Exam 5, Chapters 16-19
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Which hormones are released by the anterior pituitary gland and what are their actions?
adrenocoricotropic hormone (ACTH) - release cortisol
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) - stimulates follicular cells to secrete estrogen (F); stimulates production of sperm cells (M)
growth hormone (GH) - promotes growth of long bones
luteinizing hormone (LH) - triggers ovulation
prolactin (PRL) - milk production after birth
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) - controls secretion of hormones from thyroid gland
What are the functions of parathyroid glands and where are they located?
posterior surface of thyroid gland
secrete parathyroid hormone
released when blood calcium levels too slow… need calcium balance
increase release of calcium ions from bone by stimulating osteoclasts
increasing absorption of dietary calcium ions by small intestine
increasing reabsorption of calcium ions from fluid in kidneys
Explain the concerns surrounding Rh(-) mothers who are pregnant with Rh(+) fetuses.
hemolytic disease caused by maternal antibodies attacking fetal red blood cells
Know the characteristics of erythrocytes (RBCs).
biconcave discs
increased flexibility, easy flow
lack nuclei, mitochondria
carry more oxygen
transport oxygen
hemopoiesis - producing formed elements
fractionation - process of separating whole blood for clinical analysis into plasma & formed elements
38C (100.4F) is normal temperature
high viscosity
pH of 7.4
7% of body weight
cannot divide
Which vitamins are required for RBC production?
vitamin B12 - for DNA synthesis
vitamin B6 - for hemoglobin synthesis
amino acids - building blocks for globin
iron - form heme of hemoglobin
folic acid - for DNA synthesis and cell division
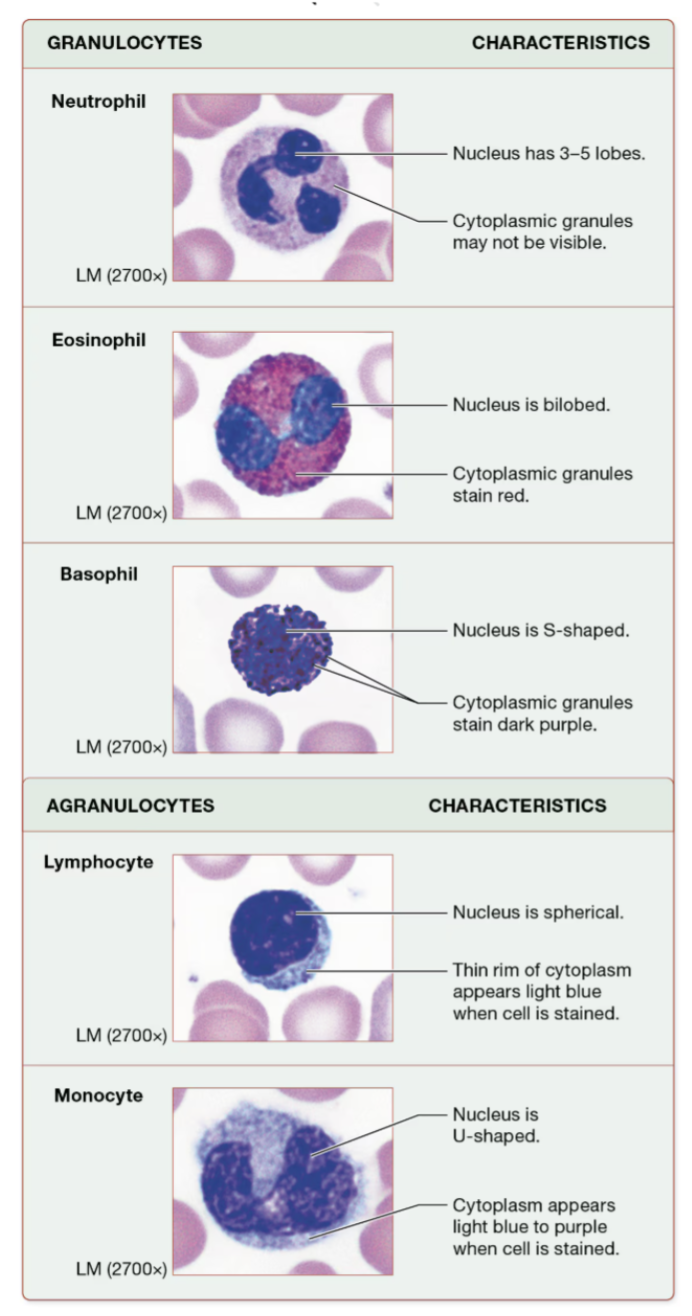
Know the generalized functions of the following: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes.
neutrophils - ~60%, fight bacterial infections
eosinophils - ~3%, defense against parasitic worm infestations & allergic reactions
basophils - <1% , release chemicals helping with inflammation
lymphocytes - ~30%, immunity
T cells - attack foreign cells
B cells - produce antibodies
monocytes - ~6%, largest; phagocytize bacteria, dead cells, and other debris
Describe the basic steps of hemostasis (blood clotting).
Vascular Phase - vascular spasm, blood vessel vasoconctricts
Platelet Phase - platelet adhesion (attachment) & platelet aggregation (stick together)
Coagulation Phase - blood clotting (coagulation)
Know the composition of plasma including the plasma proteins.
water (~90%)
plasma proteins (~9%)
albumin - transport substances (fatty acids, thyroid hormones, steroid hormones)
globulin - antibodies, aka immunoglobulins; transport globulins
fibrinogen - form clots and produce long, insoluble strands of fibrin
transferrin
small solutes (~1%)
nutrients (glucose, amino acidsm nitrogenous wastes, ions, dissolved gases of oxygen and carbon dioxide)
What is the equation for stroke volume?
SV = EDV - ESV
SV = stroke volume
EDV = end diastolic volume, filling/relaxing
ESV = end systolic volume, contracting
Where can a pulse be located?
brachial, carotid, radial, femoral, dorsalis pedis, posterior tibial arteries
Why are the action potential and contractile phase longer in cardiac muscle than skeletal muscle? How does cardiac muscle compare to skeletal and smooth muscles?
allow blood ejection from heart
Skeletal - striated, voluntary, attached to bones
Cardiac - striated, involuntary, heart
Smooth - non-striated, involuntary, walls of organs
Know the 5 factors that increase blood pressure.
increased heart rate
increased stroke volume
increase blood viscosity
increased peripheral resistance
increased blood volume
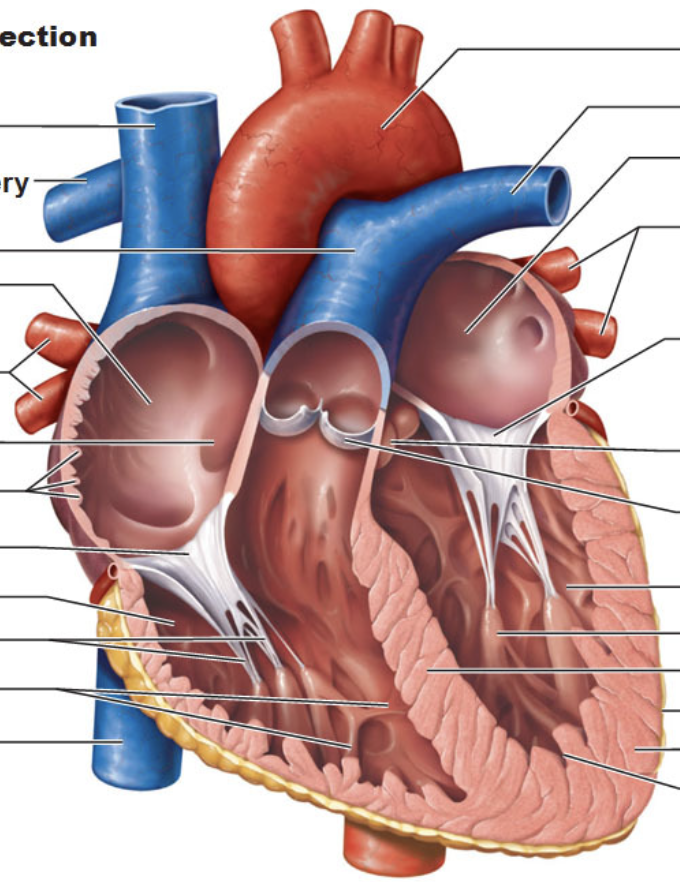
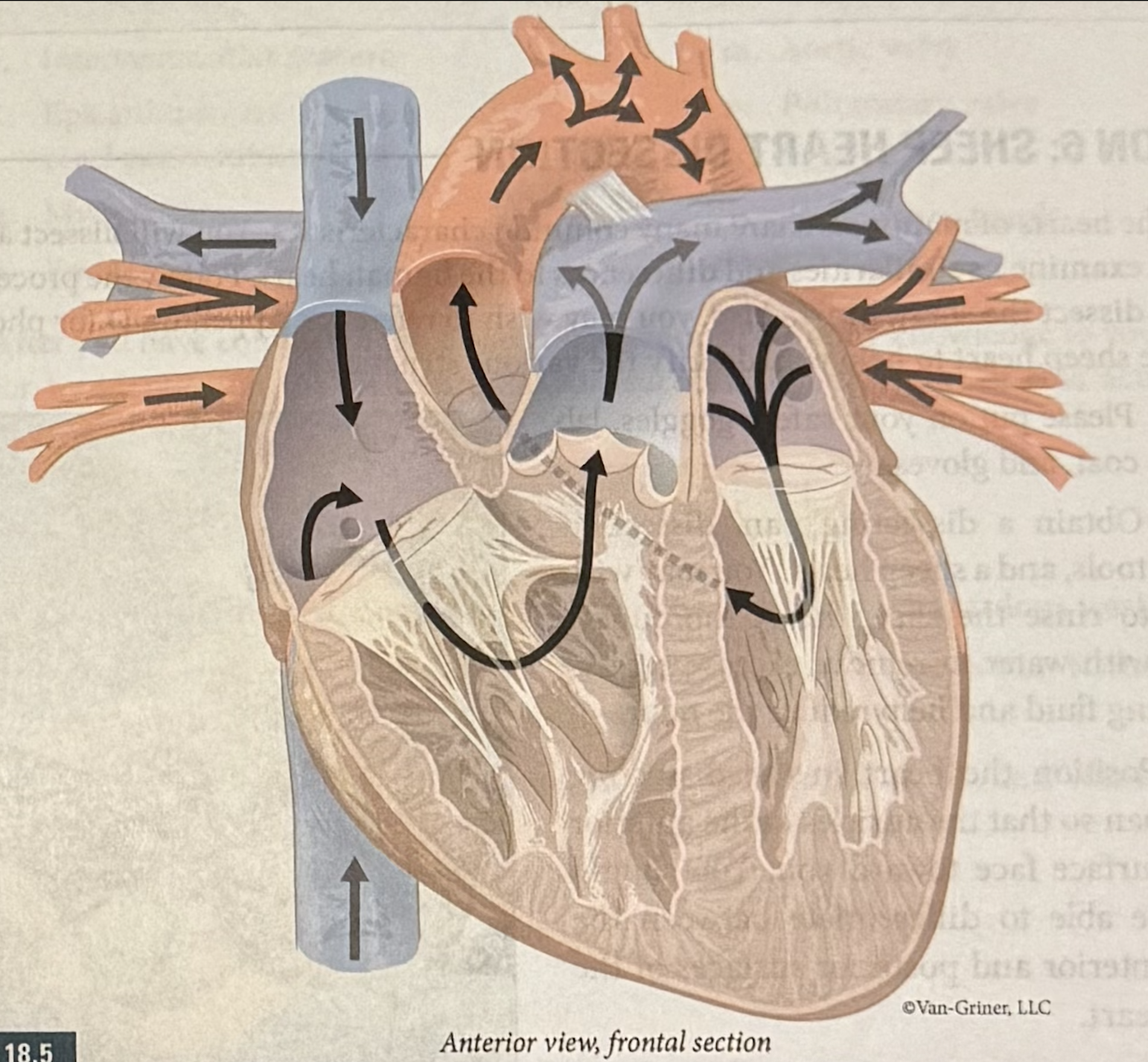
Label blood flow and know the steps.
Superior and Inferior vena cavae and Coronary sinus (veins) → right atrium (receiving chamber) → tricuspid valve (AV valve) → right ventricle (pumping chamber) → pulmonary valve (semilunar valve) → pulmonary trunk (artery) branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries (artery) → gas exchange at lungs (blood loses CO2 & gains O2) → right and left pulmonary veins (veins) → left atrium (receiving chamber) → bicuspid valve (AV valve) → left ventricle (pumping chamber) → aortic valve (semilunar valve) → aorta branches into systemic arteries (arteries) → gas exchange at the tisses (blood loses O2 & gains CO2)
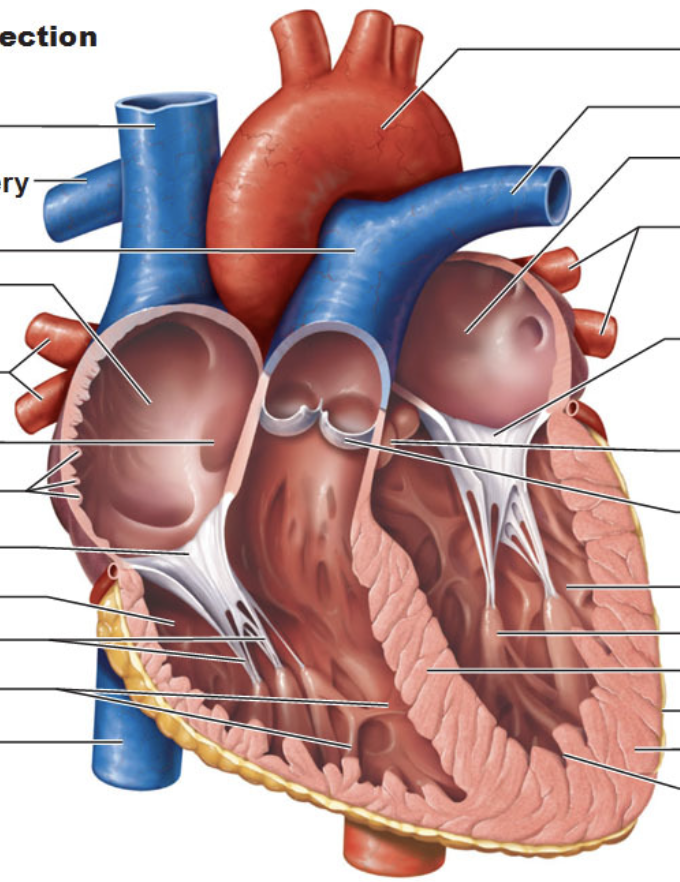
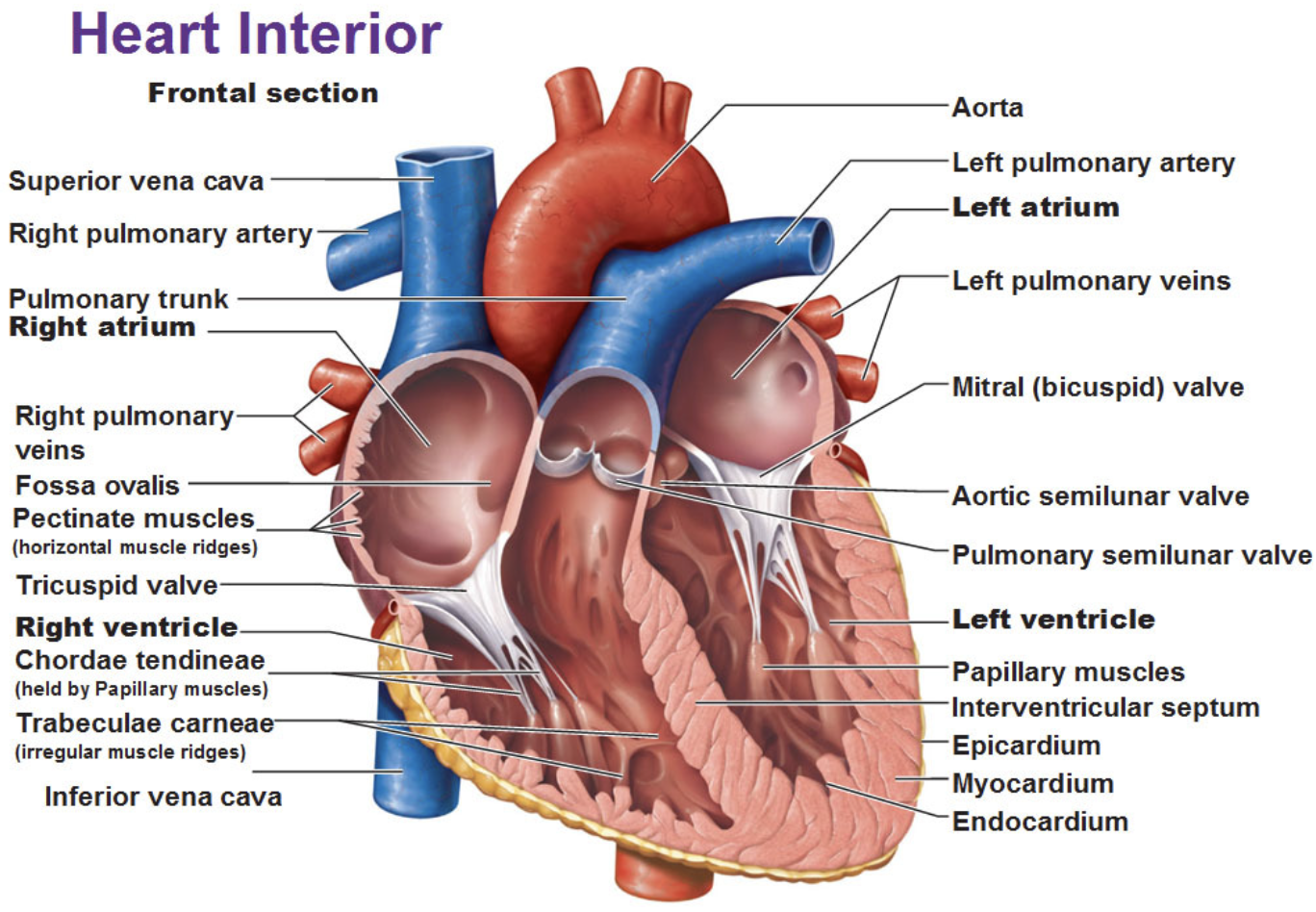
Label heart.
What are the basic structures of steroid hormones and non-steroid hormones?
steroid hormones - derived from cholesterol, with core hydrocarbon rings
hydrophobic & interact with plasma membrane or intracellular receptors
sex hormones, adrenal cortex hormones
non-steroid hormones - amino acid-based, water-soluble, use second messengers
amines, proteins, peptides, glycoproteins
What substance is needed to make steroids?
cholesterol
Name the hormones which are derived by cholesterol.
cortisol, aldosterone, estrone, progesterone, testosterone
Describe the steps of the hypothalamus in controlling endocrine functions.
hypothalamus → anterior pituitary gland → peripheral endocrine gland → target cells → action
production of ADH and oxytocin
secretion of regulatory hormones to control activity of anterior lobe of pituitary gland
control of sympathetic output to adrenal medullae
What are the functions of the two hormones of the posterior pituitary hormones?
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - causes kidneys to reduce water excretion
oxytocin (OT) - milk ejection
List the endocrine glands and their basic functions.
hypothalamus - links nervous & endocrine systems
pituitary gland - produce hormones, release ADH & oxytocin
thyroid gland - produce T3 & T4, regulate metabolism
thymus - help make T-lymphocites
parathyroid glands - increase blood calcium levels
pineal gland -
adrenal glands - fight or flight response, respond to stress
pancreas - regulate blood glucose levels
testes - produce testosterone, control sperm production
ovaries - produce estrogen and progesterone, regular menstrual cycle & pregnancy
Describe how the three calcium controlling hormones work.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) - stimulus for release is decrease in plasma Ca2+ monitored by Ca2+-sensing receptor
raises plasma Ca2+ in three ways
mobilizes calcium from bone
enhances renal reabsorption of calcium
indirectly increases intestinal absorption of Ca2+
Calcitrol - aka vitamin D3
primary hormone responsible for enhancing Ca2+ uptake
facilitates renal absorption of Ca2+ out of bone
production is regulated by action of PTH
Calcitonin - released when plasma Ca2+ increases
decreases bone resorption
increases renal calcium excretion
Describe the important functions of calcium.
calcified matrix of bone and teeth
neurotransmitter release at synapse
role in myocardial and smooth muscle contraction
cofactor in coagulation cascade
“cement” for tight junctions
influences excitability of neurons
muscle contraction
signal in second messenger pathaways
Know the hormones of the adrenal medulla and the cortex and describe their functions.
adrenal medulla:
epinephrine (E) & nonrepinephrine (NE)
fight or flight
blood glucose increases
blood glycerol and fatty acids increase
heart rate increases
blood pressure rises
breathing rate increases
air passages dilate
blood flow redistributes
adrenal cortex:
cortisol - stress hormone, stimulates fluconeogenesis, fat & protein breakdown, inhibits inflammatory response
aldosterone - increase reabsorption of sodium ions & water, secretion of potassium & hydrogen ions, maintaining blood pressure & acid-base homeostasis
androgens - sex hormones affecting reproductive organs that trigger development of male physical characteristics
How does cortisol affect the immune system?
acts as anti-inflammatory agent by decreasing levels of leukocytes
suppress immune response
Describe how the pancreas can function as an endocrine and exocrine gland.
has two major types of secretory tissue
two groups of cells within pancreas
endocrine cells - islet cells
secrete glucagon (alpha), insulin (beta), somatostatin (delta)
exocrine cells - acinar cells
digestive enzymes
Know the functions of blood.
regulate pH & ions
restrict fluid losses at injury sites
defense against toxins & pathogens
transport materials to & from cells
oxygen & carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, waste products, immune system components
exchange gases
distribute solutes
maintain body temperature
stabilize blood pressure
Know the 3 components that make up blood.
plasma - ~55%
water, plasma proteins, small solutes
buffy coat - <1%
white blood cells, platelets
RBC - ~44%
erythrocytes
Define hemoglobin and understand its functions.
protein molecule consisting of four polypeptide subunits of iron ions
heme binds to oxygen where oxygen levels are high forming oxyhemoglobin
when oxygen levels are low, hemoglobin releases oxygen to become deoxyhemoglobin
Understand why Type O blood individuals are universal donors and why Type AB blood individuals are universal recipients.
Type O = no antigens, donor
Type AB = no antibodies, recipients
antibodies attack antigens
Name 2 substances required for blood coagulation.
calcium, vitamin K
What is the function of auricles?
appendages that increase atrial volume
What is the function of papillary muscles? What are the chordae tendineae? What is their function?
papillary muscles attach to chordae tendineae
prevent cusps from ballooning back to atria
What three veins empty into the right atrium? What veins empty into the left atrium?
right atrium - superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
left atrium - pulmonary veins
Know the location of AV valves.
tricuspid valve - between right atrium and right ventricle
bicuspid - between left atrium and left ventricle
Know the flow of blood through the pulmonary and systemic circuit.
right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary trunk → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body → right atrium
right side receives oxygen-poor blood from tissues
pumps to lungs to get rid of CO2, pick up O2, via pulmonary circuit
left atrium receives blood from pulmonary circuit
right ventricle pumps blood through pulmonary circuit
left side receives oxygenated blood from lungs
pumps to body tissues via systemic circuit
right atrium receives blood returning from systemic circuit
left ventricle pumps blood through systemic circuit
What is the function of the coronary sinus?
where heart’s veins empty which then drains into right atrium
Define myocardial infarction.
heart attack
occurs when plaques in coronary arteries rupture & clot forms that obstructs blood flow to myocardium
What is the function of intercalated discs?
anchor cardiac cells
What are the 3 parts of the cardiac action potential? What ions are involved?
depolarization - Na+ in
plateau phase - Ca2+ out
repolarization - K+ out
Describe what occurs during the phases of an ECG: P wave, QRS complex, T wave.
P wave - depolarization SA node → atria
QRS complex - ventricular depolarization & atrial repolarization
T wave - ventricular repolarization
Know the “sounds” of the heart, 1st and 2nd. LUB-DUP
1st - lub; AV valves close, beginning of systole
2nd - dup; SL valves close, beginning of ventricular diastole
Define CO, SV, HR. How are they connected?
CO = HR x SV
CO = cardiac output, normal = 5.25 L/min
HR = heart rate, number of beats per minute
SV = stroke volume, volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each beat
Define preload, contractibility, afterload.
preload - degree of stretch of cardiac muscle cells before they contract
contractibility - contractile strength at given muscle length, independent of muscle stretch & EDV
afterload - pressure ventricles must overcome to eject blood
How does epinephrine, norepinephrine, ANG II, ADH, ANP (lowers BP), and aldosterone affect blood pressure?
epinephrine - increase BP
norepinephrine - increase BP
ANG II - increase BP, vasoconstriction
ADH - increase VP, water retention
aldosterone - increase BP, retain sodium
ANP - decrease BP, vasodilation
What are the functions of angiotensin II?
increase thirst
sodium ion retention
secretion of aldosterone
increase blood volume
What are the 3 mechanisms used to move blood through the veins?
skeletal muscle pump
respiratory pump
venous valves