Family Health and Infants (week 8)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
defining family
primary unit of socialization
influenced by ppl/institutions
no universal definition
nuclear
multigenerational/extended
blended
lone-parent
same-sex parent
impact of change on family system
one-parent family
divorce
ill family member
complex med conditions
family’s role in growth/develpment
proved safe, caring, supportive environment
help children learn, grow, build confidence
teach values, culture, traditions passed via generations
sense of identity/belonging
Calgary Family Assessment Model
CFAM
guide to understand family structure, development, functioning
structural assessment (CFAM)
identify family members, relationships, contet
genograms (family trees) + ecomaps (outside connections (social relationships/supports))
sample questions
Who are the members of your family?
Has anyone moved in or out lately?
Are there family members who don’t live with you?
developmental assessment (CFAM)
describe development life cycle/stages
sample questions
What do you most enjoy about your life?
What do you regret?
Have you planned for care as health declines?
functional assessment (CFAM)
how family members interact
instrumental aspects = daily activities (meals, meds)
expressive aspect = communication, problem solving, roles
sample questions
Who ensures Grandma takes her medicine?
Whose turn is it to make dinner?
How can we get Martin to help with care?
cultural safety
ensure care is free of discrimination/racism
focuses on power balance in nurse-pt relationship
pt decides if care feels safe
cultural humility
approach as learner, reflecting on own biases
build respect, trust-based relationships
recognized that your cultural norms are NOT the standard
family decision making + nurses support
families create own way to solve problems/make decisions
choices based on values, beliefs, social influences
decision-making stems from tradition or discussion
all families = strength/potential for growth
nurses recognize/support strengths to promote well-being
Family Nursing
families central to perinatal/paediatric nursing
nurses treat families with respect/dignity
listen to family POV/honor choices
share info clear, accurate, helpful
Support families to take part in care/decisions at their comfort level
Family Nursing - Family-Centred Care
nurse = unique communication style/beliefs
nurses must respect culture differences
focus on whole family, not just indivisuals
consider home, community, social factors that affect health
build meaningful relationships to support wellness/equity
Summary of Family Nursing
collaborative - family needs/goals
strength-based - family + communication resources
respectful - value family knowledge/expertise
family-centered - multidisciplinary/family-focused care principles
Paediatric nursing
improve quality of healthcare for children/families
health promotion/surveillance - well-child/baby visits
developmental
nutrition
oral health (start solids)
children health problems
trusting/collaborative relationship with child/family
philosophy of care - paediatric nursing
Canadian Paediatric Nursing Standards (5 standards)
I = supporting/partnering with child + family (engagement/empowerment)
II = advocating for equitable access + rights of children + their family (SDOH + systematic influences)
III = delivering developmentally appropriate pediatric care (validated tools, knowledge of growth, developmental parameters)
IV = creating child-and-family-friendly environment (family assessment, inclusive/safe)
V = enabling successful transitions
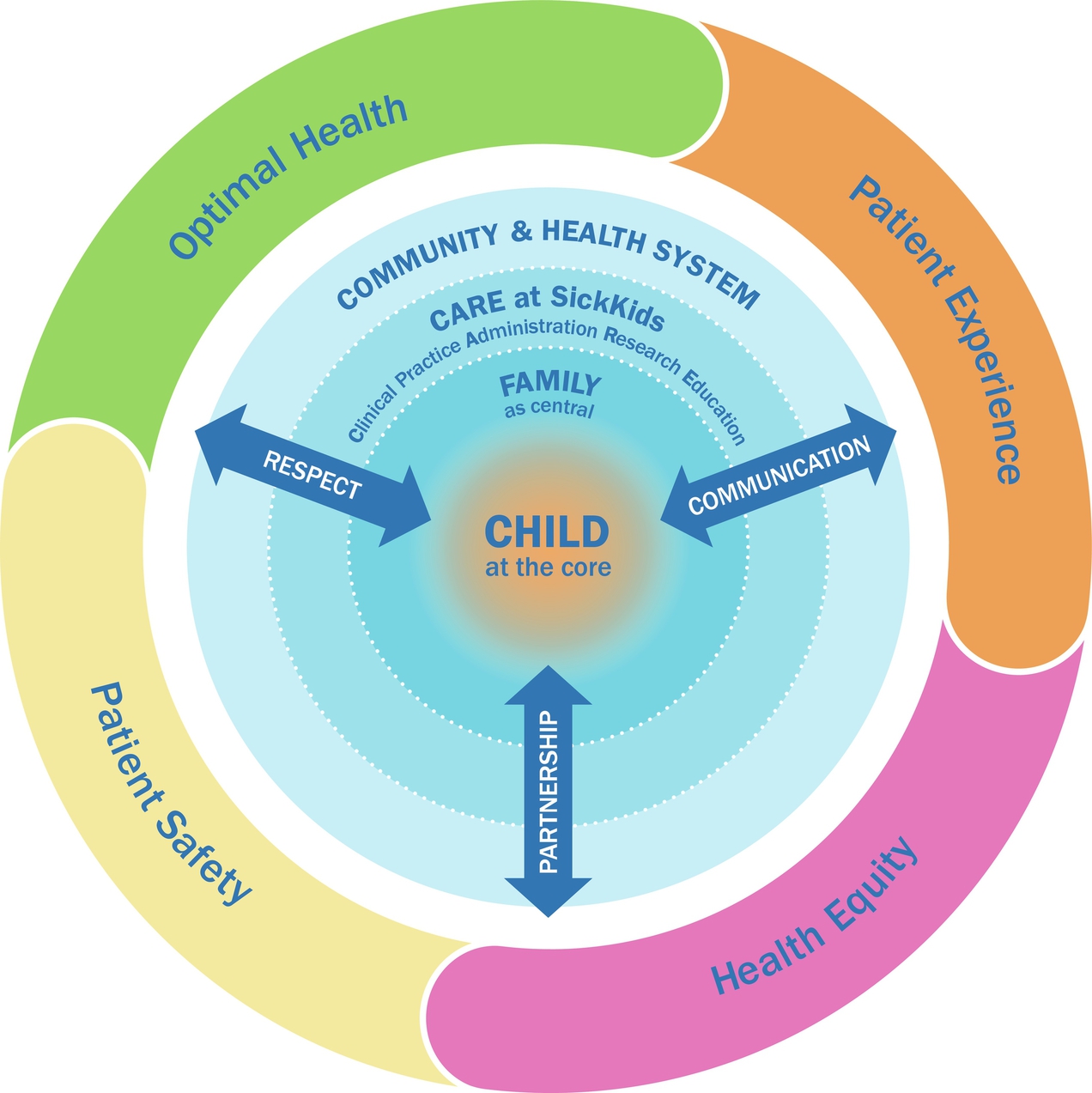
family-centered care + SickKids Model of Child/family-centered care - paediatric nursing
enable and empower
SickKids
respect
communication
partnership
pt experience
pt safety
health equity
optimal health
atraumatic care - paediatric nursing
WHO, WHAT, WHERE, WHEN, WHY, HOW of any procedure
minimize physical/psychological distress
do no harm
Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE)
negative impacts on children’s experience
impacts mental and physical health
from childhood carried through to adulthood
we want to minimize the risk of retraumatization the patient
therapeutic relationships
boundaries established
communication with families + children
appropriate introduction
assurance of privacy/confidentiality
parents - communicating with families
encourage parent to talk
directing focus
listening/cultural awareness
providing anticipatory guidance
avoiding communication blocks
communication barriers
info overload
communicating with families via interpreter
children - communicating with families
infancy
non-verbal communication
rely on cues
infants respond to adults non-verbal behaviours
early childhood
<5 yrs
egocentric = communication focussed on them
touch/examine articles
“stick in the arm” is literal to them = avoid (unfamiliar equipment kept out of view)
school-aged
rely on what they know
want to know function of objects
concern with body integrity = provide reassurance
adolescence
more willing to interact with someone outside the family
reject those who try to impose their own values on them
if parent present, talk with adolescent first
confidentiality important
identifying info - PED health hx
name, DOB, gender, religion, place of birth
adress, phone #, email
date of interview, name of informant, relationship to pt
presenting health concern - PED health hx
RSC
avoid leading/labelling-type questions
hx of present illness (HPI) - PED health hx
onset/duration of symptoms
description/progression of illness
current status of condition
RSC now
past health hx - PED health hx
gives us pt risk factors
previous illness
hospitalizations
surgeries
general - PED health hx
allergies (food, med, environment, associated reactions)
current meds
immunizations
growth/development
growth patterns (weight/length), teeth, milestones (head control, sit, walk, first word), school, family incomes, MH, substance use, food security
habits
concerns of habits, activities, development
walking on ties, picky eater
family med hx - PED health hx
identify genetic/hereditary conditions and family disease patterns
assess potential exposure to communicable disease/environmental risks
smoking/chemical use
family and social background - PED health hx
family composition/home environment
occupation/education of family members
cultural, religious, community influences
family functioning/relationships
review of systems (ROS)/Head-to-toe - PED health hx
general
skin
HEENT
chest
respiratory
CV
GI
GU/GYN
MSK
Neuro
Endocrine
general ROS - PED health hx
overall health
fatigue
recent weight changes
fever
skin ROS - PED health hx
rashes (location)
pruritus (itching)
bruises
HEENT ROS - PED health hx
headaches
visual changes
eye/ear discharge
limited ROM
chest ROS - PED health hx
breast enlargement
masses
enlarged axillary nodes
respiratory ROS - PED health hx
cough
SOB
wheezing
CV ROS - PED health hx
tachycardia
pale
cyanosis
fatigue on exertion
GI ROS - PED health hx
loss of appetite
vomiting
diarrhea
GU/GYN ROS - PED health hx
dysuria
polyuria
discharge
MSK ROS - PED health hx
weakness
fractures
abnormal gait
neuro ROS - PED health hx
seizures
tremors
speech impairment
endocrine ROS - PED health hx
excessive sweating
early/late puberty
general approach to examining children
least → most invasive (BP, rectal temp, ears, eyes, throat)
use developmental/chronical age
minimize stress/anxiety associated with assessment
foster trusting nurse-child-parent relationship
all max prep of the child
preserve security of parent-child relationship (young children)
max accuracy/reliability of findings
assessment approach - infants
before able sit alone = examine on parent lap when possible
after able to sit alone
examine on parent lap or exam table
always keep parent in full view
prep tips
undress infant, but keep warm
use distraction aid cooperation (toys/talking)
speak soft, gentle touch
pacifiers as permitted = sooth
involve parent for comfort/safe restraint
assessment sequence - infants
auscultation (HR, RR) - if quiet
front - back (anterior-posterior)
palpate/percuss after inspection
head-toe sequence
eyes, ears, mouth = INVASIVE (assess near end)
reflexes last (avoid distress)
PED Assessment Triangle
initial across-the-room assessment
rapid evaluation tool
establishes clinical status
identify critically ill/sudden deterioration
60 sec - no equipment
Guides clinical decision-making
• How severe is the injury/illness?
• What is the potential physiologic abnormality?
• How urgent is treatment needed?
consider child’s normal baselines
Components of PED Assessment Triangle
Appearance (TICLS)
tone
interactiveness
consolability
look/gaze
speech
Work of Breathing
breath sounds
positioning
retractions
flaring
apnea/gasping
Circulation
pallor
mottling
cyanosis
respiratory differences
narrow airway = risk of obstruction
high metabolic rate = faster RR for O2 consumption
ventilation relies on diaphragm = tire quicker
less alveoli = impaired O2 = faster RR
cardiovascular differences
low circulating blood volume = faster HR, sensitive to fluid loss
large body surface area = greater fluid loss via evaporation
neuro differences
thermoregulation no well developed (infants) = hypothermia
immature motor development = risk for falls
GI differences
high metabolic rate = high food/fluid requirements
poor glycogen storage = rapid hypoglycemia
renal differences
inability to concentrate urine = water loss
expected urine OP = 1-2mL/kg/day
slower excretion of some drugs
airway
patent
smaller airway - obstruction risk
supporting cartilage
not developed until school aged
larynx = anterior-superior
narrowest portion at cricoid cartilage
large tongue/head + weak neck muscles = obstruction risk
neonates = nose breathers
breathing
small thorax + closely positioned organs
cartilaginous ribs (twice as flexible as adults)
chest retractions = distress
horizontal ribs = limited chest expansion
underdeveloped intercostal muscles
relies on diaphragm/abdo muscles
lower lung volume/compliance = less compensatory reserve
tires easily
immature immune system (lower IgA (secretions, first line of defense), IgG (long-term immunity, secondary immune response)
higher risk of infections
breathing - normal findings
regular breath pattern
no extra effort/audible sounds
thin, flexible chest wall
movements/sounds easily seen/heard
beginning - respiratory distress to failure continuum
tachypnea
nasal flaring
stridor
expiratory wheeze
pale
compensate for long time but crash quickly
middle - respiratory distress to failure continuum
tachypnea, RR >60
grunting
mottled
head bobbing
inspiration/expiration wheeze
diminished air entry
compensate for long time but crash quickly
end - respiratory distress to failure continuum
dyspnea
seesaw respirations
grey/cyanotic
silent chest
changes in LOC/activity
stop breathing → cardiac arrest next
compensate for long time but crash quickly
circulation
growth = HR decrease, BP increase (normal trend)
cardiac output depends on HR
decrease HR = decrease CO
hypotension late sign of cardiac compromise (opposite of adults)
infants SBP <79 mmHG = hypotension
infant is compensating, will crash quickly
circulation - normal findings
skin = warm, normal colour, well-perfused (cap refill)
pulse = central/peripheral strong/equal
assess quality, intensity, rate, rhythm, presence of murmurs, apical impulse location
neuro
cerebral cortex function
AVPU response scale
glasgow coma scale
LOC
mental status, interaction
activity, movement, muscle tone
age-appropriate responses
neuro - glasgow coma scale PED
eye - 4
1 = no eye open
2 = to pain
3 = to speech
4 = spontaneous
verbal - 5
1 = none
2 = moan to pain
3 = inappropriate words
4 = cries but consolable
5 = coos/babbles (normal for age)
motor - 6
1 = no movement
2 = abnormal extension
3 = abnormal flexion
4 = withdraws from pain
5 = localizes pain (move to pain)
6 = obeys commands/moves appropriately
score
<8 = severe injury/coma
9-12 = moderate injury/decreased LOC
13 - 15 = midl injury/ fully alert
neuro - AVPU PED
Alert
awake, interacts appropriately for age
eye contact, track movements, smiles, cries appropriately, responds to caregivers/toys
responds to verbal stimuli
responds when spoken to/caregiver voice heard
turns head to voice
opens eyes/noise when called
responds to pain
not to voice but painful stimulus
cries, withdraws, grimace
unresponsive
no response to voice/pain
no movement, cry, eye open
flaccid tone
head and neck
shape and symmetry
even moulding
occipital prominence
fontanelles + suture lines (smooth, flat, not bulging (intracranial pressure) or sunken (dehydration))
anterior closes @ 12-18 months
posterior closes @ 2 months
large head + shorter neck
thyroid NOT visible
eyes
light perception, fix + follow
fixate on one visual field, binocularity (use both eyes together) 3-4 months
depth perception 7-9 months
mouth + throat
pink, moist, smooth lip + mucous membrane
large tongue = obstruction risk
primary teeth (5-6 months)
lower central incisors = drooling
abdomen
round, cylindrical/prominent (especially after feeds)
active BS, peristaltic waves
immunologic system maturation
maternal IgA = passive immunity for 1st few months of life
IgG = systemic, long-term defense, crosses placenta, secondary (memory)
hematologic system maturation
transition from fetal Hg (HgbF) → hemoglobin (HgbA)
may cause physiological anemia 2-3 months
digestive system maturation
enzyme activity (amylase (carbs), lipase (fats)) immature
limiting fat/starch digestion
thermoregulation maturation
more efficient as infant matures
renal function maturation
immature kidneys = limited ability to concentrate urine
high risk of dehydration
sensory development maturation
hearing well developed
vision improves gradually
binocularity + depth overtime
bino = 3-4 months
depth = 7-9 months
infant vital signs
Temp ALWAYS 36.5°C – 37.5°C
HR decrease with age
RR decrease with age
BP increase with age
always consider child’s normal range, clinical condition, VS trend
0-3 months - infant vital signs
HR = 100 - 160
BP = 65-85/45-55
RR = 30-60
Temp = 36.5°C – 37.5°C
3-6 months - infant vital signs
HR = 90-120
BP = 70-90/50-65
RR = 30-45
Temp = 36.5°C – 37.5°C
6-12 months - infant vital signs
HR = 80-120
BP = 80-100/55-65
RR = 25-40
Temp = 36.5°C – 37.5°C
assessing vital signs
temp = axillary/rectal
pulse
apical 1 min
rate, rhythm, quality
location = 4th intercostal, left midclavicular line
resp
1 min count
crying? - wait to do RR
BP
not in healthy newborns
cuff size (40% arm circumference = width, 80-100% = length)
method
O2 sat
adhesive sensor or clip on
location
pain
FLACC (face, legs, activity, cry, consolability)
NIPS (face, cry, breathing, arms, legs, arousal)
doppler BP
ONLY SYSTOLIC measurement
doppler detects arterial BF = sounds each heart beat
inflate cuff to stop BF
deflate slowly until sounds returns = SBP
4 screening tools + growth charts
Rourke baby record
nipissing district developmental screen (NDSS)
greig health record
WHO growth charts
Rourke baby record
newborn - age 5
documentes
well-baby
child visits
immunizations
resources
Growth monitoring, assessing nutrition, physical examination, education, and health care advice
chart development, child behaviour, parenting resources, immunization, and infectious diseases
Visits at 1 and 2 weeks; 1, 2, 4, 6, 9,12, 15, 18, 24,
36, 48, and 60 month
nipissing district developmental screen (NDSS)
parent-completed tool screen
for developmental delays
1 month - age 6
age-specific checklist
promotes early detection + intervention
fine/gross motor skills, speech/language, cognitive, social/emotion, self-help/adaptive skills
WHO growth standard - WHO growth charts for canada
assess ideal growth
monitor growth (weight, length, height, head circumference, BMI)
birth - 59 months (age 5)
ID growth patterns/nutritional/health concerns
WHO growth references - WHO growth charts for canada
observe growth
track school-aged and adolescent trends
5 to 19 yrs
parameters plotted - WHO growth charts for canada
weight for age
length/height for age
weight for length
BMI for age
head circumference for age
data plotted as percentiles
ex. 10th percentile weight =
10 children weigh less
90 children weigh more
can be normal if child is still on growth curve
skipping curves = concern
weight - normal growth/development
gains 150-200g/week until age 5-6 months
30grams/day 1 month
20grams/day 4 months
double birth weight by 4-6 months
triple birth weight by 1 yr
height - normal growth/development
increased by 2.5 cm per month for 6 months
then in “spurts”
Biologic growth is influenced by…
Genetic
Metabolic
Environment
Nutrition
Health status
fine motor development
birth = hands closed, grasp, clench
5 months = grasp voluntarily
6 months = grasp/manipulate small objects
8-10 months = crude pincer = whole hand + thumb
11 months = neat pincer = tip of hand + thumb
12 months = turns pages of book
gross motor development
head 1st, then trunk
birth = marked head lag
2 months = less head lag
4-6 months = good head control
5 months = sit with support, turn abdo to back
6 months = back to abdo, sit with support
8 months = sit WITHOUT support
11 months = cruises + furniture hold
12 months = walk with 1 hand held
Erikson - psych development
trust vs mistrust
birth 1 yr
importance of caregiver/infant relationship
caregiver ID cries
Piaget - cognitive development
sensorimotor stage
senses + ability to move = understand the world
colour, images, sounds, etc
birth - 24 months
object permanence
visualize object that is outside field of view
reflective → simple repetitive acts
language + personal-social behaviour
cry = 1st communication
vocalization week 5-6
cries → coos → babbles
“dada” + “mama” with meaning + ‘bye'-bye” @ 10 months
12months - 3-5 words
concerns related to normal growth/development
attachment
separation anxiety = 6-8 months
stranger danger/fear
limited setting/discipline
time-out (playpen, baby gate)
no cost-effect
put way dangerous household items
thumb sucking/pacifier
teething
Health Promotion and Anticipatory Guidance for Familie
nutrition
sleep
immunizations
dental health
injury prevention/safety
falls, MVA, choking, burn, abusive head trauma (shaken baby syndrome)
ingestion
infant nutrition
6 months = BF/formula
solids at 6 months
iron fortified cereal
rice, barley, oatmeal, multigrain
veggies, fruits, strained meats
introduce 1 at a time
eggs/nuts
NO LONGER delayed to 1 yr
introduce allergens one at a time when introducing solids
whole cows milk/honey
DELAYED until 1 yr
milk = affects Fe absorption = anemia
honey = botulism (blood poisoning) = paralysis
vitamin D (400 IU daily)
2-4 months immunizations
DTap-IPV-Hib
Pneu-C-13
Rota
6 months immunizations
DTap-IPV-Hib
Rota
12 months immunizations
Men-C-C
MMR
Pneu-C-13
additional immunizations
influenza - during flu season
RSV - for high risk pt
Hep B - if warranted
bronchiolitis
LOWER resp tract infection
caused by RSV (incubation period 2-8 days)
epithelial cells of resp tract swell, fuse, obstruct
highly contagious
common <2yrs (day care)
droplet + contact (NOv-Apr)
risk factors for severe bronchiolitis
chronic lung disease
congenital heart defects (ex. PDA)
neuromuscular/immunodeficiency comorbidities