ANSC 300 - Ch. 6 - Endocrinology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Biochemical communication
Secreted signals
Electrical communication
Ion flow
Direct contact communication
Gap junctions or cell surface proteins
Juxtacrine
Next to each other
Ex: gap junctions and cell adhesion molecules
Autocrine
Cell sends signal to itself
Paracrine
Cell send signals to cells nearby
Endocrine
Transports through the blood
Ex: Hormones
Exocrine
Goes outside the body
Ex: Pheromones
Homeostasis
Goal is to maintain stability over time
Regulatory mechanisms are required
Stimulatory and Inhibitory Mechanisms
Cells sometimes have both
Signals must be integrated
Stronger signal wins out
Homeorhesis
Changes parameters over time
Regulatory mechanisms alter trajectory and magnitude of change
Ex: Growth, lactation, aging, pregnancy
What is the best example of molecular complementarity?
Antibody-antigen interaction
GPCR
Seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors
Peptide and amino acid derivatives
Polypeptides (insulin, growth hormone)
Small peptides (GnRH, oxytocin)
Dipeptides (thyroid hormone)
Single amino acid (catecholamines)
Cholesterol derivatives (steroids)
Adrenal and gonadal steroids
Vitamin D
Fatty acids
Prostaglandins and Prostacyclins
Ions
Calcium
Endocrinology
Study of the production, regulation and action of hormones produced from endocrine glands
Hormone
Term coined over 100 years ago by Starling and Bayliss in conjunction with their landmark study on secretin production by the small intestine
Examples of endocrine glands
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Pineal
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Pancreas
Adrenal
Ovaries
Testes
Examples of endocrine tissues
Adipose
Heart
Placenta
Kidney
Liver
Hypothalamus endocrine functions
Growth hormone - skeletal growth
ADH - water balance
Reproductive endocrine systems
Ovaries and Testes
Pulsatile secretion
Occurs in the hypothalamus and pituitary
Diurnal secretion pattern
Occurs with GH and melatonin
Cyclical secretion pattern
Occurs only in females
Episodic secretion pattern
Occurs with insulin and epinephrine
Specificity endocrine signaling
Expression of receptors by a cell confers the ability to respond to specific hormones
Sensitivity endocrine signaling
Determined by the number and “activity” of hormone receptors
Measured in terms of a response to the hormone
Neuroendocrinology
Study of the relationship between the nervous and endocrine systems
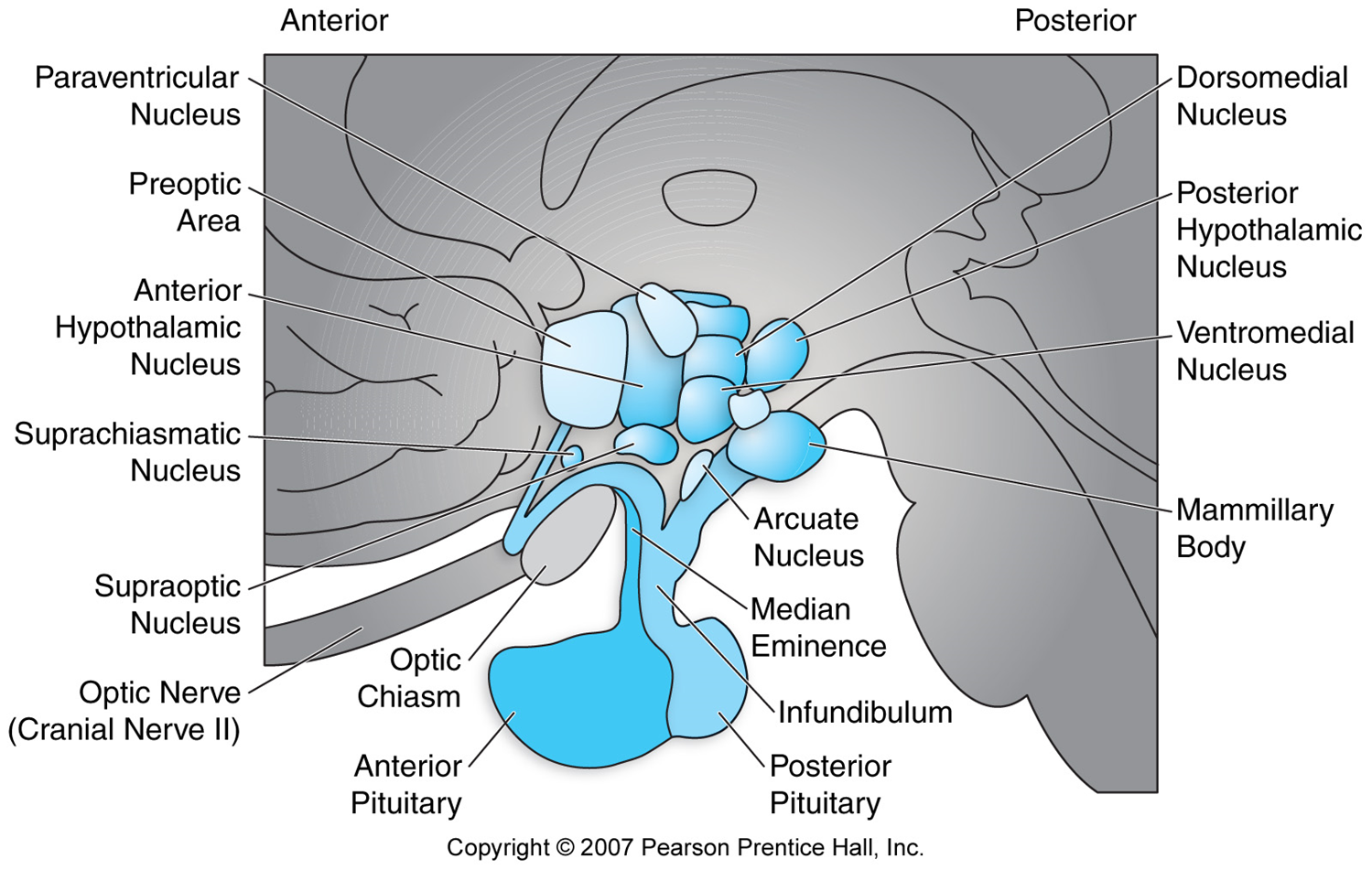
Hypothalamus structure and function
Structure: Small area of the brain; organized into nuclei
Function: produces releasing hormones; subject to regulation by higher brain centers
Pituitary gland
Directly regulated by the hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Entrains hormone secretion to light/dark cycle
Portal Circulation
Closed system
RHs usually released in primary plexus (median eminence)
Capillary fenestrations (leaky) promote RH uptake
Capillary fenestrations in secondary plexus promote RH release into AP
Acidophil
Somatotroph (GH) and mammotrophs (prolactin)
Basophil
Corticotrophs (ACTH), gonadotrophs (LH/FSH) and thyrotrophs (TSH)
What are the benefits of the hypothalamic-pituitary portal system?
Faster communication between hypothalamus and pituitary
Less hypothalamic hormone is needed to elicit response in pituitary,
Better responsiveness to changing physiological conditions
POMC-derived hormones
ACTH, LPH, MSH, beta-endorphin
ACTH actions
Stress adaptation; stimulates cortisol and aldosterone secretion from adrenal gland
LPH actions
Stimulates lipolysis in adipocytes
MSH actions
Stimulates melanin synthesis and reduce food intake
Beta-endorphin actions
Endogenous opioid; decreases pain sensors; stimulates PRL and GH and inhibits GnRH release
Cushing’s Disease
Disease that involves excessive cortisol secretion
Involves fat redistribution to the face and neck
Includes fragile skin (tearing, bruising)
Includes high BP, glucose, fatigue, and thirst
Glycoprotein hormones
TSH, LH, FSH, and hCG
TSH actions
Stimulates release of thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
FSH action
Follicle growth + sperm production
LH actions
Progesterone and testosterone production; Pregnancy
hCG actions
Maternal recognition of pregnancy
Somatomammotropic hormones
GH and PRL
GH actions
Bone and muscle growth; fat and sugar metabolism; anabolic which causes nitrogen retention and increased muscle mass
PRL actions
Mammary development and lactation; reproduction; growth; stress
Posterior pituitary hormones
Oxytocin and Vasopressin
Oxytocin actions
Milk letdown and parturition
Vasopressin actions
Water reabsorption; blood pressure; glycoprotein breakdown; memory and learning
What hormones stimulate maternal behavior?
Prolactin and Oxytocin
Describe how pup retrieval behavior is assessed?
Observing the amount of time it takes the mother to retrieve displaced pups
Monogamy Model
Monogamous in the wild (socially and sexually)
Coparent young
Pair bond formation
24 hours of contact
Breeding contact
Pair bond establishment
Increased affiliative behavior towards mate
Increased aggression towards strangers
Agonist
Partner preference formed after 6 hours (no estrus or breeding behavior)
Antagonist
Failure to form pair bond after 24 hours of exposure while in estrus
Traumatic Brain Injury
Most common cause of death in young adults
Can result from repeated head trauma
Causes high incidence of chronic hypothalamic and/or pituitary dysfunction
Which hormones are part of a larger pro-protein?
ACTH, oxytocin, ADH
Qualities of endocrine diseases
Hormone overproduction/deficiency
Tumors
Often mimic other diseases
Slow to develop
Treatment depends on cause of disease
Grave’s Disease
Swelling and enlargement of the extraocular muscles behind the eye cause the eyeball to “pop” forward
Acromegaly
Unregulated growth hormone release
PCOS
Multiple non-ovulatory follicles
High androgen production
Insulin resistance
Obesity
Negative Feedback
Major regulatory mechanism for regulating hormone production
Allows for fine control of cellular responses
Changes depending on stage of cycle