Biology Sem 2 Stage 1 Exam
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Simple diffusion
moves with the concentration gradient
Molecules keep moving until equillibrium
Passive transport
Facilitated Diffusion
move with the concentration gradient
for larger molecules such as ions, water and glucose
uses protein channels
Factors affecting rate of diffusion
distance
temperature (higher temp. = increased rate of diffusion)
characteristic of solute (mass)
density of solent (jelly or water)
characeristic of barrier (cell membrane)
osmosis
passive transport
goes with concentration gradient
from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
movement of water through semi-permeable membrane
hypertonic
high solute, low water
water moves out of cell
plants - plasmolysed
animals - shriveled
hypotonic
low solute, high water
water moves in to cell
plants - turgid (normal)
animals - lysed
isotonic
conc. of water = conc. of solute
plants - flaccid
animals - normal
passive transport
no energy
active transport
requires energy
uses carrier proteins that open and close using ATP
Aerobic respiration
uses oxygen
produces 36 - 38 molecules of atp
oxygen + glucose —> water + carbon dioxide + ATP
Anaerobic respiration
without the presence of oxygen
fermentation
produces 2 molecules of ATP
In plants:
glucose —> ethanol + carbon dioxide + ATP
In animals:
glucose —> lactic acid + ATP
glycolysis
happens in both anaerobic and aerobic
occurs in cytoplasm
braking of glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules
Glycolysis needs 2 ATP molecules to work
At the end of the process, it produces 4 ATP
Therefore profit of 2 ATP
Krebs cycle (aerobic)
produces two ATP from the two pyruvates
Also produces 2 NADH
occurs in mitochondria
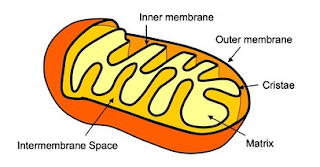
Electron transport chain (aerobic)
occurs in cristae of mitochondria
produces 32-34 molecules of ATP
Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen + ATP
Cell signalling
receptors allow signal molecules (ligands) to bind to them
pathogens can bind to cell receptir
function of endocytosis
cells engulf particles or materials from the outside to the inside of the cell using vesicles
types of endocytosis
pintcytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
fluid (containing nutrients) is engulfed by a vesicle from the phospholipid bilayers
phagocytosis
solid particle is englufed through a vesicle
function of exocytosis
exports particles and material out of the cell through vesicles
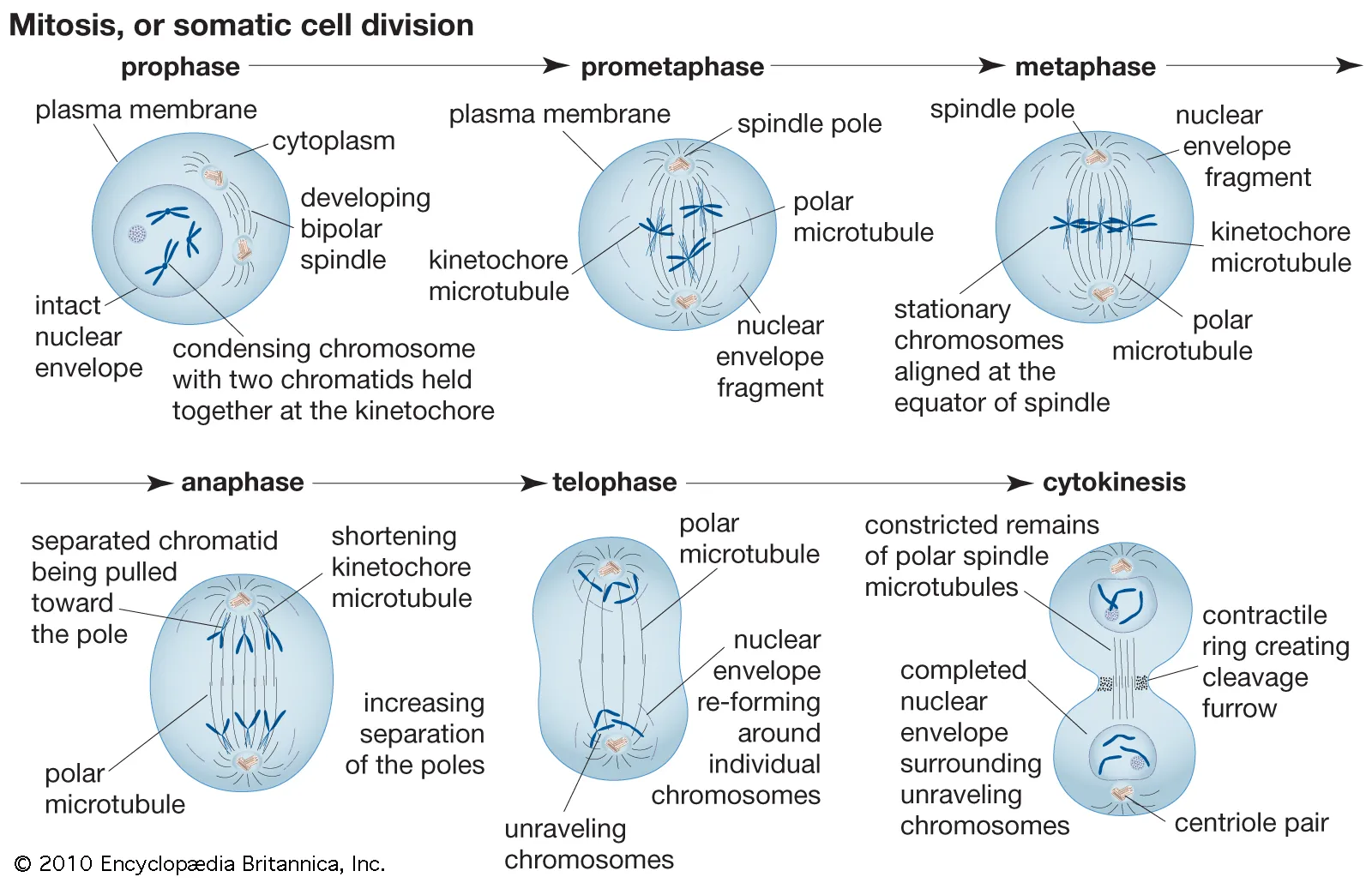
Stages of meiosis
prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2 and telophase 2
What is meiosis
contributes to genetic variety
replication of gametes
gametes have 23 chromosomes, while body cells have the total 46 chromosomes
interphase happens before interphase and cytokenisis happens after.
Are the daughter cells of meisosis diploid or haploid?
haploid (n)
prophase 1
chromosomes condense
nuclear membrane disintegrates
spindle fibres form
chromosomes line up with homologous pairs
homologous pairs of same size and same allele location
homologous pairs transfer genes in crossing over
metaphase 1
Chromoses line up at the centre of the cell as pairs
anaphase 1
crossed over chromsomes are pulled away by spindle fibres to opposite poles of the cell
telophase 1
two formed nuclei
prophase 2
no crossing over
spindles form
metaphase 2
chromatids line up at the centre of the cell
do not pair up, instead line up on top of each other
anaphase 2
sister chromatids are pulled apart from the centromere by the spindle fibres to opposite poles of the cell
telophase 2
nuclei forms in both cells, creating four daughter cells and hence forming 4 cells with 23 chromosomes each.
How many chromsomes does an organism have in a replicated gamete cell with diploid number 28?
14 chromosomes
differences between mitosis and meiosis
mitosis:
produces 2 genetically identical daughter cells
genetic variation does not change
consists of four stages
daughter cells are diploid
meiosis:
produes 4 genetically unique daughter cells
genetic variation increases
consists of eight stages
daughter cells are haploid
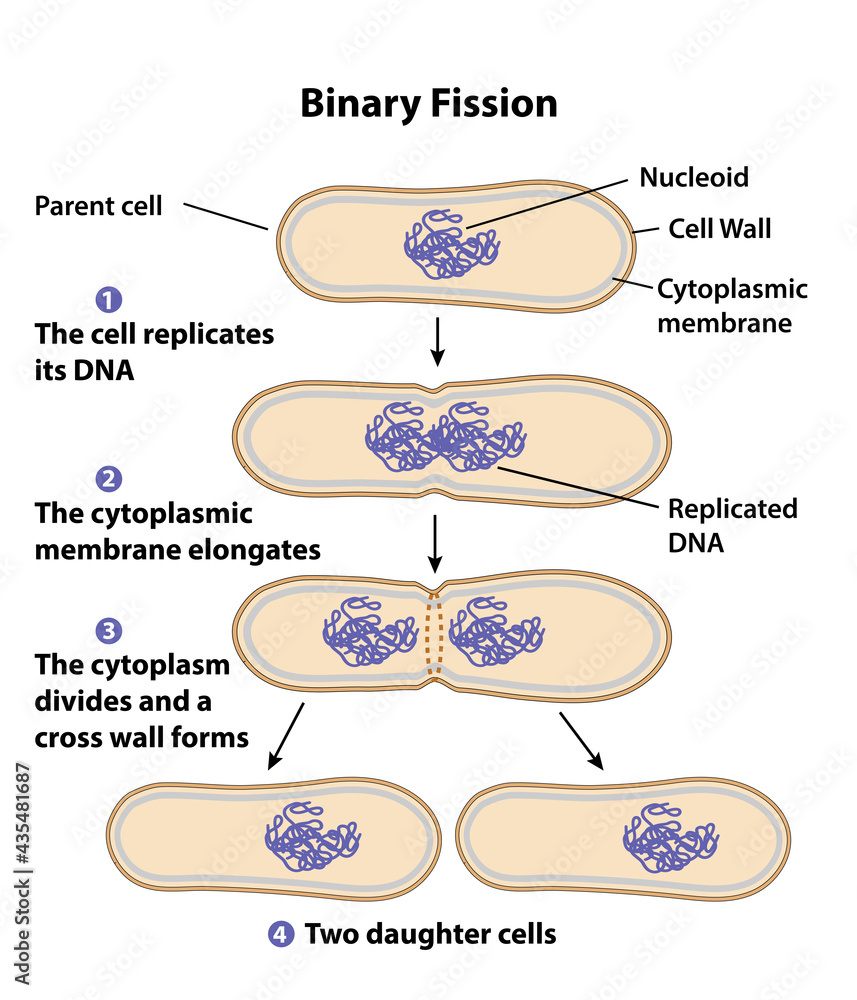
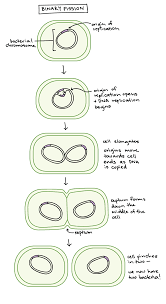
what is binary fission the replication of?
prokaryotes
binary fission steps
Mitosis steps
What are the types of prokaryotes
archaea and bacteria
characteristics of prokaryotes
unicellular
no membrane bound organelles
no nucleus
have DNA information in the form of circular chromsomes and plasmids
cell membrane (cell wall)
have ribsomes and cytoplasm
types of eukaryotes
eukarya (protsists, animals, plants and fungi)
charactertistics of eukaryotes
more complex
multicellular
have membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts (plants), nucleus, ER and golgi body)
G1
cell increases in mass
G2
protein synthesis
increases in size
S (interphase)
synthesis of DNA
Replication of chromosomes
Cytokenisis
cell membrane moves inwards to create daughter cells
How are the chromosomes replicated in binary fission
copying of DNA begins at the sprot of chromosome called origin of replication. This is where the chromosome will replicate the genes and go along the chromosome until all genes have been replicated and there are two genetically identical chromosomes in the prokaryotic cell.
Why is surface area to volume ratio important for cells survival
important to allow cells to quiclly exchange materials and wastes for its survival
Optimum conditions for Bacteria
35 - 37 degrees celcius
neutral pH
constant supply of water and oxygen
mechanism removing waste
What types of bacteria benefit humans?
decomposers and nitrogen fixation (←idk what that is either)
decomposers
decomposers break down dead matter into inorganic materials that can be used by producers/plants for growth
Factors affecting growth of microbes
warmth
moistre
ph
oxygen levels
nutrients
Nucleolus
site of ribosome synthesis
ribosome
produce proteins
golgi body
recieves proteins from the ER, and packages and distributes them to other parts of the cell
Smooth ER
involved in lipid manufacture and storage
Rough ER
has ribosomes and is involved in production, folding and transportation of proteins
Ribosome
small round bodies that produce proteins
lysosome
small round organelle that contains chemicals that break down particles
vacuole
stores water and nutrients, and supports plant cells
cytoskeleton
supports structure of cell
Limitations of antibiotics
can experience antibiotic resistance
What are the uses of antibiotics
fights bacterial infections
What is the enzyme called in recombinant technology that snips the gene sequence
Resistance enzyme
What is the enzyme called that resticks the gene of interest into the plasmid of a prokaryotic cell
DNA Ligase
How does sugar and salt preserve food
through osmosis
how does cooling food preserve it
slows down enzyme activity that rot food and slows down growth and reproduction of microorganisms.
What is competition
the rivarly between species or in a population for resources
how much energy is passed on at each trophic level
10%
how does fertilisation affect environment
nitrogen in fertilisation seeps in soil and creates an optimum condition for weeds to grow in
what is a niche
describes an organisms physical and environmental conditiosn it requires to survive. it is the role that an organism plays in its community.
what is an ecosystem
a community of organisms and how they interact with their environment.
what is the order of hierarchy
domain
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species