Lecture 5: Staphylococcus species
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Describe the key features of Staphylococcus
Facultative Anaerobe
Gram + Cocci
Clusters
Commensal on skin and mucosa
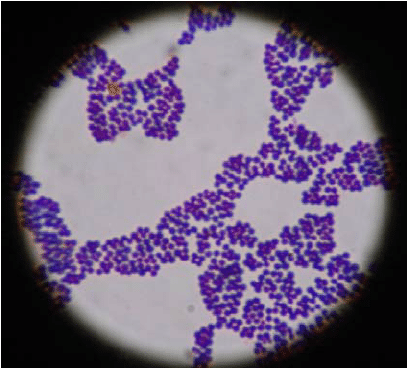
A coagulase assay is a common test performed on bacteria, what is coagulase and what does it do?
Coagulase is an enzyme that clots plasma into fibrin clots
Coagulase hides bacteria from PMNs
Therefore it positively contributes to a bacteria’s virulence
What are the Coagulase + and Coagulase - staphylococcus?
C+
S. aureus
S. pseudintermedius
S. coagulans
S. hyicus
C-
S. epidermidis
S. felis
S. chromogenes
Staphylococcus that are CPS (Coagulase psotive staphylococci) and grown on a blood agar plate can create a _____ ___ hemolysis
Double Zone
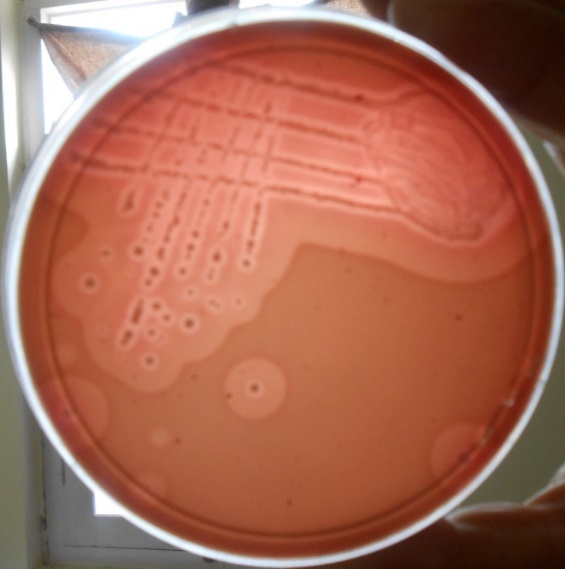
Staphylococci that are CPS will have _________ and ________
+ Hemolysis and + Coagulase
Why is S. aureus so dangerous?
It has MANY virulence factors
Capsule, Protein A, Extracellular toxins and free coagulase
These factors allow it to adhere, invade, survive and cause damage within the host
It also is antimicrobial resistant
MRSA
How did Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) get so bad?
The gene that is responsible for the resistance, SCCmec, can be passed between S. aureus
This gene gives S. aureus resistance to all beta-lactams
Coupled with inappropriate antibiotic use
T/F: SCCmec makes S. aureus more virulent
False, it makes it harder to treat, not necessarily more virulent
What is a Clone?
A group of strains with the same genotype with a common ancestor
S. aureus human and animal clones are different but closely related, why is that an issue?
Bc it increases the chances for them to be zoonotic
MRSA clones easily colonize and spread amongst different host species
Which animal is a major reservoir for MRSA for humans?
Pigs
S. aureus is referred to as a “pathogen for all ________”
Seasons, because it can do it all
What does nosocomial mean?
It means that something is hospital associated
T/F: S. aureus is a primary and opportunistic pathogen
True
T/F: S. aureus is zoonotic and anthropozoonotic
True, it means it can go from animals to humans or from humans to animals
S. aureus is known to cause what affliction in lambs in the UK and Ireland? Describe a bit about the infection
“Tick pyaemia“ abscesses
This is an opportunistic infection by S. aureus
The opportunity is triggered by immunosuppression of the host, caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum (tick borne disease)
S. aureus is in the tick bites/wound and then it abscesses into the joints and organs (liver) of the animal

What disease does S. aureus subsp. anaerobius cause? and in what species?
Morel’s Disease in Sheep/Goats
Abscesses near cervical lymph node and in lungs
The abscesses are caused by coordination w. Cornybacterium pseudotuberculosis (which causes Caesous lymphadenitisi)

What common foot disease does S. aureus cause in raptors/poultry?
Bumblefoot
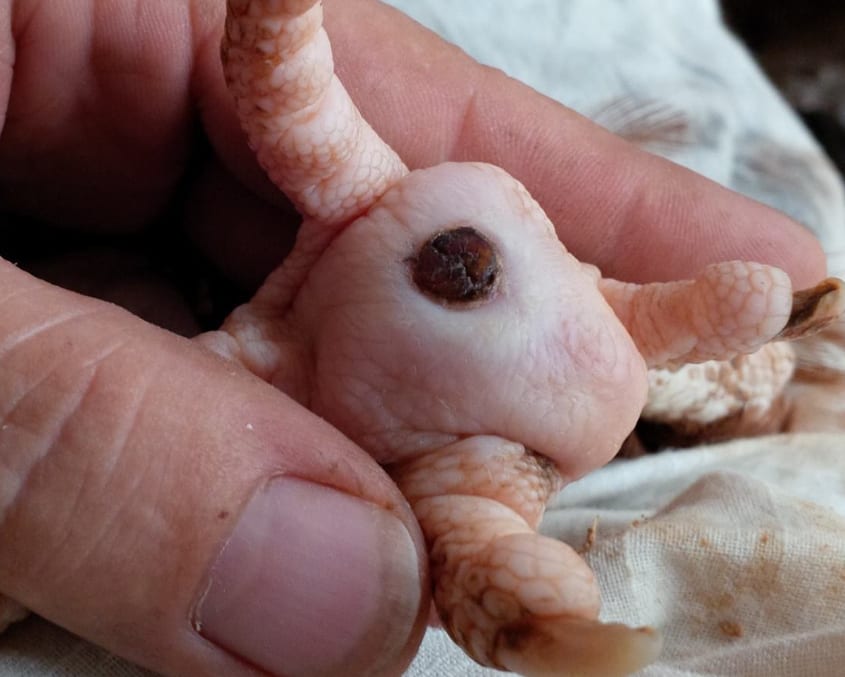
S. aureus causes what disease in guinea pigs?
Pododermatitis
S. aureus is a VERY common cause of ______ _____ _____ in cattle
Chronic Bovine Mastitis
S. aureus is a ______ mastitis pathogen in cattle
Contagious
transmits between the environment, humans, and cattle
Why does the S. aureus that causes C.B.M in cattle have a poor response to antimicrobials?
This iteration of S. aureus “hides“ in abscesses within the udder
The antimicrobials don’t work because they can’t reach the bacteria
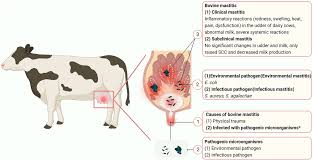
How is C.B.M managed in herds?
Since antimicrobials are not effective against this form a S. aureus infected cattle must be culled or segregated
What type of S. aureus cause C.B.M in cattle?
S. aureus clone ET3
What is the severe form of C.B.M called?
Severe Chronic Mastitis botryomycosis lesions
T/F: CNS bacteria are normal flora of the of the udder
true
What is the new definition for some CNS bacteria?
Mammaliicoccus species
What is the most important CPS in dogs?
Staphylococcus pseudointermedius
T/F: 90% of dogs are colonized with S. pseudointermedius
True
S. pseudointermedius is both _______ and ________ to dogs
Commensal, pathogenic
S. pseudointermedius has similar virulence factors to which other CPS bacteria?
S. aureus
S. pseudointermedius is coagulase and catalase +
It produces exfoliative toxins that damage epidermal cells and cause pyoderma
What happens when dogs with S. pseudointermedius infection are treated with Cephalexin?
Within 1 week they detected MRSP
the Cephalexin selects for MRSP by removing the sensitive strains of S. pseudointermedius
What is co-selection and why is it so dangerous?
The treatment of one antimicrobial can select for resistance across antimicrobial classes
It can create resistance superbugs
S. pseudointermedius
Low
Dogs
Very Common
Frequent
S. aureus
Increased
Humans, livestock, horses
Less common
Rare
CPS are ________ pathogens in inflamed ears, what 2 species are usually responsible for chronic otitis externa in canines?
Opportunistic
S. pseudointermedius and S. coagulans
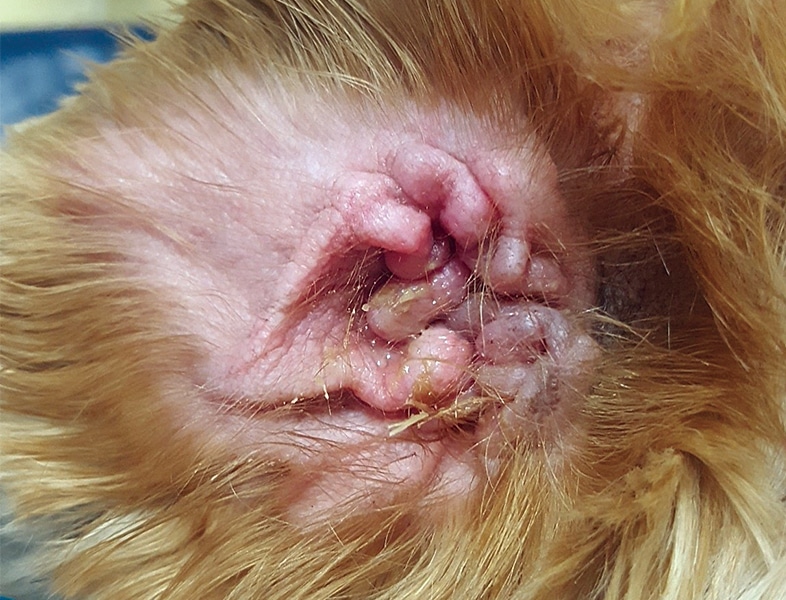
All Staphylococcus species (CPS and CNS) produce the ______ enzyme, what conditions can this enzyme cause?
Urease
Hydrolyses urea and causes UTIs and or Bladder Stones
Staphylococcus felis is a pathogenic ___ in cats
CNS (Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus)
What are some C.S of S. felis?
UTIs
Otitis externa, dermatitis, abscesses, wound infections
T/F: S. felis has low zoonotic potential
True, but it still can be zoonotic
What is the staph species found in pigs? Is it CNS or CPS?
Staphylococcus Hyicus
CPS, but an abnormal one
Why is S. Hyicus an abnormal CPS?
It is non-hemolytic
Produces “china-white“ colonies
Variable to have coagulase 50/50
What common pig disease does S. hyicus cause?
Greasy Pig Disease
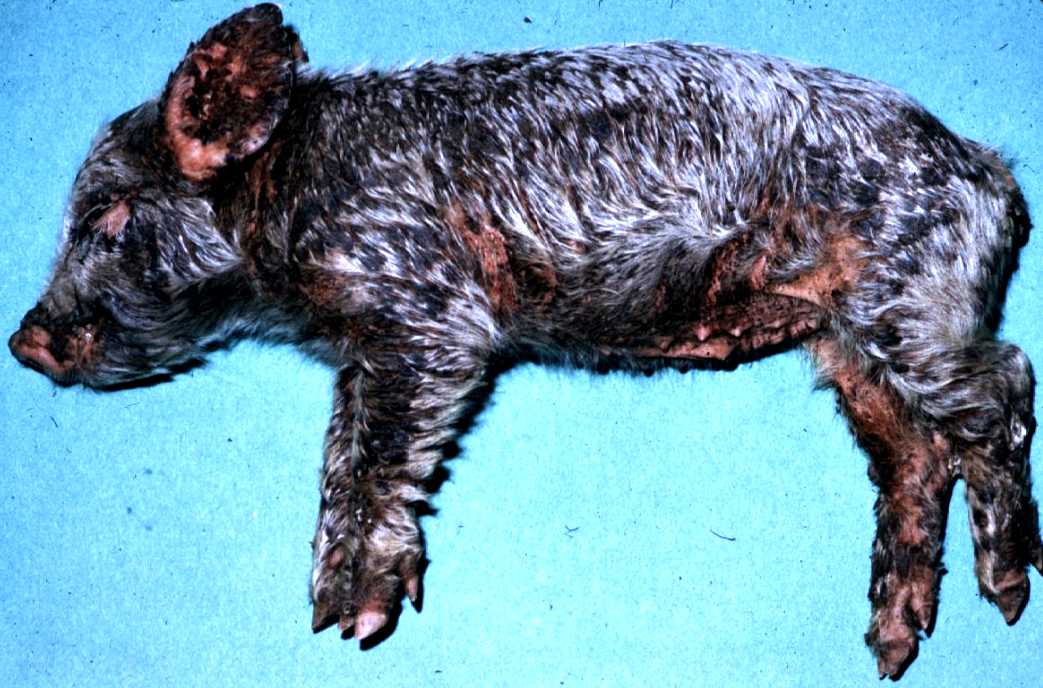
What are some clinical symptoms of a S. hyicus infection in pigs?
Contagious, debilitating dermatitis in young pigs
Secondary bacterial infections
S. hyicus produces an ______ toxin
Exfoliative
irulence factors produced by the bacterium Staphylococcus hyicus, which cause exudative epidermitis, commonly known as greasy pig disease
T/F: CPS are pathogenic while CNS are not
False
T/F: S. pseudointermedius is more common than S. aureus in dogs
True
T/F: Clones are unique to each animal species and cannot spread between humans an animals
False
T/F: The staphylococci MecA gene confers resistance to all beta-lactam antimicrobials
False, it provides resistant to most not all beta-lactams
T/F: Antimicrobial treatment for canine dermatitis can select for multidrug-resistant resistant-MRSP
True
T/F: Exudative epidermitis in pigs is caused by strains of S. hyicus, which produce a toxin causing damage to the epithelial cells
True (Exfoliative toxin)