Biology 1 - Mod 3 Cell Discovery
Discovery of the Cell
1590: Zacharias Janssen
- First compound microscope
1665: Robert Hooke
- Looked at cork under the microscope
- Called the empty chambers he saw ‘cells’
1674: Matthias Schleidon
- All plants are made from cells
1839: Theodor Schwann
- All living things are made of cells
1855: Rudolf Virchow
- New cells only come from existing cells
Cell Theory
- All living things are made of 1 or more cells
- Cells are the smallest units of function and structure in life
- New cells are produced from existing cells
All cells have 4 things in common:
- Cell membrane
- DNA
- Cytoplasm
- Ribosomes
Types of Cells
Prokaryotes
- Do NOT contain a membrane-bound nucleus/organelles
- Have genetic information, but it isn’t stored in the nucleus.
- Have the 4 things in common
- Unicellular
Example: Bacteria (only remaining prokaryote)
Eukaryotes
- Have a nucleus (contains the DNA)
- Have organelles (little organs)
- Unicellular or Multicellular
Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, and protists
Cell Specialization
- a cell’s shape (structure) relates to what it does
Example: White blood cells change shape (fit through tight spaces and engulf invaders)
Cell Organization
Cell → Tissues → Organ → Organ System → Organism
Example: Muscle cell → smooth muscle → tissue → stomach organ → digestive system
Cell Membrane
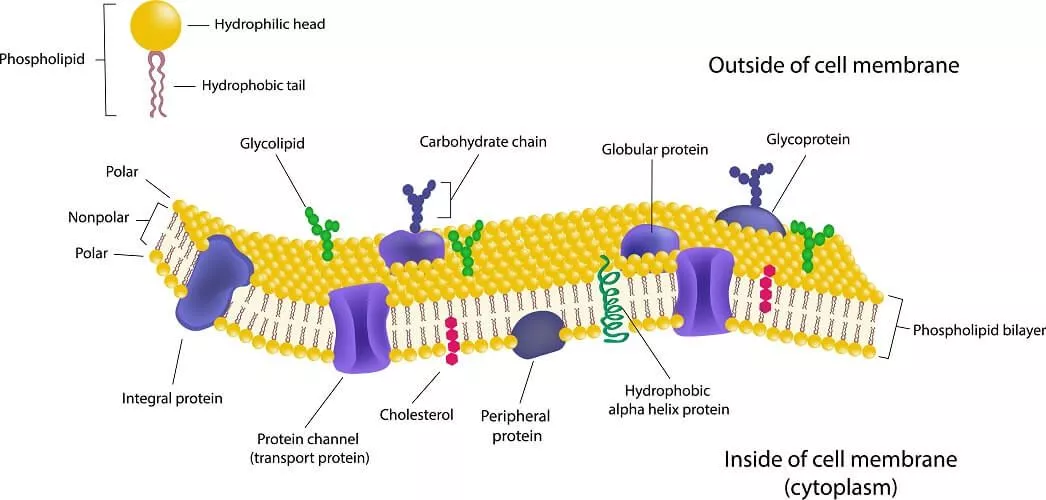
Cell Membrane Structure
Phospholipid bilayer
Glycerol head and 2 fatty acid tails
2 layers
Cholesterol - Prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together, maintains flexibility
Carbohydrates - identify chemical signals