Buffer
A solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base.
ka
ka=(H+)(A-)/(HA)
pKa
The negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka), indicating the strength of an acid.
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
An equation used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution, given by pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]).
Beer lambert equation
A=€cl
stronger acid = ___ pka
smaller
Lysozyme
An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in peptidoglycan, leading to cell wall rupture.
Peptidoglycan
A polymer consisting of sugars and amino acids that makes up the cell wall in bacteria.
lysozyme
cataylzes the hydroylsis of Beta 1 to 4 glycosidic bonds between NAG and NAM
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
A technique used to separate molecules based on their net charge.
Homodimer
A protein composed of two identical subunits.
Cation exchange
A method using negatively charged resin to bind positively charged proteins. (CM sepharose) -positive charged will bind
Anion exchange
A method using positively charged resin to bind negatively charged proteins. (DEAE sepharose)- negative charge will bind
pH < pI
protein has positive charge
pH > pI
protein has negative charge
lysozyme PI
very high -10.7
Biuret method
A colorimetric assay for detecting the presence of proteins based on the formation of a colored complex with copper II ions.
Color changes from light blue to dark purple
not very sensitive
ELISA
A technique that uses antibodies to detect the presence of specific antigens in a sample.
function of BSA in ELIZA
excess inert protein that locks sites not covered by protein
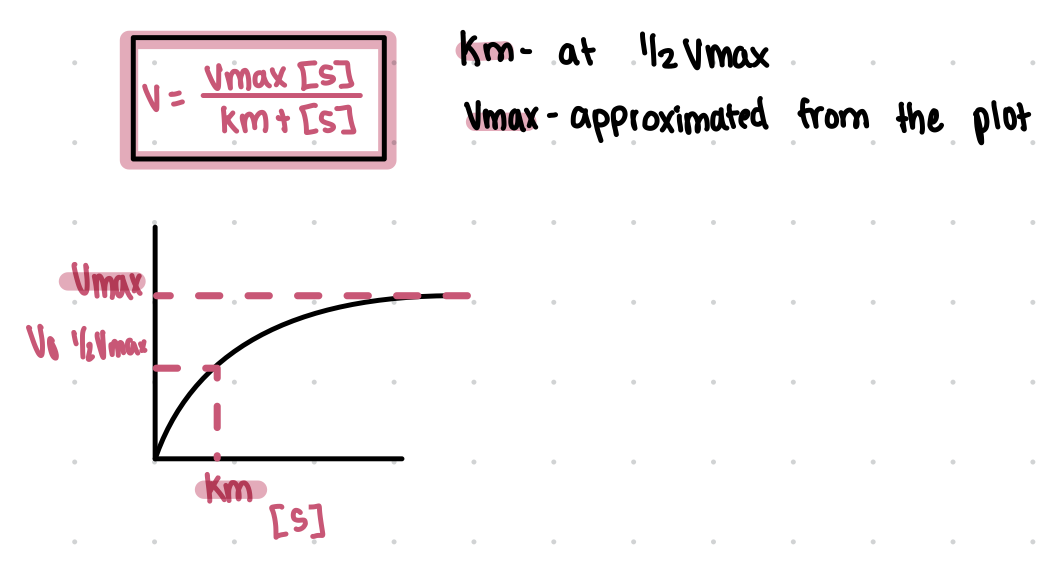
Michaelis-Menten equation and plot
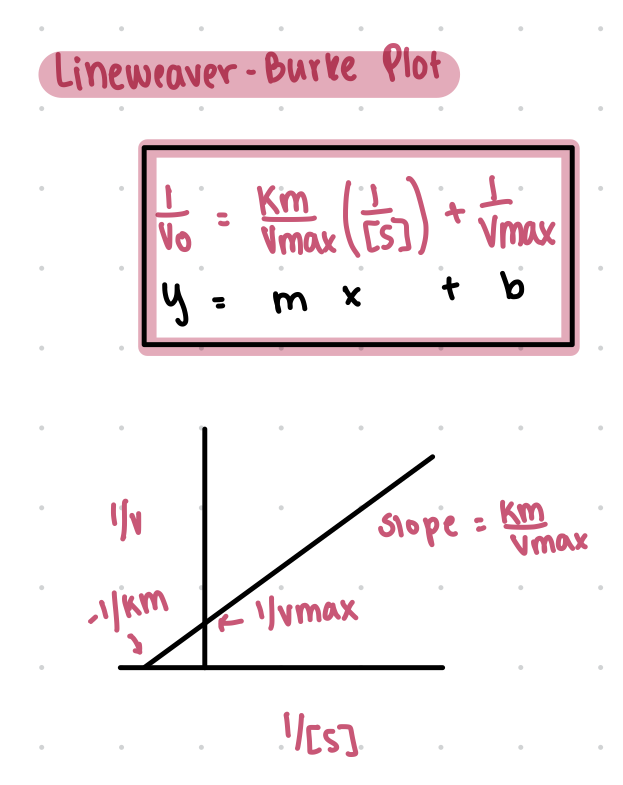
lineweaver burke plot
Salt precipitation
A method used to purify proteins by adding salt to precipitate proteins out of solution. disrupt hydration sphere, salt pulls water molecules from surface of protein, forcing protein molecule to aggregate
-maintains protein native structure
how is got activity indirectly measured
oxaloacetate reacts with NADH to create L-malate and
NAD+, NADH absorbs at 340 but NAD+ does not
Heat denaturation
The process by which proteins lose their structural integrity and function due to high temperature. irreversible
IU/Ml equation:
Specific Activity equation:
Total GOT activity equation:
%yield fraction:
Degree of purity:

Coomassie Blue
A staining dye used in electrophoresis. we use with acid/methanol mixture to fix proteins to the gel to prevent protein form diffusing in gel or being washed out
BME (Beta-Mercaptoethanol)
A reducing agent used to break disulfide bonds in proteins during SDS-PAGE.
SDS-PAGE
A technique that separates proteins based on their size by using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with sodium dodecyl sulfate.
Native PAGE
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis that maintains the native structure and charge density of proteins.
Polyacrylamide gel
A cross-linked polymer of acrylamide and bis-acrylamide used as a medium for gel electrophoresis to separate proteins based on size
higher % acrylamide to seperate ___ (big/small) proteins
small- dense matric- restrict movement of the large proteins
SDS
used to break non-covalent interactions (all become neg charged and linear)
BME
reducing agent to reduce (break) disulfide bonds
reducing conditions
BME+SDS
disulfide bonds broken
non-cov broken
non-reducing conditions
SDS only
disulfide not broken
non- cov broken
bromophenol blue in sds-page
doesn’t stain proteins, just shows progress of electrophoresis