Eyes and Ears (HA)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
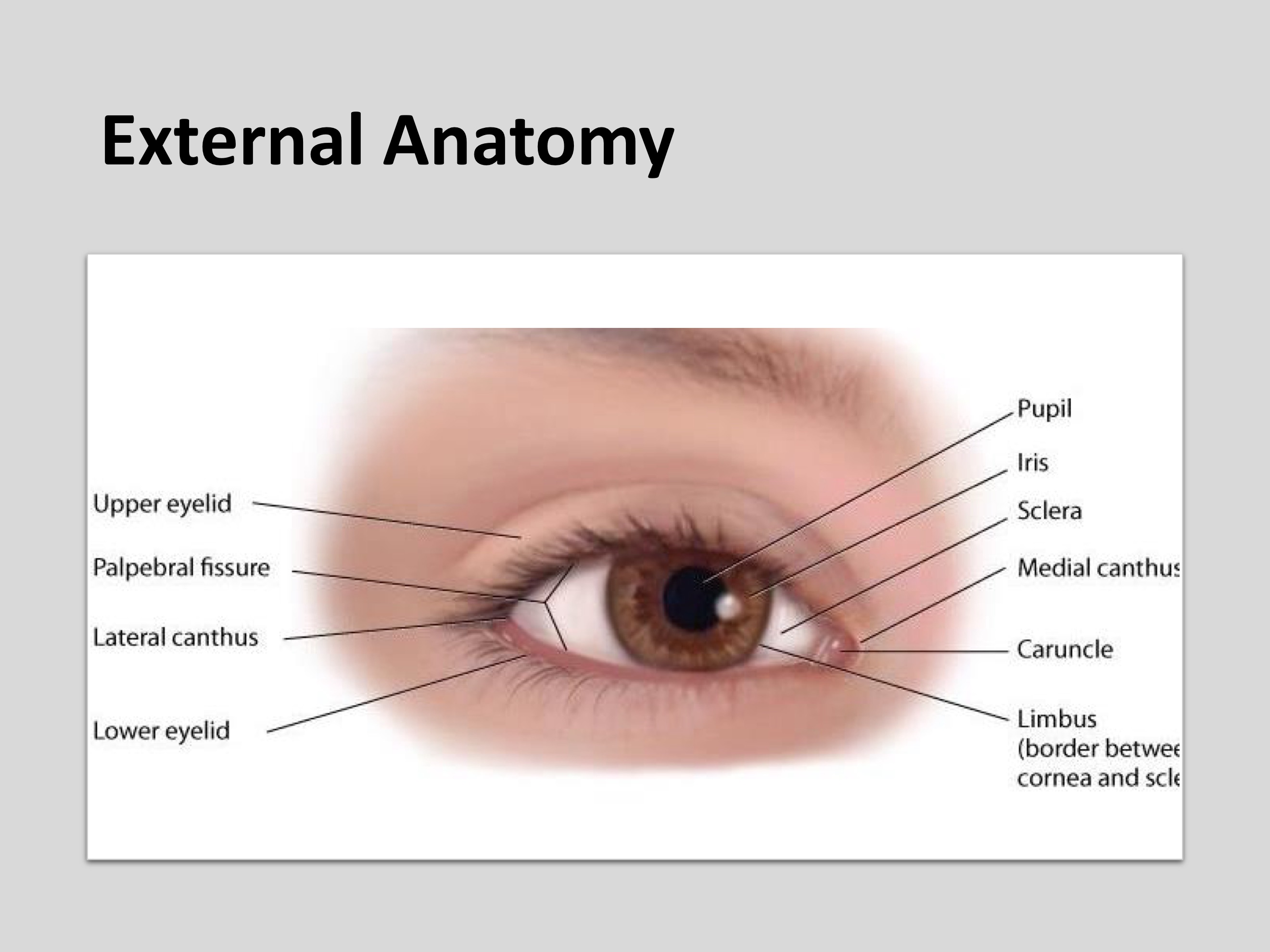
External anatomy of the eye
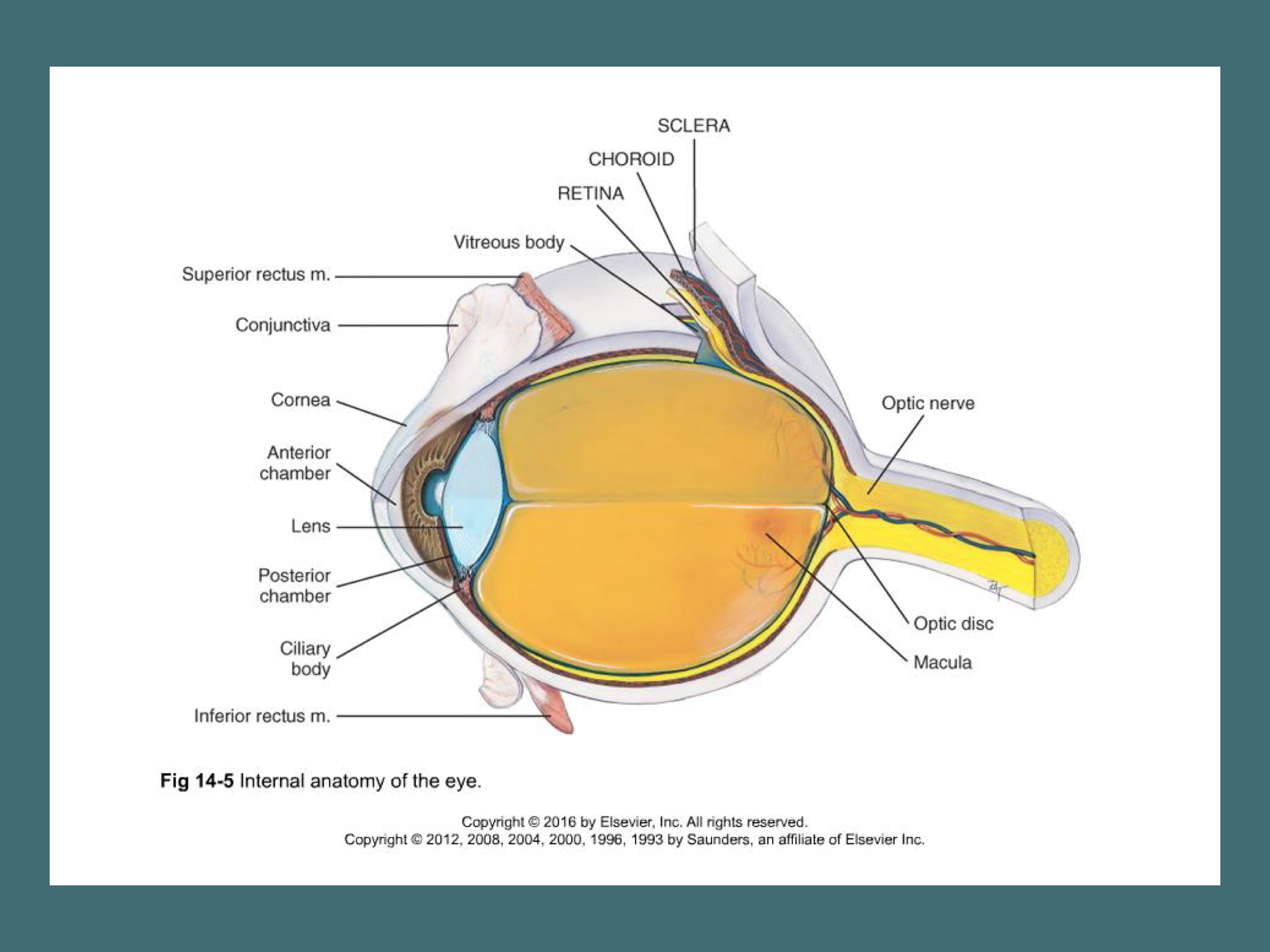
Internal anatomy of the eye
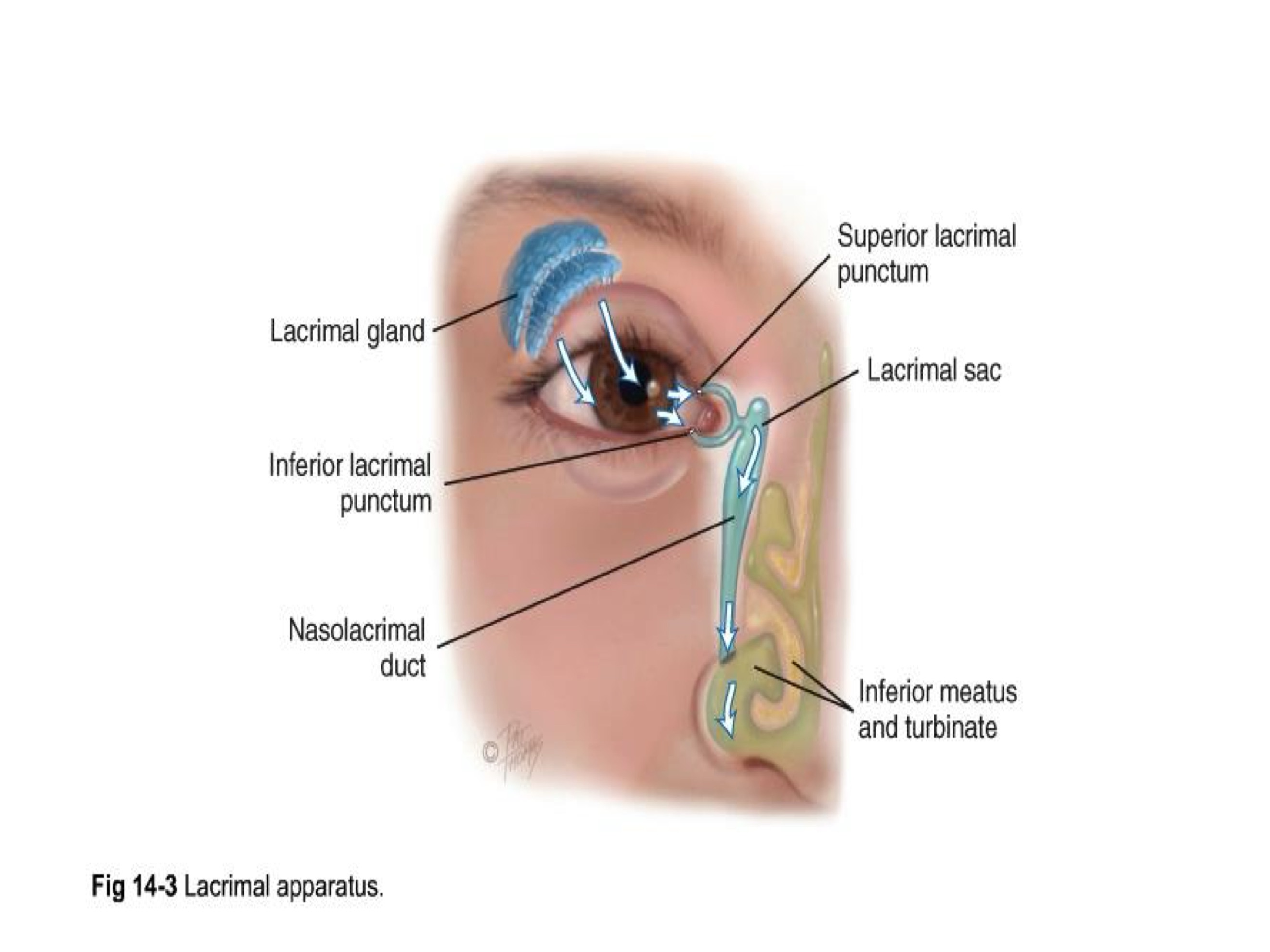
lacrimal apparatus
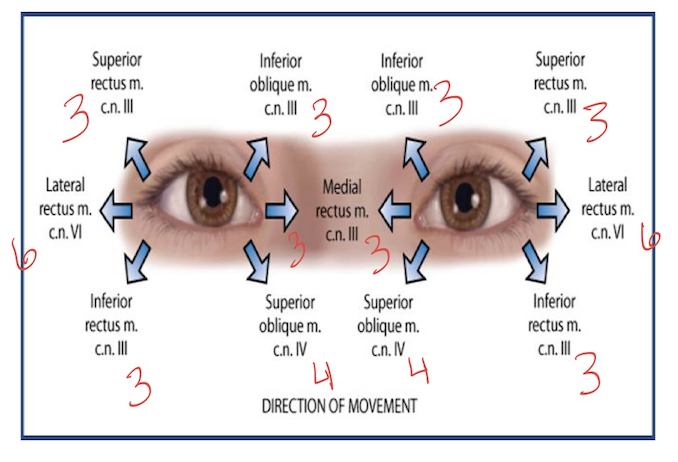
eye muscles + cranial nerves
CN 3- oculomotor
CN4- trochlear
CN 6- abducens
subject data - eye
vision
pain
strabismus (eye misalignment)
diplopia (double vision)
redness
swelling
ptosis (droopy eyelids)
watery discharge
history of eye surgery or injury
glaucoma (been tested? fam history?)
corrective lens
Snellen eye chart

corneal light reflex testing
assess alignment of eyes by having patient look at a penlight. the light reflex should fall within the pupil bilaterally
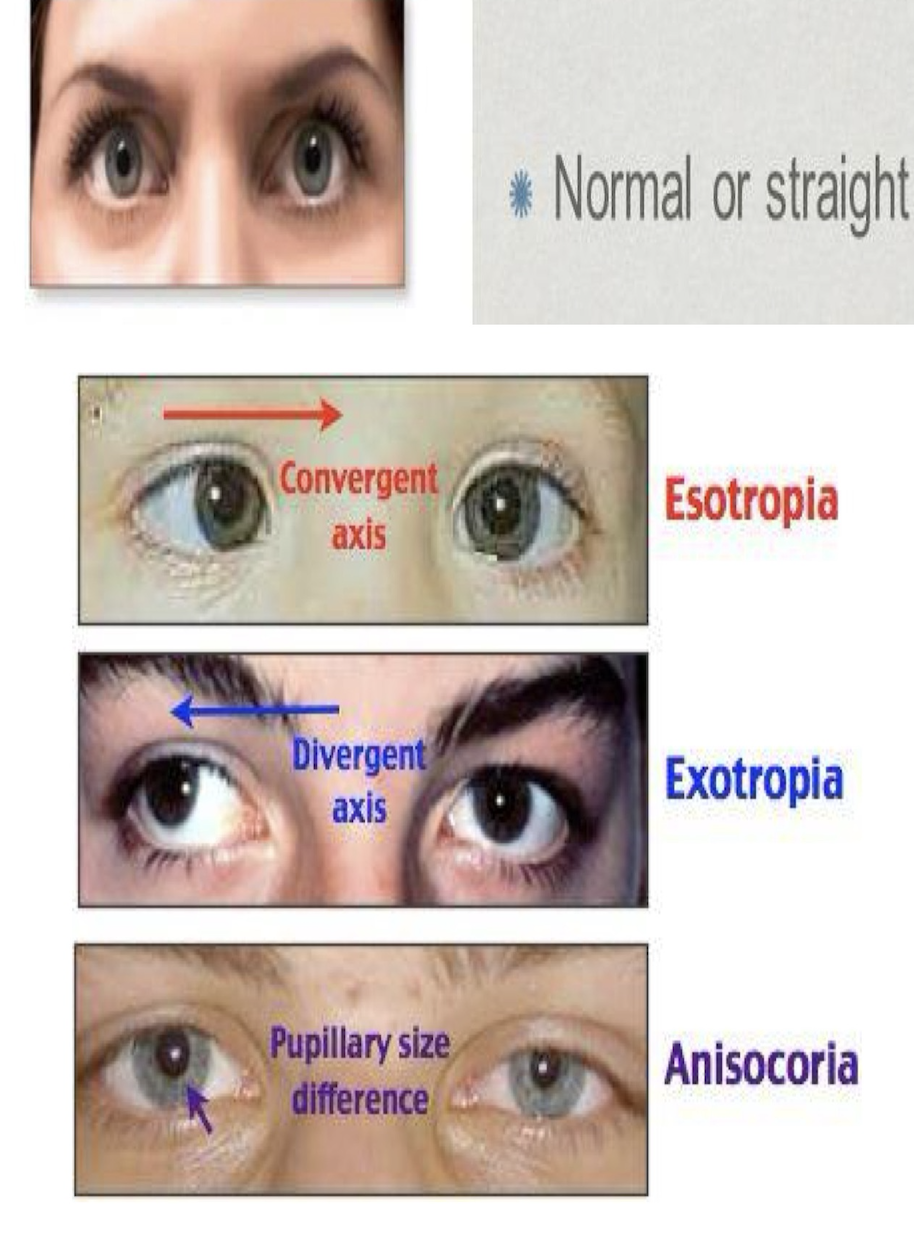
Cover - uncover test
testinging peripheral vision
testing visual fields
confrontation test
inspect the conjunctiva and sclera
inspection of ocular structures
inspection of anterior eyeball
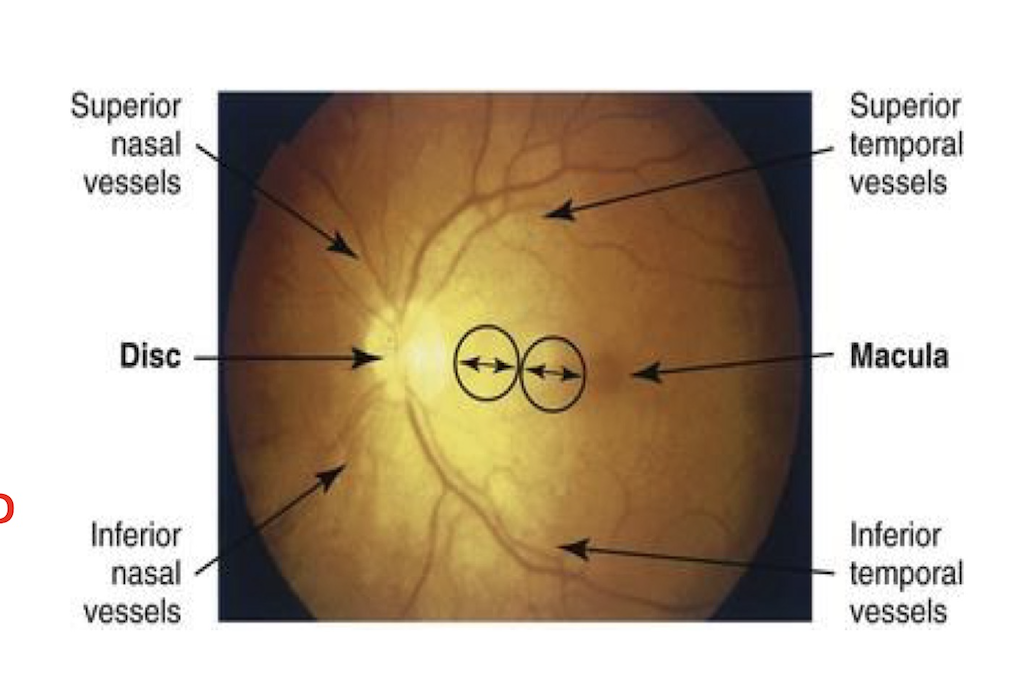
documenting PERRLA
far vision- pupils dilate
near vision- pupils constrict
pupils are equal round and reactive to light and accommodation
developmental competence: aging adults
pupil size decreases
lens loses elasticity, becoming hard decreased ability to accommodate for near vision; called presbyopia (farsightedness)
visual acuity may diminish gradually after age 40 and more so after age 70
by age 70, lens begin to thicken and yellow the beginning of cataracts
cataracts- results from a clumping of proteins in lens
glaucoma- increased intraocular pressure most common type (loss of peripheral vision)
macular degeneration or break down of cells in macula- loss of central vision is most common cause of blindness
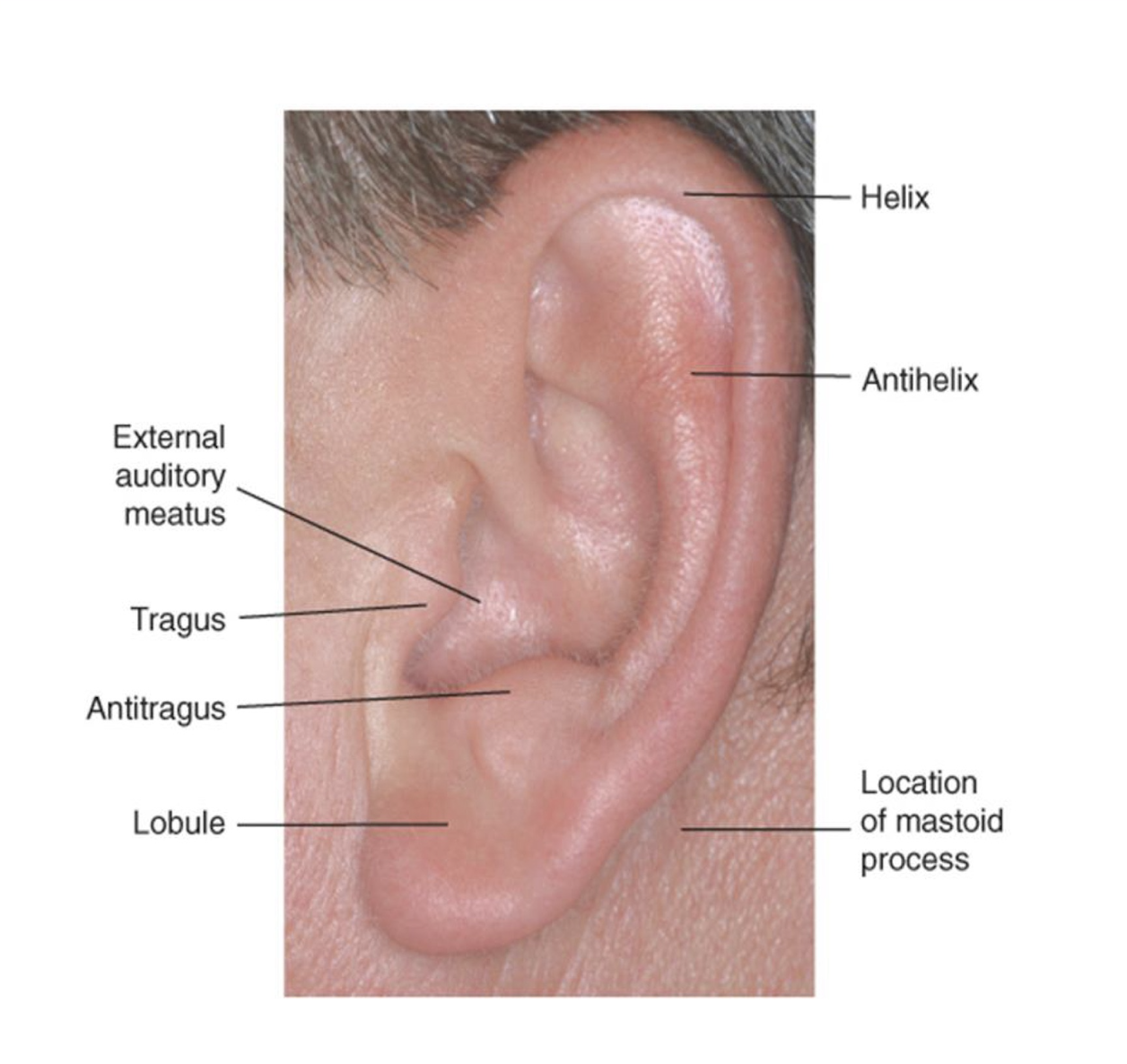
External ear
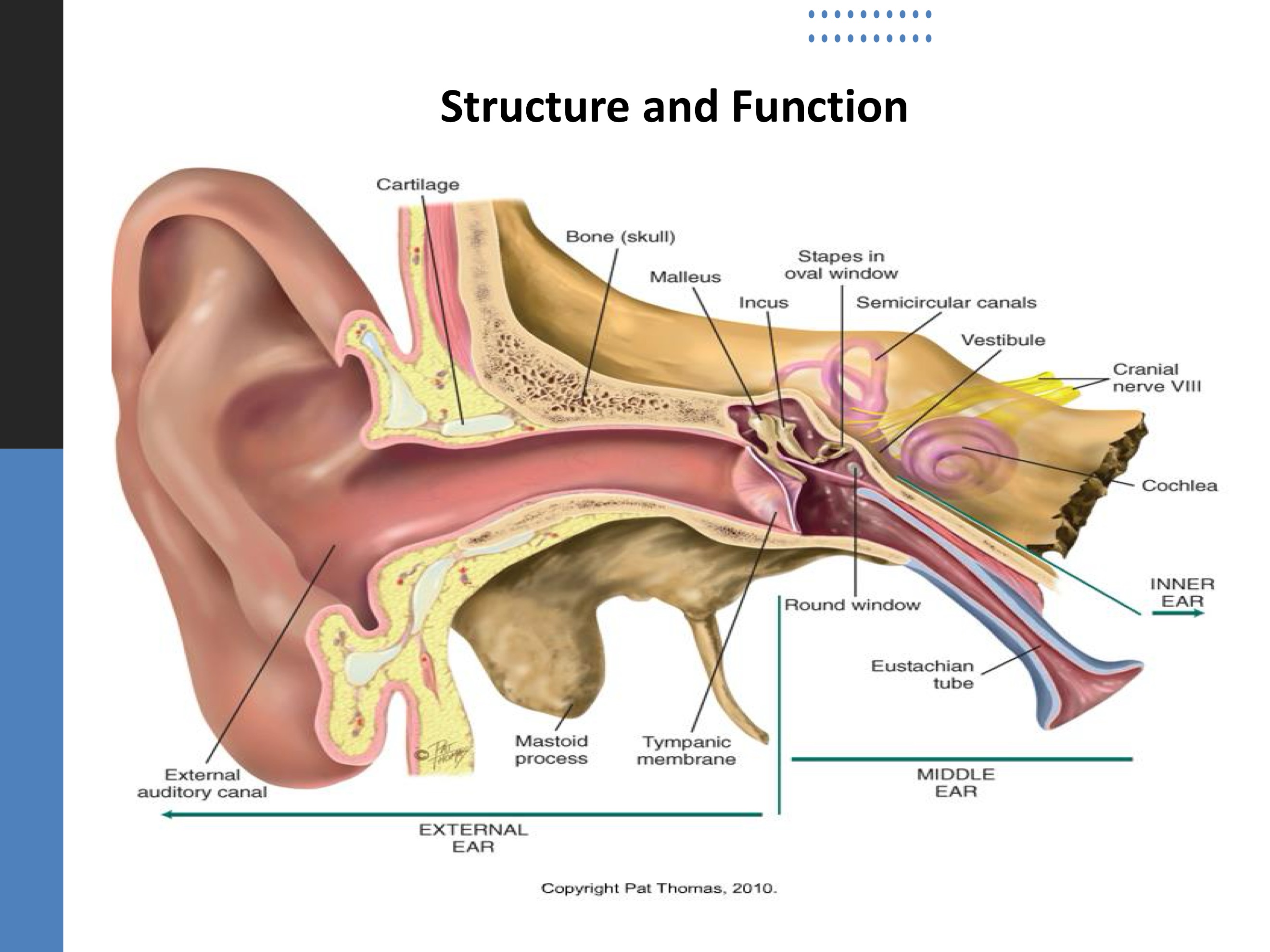
Internal ear
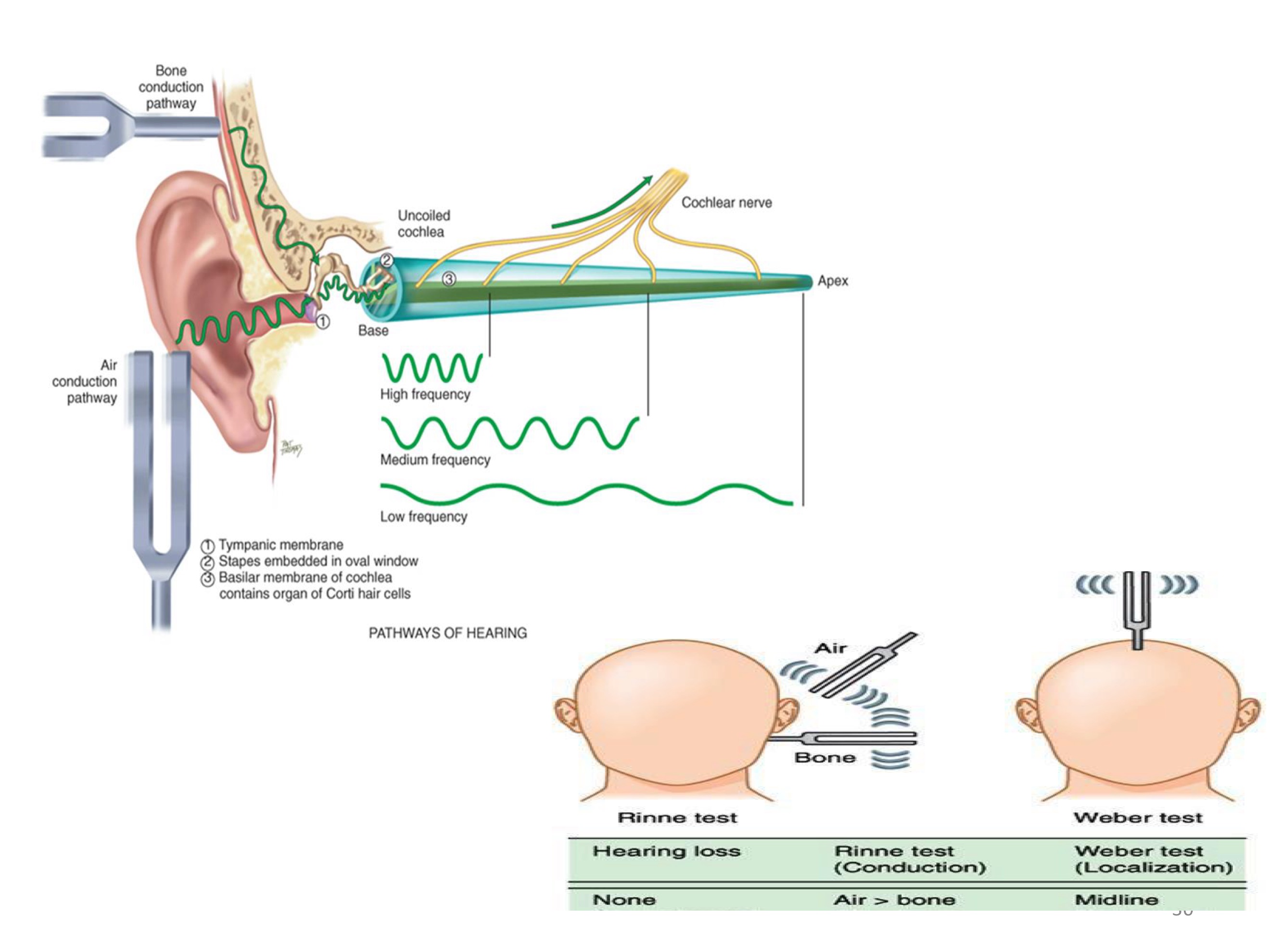
Rinne and Weber test
Equilibrium
the semicircular canals in inner ear constantly feed information to brain about body’s position in space
if canal becomes inflamed, it feeds wrong information to brain, creating a staggering gait and a strong spinning whirling sensation called vertigo
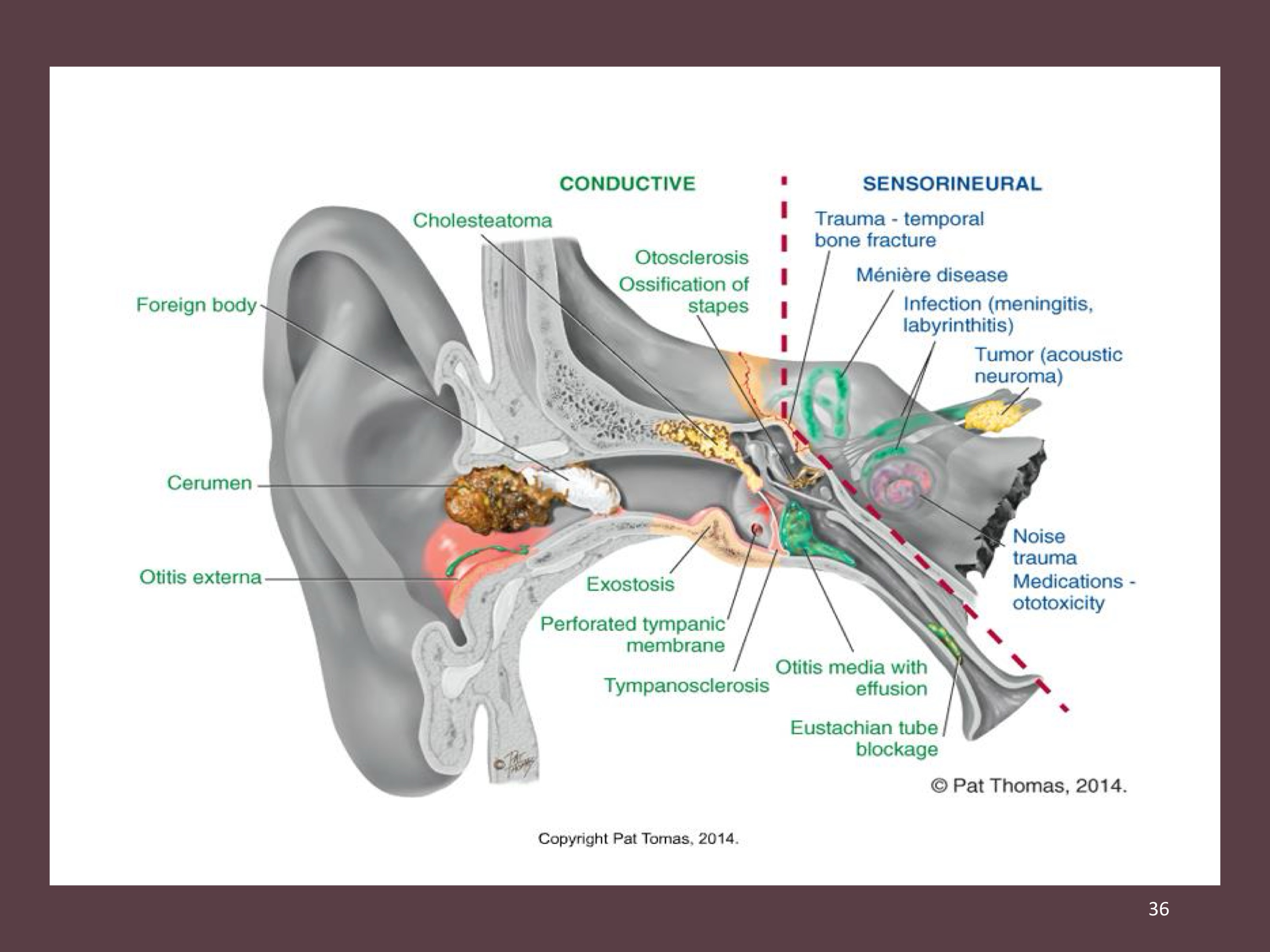
Otosclerosis
common cause of conductive hearing loss in young adults between ages 20 and 40
gradual hardening that causes stapes to become fixed, impeding transmission of sound and causing progressive deafness
presbycusis
age-related hearing loss, is the cumulative effect of aging on hearing by nerve degeneration
usually occurs in 50s and slowly progresses
impacted cercum is a common but reversible cause of hearing loss in older people
accumulated cerumen is drier with aging because of atrophy of apocrine glands (dying of sweat glands)
hearing loss
Hearing loss:
anything obstructing transmission of sound impairs hearing
Conductive hearing loss:
involves a mechanical dysfunction of external or middle ear
sensorineural hearing loss
involves pathology of the inner ear, CN 8. Can be caused by prebycusis or ototoxic drugs
mixed hearing loss
is combination of conductive and sensorineural types in same ear
Conductive vs. Sensorineural
subjective data- ear
earaches
infections
discharge
hearing loss
environmental noise
tinnitus- ringing in ears
vertigo/ dizziness
physical exam
external ear (inspect and palpate)
otoscopic examination
external canal
tympanic membrane
adult: pull ear up and back
child 3 or younger: pull ear down and back
testing hearing acuity
conversational speech (CN8, vestibulocochlear is or is not in tact)
whispering voice test (CN8)
tuning fork test
weber test
rinne test
Romberg Test
assesses ability of vestibular apparatus in inner ear to help maintain standing balance
they need to keep their eyes closed for 20 sec
put your arm in front and behind them so that they don’t fall (should not need assistance)