Final Exam Practice Foundations Cell Molecular Biology
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts, definitions, and processes related to cell and molecular biology as outlined in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What function of the plasma membrane is possible without membrane proteins?
Selective permeability.
What type of lipids is the most abundant in the plasma membrane?
Phospholipids.
What behavior do membrane lipids exhibit?
Membrane lipids diffuse laterally within the plane of the membrane.
Which type of lipid movement does NOT occur spontaneously in biological membranes?
Moving between lipid layers.
What function is NOT influenced by cholesterol in mammalian cells?
Membrane thickness.
What is the principal fibrous protein in the cortex of red blood cells?
Spectrin.
Which stage generates the most ATP during the breakdown of food?
Oxidative phosphorylation.
Which type of simple subunits is used preferentially as an energy source?
Simple sugars.
What is the final metabolite produced by glycolysis?
Pyruvate.
How many activated carrier molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose in glycolysis?
2 ATP, 2 NADH.
Which enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate in glycolysis?
Aldolase.
What does a kinase enzyme catalyze?
The addition of phosphate groups to other molecules.
Fill in the blank: Fermentation is a(n) ____ process that converts _______ into carbon dioxide and ____.
Anaerobic; pyruvate; ethanol.
What are the products when succinate is oxidized by succinate dehydrogenase?
Fumarate, FADH2.
What happens when a G-protein-coupled receptor activates a G protein?
The α subunit exchanges its bound GDP for GTP.
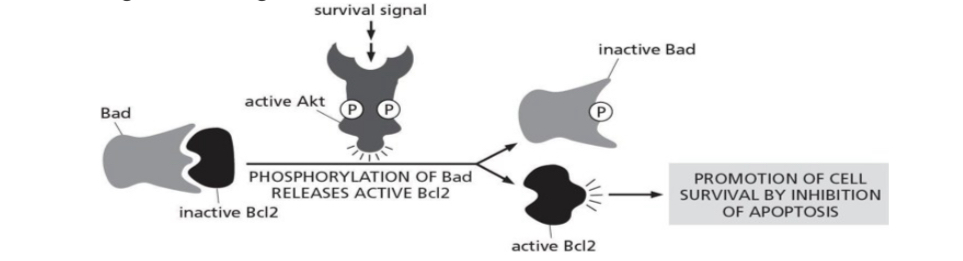
Which of the following statement is false?
In the absence of survival signal, bad is phosphorylated.
Which statement about signaling molecules is FALSE?
Dissolved gases such as nitric oxide can act as signaling molecules, but because they cannot interact with proteins, they must act by affecting membrane lipids.
What does NOT usually occur during interphase?
The nuclear envelope breaks down.
In which phase do cells check for correct DNA replication?
At the end of G2.
Why do cyclins bind to Cdks for cell cycle progression?
The binding of a cyclin to Cdk is required for Cdk enzymatic activity.
What effect does higher cholesterol have on membrane fluidity at low temperatures?
Fluidity will increase because cholesterol helps prevent phospholipids from packing too tightly.
What activates the G1 DNA damage checkpoint?
Involve the inhibition of cyclin-Cdk complexes by p21
Cells in the G0 state are described as:
Do not divide.
What does NOT occur during M phase in animal cells?
Growth of the cell.
What holds sister chromatids together at the end of DNA replication?
Cohesins.
Which statement about the mitotic spindle is true?
The mitotic spindle helps segregate the chromosomes to the two daughter cells.
What is the principal microtubule-organizing center in animal cells?
Centrosome.
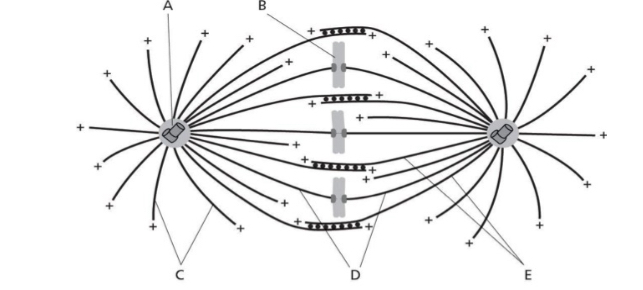
What best describes the phase in mitosis during chromosome attachment to microtubules?
Metaphase
Programmed cell death occurs by means of which process?
By means of an intracellular suicide program.
What distinguishes necrosis from apoptosis?
Causes cells to swell and burst, whereas apoptotic cells shrink and condense
What phase do most liver cells stay in when undamaged?
G0.
Predict the relative rates of diffusion of the following molecules: alanine, propanol, sodium, estrogen.
Estrogen > propanol > alanine > sodium.
Estrogen: hydrophobic
Propanol: small polar
Alanie: large, polar ions
Which ion is most abundant inside a typical mammalian cell?
K+.
What type of transport do pumps facilitate?
Active transport.
What happens to the resting membrane potential when Na+ channels open?
It becomes more positive.
What is the effect of a mutation in Ras that locks it in the GTP-bound form?
It will divide and proliferate continuously, even without growth factor.