Mech Test 3
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:11 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
1
New cards
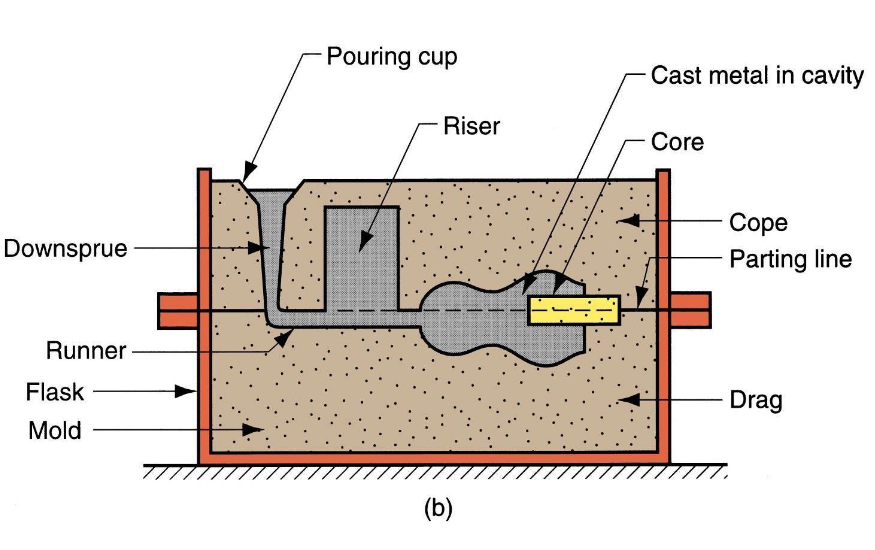
Sand casting mold
purple is gate
2
New cards
Quiz 8 (26)
Quiz 8 (26)
3
New cards
Which of the following is NOT one of the usual objectives of heat treatment?
increase recrystallization temperature
4
New cards
Of the following quenching media, which one produces the most rapid cooling rate:
brine
5
New cards
On which one of the following metals is the treatment called austenitizing performed:
copper alloys
6
New cards
The treatment in which the brittleness of martensite is reduced is called which one of the following:
tempering
7
New cards
The Jominy end-quench test is designed to indicate which one of the following:
hardenability
8
New cards
In precipitation hardening, the hardening and strengthening of the metal occurs in which one of the following steps:
aging
9
New cards
Which one of the following surface hardening treatments is the most common?
carburizing
10
New cards
Which of the following is not a selective surface hardening method?
austenitizing
11
New cards
Assignment 7 (10,11)
Assignment 7 (10,11)
12
New cards
Identify some of the important advantages of shape-casting processes.
Advantages include (1) complex part geometries are possible; (2) some casting operations are net shape processes, meaning that no further manufacturing operations are needed to accomplish the final part geometry; (3) very large parts are possible; (4) casting is applicable to any metal that can be melted; and (5) some casting processes are suited to mass production.
13
New cards
What are some of the limitations and disadvantages of casting?
Disadvantages include (1) limitations on mechanical strength properties; (2) porosity; (3) poor dimensional accuracy; (4) safety hazards due to handling of hot metals; and (5) environmental problems.
14
New cards
What is a factory that performs casting operations usually called
A foundry
15
New cards
What is the difference between an open mold and a closed mold
An open mold is open to the atmosphere at the top; it is an open container in the desired shape which must be flat at the top. A closed mold has a cavity that is entirely enclosed by the mold, with a passageway (called the gating system) leading from the outside into the cavity. Molten metal is poured into this gating system to fill the mold.
16
New cards
Which casting process is the most important commercially?
Sand casting is the most important casting process
17
New cards
What is the difference between a pattern and a core in sand molding?
The pattern determines the external shape of the cast part, while a core determines its internal geometry if the casting includes a cavity.
18
New cards
How does solidification of alloys differ from solidification of pure metals?
Pure metals solidify at a single temperature equal to the melting point. Most alloys (exceptions are eutectic alloys) start to solidify at the liquidus and complete solidification occurs at the solidus, where the liquidus is a higher temperature than the solidus
19
New cards
What is a eutectic alloy?
A eutectic alloy is a particular composition in an alloy system for which the solidus and liquidus temperatures are equal. The temperature is called the eutectic temperature. Hence, solidification occurs at a single temperature, rather than over a temperature range.
20
New cards
What is the relationship known as Chvorinov's rule in casting?
. Chvorinov's rule is summarized: *TTS* = *Cm*(*V*/*A*)2, where *TTS* = total solidification time, *Cm* = mold constant, *V* = volume of casting, and *A* = surface area of casting.
21
New cards
Identify the three sources of contraction in a metal casting after pouring.
The three contractions occur due to (1) contraction of the molten metal after pouring, (2) solidification shrinkage during transformation of state from liquid to solid, and (3) thermal contraction in the solid state.
22
New cards
Name the two basic categories of casting processes.
The two categories are (1) expendable mold processes, and (2) permanent mold processes.
23
New cards
There are various types of patterns used in sand casting. What is the difference between a split pattern and a match plate pattern?
A split pattern is a pattern that consists of two pieces; a match‑plate pattern consists of the two split patterns attached to opposite sides of a plate.
24
New cards
What is a chaplet?
Chaplets are metal supports of various designs used to hold the core in place in the sand mold.
25
New cards
What properties determine the quality of a sand mold for sand casting?
The usual properties are (1) strength ‑ ability to maintain shape in the face of the flowing metal, (2) permeability ‑ ability of the mold to allow hot air and gases to escape from the cavity, (3) thermal stability ‑ ability to resist cracking and buckling when in contact with the molten metal, (4) collapsibility ‑ ability of the mold to give way during shrinkage of the solidified casting, and (5) reusability ‑ can the sand be reused to make other molds?
26
New cards
What are the most common metals used in die casting?
Common die-casting metals include zinc, tin, lead, aluminum, brass, and magnesium.
27
New cards
What is flash in die casting?
Flash is a thin portion of metal at the exterior of a casting that results from molten metal being squeezed into the spaces between the die halves of the mold at the parting line, or into the clearances around the cores and ejector pins.
28
New cards
What is the difference between true centrifugal casting and semicentrifugal casting?
In true centrifugal casting, a tubular mold is used and a tubular part is produced. In semicentrifugal casting, the shape is solid; an example is a railway wheel. The mold is rotated so that centrifugal force is used to distribute the molten metal to the exterior of the mold so that the density of the final metal is greater at the outer sections.
29
New cards
What is a cupola?
A cupola is a vertical cylindrical furnace equipped with a tapping spout near its base. Cupolas are used for melting cast irons.
30
New cards
What are some of the operations required in sand casting after the casting is removed from the mold?
The operations include (1) trimming, in which the sprues, runners, risers, and flash are removed, (2) core removal, (3) surface cleaning, (4) inspection, (5) repair if needed, (6) heat treatment, and (7) machining
31
New cards
What are some of the general defects encountered in casting processes? Name and briefly describe three.
General defects include: (1) misruns, in which the casting solidifies before filling the mold cavity; (2) cold shuts, in which two portions of metal flow together but there is lack of fusion at the joint; (3) cold shots, where solid globules of cast metal become entrapped in the casting; (4) shrinkage cavity, which is a depression on the casting surface or an internal void in the casting caused by solidification shrinkage; (5) microporosity, which is a network of small voids throughout the casting caused by localized solidification shrinkage; and (6) hot tearing, which is a crack in the casting caused by a mold that does not yield to the metal during the early stages of solidification shrinkage.
32
New cards
Quiz 7 (18,19)
Quiz 7 (18,19)
33
New cards
A circular sheet metal slug produced in a hole punching operation will have the same diameter as which of the following:
the die opening
34
New cards
Most sheet metalworking operations are performed as which of the following:
cold working
35
New cards
Sheet metal bending does NOT involve which of the following stresses and strains:
shear
36
New cards
Springback in a sheet metal bending operation is the result of which one of the following:
elastic recovery of the metal
37
New cards
The cutting force in a sheet metal blanking operation depends on which mechanical property of the metal (one correct answer):
shear strength
38
New cards
The maximum possible draft in a rolling operation depends on which of the following parameters:
coefficient of friction between roll and work
39
New cards
The starting workpiece in steel hot rolling of plate and sheet stock is which of the following (one best answer):
slab
40
New cards
Which of the following bulk deformation processes is involved in the production of nails for lumber construction:
bar and wire drawing
41
New cards
Which of the following is classified as a forging operation:
coining
42
New cards
Which of the following stress or strength parameters is used in the computation of the maximum force in a forging operation (one best answer):
final flow stress
43
New cards
Assignment 8 (26)
Assignment 8 (26)
44
New cards
Why are metals heat treated?
Metals are heat-treated to effect metallurgical changes that beneficially alter properties.
45
New cards
Identify the important reasons why metals are annealed.
The purposes of annealing include (1) to control properties, (2) to reduce brittleness and improve toughness, (3) to recrystallize cold‑worked metals, and (4) to relieve stresses from prior metalworking. At least 3 out of the four
46
New cards
What is the most important heat treatment for hardening steels?
The most important heat treatment for steels is martensite formation by heating steel into the austenite region and quenching.
47
New cards
What is the mechanism by which carbon strengthens steel during heat treatment?
When steel containing carbon is heat-treated, martensite is formed which is a hard and brittle non-equilibrium phase of steel. The extreme hardness of martensite results from the lattice strain created by carbon atoms trapped in the body-centered tetragonal structure, thus providing a barrier to slip.
48
New cards
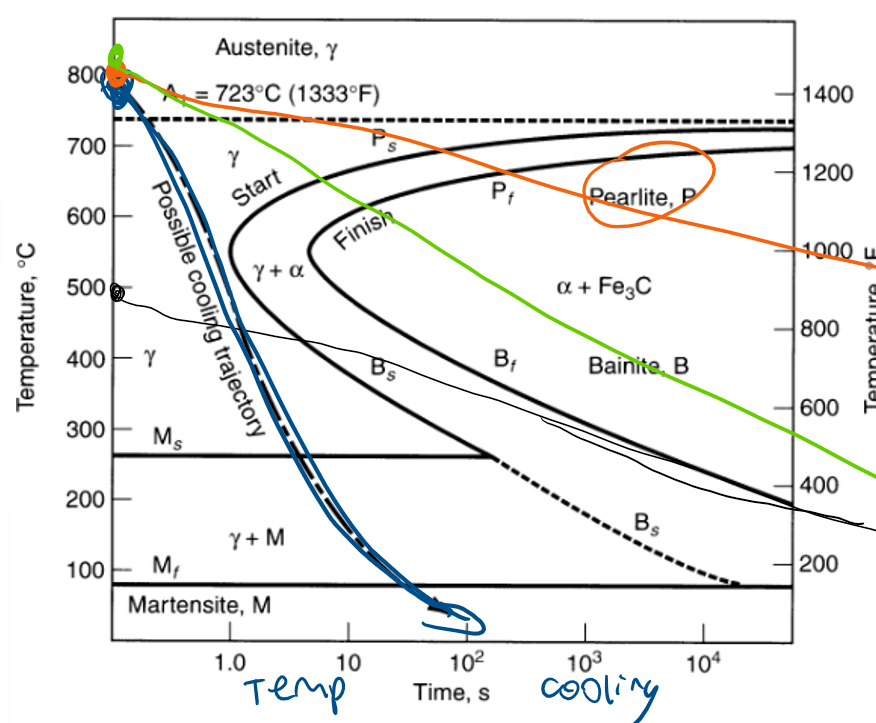
What information is conveyed by the TTT curve?
The time-temperature-transformation (TTT) curve indicates what phases in the iron‑carbon phase diagram will be produced under various conditions of cooling
49
New cards
What function is served by tempering?
Tempering involves heating and soaking of martensite for about one hour at a temperature below the austenitizing region, followed by slow cooling to reduce brittleness, relieve stresses, and increase toughness and ductility.
50
New cards
Define hardenability
Hardenability is the relative capacity of a steel to be hardened by transformation to martensite.
51
New cards
Name some of the elements that have the greatest effect on the hardenability of steel.
Important hardenability elements are chromium, manganese, molybdenum, and nickel *at least two.*
52
New cards
Indicate how the hardenability alloying elements in steel affect the TTT curve.
The hardenability alloying elements operate by pushing the nose of the TTT curve to the right, thereby permitting slower cooling rates for conversion of austenite to martensite
53
New cards
Define precipitation hardening.
Precipitation hardening is a heat treatment in which very fine particles (precipitates) are formed so that dislocation movement is blocked and the metal is thus strengthened and hardened.
54
New cards
How does carburizing work?
Carburizing adds carbon to the surface of low‑C steel, thereby transforming the surface into high‑C steel for greater hardening potential.
55
New cards
Identify the selective surface-hardening methods.
The selective surface-hardening methods include flame hardening, induction hardening, high‑frequency (HF) resistance heating, electron beam (EB) heating, and laser beam (LB) heating.3 out of 5.
56
New cards
26 Prezi
26 Prezi
57
New cards
Austenizing
Gamma, rapid cooling, increase hardness and strength
58
New cards
tempering
500 C, air cooling, increase toughness
59
New cards
Annealing
gamma, slow furnace cooling, ductility
60
New cards
gamma, air cooling, most predictable uniform grain structure
normalizing
61
New cards
blue austenitizing, black tempering, orange annealing, green normalizing
Time-temperature-transformation curve
62
New cards
tensile strength and yield strength go up but area and elongation are reduced
If you add carbon in steel
63
New cards
for softer materials
Brinell
64
New cards
increase hardness.
Not a reason to anneal a metal
65
New cards
reduce brittleness, improve toughness, relieve stresses, recrystallize coldworked metals
Annealing will
66
New cards
Chapter 7 Ceramics Prezi
Chapter 7 Ceramics Prezi
67
New cards
Ceramic
An inorganic compound consisting of a metal or semi metal and one or more nonmetals
68
New cards
* Properties of ceramic materials
* High hardness, electrical and thermal insulating, chemical stability, and high melting temperatures
* Brittle, virtually no ductility-can cause problems in both processing and performance of ceramic products
* Some ceramics are translucent, window glass (based on silica) being the clearest example
* Brittle, virtually no ductility-can cause problems in both processing and performance of ceramic products
* Some ceramics are translucent, window glass (based on silica) being the clearest example
69
New cards
Density of ceramics
most ceramics are lighter than metals but heavier than polymers
70
New cards
Melting temperatures of ceramics
higher than for most metals
71
New cards
Electrical and thermal conductivities for ceramics
lower than for metals, but the range of values is greater, so some ceramics are insulators while others are conductive
72
New cards
Thermal expansion of ceramics
somewhat less than for metals, but effects are more damaging because of brittleness
73
New cards
Quiz 9 (7,8)
Quiz 9 (7,8)
74
New cards
Among the thermosetting polymers, the most widely used commercially is which one of the following:
phenolics
75
New cards
Glass products are based primarily on which one of the following minerals:
silica
76
New cards
Of the three polymer types, which one is the most important commercially:
thermoplastics
77
New cards
Synthetic diamonds date to:
1950s
78
New cards
The leading commercial synthetic rubber is which one of the following:
styrene-butadiene rubber
79
New cards
Which of the following ceramics are commonly used as abrasives in grinding wheels:
aluminum oxide
80
New cards
Which one of the following comes closest to expressing the chemical composition of clay:
Al2(Si2O5)(OH)4
81
New cards
Which one of the following is the chemical formula for the repeating unit in polyethylene:
C2H4
82
New cards
Which one of the following materials is closest to diamond in hardness:
cubic boron nitride
83
New cards
Which one of the three polymer types does not involve cross- linking:
thermoplastics
84
New cards
Quiz 10 (13)
Quiz 10 (13)
85
New cards
A thermoforming mold with a convex form is called which one of the following:
a positive mold
86
New cards
In rotational molding, centrifugal force is used to force the polymer melt against the surfaces of the mold cavity where solidification occurs:
false. It is the force of gravity in the doubly rotating mold that forces the polymer against the mold surfaces.
87
New cards
In which of the following property categories do plastic parts often compare favorably with metals:
impact resistance,
\
\
88
New cards
The function of the ejection system in injection molding is which one of the following:
separate the part from the cavity after molding
89
New cards
The parting line in injection molding is which one of the following:
where the two mold halves come together
90
New cards
The two principal components of an injection molding machine are which of the following:
clamping and injection units
91
New cards
Which of the following defects or problems is associated with injection molding:
\
\
flash
92
New cards
Which of the following is a section of a conventional extruder barrel for thermoplastics:
compression section
93
New cards
Which of the following processes are generally limited to thermoplastic polymers:
blow molding
94
New cards
Which of the following processes is associated with the production of plastic sheet and film:
blown-film extrusion process
95
New cards
Assignment 9 (7,8)
Assignment 9 (7,8)
96
New cards
What is a ceramic?
A ceramic is an inorganic compound, consisting of a metal (or semi-metal) and one or more non-metals.
97
New cards
What is the difference between the traditional ceramics and the new ceramics?
Traditional ceramics are based primarily on clay products (e.g., pottery, bricks) while new ceramics are more recently developed ceramics which are generally simpler in chemical composition (e.g., oxides, carbides).
98
New cards
What type of atomic bonding characterizes the ceramics?
Covalent and ionic bonding.
99
New cards
What is glazing, as applied to ceramics?
Glazing involves the application of a surface coating of oxides such as alumina and silica, usually to a porous ceramic product such as earthenware, to make the product more impervious to moisture and more attractive.
100
New cards
What is one of the important applications of titanium nitride, as mentioned in the text?
As a thin coating on cutting tools to prolong tool life.