Anatomy Unit 1 part 1
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
electronegativity
A molecule’s ability to attract electrons to itself
electrons suspended within covalent bonds in molecule pulled away from hydrogen nucleus by oxygen nucleus
polarity
Distribution of electrons within a molecule resulting in a electric charge
Hydrogen positive, oxygen negative
Hydrogen bond
Weakest bond formed from dipole moments
Positive H attracted to negative O
Solvent
Dissolves waste and carries nutrients in and out of cells
Polar water molecules pull ions apart via charge repulsion
lubricant
Substance used to reduce friction
Cohesion
occurs due to hydrogen bonding, happens between water molecules
adhesion
occurs due to hydrogen bonding, happens between water molecules and other polar surfaces
temperature regulator
water evaporating on skin (sweating) cools human body to protect internal organs from overheating during exercise or due to climate
Homeostasis
self regulating process by which a living organism can maintain stability
pH
Measures acidity of solution, distinguishing between acid/base with 10x difference between numbers on scale
Measure of H ion concentration
acid
Substance or compound that releases H ions in solution
base
Substance or compound that takes H ions out of solution, and produces OH ions
pH of acid
pH < 7
pH of pure water
pH = 7
pH of base
pH > 7
why is pH maintenance in the human body important?
Normal pH of human blood is 7.4, and if the pH is too high or too low (too acidic/basic) then it’s fatal. This could happen when we exercise and lactic acid is released, our blood’s pH drops and if our buffer system doesn’t work properly to bring us back to 7.4, we could die.
Buffer
weak acid or base that prevent large changes in pH and keep it stable.
How do buffers act with an acid
acts as a base and takes up H ions
how to buffers act with a base
acts as an acid and releases H ions
monomer
Small building block of a molecule
polymer
Chain of monomers
dehydration synthesis
Removing water to create a covalent bond between monomers
hydrolysis
Adding water to polymer to break covalent bond
glucose
monomer of carbs
4 functions of carbohydrates
short term energy supply
long term energy storage
cell membrane markers
structural material
carb function short term energy supply example
glucose used by cells to produce energy
carb function long term energy storage example
glycogen stored in liver, muscles
starch stored in plants
carb function cell membrane marker example
used as “identification tags” to differentiate good from bad cells
carb function structural material example
plant cell walls = cellulose
carbohydrate empirical formula
C:H:O = 1:2:1
bond that connects glucose molecules
glycosidic bonds
starch
storage of glucose in plant cells,
unbranched or slightly branched
glycogen
storage of glucose in animal cells
highly branched
cellulose
component of plant cell walls
reason cellulose is indigestible for humans
alternating oxygen linkage between glucose molecules
name of 2 bonded glucose molecules
maltose
charge repulsion
2 negatives repel each other, 2 positives repel each other
pH of human blood
7.4
Human body buffer system example
exercise = lactic acid build up = body pH decreases
if body does not have enough HCO3 or HPO, then there is metabolic problem, cannot regulate pH
property of water which makes them polar
electronegativity of oxygen
process which makes water dissolve other polar substances
charge repulsion
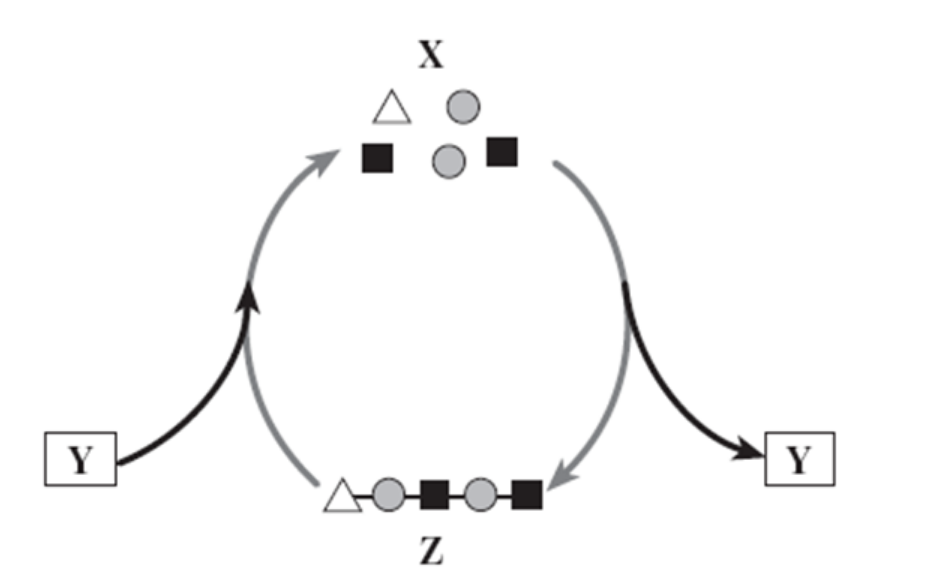
X, Y, Z in the diagram below would be (in order)
monomers, water, a polymer
organic polymers
molecules of life that contain carbon and hydrogen
process of water evaporation
adding energy (heat) makes water molecules vibrate, causing evaporation