Organic Chemistry 2 Final Exam
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
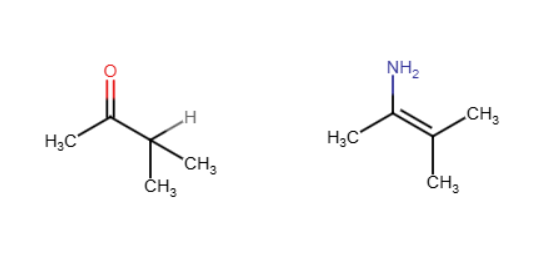
Enamines
N is bonded to C instead of O. One H from the amine replaces the O. Only with 2° amines. Double bond forms between the C
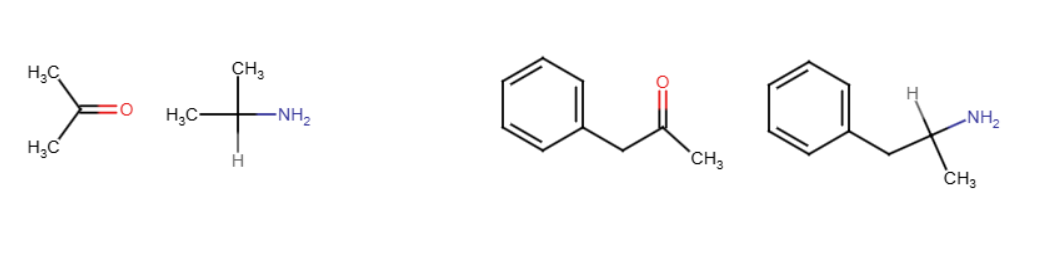
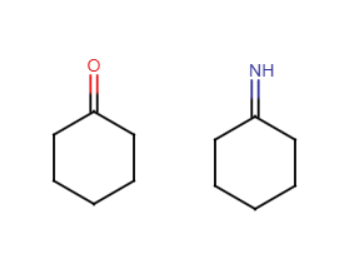
Imines
N is double bonded to C instead of O. One H from the amine replaces the O. Only with 1° amines
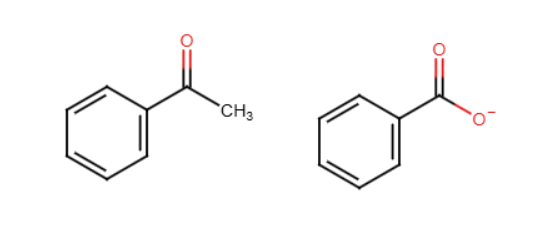
Haloform reaction
When there is a methyl ketone and excess X2 is added, the methyl group is replaced by an O-, resulting in CHX3
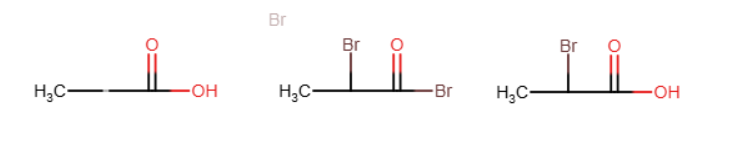
Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction
A carboxylic acid where an H on the alpha carbon is replaced by Br. OH is also temporarily replaced by Br
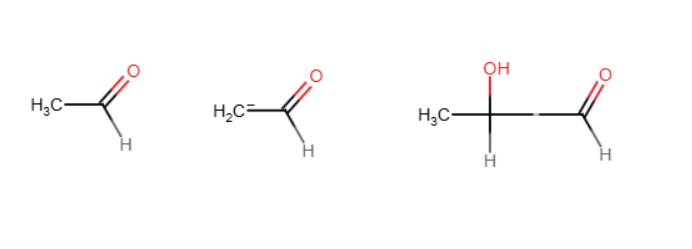
Aldol reaction
2 molecules of an aldehyde or ketone react in the presence of a base to bond with each other
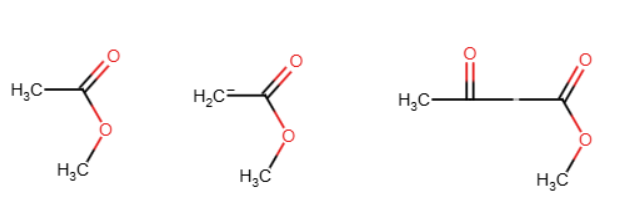
Claisen condensation
Same as an aldol reaction but with esters. Also, the OR group detaches, unlike the H in the aldol reaction. No OH forms
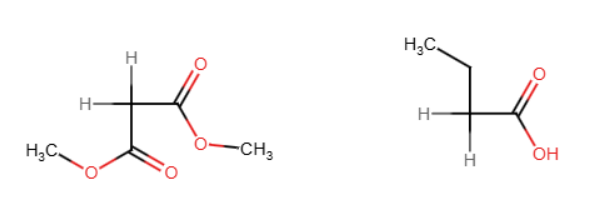
Malonic ester synthesis
Diethyl malonate is turned into acetic acids using NaOEt,H3O, and heat. NaOEt replaces an H with the adding group and H3O/heat replaces COOEt with H and the other with COOH
Acetoacetic ester synthesis
Same as malonic ester synthesis except there’s only one COOEt which gets completely replaced by an H
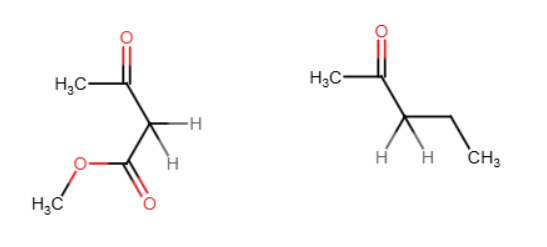
Michael reaction
A nucleophile is added to the beta carbon
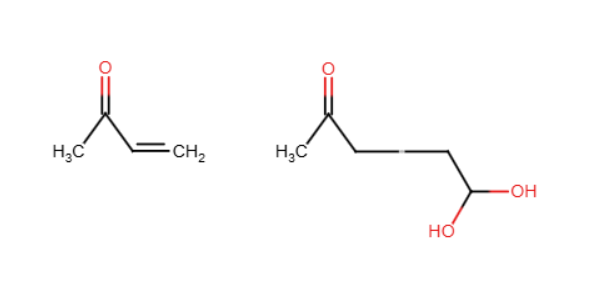
Robinson annulation
2 cyclohexenes form under OH in H2O
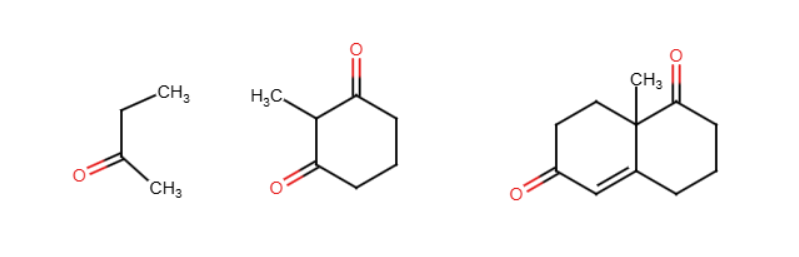
Fischer esterfication
Addition of an alcohol to a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid, typically H2SO4, to form an ester. The group coming in replaces the H in the alcohol
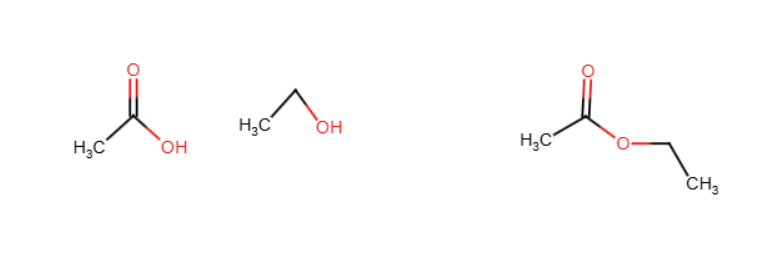
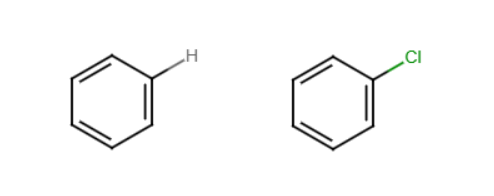
Halogenation
Benzene reacts with Cl2 or Br2 in the presence of an acid to perform a substitution
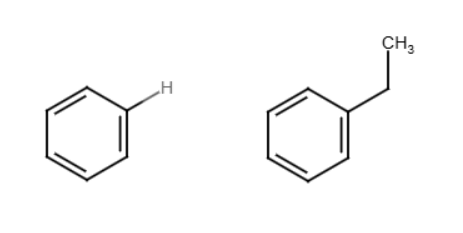
Friedel crafts alkylation
Benzene reacts with an alkyl halide and acid, typically AlCl3, to form an alkyl benzene. Similar to halogenation except a new group attaches instead of Cl or Br
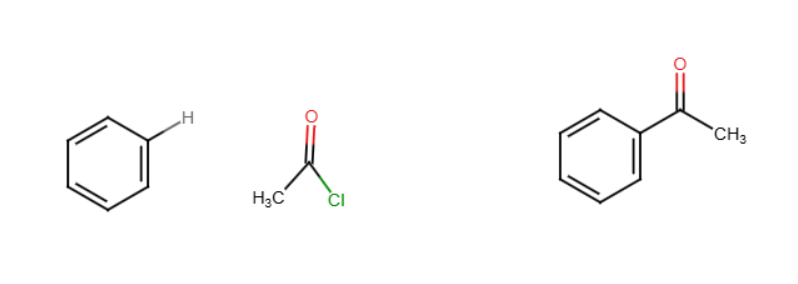
Friedel crafts acylation
Benzene reacts with an acid chloride (RCOCl) and acid, typically AlCl3, to form an aryl ketone
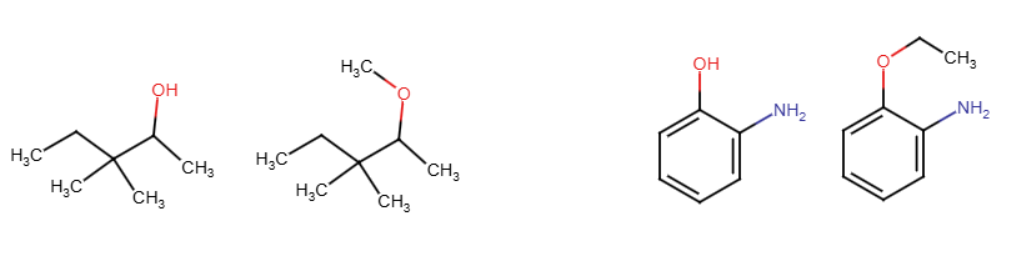
Na/NaH/NaOH
The entering group attaches to the alcohol, causing the H to leave
H2SO4
Ultimately, an H2O leaves the reaction
HBr/HI
They remove the group off of an oxygen, causing alcohol or water to form. It replaces every oxygen with itself
H2SO4
When working with a nitrogen or sulfur group, the entering group replaces the H. HNO3 becomes NO2 and SO3 becomes HSO3. If H is not present and there is a group instead, the NO2/HSO3 attaches to the ortho or para location typically
AlCl3
The incoming group completely replaces the H. HCl also forms. If H is not present, the group attaches at the para or ortho location
PPh3
Used with Pd(OAc)2. Two groups connect by replacing a bromine/iodine with a bond
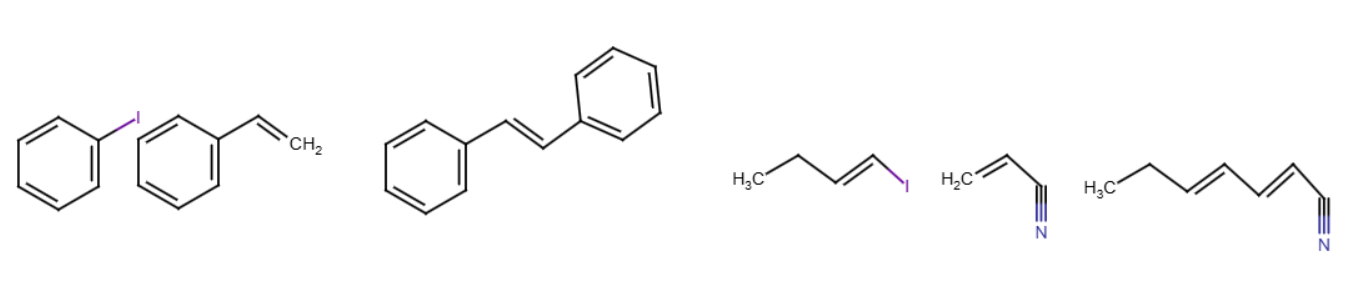
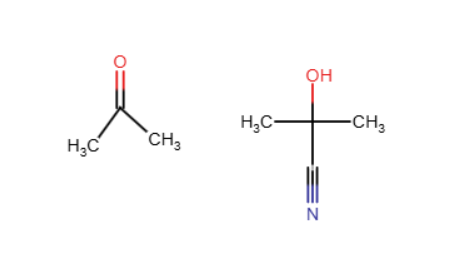
NaCN
A CN is added to the molecule by breaking the double bonded oxygen and turning it into an alcohol
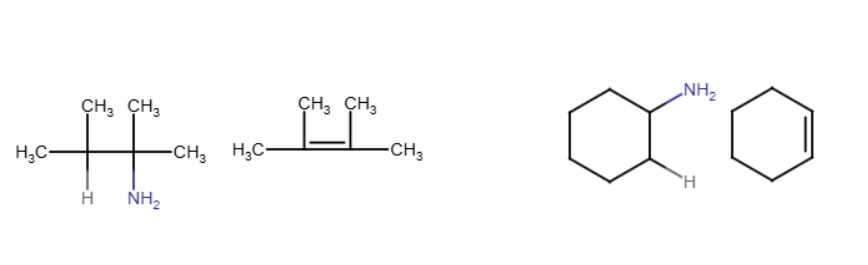
Ag2O/heat
The nitrogen group and a hydrogen are removed and a double bond forms between the carbons
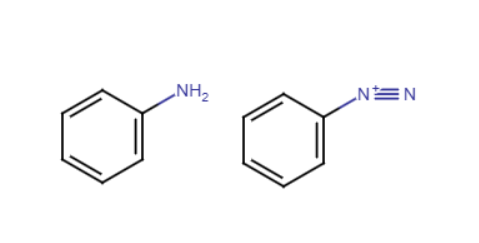
NaNO2
Turns NH2 into N2
CuCN
Turns N2 into CN
NaBH3CN/LiAlH4
A double bonded oxygen breaks and is replaced by NH2 and H