8. Foams, gels and the colloidal glass transition
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Types of foam (shape)
Spherical foams:
It has more continuous phase
Example shaving foam
Polyhedrical foams:
It has thin continuous phase
Example beer foam
Spherical foams might transfer to polyhedrical

Types of foam (stability)
Transient foams:
A foam that is not stable tends to collapse quickly
Examples: detergents, beer, champagne
Stable foams
A foam that is stable doesn’t tend to collapse quickly
Examples: styrofoam, bread etc. (since continuous phase is a solid)
Foams
• Associative liquids → interface with air → needs stabilization by surface active molecules
• Surface costs energy! (high surface energy)
• Gas is hydrophobic since there is low inter-molecular interaction
• Pure liquids do not foam
• Creation of foams
– Whipping/vigorous stirring
– Through small pores
– In situ (gas generation)
Stability of foams
The stability of foams is affected by
Draining
Coalescence
Disproportionation
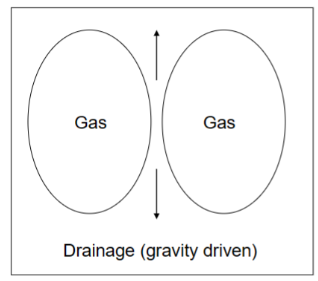
Drainage
liquid between bubbles will drain because of gravity
Fast without surface film (adsorbed layer of surfactant)
Slower with surface film
Rate of drainage depends on the viscosity of the liquid phase (by increasing viscosity (adding thickening agent)→ draining rate will decrease) - for example maräng
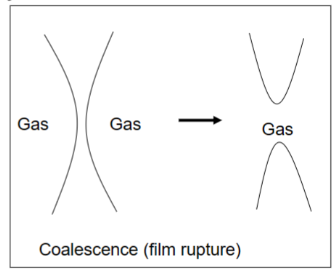
Coalescence can occur
Presence of solid particles
Presence of spreading oils destabilizes aqueous interfaces
Coalesence in presence of solid particles
Penetrating particles destabilize → rupture of interface
Typically particles that are not wetted by the liquid phase
Non-penetrating particles stabilize → increase in viscosity of the liquid phase
Coalence in presence of spreading oils destabilizes aqueous interfaces
Spreading along the interface occurs if: γwater/air > γoil/water + γoil/air
Air/water interface collapses
Thick adsorbed layers are more stabilizing → more resistant to deformation.
Large bubbles are less stable against coalescence → more easily deformed
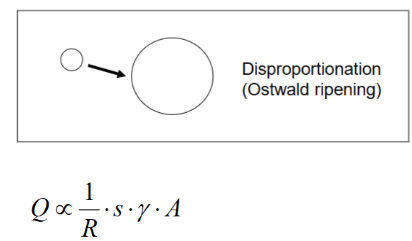
Disproportionation (Ostwald ripening)
Small bubbles “disappear” and large bubbles grow
Driven by the Laplace pressure.
Individual gas molecules dissolve from small bubbles and diffuse to large bubbles.
R=bubble radius
s=solubility of gas
γ=surface tension
A=area of film (per volume gas phase)
Gel formation
• A gel is a system with a considerable yield value (overcome yield value → to make it flow)
• Requires a continuous 3D-network of polymers or particles
Viscous flow can be very low
• Relaxation from one state to another can be very slow
– The time for observing viscous flow can be very long
– Very viscous ”liquids” can appear solid (depending on how long observe it)
Types of gels
• Particle gels
• Polymer gels
• Lamellar structures of surfactants and lipids (cosmetic products like creams → incorporates into the skin)
Polymer gels can form by being
– Covalently linked
– Linked through physical interaction:
• Ion bridges
• Hydrophobic interaction
• Partial crystallization
• Helix formation
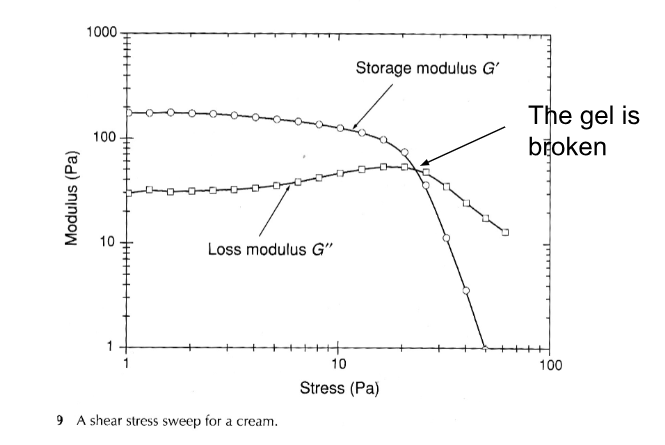
Viscoelasticity for gels
G’= ”in phase” shear modulus = storage modulus = elastic response=”solid-like” contribution.
G’’=”out of phase” shear modulus = loss modulus = viscous response=”liquid-like” contribution.
A characteristic of gels is that G’ > G’’ at low deformation
Colloidal glass
It is formed when colloidal particles are densely packed in a suspension to the point where they form a disordered, amorphous solid-like structure.
Transition from liquid to solid doesn’t depend on temperature and instead occurs at different volume fractions depending on:
• Attractive interaction
• Repulsive interaction
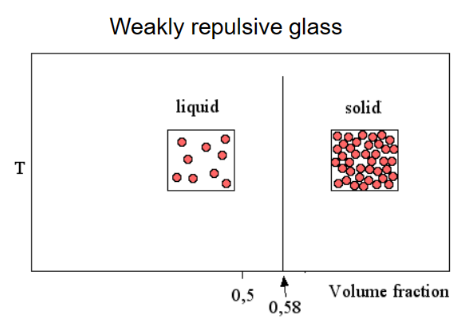
Repulsive glass
Repulsive forces between particles will lead to a transition at higher particle volume fraction. They are forced together even though there is repulsion between them, since there is no more space. It occurs around φg≈0.58
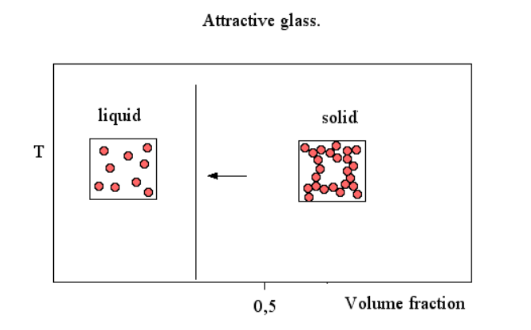
Attractive glass
Attractive forces between particles will lead to a transition at lower particle volume fraction, since it flocculates
Cage effect
One particle is caged by other particles. Occurs for repulsive glass
Long range repulsion compared to short range repulsion
Long range repulsion in a dispersion shifts the colloidal glass transition to a lower volume fraction compared to short range repulsion.