6.3 Photochemical smog
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Primary pollutants
Pollutants emitted directly from a process. Process can be natural (volcanic eruption) or anthropogenic (cars)
Ex: Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, particulate matter
Secondary pollutants
Formed when primary pollutants undergo a variety of reactions with other chemicals already present in the atmosphere. Very commonly catalyzed by exposure to water or sunlight.
Ex: Tropospheric ozone
Formation of tropospheric ozone
When nitric oxide reactions with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide. This then reacts with sunlight to produce nitric oxide and oxygen. The oxygen reacts with an oxygen molecule and produces ozone.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
A primary pollutant that is a colorless and odorless gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline and natural gas.
Nitrous oxide (NO)
A primary pollutant that is produced by the burning of fossil fuels and the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. Can also contribute to creation of tropospheric ozone.
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
A primary pollutant which is a gas produced by the burning of fossil fuels and the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. Can also contribute to the formation of ground level ozone.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
A primary pollutant which is a gas produced by the burning of fossil fuels that contain sulfur such as coal and oil. Contributes to the formation of acid rain.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Organic compounds which are primary pollutants that evaporate easily at room temperature. They are emitted by various processes and are present in paints and cleaning products. They can cause adverse effects on human health.
Particulate matter (PM)
A mixture of solid particles that are suspended in the air. Is a primary pollutant and depending on the size of the particle can cause varying levels of harm to human health. Can be carcinogenic.
PM 10: Dust, pollen
PM 2.5: Smoke particles (more dangerous as can penetrate deeper into lungs)
Photochemical smog
The interaction of chemicals suspended in the atmosphere that react with the sunlight to form a mixture of primary and secondary pollutants mainly composed of nitrogen dioxide and ozone to form a thick layer of smog.
Typically worsens due to climate and geographic location with lower elevated cities having worse effects.
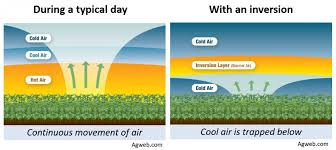
Thermal inversion
When a warm layer of air rises, trapping cooler air below, causing the pollutants to be trapped, worsening the smog.
Ways to reduce urban air pollution
Burn less fossil fuels
Change to renewable energy sources
Use catalytic converts to clean primary pollutants
Plant more trees