Heart and Fetal circulation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
In the mediastinum
Between the 2nd rib and 5th intercostal space
2/3 of the heart lies to the left of the midsternal line
rest on the diaphragm
Location of the heart
Base of the heart
Towards the right shoulder
Great vessels (pulmonary trunk and aorta) exit here
Apex of the heart
Points towards the left hip
Composed primarily of the left ventricle
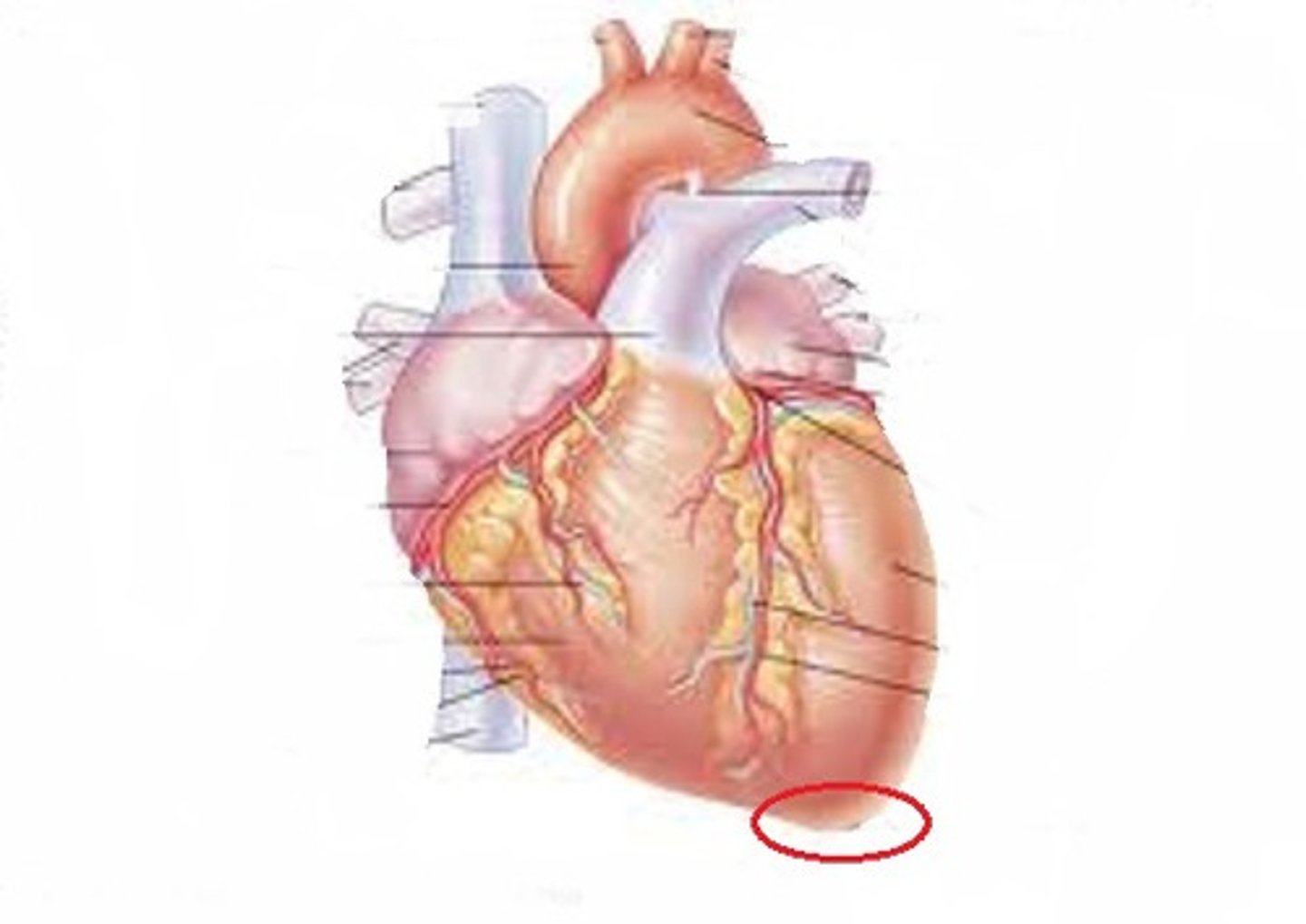
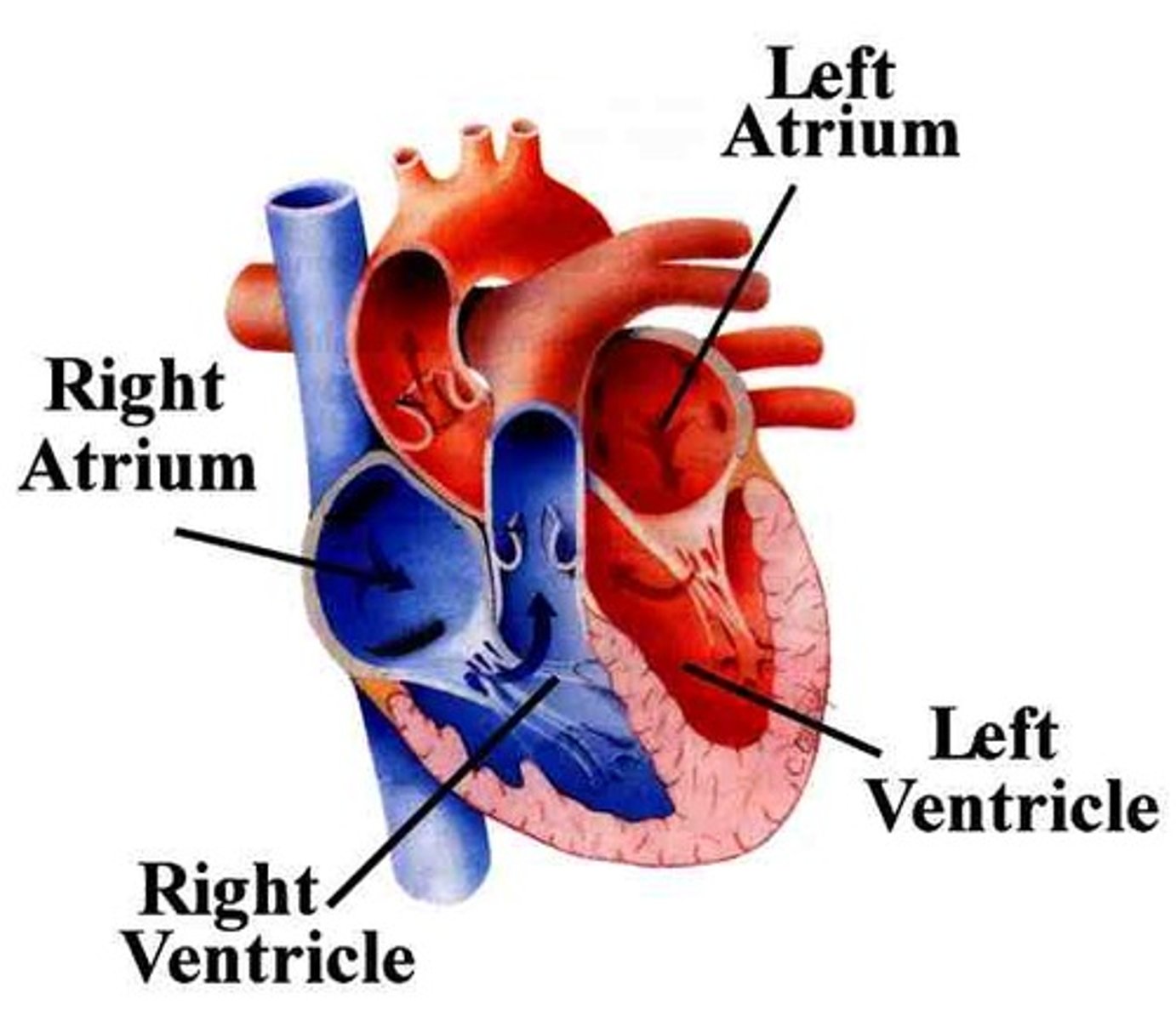
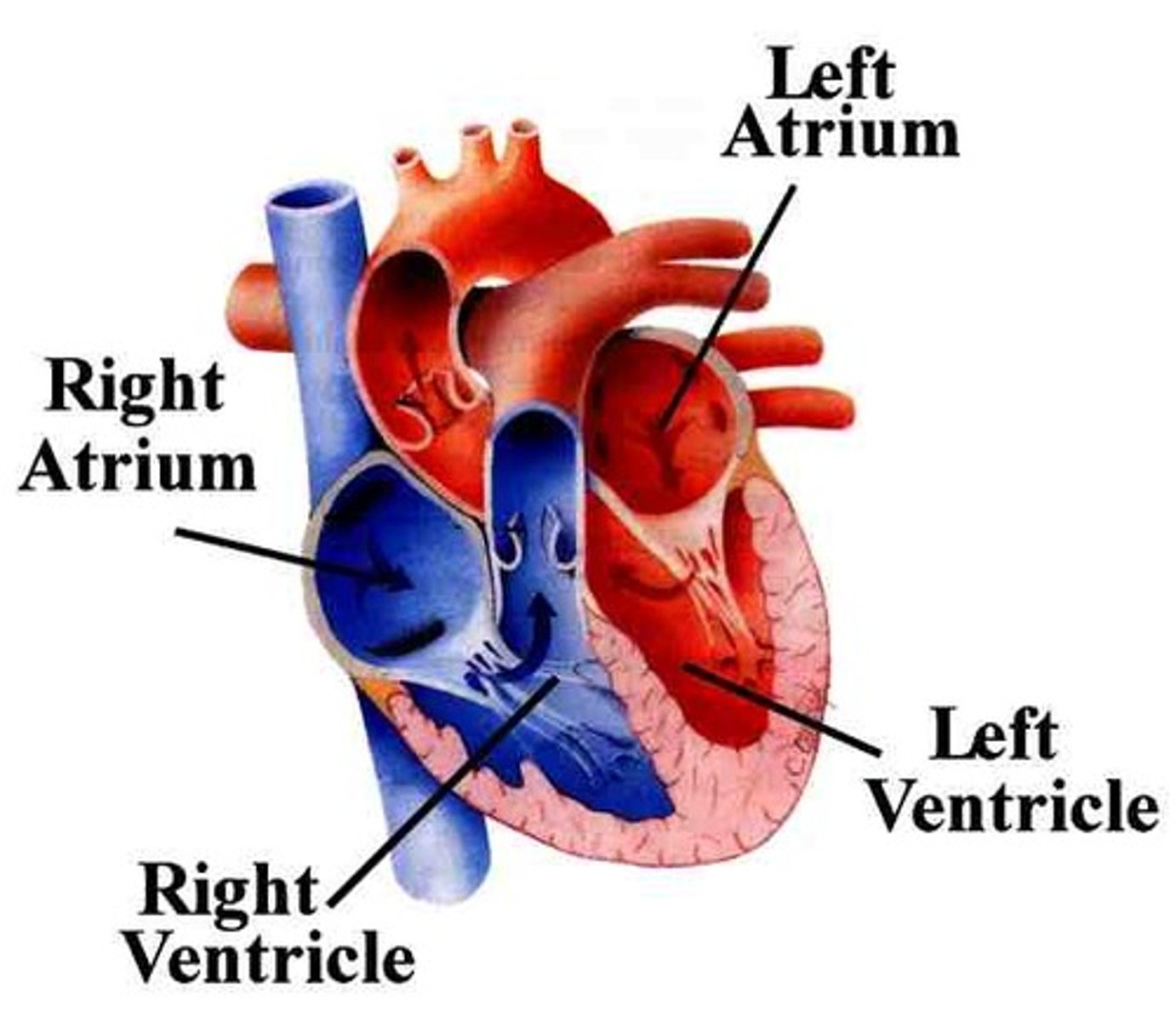
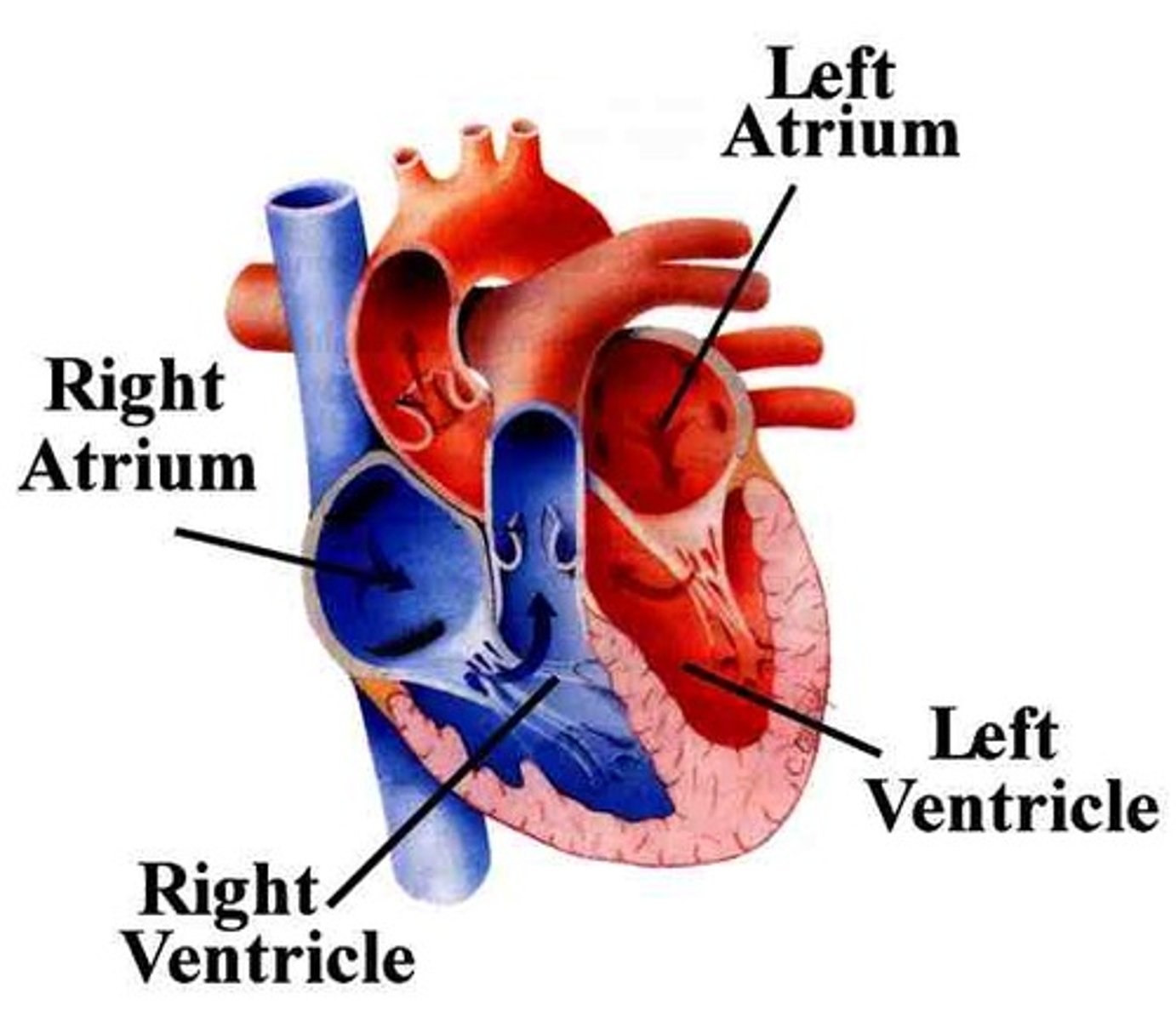
Two atria; right and left (receiving chambers)
Two ventricles; right and left (discharging chambers)
Name the four chambers
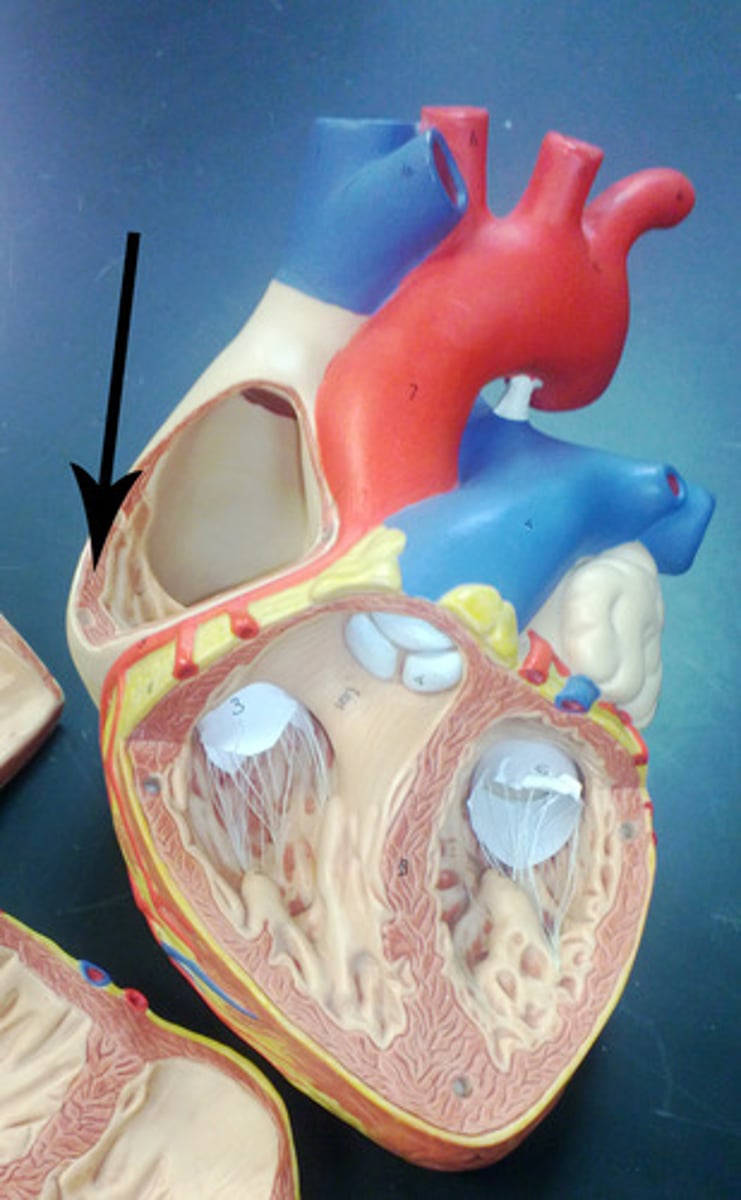
Pectinate muscles
Ridged wall of atria (contracts)
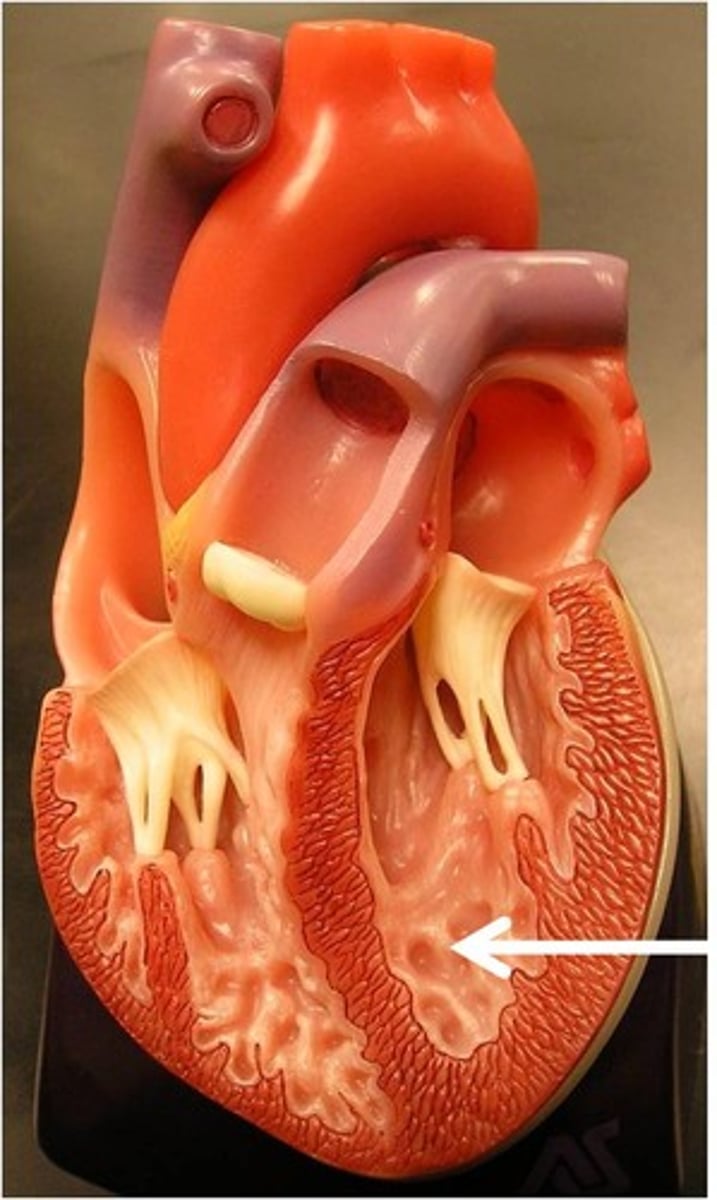
Trabeculae carneae
Ridged wall of the ventricles (contracts)
Papillary muscles
Have chordae tendineae that are attached to the valve flaps so they don't prolapse
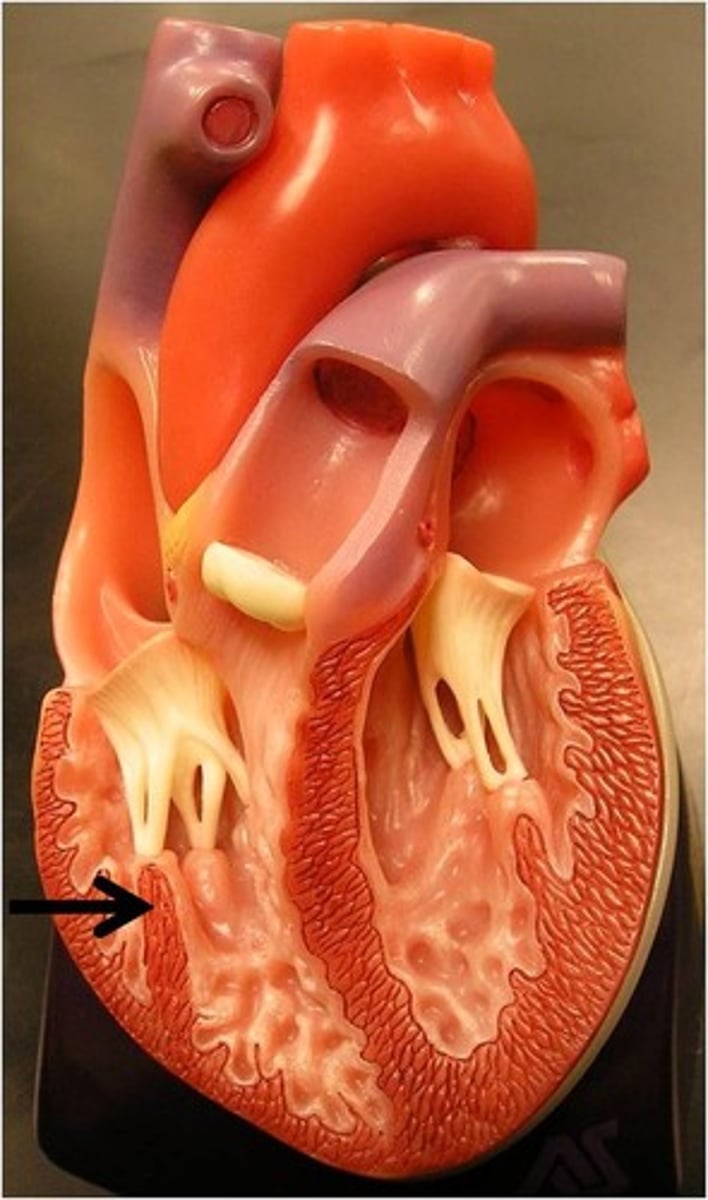
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Coronary sinus
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from:
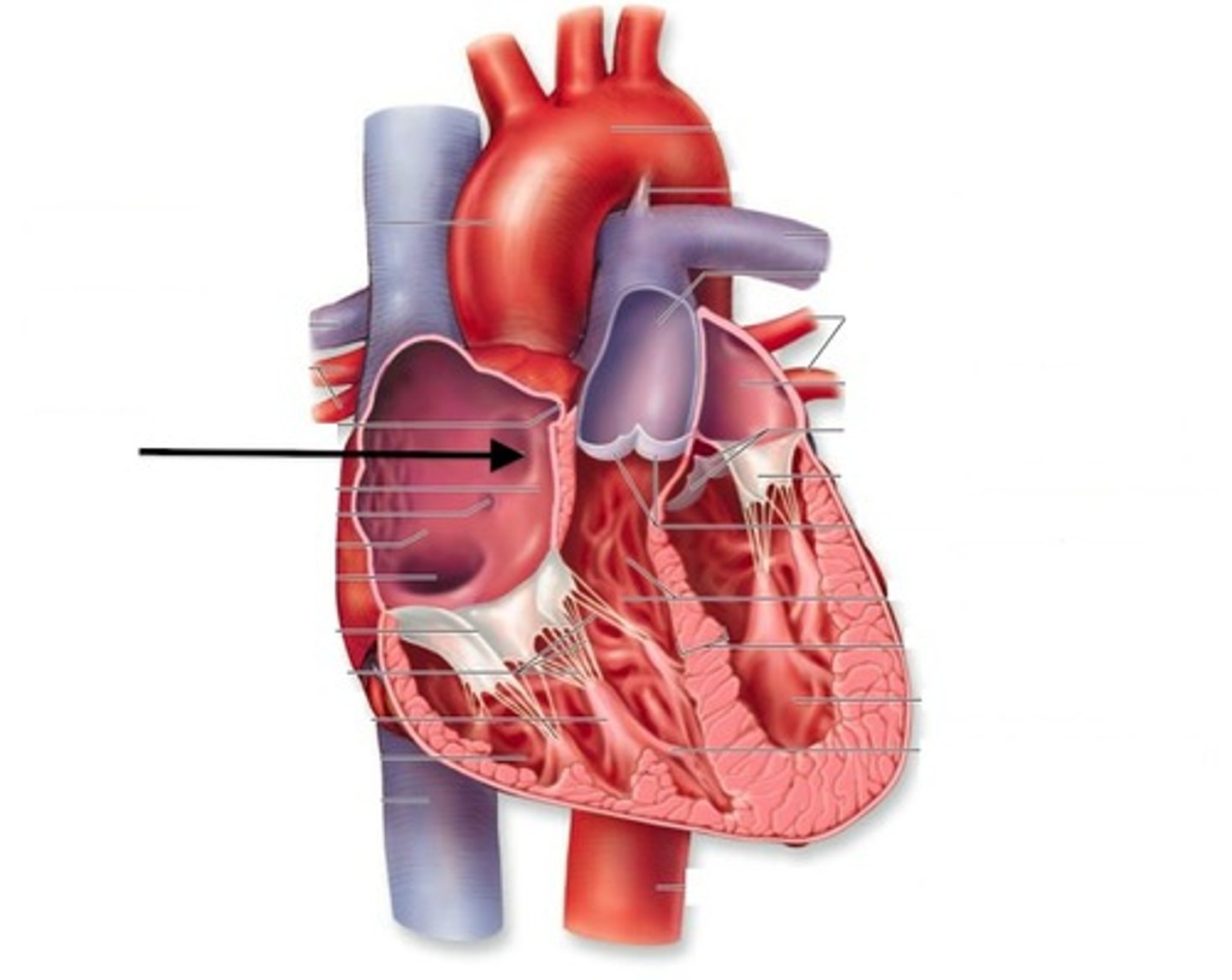
Foramen ovale, remnant structure is fossa ovalis
During embryonic development, shunts blood from the right atrium to the left atrium to bypass the nonfunctional lungs
The four pulmonary veins (right superior, right inferior, left superior, left inferior)
The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from:
From: Left atrium through the bicuspid valve
To: Aorta through semilunar valve to systemic system
The left ventricle receives blood from:
and sends it:
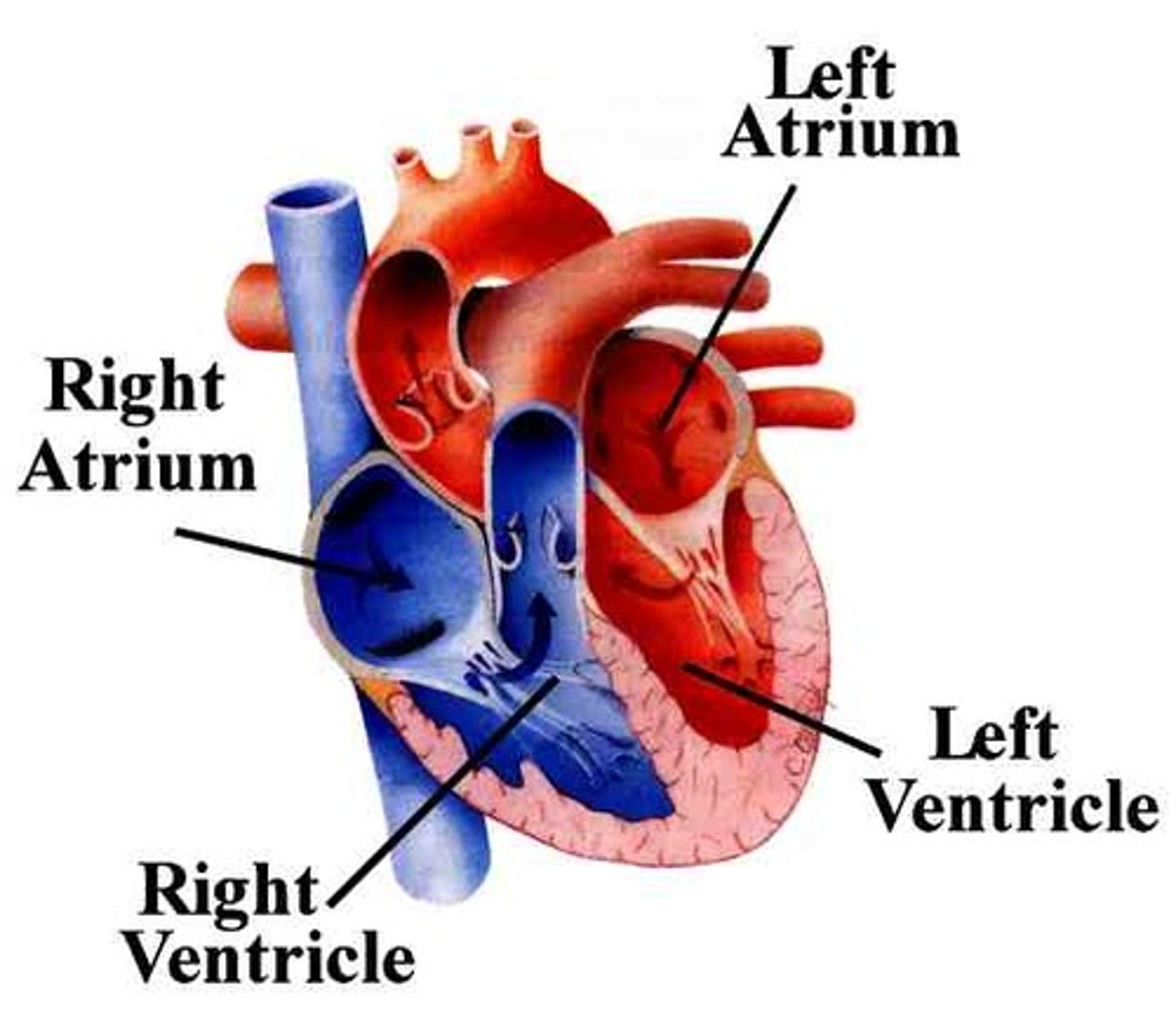
From: Right atrium through tricuspid valve
To: Pulmonary trunk (artery) through semilunar valve to lungs then pulmonary veins
The right ventricle receives blood from:
and sends it:
Ductus arteriosus
During embryonic development, shunts blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta to bypass the nonfunctional lungs
Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and bicuspid)
Prevents back flow into atria
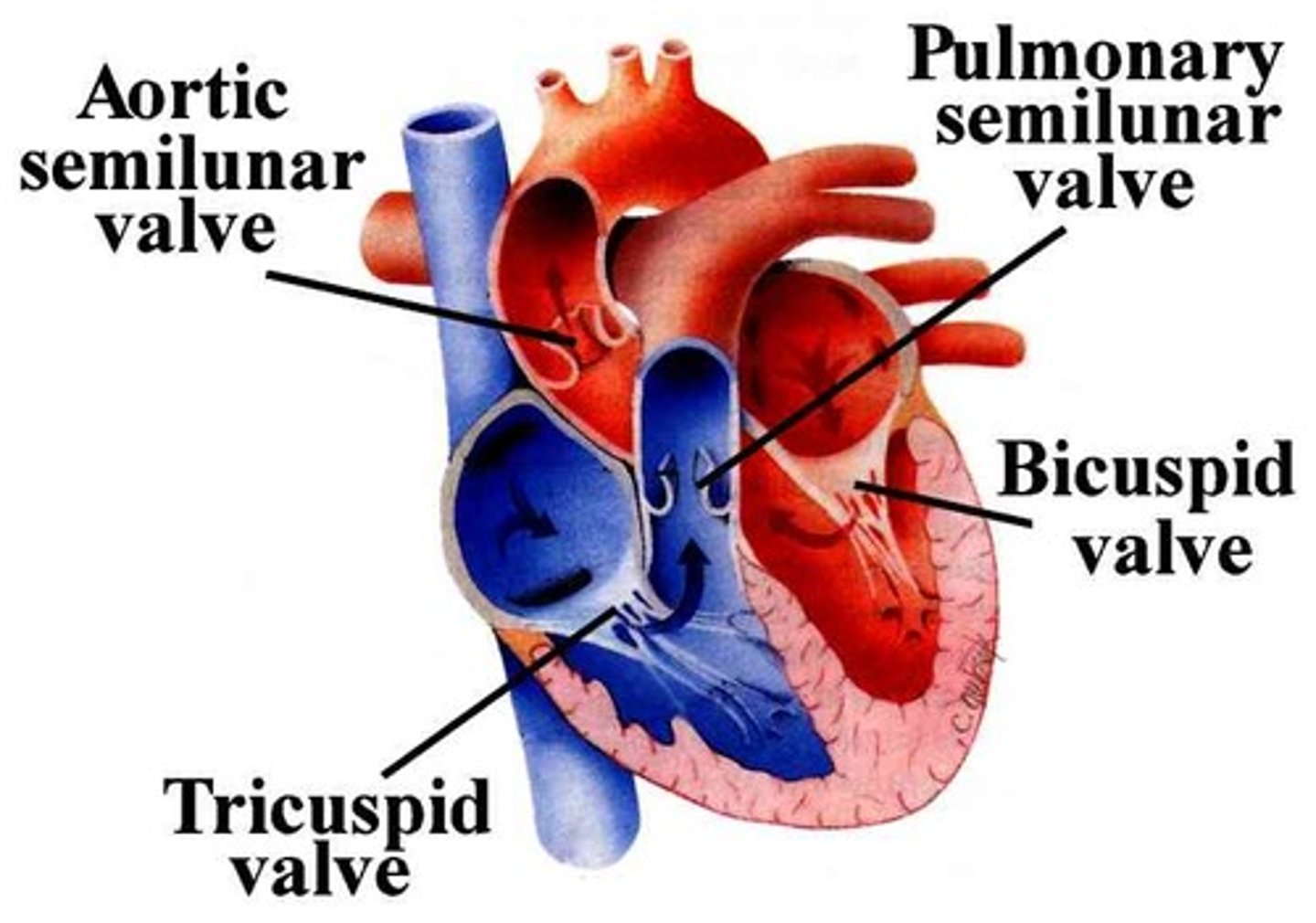
Semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary)
Prevents back flow into ventricles
Both have three flaps
Don't have papillary muscles
False, the changes in pressure open and close the AV valves
True or False: The contraction and relaxation of the papillary muscles open and close the AV valves
True
True or False: The ventricles and papillary muscles contract concurrently
Lub
The first heart sound
Closing of the AV valves (tricuspid and bicuspid)
Signifies the beginning of ventricular systole (contraction)
Dub
The second heart sound
Closing of the semilunar valves
Signifies the beginning of ventricular diastole (relaxation)
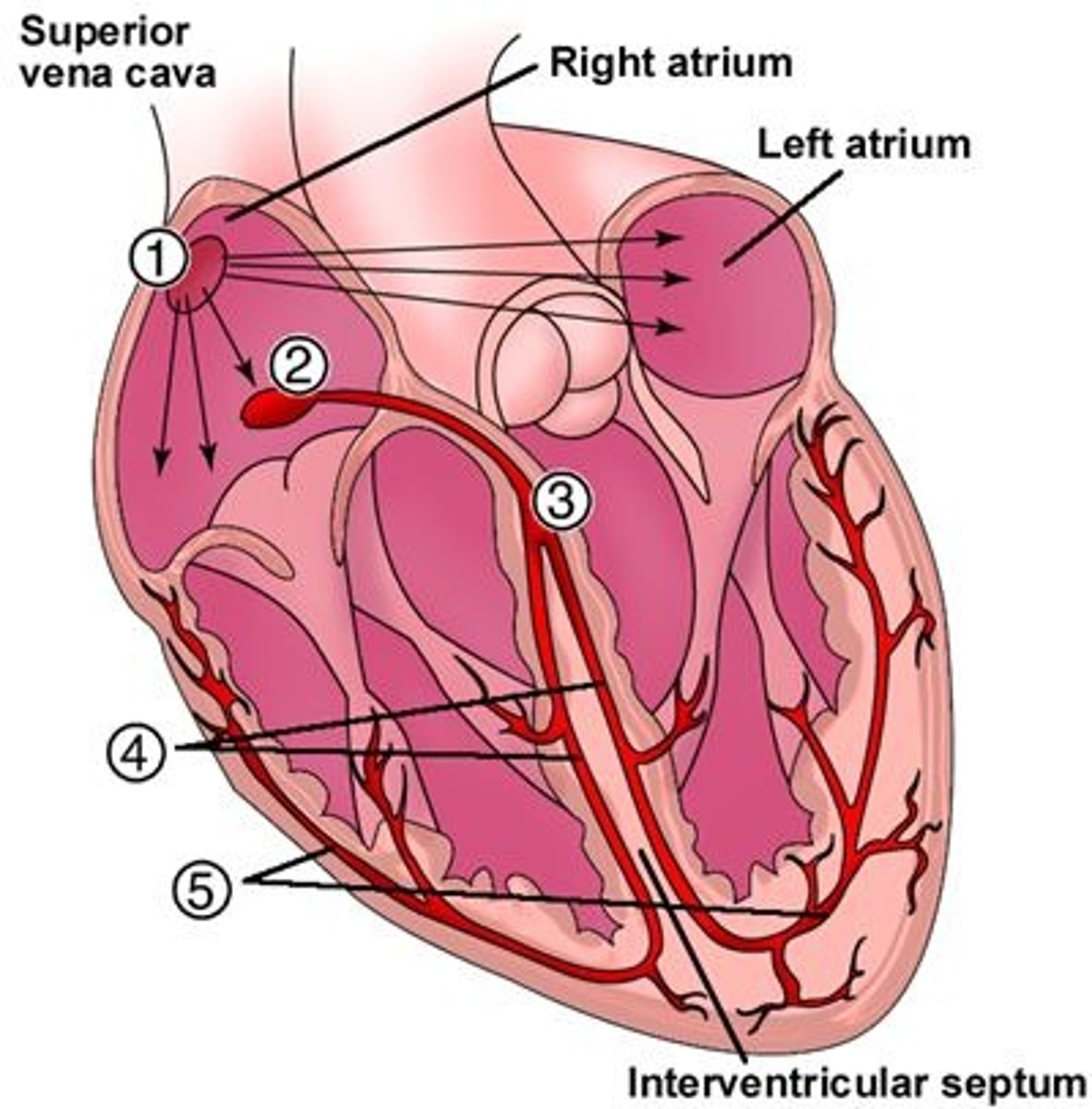
Coronary arteries (right (A) and left(D))
First branch off the base of the aorta
Blocked when aortic semilunar valve opens
Supplies blood to the heart muscles
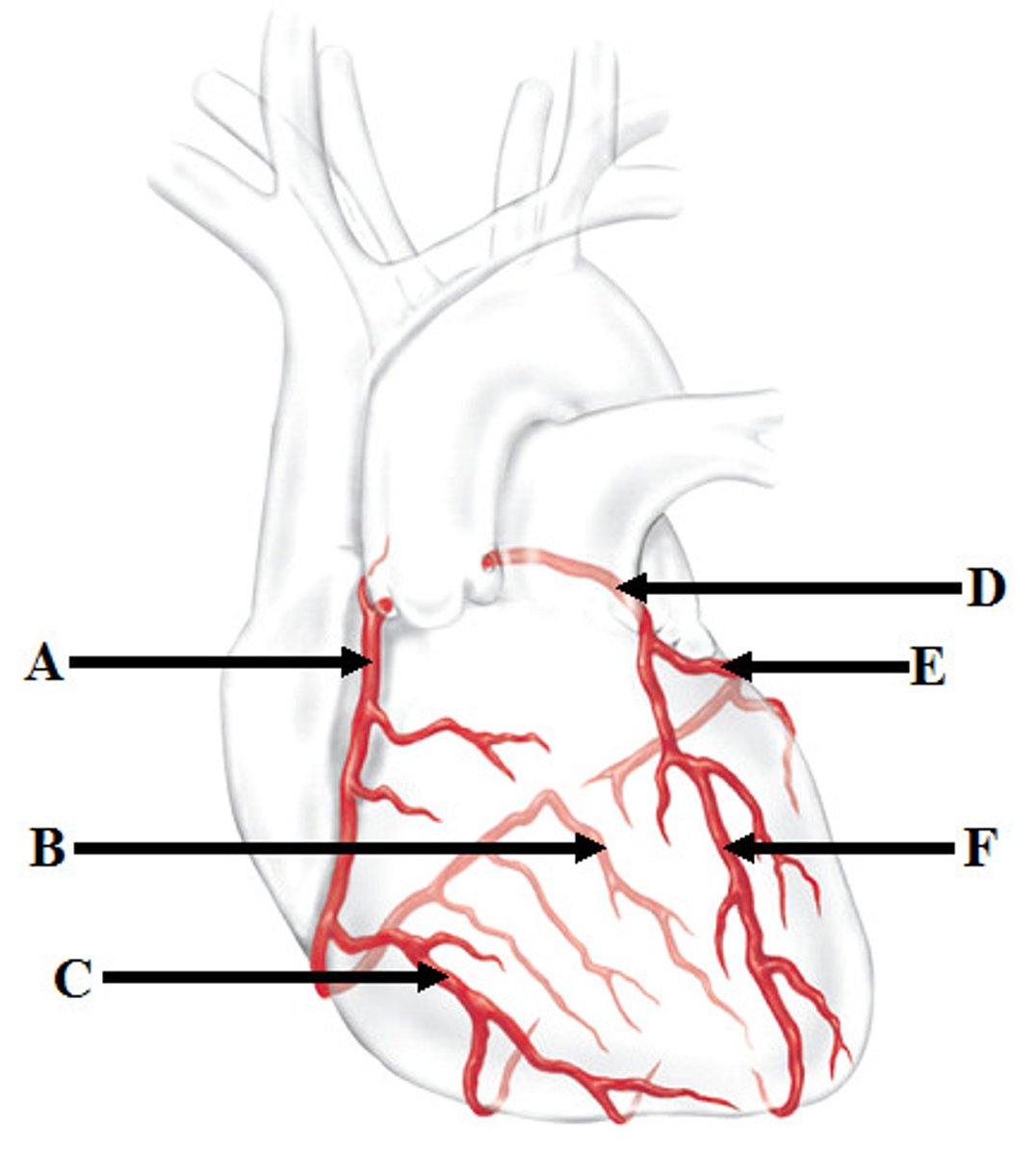
Marginal artery (C) and Posterior Interventricular artery (B)
Branches of right coronary artery
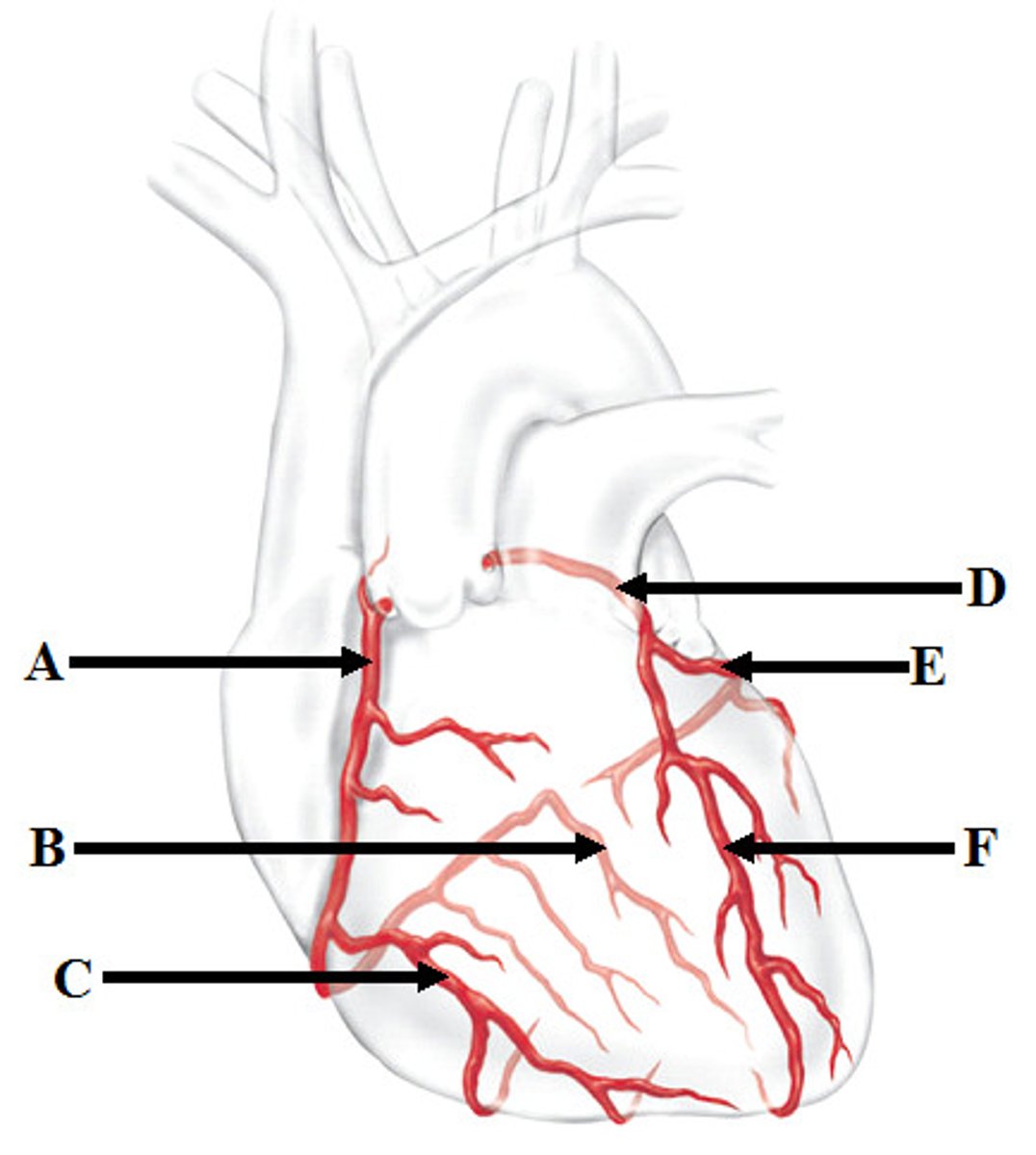
Anterior Interventricular artery (F) and Circumflex artery (E)
Branches of the left coronary artery
Intrinsic conduction system
The cardiac muscle is able to depolarize and contract without impulses from the nervous system because of the
Sinoatrial (SA) node -> Atrioventricular (AV) node -> Atrioventricular Bundle or Bundle of His -> Right and Left Bundle Branches -> Purkinje Fibers
Intrinsic conduction system pathway