Chromosomes
segregates them during cell division
Diploid vs Haploid
diploid is two sets of chromosomes (humans have 46)
haploid is one set of chromosomes (humans have 23)
Meiosis is known as ________ division because...
reduction division
bc parent cell is diploid and daughter cell is haploid
i.e. bc meiosis reduces # chromosomes
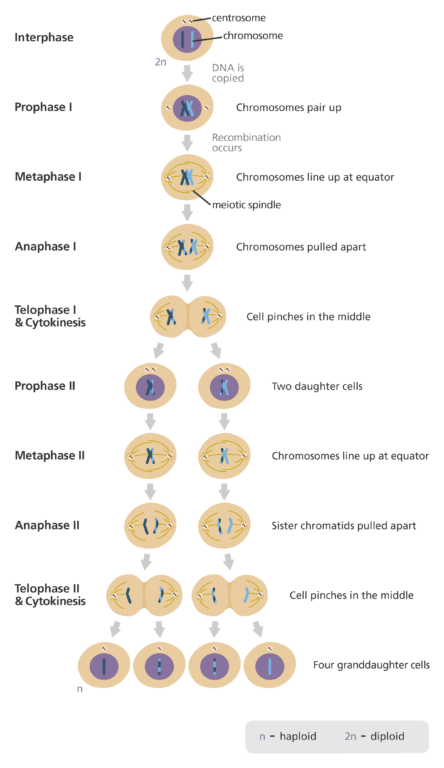
Purpose of 2 nuclear divisions in meiosis
Meiosis I: segregates homologous chromosomes to produce 2 haploid cells
Meiosis 2: segregates sister chromatids to produce 4 haploid cells
Prophase I in Meiosis
Chromatin condenses to chromosomes homologous chromosomes pair up and form bivalents
alleles switch
nuclear envelope breaks down
Metaphase I in Meiosis
spindle fibers move bivalents to equator in random order
Anaphase I in Meiosis
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to poles of the cell by spindle fibers
Telophase I in Meiosis
Chromosomes, at pole, uncoils
nuclear membrane forms around sister chromatids at each pole
Meiosis II
PMAT occurs again, but with sister chromatids now
@ end of Meiosis 1, cell are haploid
@ end of Meiosis 2, cells are diploid
Zygote
At fertilization, egg & sperm fuse to form a zygote
Meiosis is a source of variation. True or False?
True
Formation of bivalents and random swapping of sections of sister chromatids produce genetically different chromosomes
Cell proliferation
process of exponentially increasing cell numbers by mitotic division
ex) Plant meristems are undifferentiated & differentiate to produce plant tissue/organs
ex) Embryos grow by cell proliferation thru mitosis and cytokinesis
Cyclins
proteins which drive the cell cycle forward
bind to CDKs to be phosphorylated, trigger rxn cascade in cell cycle
tumor supressor genes
regulate/inhibit cell growth
mutations --> uncontrolled cell division
proton-oncogenes (Mutated version: oncogene)
promote normal, regulated, cell growth
mutations --> uncontrolled cell division