Vocab Unit 8
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Bureaucracy
A system of government or organization where decisions are made through a hierarchy of officials. It behaves impersonally and follows a merit principle.
Patronage
One of the key inducements used by party machines. A patronage job, pro-motion, or contract is one that is given for political reasons rather than for merit or competence alone.
Pendleton Civil Service Act
Passed in 1883, an act that created a federal civil service so that hiring and promotion would be based on merit rather than patronage.
Hatch Act
A federal law prohibiting government employees from active participation in partisan politics while on duty or for employees in sensitive positions at any time.
Office of Personnel and Management
The office in charge of hiring for most agencies of the federal government, using elaborate rules in the process.
Independent Regulatory Commission
A government agency with responsibility for making and enforcing rules to protect the public interest in some sector of the economy and for judging disputes over these rules.
Independent Executive Agency
The government agencies not accounted for by cabinet departments. Their administrators are appointed by the president and serve at the president's pleasure. NASA is an example.
Standard Operating Procedures
Better known as SOPS, these procedures for everyday decision making enable bureaucrats to bring efficiency and uniformity to the running of complex organizations. Uniformity promotes fairness and makes personnel interchangeable.
Regulation
The use of governmental authority to control or change some practice in the private sector.
Deregulation
The lifting of government restrictions on business, industry, and professional activities.
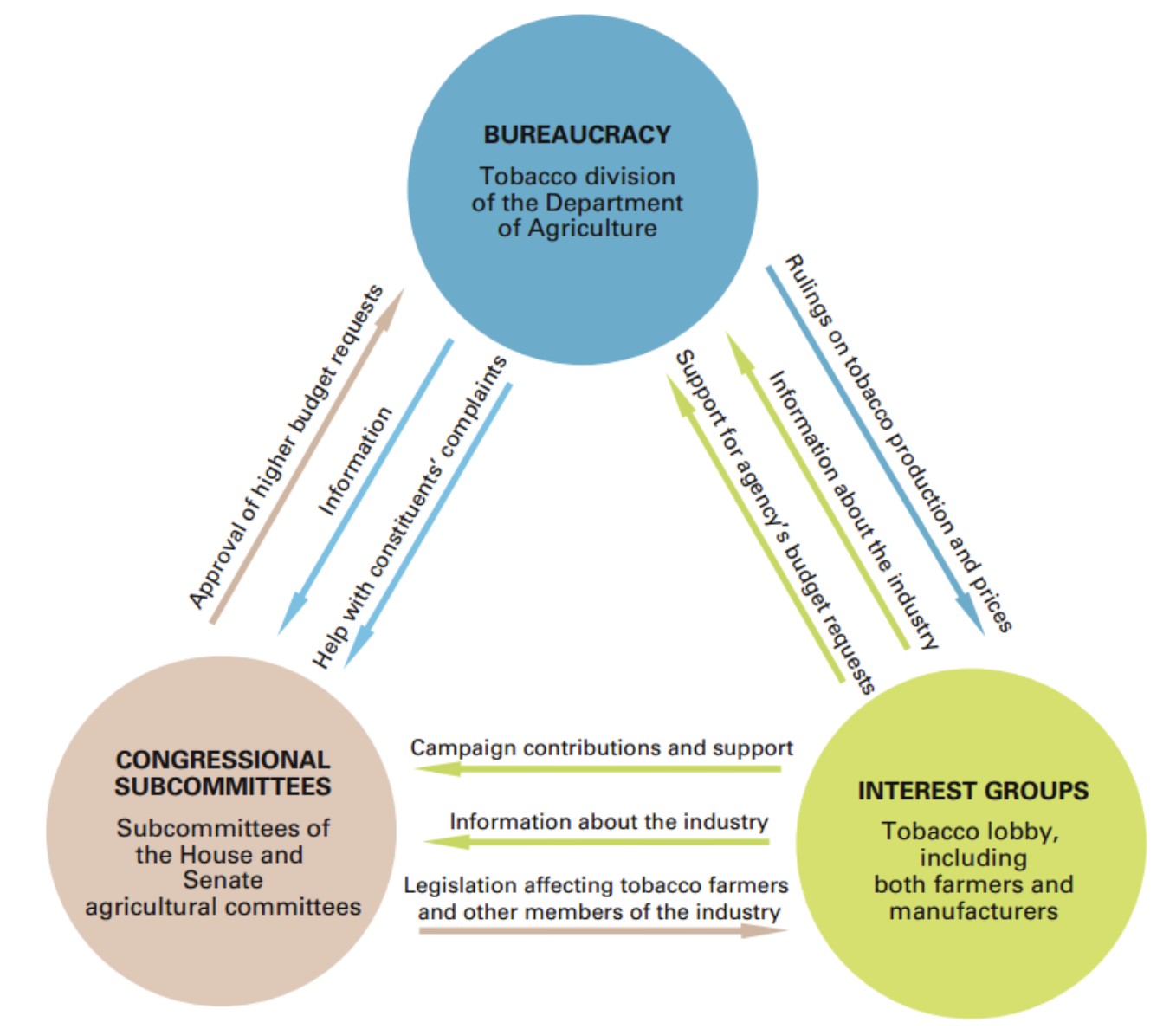
Iron Triangles
Also known as subgovernments, a mutually dependent, mutually advantageous relationship between bureaucratic agencies, interest groups, and congressional committees or subcommittees. Iron triangles dominate some areas of domestic policymaking.
Expenditures
Government spending. Major areas of federal spending are social services and national defense.
Income tax
Shares of individual wages and corporate revenues collected by the government. The Sixteenth Amendment explicitly authorized Congress to levy a tax on income.
Tax expenditure
Revenue losses that result from special exemptions, exclusions, or deductions allowed by federal tax law.
Incrementalism
A description of the budget process in which the best predictor of this year's budget is last year's budget, plus a little bit more (an increment). According to Aaron Wildavsky, "Most of the budget is a product of previous decisions."
Uncontrollable expenditures
Expenditures that are determined by how many eligible beneficiaries there are for a program or by previous obligations of the government and that Congress therefore cannot easily control.
Entitlements
Policies for which Congress has obligated itself to pay X level of benefits to Y number of recipients. Social Security benefits are an example.
House Ways and Means
The House of Representatives committee that, along with the Senate Finance Committee, writes the tax codes, subject to the approval of Congress as a whole.
Committee Senate Finance Committee
The Senate’s committee that, along with the House of Representatives committee, writes the tax codes, subject to the approval of Congress as a whole.
Authorization Bill
An act of Congress that establishes, continues, or changes a discretionary government program or an entitlement. It specifies program goals and maximum expenditures for discretionary programs.
Appropriations Bill
An act of Congress that actually funds programs within limits established by authorization bills. Appropriations usually cover one year.
Revenues
The financial resources of the government. The individual income tax and Social Security tax are two major sources of the federal government's revenue.