S2 Chemistry HL
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Define Ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Define Covalent bonding
Electrostatic attraction between a shared pair and positively charged nuclei.
Define Metallic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cations and a sea of delocalised electrons
Properties of Ionic bonding
High melting points, low volatility, generally high solubility (in polar compounds), high conductivity (when molten), high brittleness
Properties of Covalent bonding
Low melting point, high volatility, low solubility, poor conductivity, high brittleness
Properties of Metallic bonding
High melting points, low volatility, very low solubility, high conductivity, high malleability and ductility.
Volatility
A substance’s tendency to vaporise
Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve another substance to form a uniform mixture/solution
Conductivity
The ability of charged particles to move through a region of space
Brittleness
a material's tendency to fracture or shatter suddenly under stress with little to no plastic (permanent) deformation.
Malleability
Ability to be bent/reshaped when compressed
Ductility
Ability to be drawn out into wire when stretched
Bond polarity
Results from the difference electronegativities
Polarity
Related to the way electrons are distributed within molecules/bonds
Molecular polarity
describes electron distribution throughout whole molecules
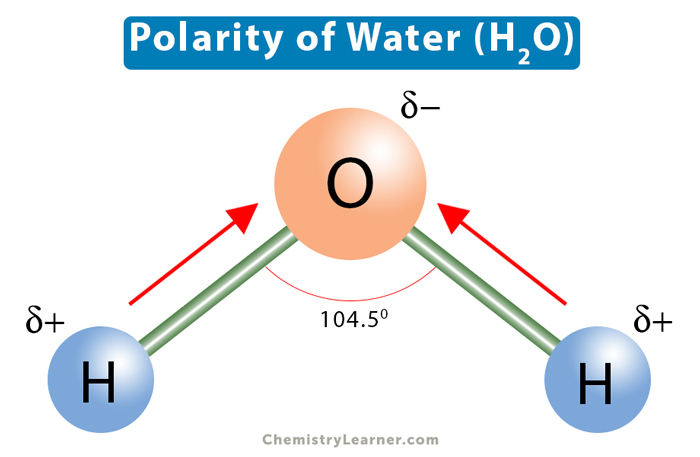
Polar molecules
When the electron distribution leads to a partial negative charge on one end of the molecule and a partial positive on the other. Creating a dipole moment, (In other words they look asymmetrical)
Intermolecular forces
Electrostatic forces of attraction that keep molecules together
London dispersion forces
Temporary induced dipole via random electron movement.
Occur in all molecules
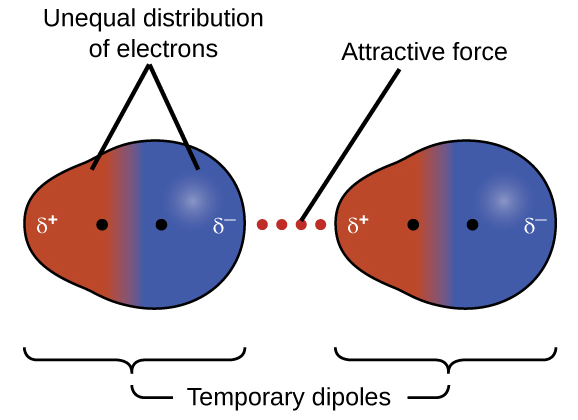
LDF Examples
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, O2, N2, I2, Cl2, CH4, C2H6, CO2
Dipole induced dipole
The presence of a permanent dipole in the polar molecule induced the formation of temporary dipole in the neighbouring non-polar molecule
Between polar and non-polar molecules
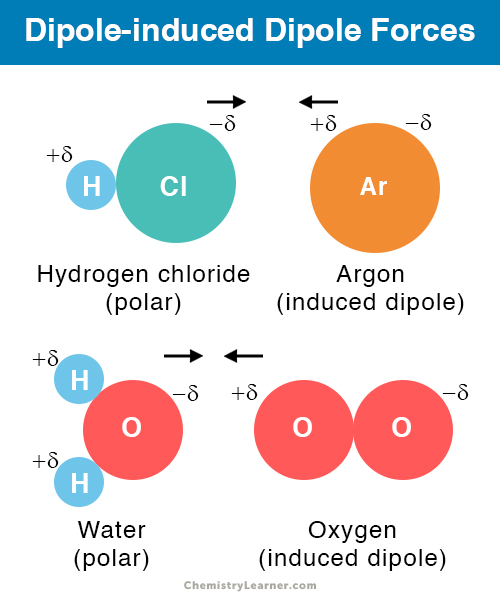
Dipole Induced Dipole examples
O2, I2, HCL, Ar
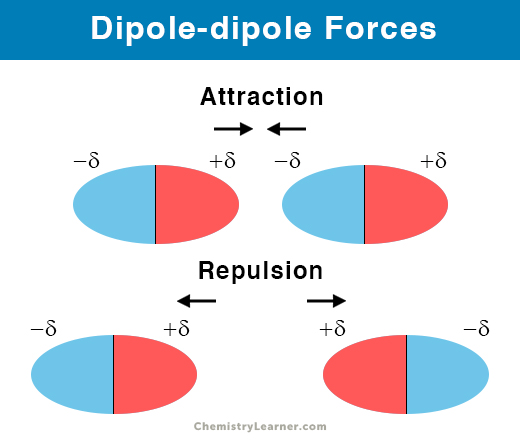
Dipole Dipole
When a molecule is polar, it has a permanent dipole, therefore experiences dipole-dipole forces of attraction with neighbouring polar molecules
Between polar molecules ONLY
Hydrogen bonding
Intermolecular attraction between two molecules which contain a hydrogen bond to a highly negative element like F,O,N
Van Der Waal Forces
LDF/Dipole-Dipole/Dipole-induced Dipole
Order of IMF (weakest-strongest)
LDF → D-ID→ D-D→ H bonds → Ionic/Covalent
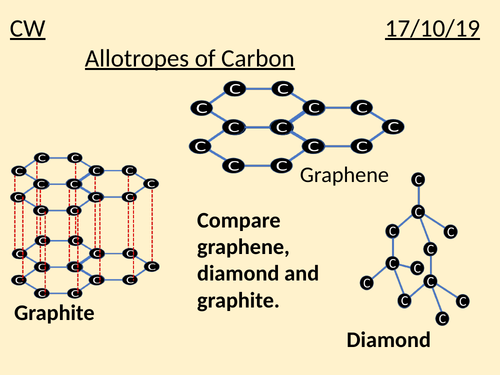
Covalent network structures
Vast/continuous 3D structures linked via strong covalent bonds/extreme hardness/high melting points
Allotropes + arrangement
Diamond (tetrahedral) / Graphite (C atom bonded to 3 other c atoms) / Graphene (one layer of graphite
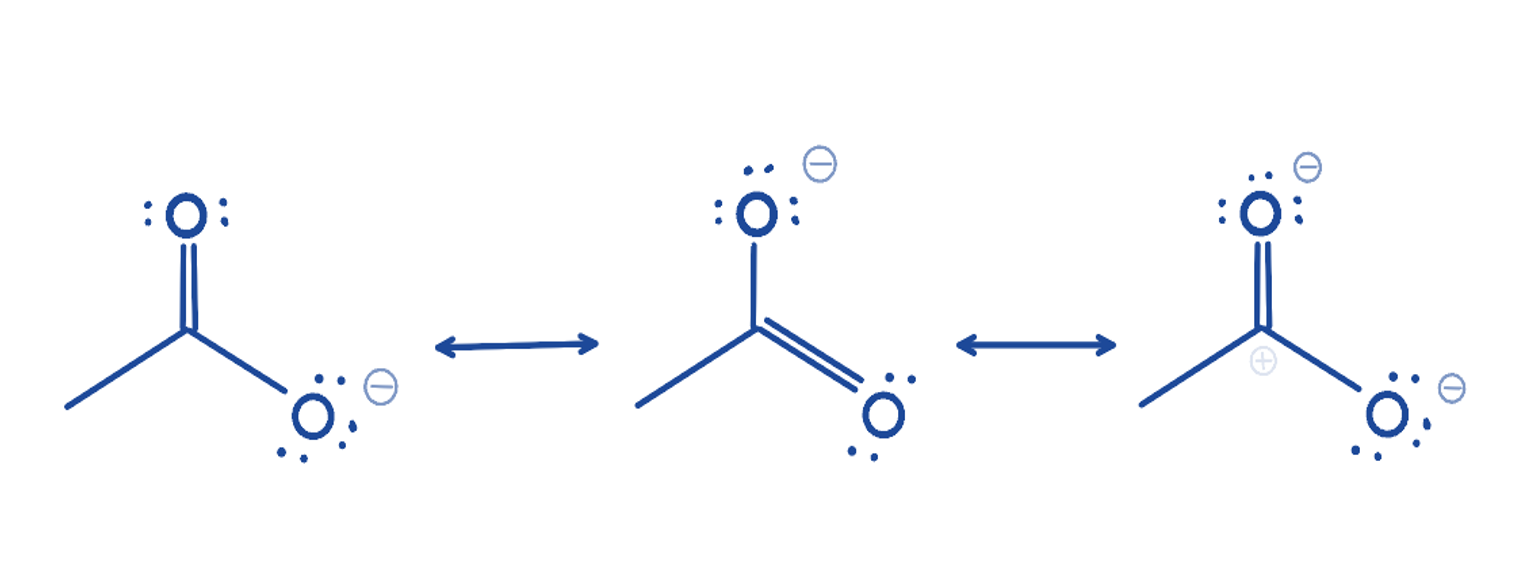
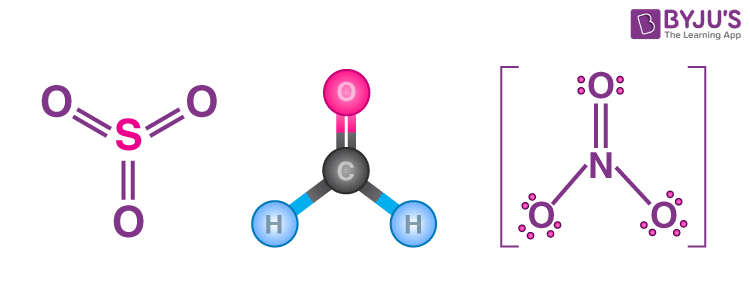
Resonance bonds AHL
Two or more possible resonance structures to represent a molecule
Hybridisation AHL
Concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals of new shapes
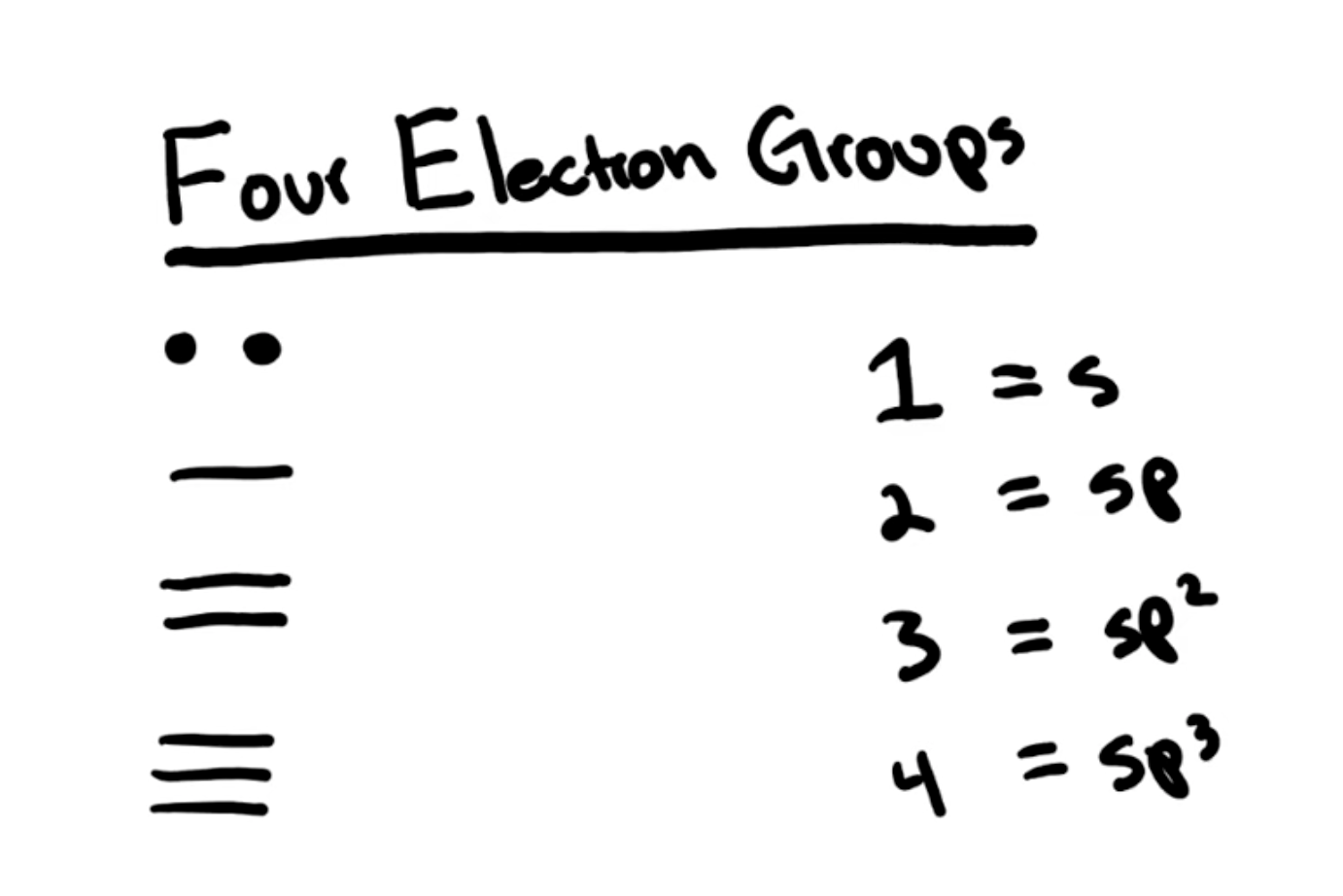
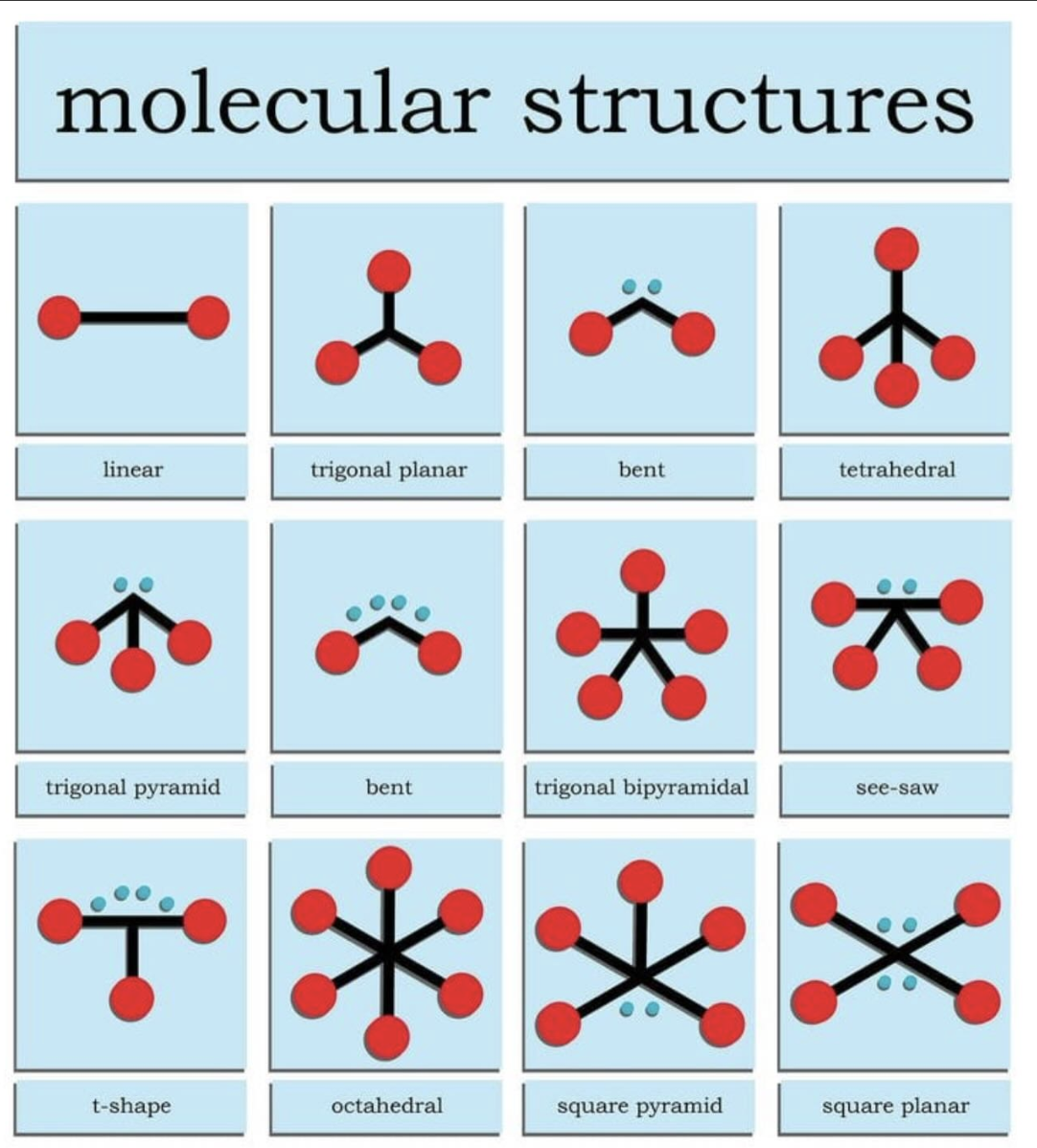
Electron geometry
determined by the total number of electron domains (both bonded pairs and lone pairs) surrounding a central atom
Molecular Geometry
Describes the arrangement of only the atoms, ignoring lone pairs, resulting in the molecule's actual 3D shape
EG:Linear (2)
2 pairs
No lone pairs = Linear
1 lone pair = Linear
EG: Trigonal Planar (3)
3 e groups
0 lone pairs = Trigonal Planar
1 lone pairs = Angular

EG: Tetrahedral (4)
4 be- groups
0 lone pairs
BA: 109.5
MG: Tetrahedral
OR
3 be-groups
1 lone pair
<109.5
MG: trigonal pyramidal
OR
2 be- groups
2 lone pairs
«109.5
MG: bent
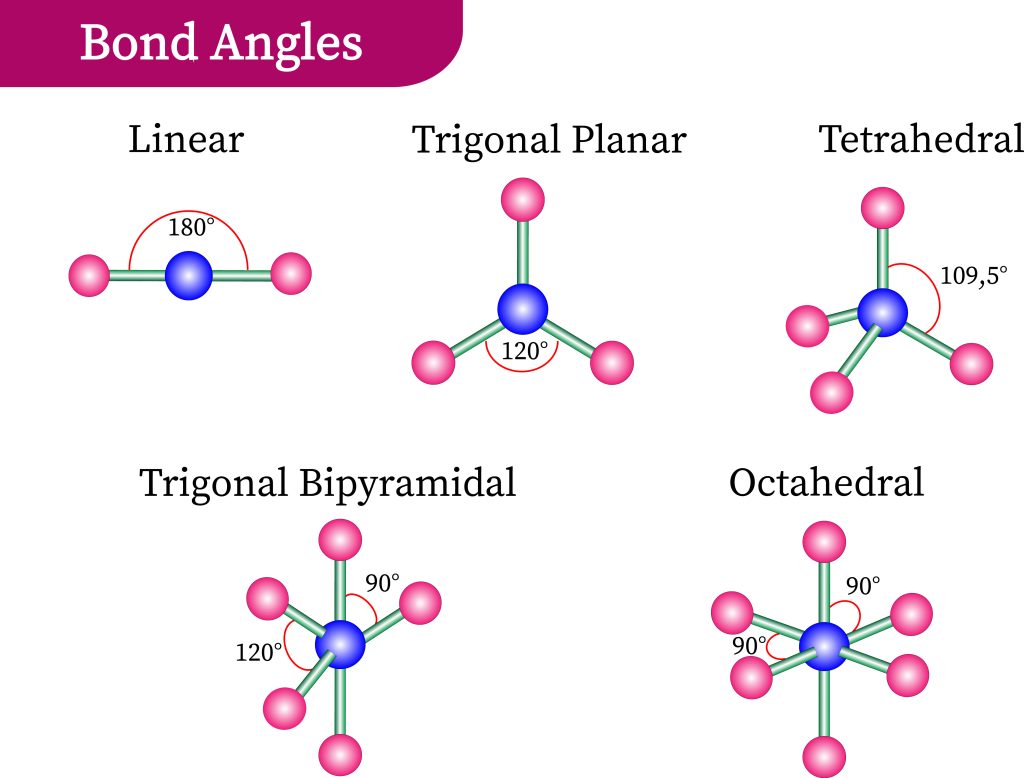
EG: Trigonal bipyramidal (5)
5 be- groups
0 lone pairs
BA: 120 (équatorial)/ 90 (axial)
MG: Trigonal bipyramidal
OR
4 be- groups
1 lone pairs
BA: <120 (équatorial)/ <90 (axial)
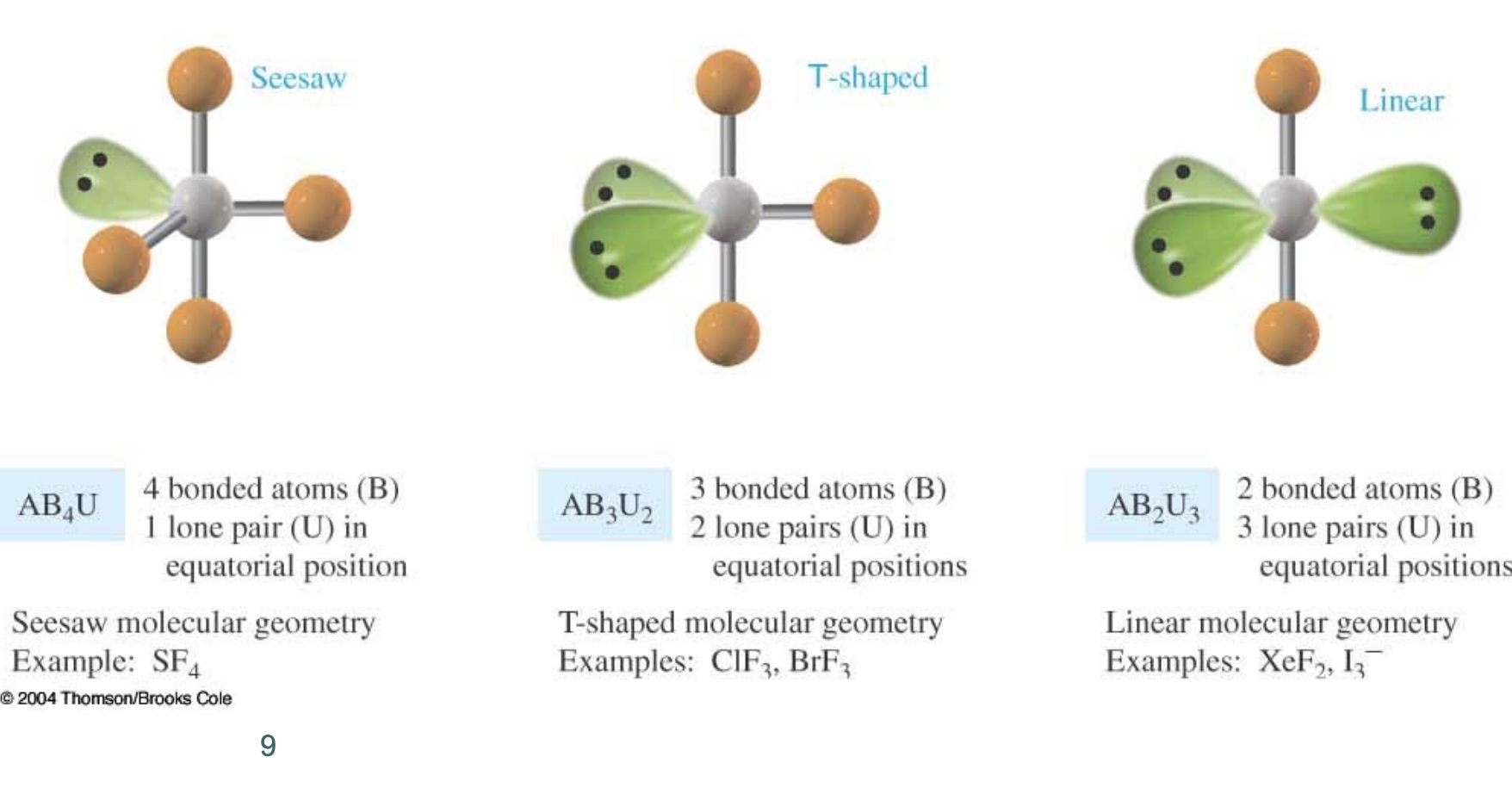
MG: Seesaw
OR
3 be- groups
2 lone paris
BA: <90
MG: T shaped
Or
2 be- groups
3 lone pairs
BA: 190
MG: Linear
EG: Octahedral (6)
6 Be- groups
0 Lone pairs
BA: 90
MG: Octahedral
OR
5 Be- groups
1 lone pair
BA: <90
MG: square pyramidal
OR
4 Be- groups
2 lone pairs
BA: 90
MG: square planar