CARBOHYDRATES & LIPIDS
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Carbohydrates that can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent are known as non-reducing sugars.
Which of the following statements concerning carbohydrates is INCORRECT?
Carbohydrates serve important energy and structural roles for plants and animals.
Monosaccharides join together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides by glycosidic bonds.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are known as simple sugars.
Humans store excess glucose for short-term energy requirements in the polysaccharide glycogen.
Carbohydrates that can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent are known as non-reducing sugars.
monosaccharide
Which type of carbohydrate cannot be converted to simpler compounds by hydrolysis?
starch
cellulose
disaccharide
polysaccharide
monosaccharide
aldoses
What are monosaccharides with a carbonyl group at C1 called?
alditols
steroisomers
anomers
aldoses
ketoses
ketotetrose
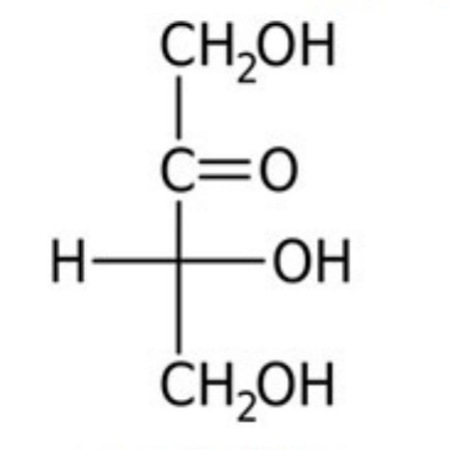
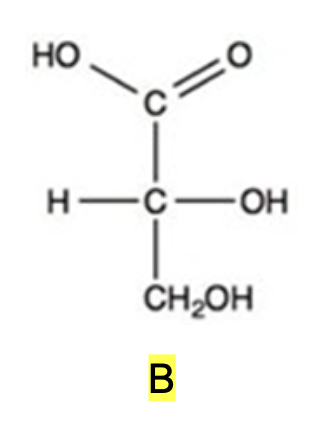
What is the classification of the compound shown below?
tetraketose
aldotriose
aldotetrose
ketotetrose
ketotriose
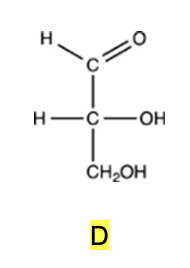
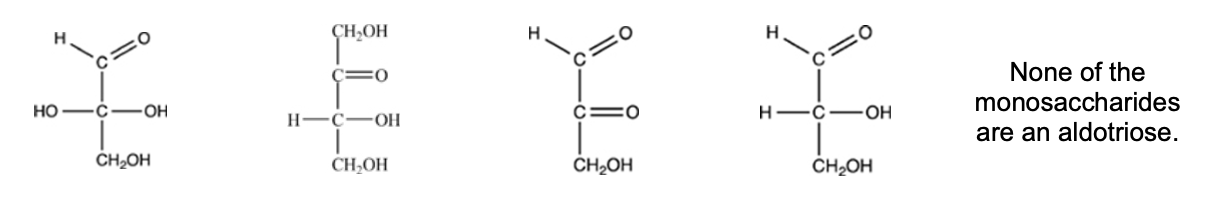
Which monosaccharide is an aldotriose?
farthest from the carbonyl group
To determine whether a monosaccharide is D or L, the configuration of the chiral center must be determined
nearest to the second -OH functional group
nearest to the carbonyl group
nearest to the third -OH functional group
in the center of the molecule
farthest from the carbonyl group
L-glyceraldehyde
Which enantiomer of glyceraldehyde is represented in the following structure?
⍺-glyceraldehyde
D-glyceraldehyde
L-glyceraldehyde
β-glyceraldehyde
farthest from the carbonyl group
enantiomers
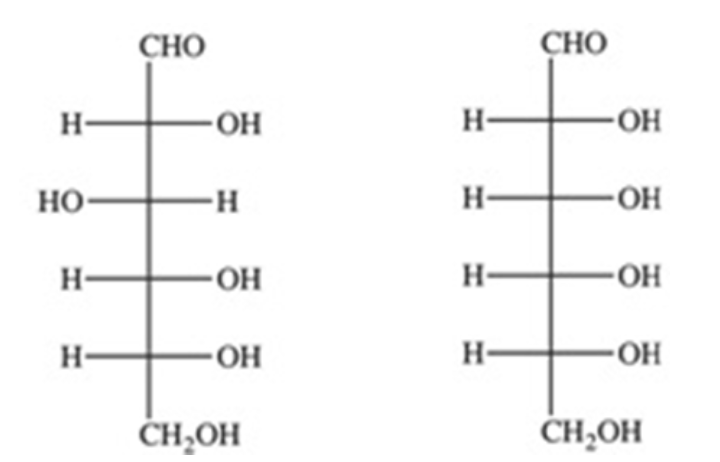
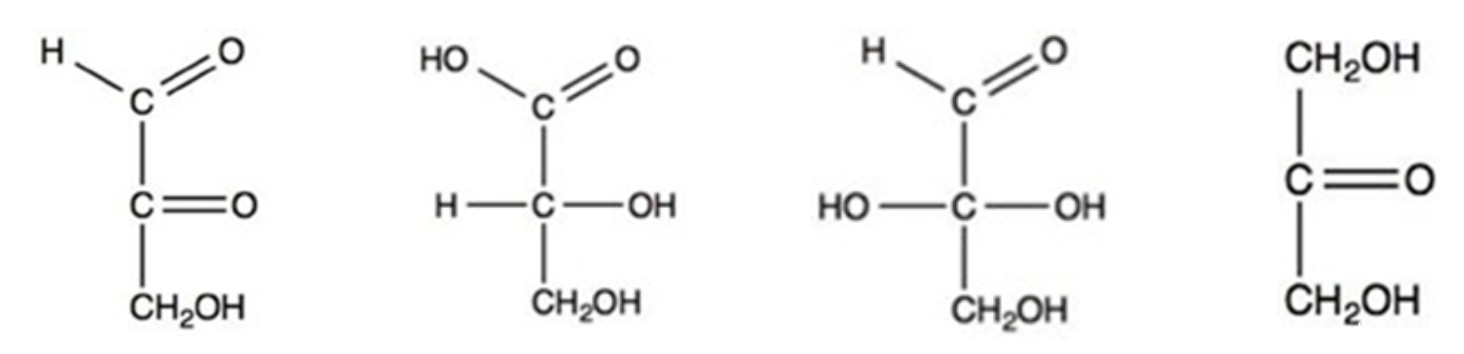
The Fischer projections of two monosaccharides are shown below. What is the relationship between the two monosaccharides?
enantiomers
cis-trans isomers
meso isomers
structural isomers
diastereomers
4
How many chirality centers are present in both compounds shown above?
2
3
4
5
6
Which monosaccharide is an aldotriose?
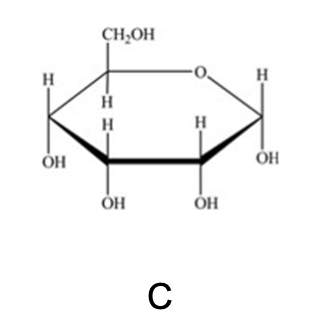
The open chain of D-allose is shown below, What is the Haworth projection for ⍺-D-allose?
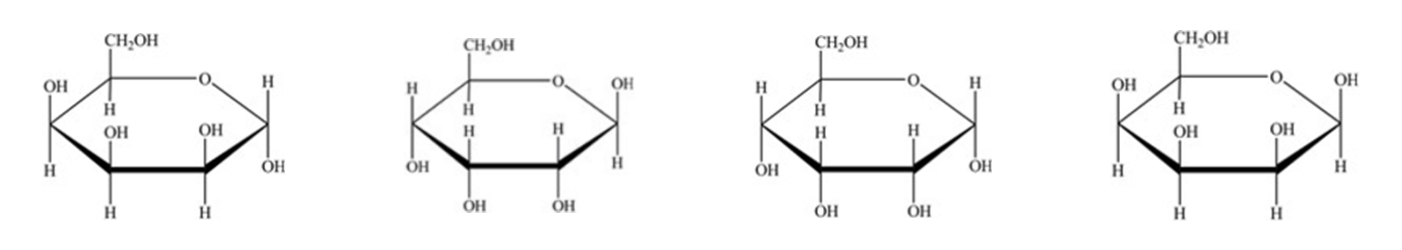
III only
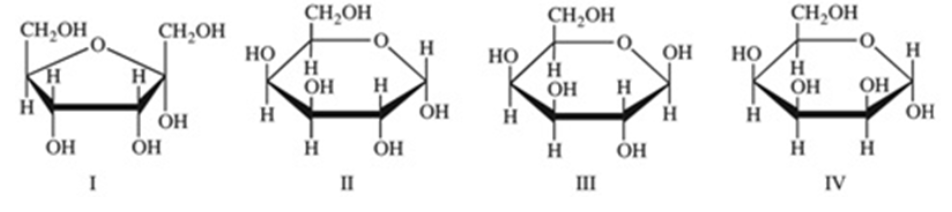
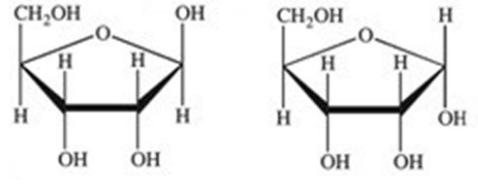
Monosaccharides exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. Cyclic hemiacetals have both an ⍺ and a β form. Which of the following monosaccharides are shown in the B form?
IV only
III only
I and III
II and IV
All of the choices
anomers
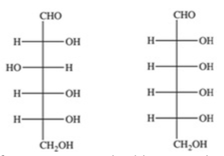
What term properly describes the relationship between the two compounds shown?
enantiomers
betamers
unrelated
anomers
constitutional isomers
What product forms when the compound below is treated with H2 in the presence of a Pd catalyst?
What product forms when the compound below is treated with Benedict's reagent?
glycosidic linkages
Disaccharides and polysaccharides contain monosaccharide units joined together by which of the following?
dipole-dipole forces
hydrogen bonding
hemiacetal bonds
glycosidic linkages
2
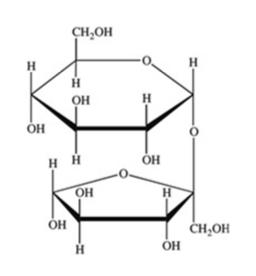
How many acetals are present in the disaccharide shown?
1
2
3
4
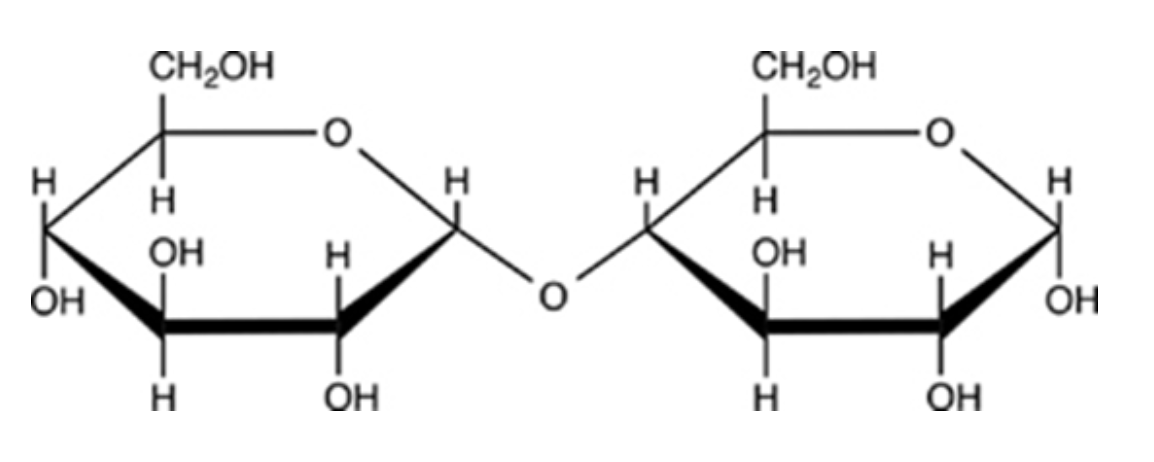
⍺-1→4
What type of glycosidic linkage is shown on the structure?
β-1→6
β-1→4
⍺-1→6
⍺-1→4
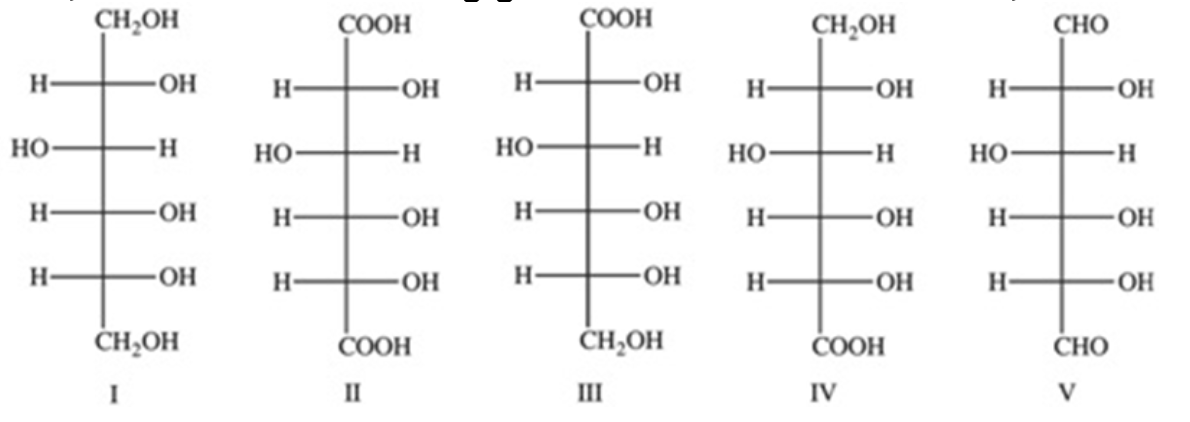
III
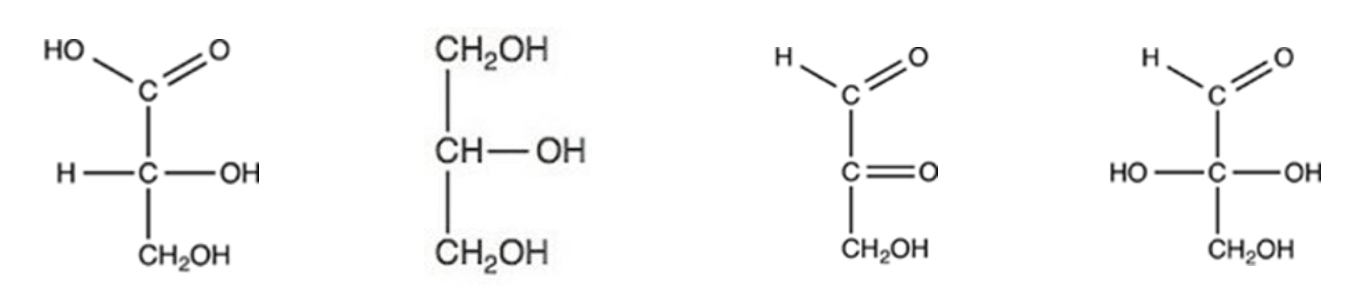
Which of the following structures represents the product formed when glucose is oxidized by CuSO4 in an alkaline solution to form gluconic acid?
I
II
III
IV
V
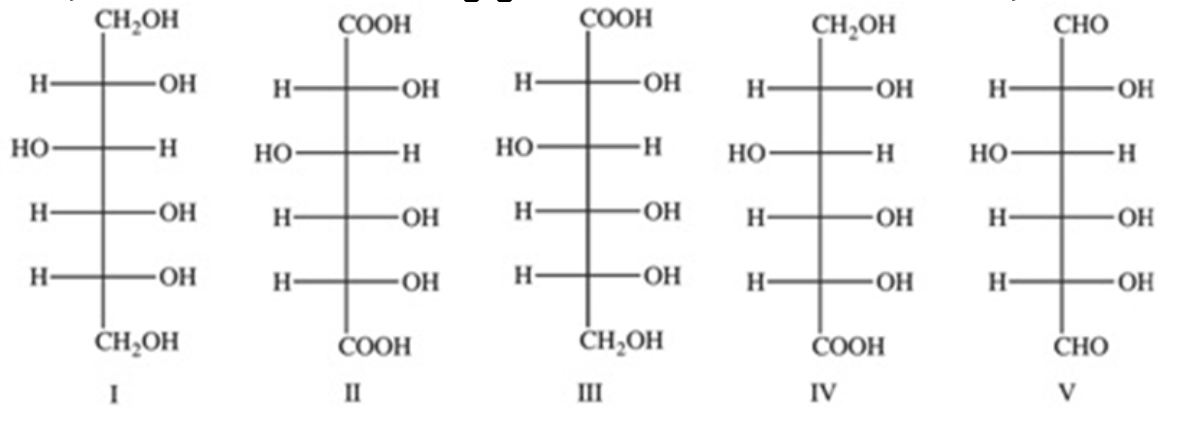
II
Which of the following structures represents the product formed when glucose is oxidized by conc. HNO3 to form glucaric acid?
I
II
III
IV
V
maltose
What disaccharide is composed of two glucose units joined together?
lactose
maltose
galactose
sucrose
cellulose
cellulose
Which polysaccharide has β-glycosidic bonds?
cellulose
glycogen
amylose
amylopectin
glycogen
What is the polysaccharide form in which glucose is stored in animals?
glycogen
amylopectin
glycosaminoglycans
amylose
hyaluronate
Which carbohydrate derivative forms a gel-like matrix in joints and the vitreous humor of the eye?
chitin
amylose
chondroitin
heparin
hyaluronate
glucose
Which monosaccharide found in the blood has its concentration regulated by the hormones insulin and glucagon?
glucose
galactose
ribose
fructose
sucrose
three or four monosaccharides attached to a membrane protein on the surface of red blood cells
What is responsible for the different blood types in humans?
three or four monosaccharides attached to a membrane protein on the surface of red blood cells
three or four proteins attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
three or four lipids attached to a membrane polysaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
three or four amino acids attached to a membrane monosaccharide on the surface of red blood cells
N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
Three of the four monosaccharides that determine a person's blood type are present in all blood types. Only __________ is present in Type A blood.
N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
D-galactose
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
L-fucose
sucrose
Which is NOT a reducing sugar?
glucose
galactose
aldopentose
fructose
sucrose
amylopectin
What type of polysaccharide is depicted in the image shown below?
glycosaminoglycans
cellulose
chitin
amylopectin
amylose
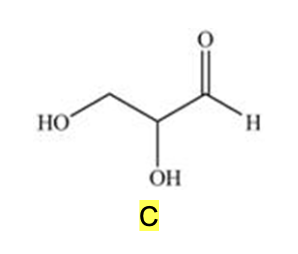
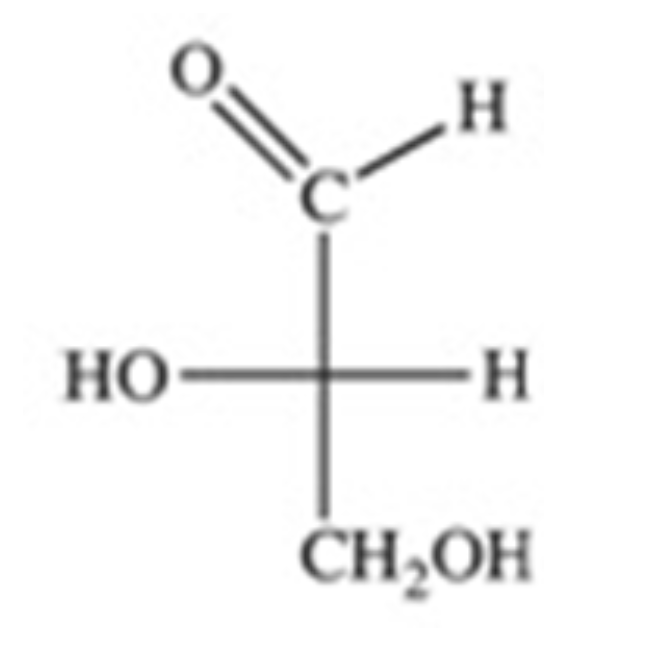
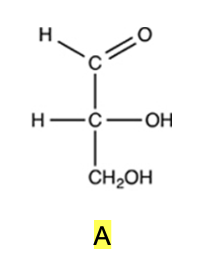
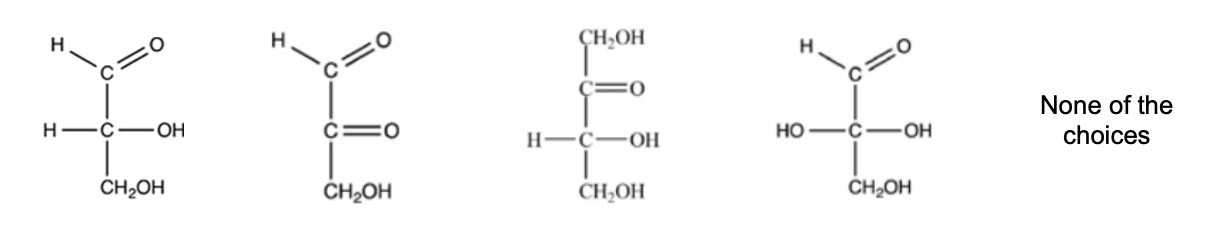
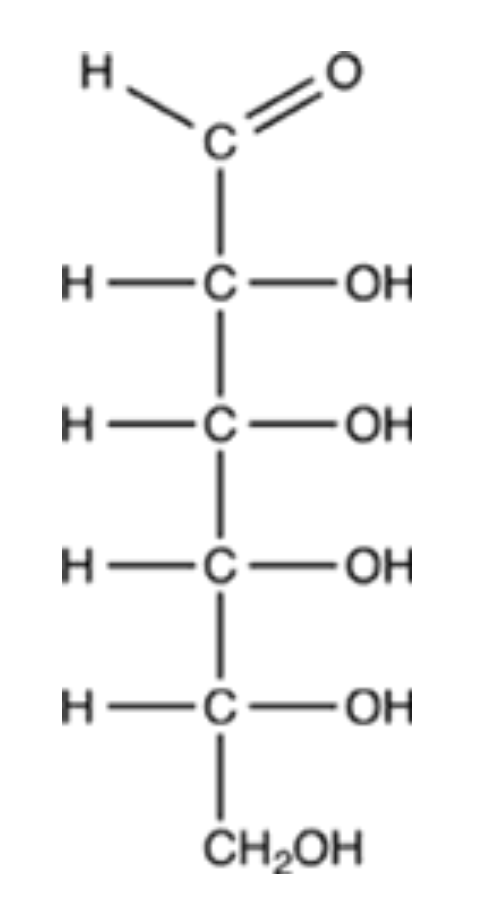
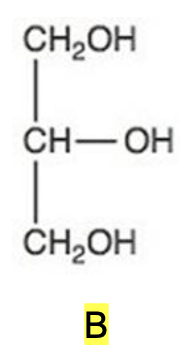
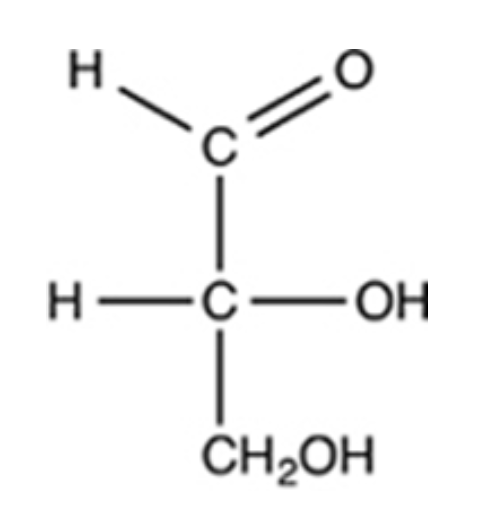
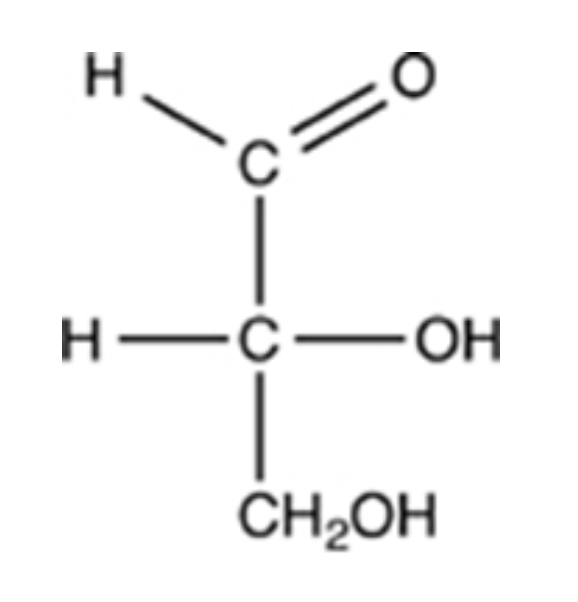
The simplest aldose is commonly called glyceraldehyde, although its IUPAC name is 2,3-dihydroxypropanal. What is the structure of this compound?
Humans store excess glucose for short-term energy requirements in the polysaccharide cellulose.
Which statement concerning carbohydrates is INCORRECT?
Carbohydrates that can be oxidized by Benedict's reagent are called reducing sugars.
Humans store excess glucose for short-term energy requirements in the polysaccharide cellulose.
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and are known as simple sugars.
Carbohydrates serve important energy and structural roles for both plants and animals.
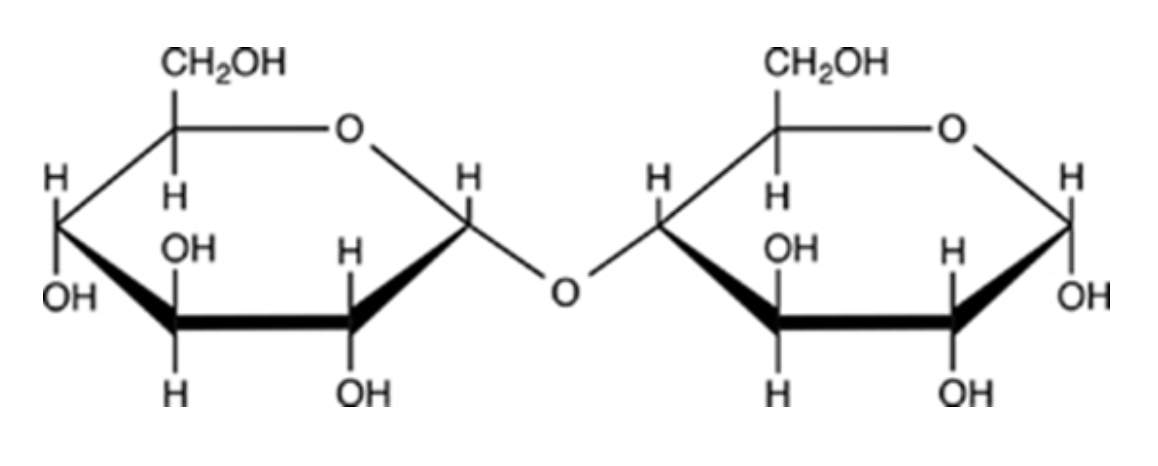
It contains an ⍺-(1→5) glycosidic linkage.
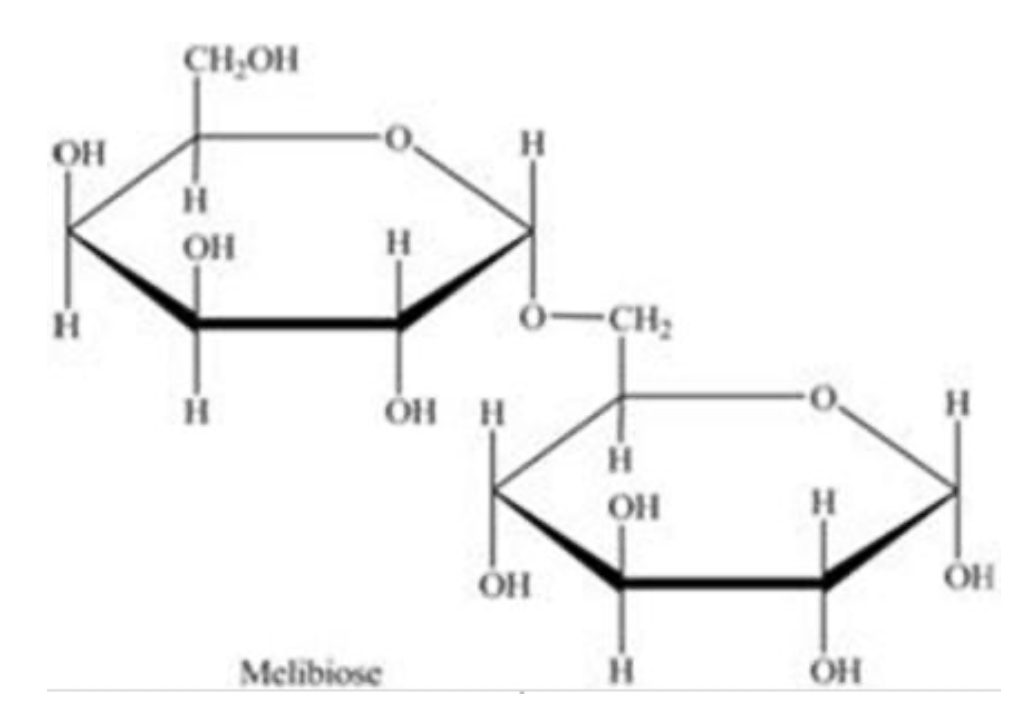
Melibiose is a carbohydrate found in some plant juices. Which statement concerning melibiose is INCORRECT?
It contains both an acetal and a hemiacetal.
It contains an ⍺-(1→5) glycosidic linkage.
It is a disaccharide.
It is composed of two different monosaccharides.
β(1→4)
What type of glycosidic linkage between glucose units is present in cellulose?
⍺(1→6)
⍺(1→4) and ⍺(1→6)
⍺(1→4)
β(1→6)
β(1→4)
glucose
What monosaccharide is found in cellulose, starch, and glycogen?
sucrose
maltose
glucose
galactose
fructose
Amylose is a linear polysaccharide and amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide.
Amylose and amylopectin are both components of starch. How do their structures differ?
Amylose is a polysaccharide, and amylopectin is a disaccharide.
Amylose is a hexose, and amylopectin is a pentose.
Amylose is a monosaccharide, and amylopectin is a polysaccharide.
Amylose is a linear polysaccharide and amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide.
Amylose is an aldose, and amylopectin is a ketose.