GENCHEM2 (Chapter 11)
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
IMF’s List them
London
dipole-dipole
H-bonding
ion-dipole
Heating Curves
Plot of temperature change versus heat added
London IMF’s
“temporary dipole”
Shape vs Size
Dipole-dipole
Polar Molecules
H-bonding
“FON”
ion-dipoles
ionic
Viscosity
resistance to flow (water vs syrup)
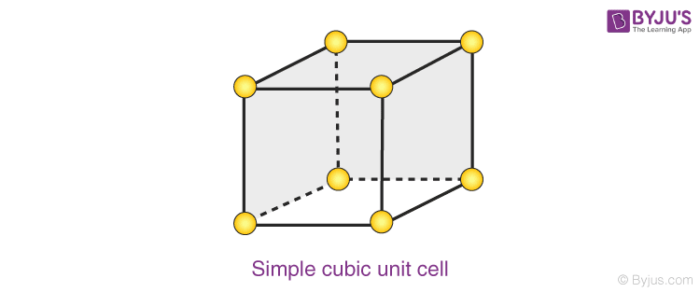
Primitive Cubic
8(1/8)=1 atom
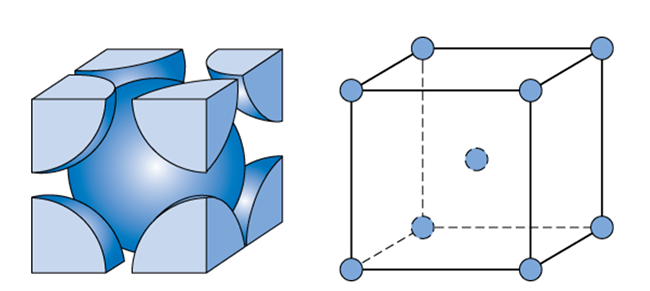
Body-centered Cubic
8(1/8)+1=2 atoms
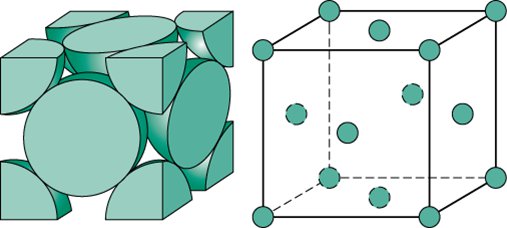
Face-centered Cubic
8(1/8)+6(1/2)=4 atoms
Vapor Pressure
at any temperature some molecules in a liquid have enough energy to escape attraction of the bulk liquid
Volatile Liquids
Liquids which easily evaporate
Critical Pressure
Pressure required for gas liquefaction
Critical Temperature
highest temperature at which a substance can exist as a liquid
Molecular Solid
consist of atoms or molecules held together by IMF’s
dipole-dipole
London
H-bonds
Weak intermolecular forces give rise to low melting points
Covalent-Network Solid
Consist of atoms held together, in larger networks or chains, with covalent bonds
higher melting points(than molecular solids)
electorns move freely through the delocalized orbitals
diamond
graphite
quarts (SiO2)
Ionic Solids
consist of ions held together by ionic bonds
hard, brittle, very high melting points
ions held together by electrostatic forces of attraction
Metallic Solids
consist entirely of metal atoms
soft or hard melting points, good electrical and thermal conductivity, ductile and malleable