The nervous system, structural/functional organization and the brain
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
what are the three main functions of the nervous system
sensory, integration, motor
what sensory functions does the NS provide
detects changes in environment (internally and externally)
what integration functions does the NS provide
processing and decision making (of sensory signals)
what motor functions does the NS provide
tells body what to do in response (to sensory signals)
what is the two functional divisions of the nervous system
sensory and motor function
what are the two structural organizations of nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
what does the CNS consist of
spinal cord and brain
what does the PNS consist of
cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses in small intestine, and sensory receptors in skin
What does the CNS do?
receives, processes, stores, and transfers information
What does the PNS do?
receives stimuli from the CNS and and initiates response
what is the main job of the CNS
integration
what is the main job of the PNS
sensory and motor functions
what is the main idea of motor fucntions
carries commanded from CNS to effectors (tissues)
what is the main idea of sensory function
carries information to CNS
what are the 2 main divisions of the peripheral nervous system
somatic and autonomic nervous system
what are two subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system
the parasympathetic and sympathetic NS and enteric nervous system
What is the somatic nervous system?
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
What is the autonomic nervous system?
responsible for control of the bodily functions such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes (involuntary control)
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy (rest and digest)
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
What is the enteric nervous system?
large network of neurons surrounding the digestive organs responsible for involuntary control of smooth muscle, glands, and endocrine cells of GI tract ( can work independently)
what nerves are involved in the parasympathetic nervous system
cranial nerves and parasympathetic nerves (located in sacral region S2-S4)
what nerves are involved in the sympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nerves ( located in thoracic region, T1-L1 segments)
What is a neuron?
Basic unit of the nervous system. (functional cell of NS)
What do neurons do?
send nervous signals to effectors, brain, and spinal cord
What is the axon?
carry electrical nervous signals away from cell body
What are dendrites?
receives signals from other neurons and helps direct signals to cell body
What is the myelin sheath?
A fatty insulation covering of the axon, speeds up electrical signals
What is the axon terminal?
end of axon, that sends signal to another neuron
what are the non nervous cells of the CNS
glial cells: oligodendrocyte, microglial cells, ependymal cells, astrocytes
what are the non nervous cells of the PNS
schwann cells and satellite cells
what is a oligodendrocyte
makes myelin sheath in CNS
What is a microglial cell?
Glial cells that defends the body against pathogens (CNS immune cells --> destory viruses and bacteria)
What is the ependymal cell?
cuboidal epithelial cells that line cavities (ventricles and central canal), that produce and circulate CSF
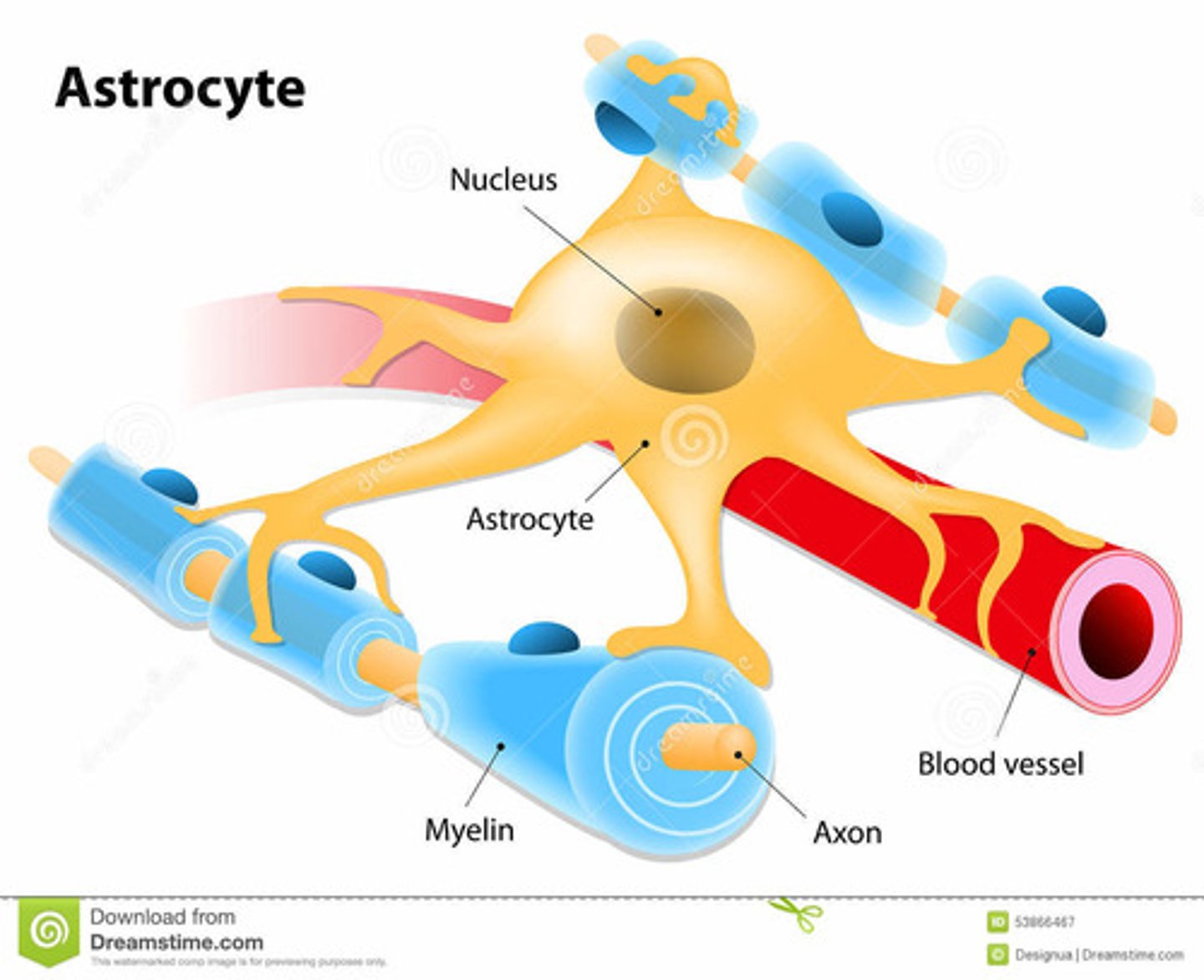
What are astrocytes?
large abundant cells located between blood capillaries and neuron that help regulate which substances can come in contact with neuron. they also provide structural support
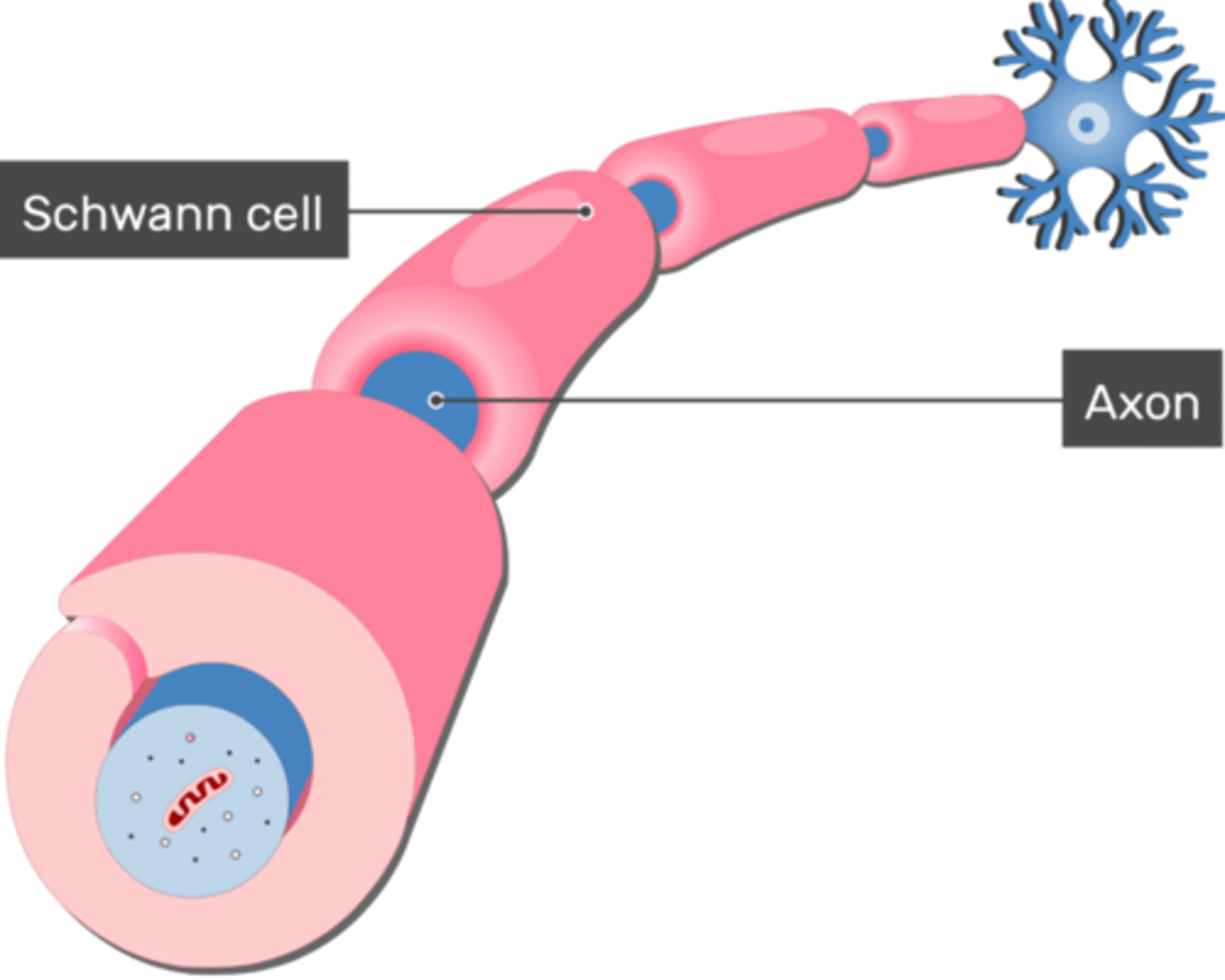
What is a Schwann cell?
They wrap the axon with myelin sheath.
What is a satellite cell?
surround cell bodies in ganglia, provide support and protection, and regulate environment around neruon
What is multiple sclerosis?
autoimmune disease that effects the CNS
what can multiple sclerosis lead to?
demyelination, axon damage, and slowed/blocked nerve conduction
What is the brain
Control center of the body
what structural organization is brain apart of?
CNS
what are the three developmental regions in brain
midbrain, forebrain, and hindbrain
what does the forebrain consist of
cerebrum, and deeper grey matter (thalamus, hypothalamus, and basal nuclei)
What is the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is the part of the brain that controls memory, senses, consciousness, and reasoning.
what does the cerebrum consist of
white and grey matter
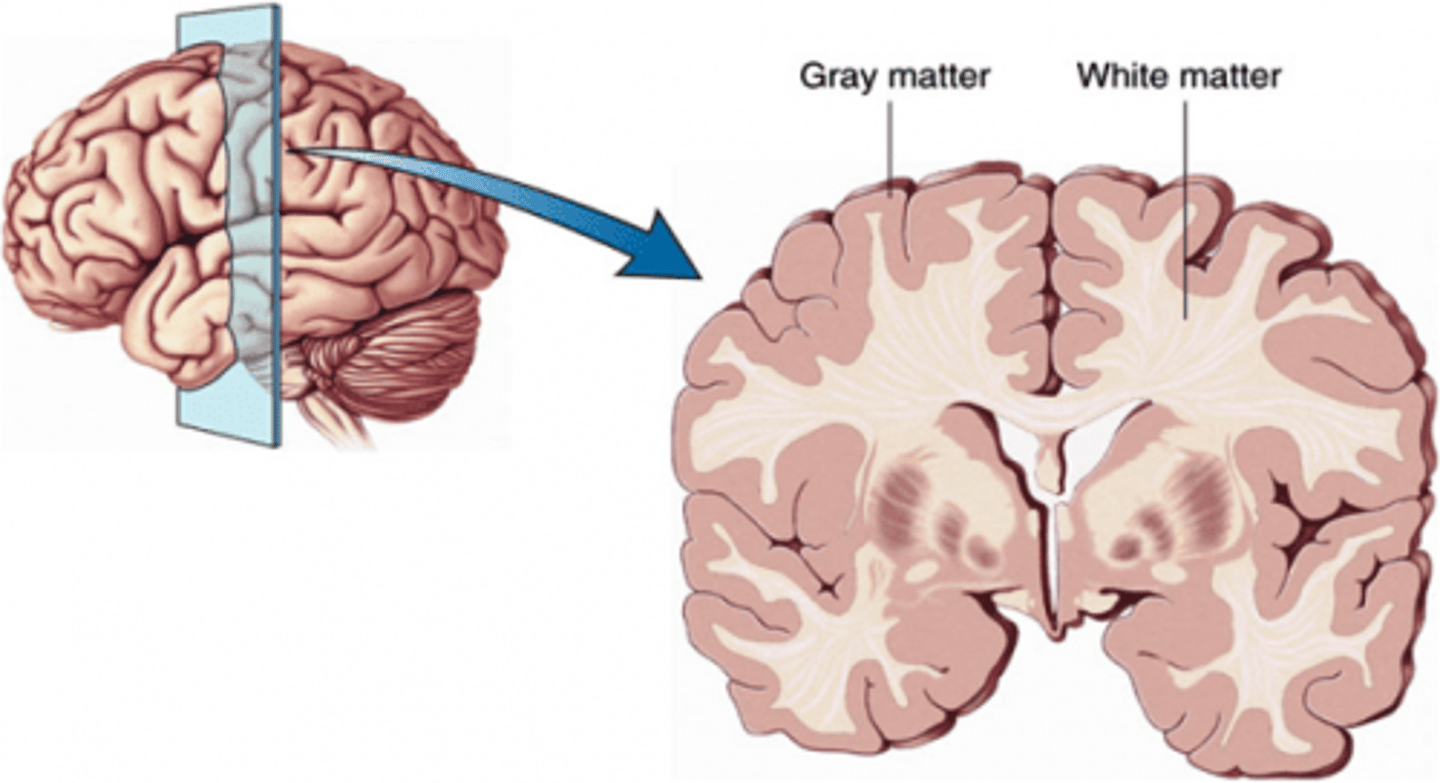
What is white matter?
myelinated axons
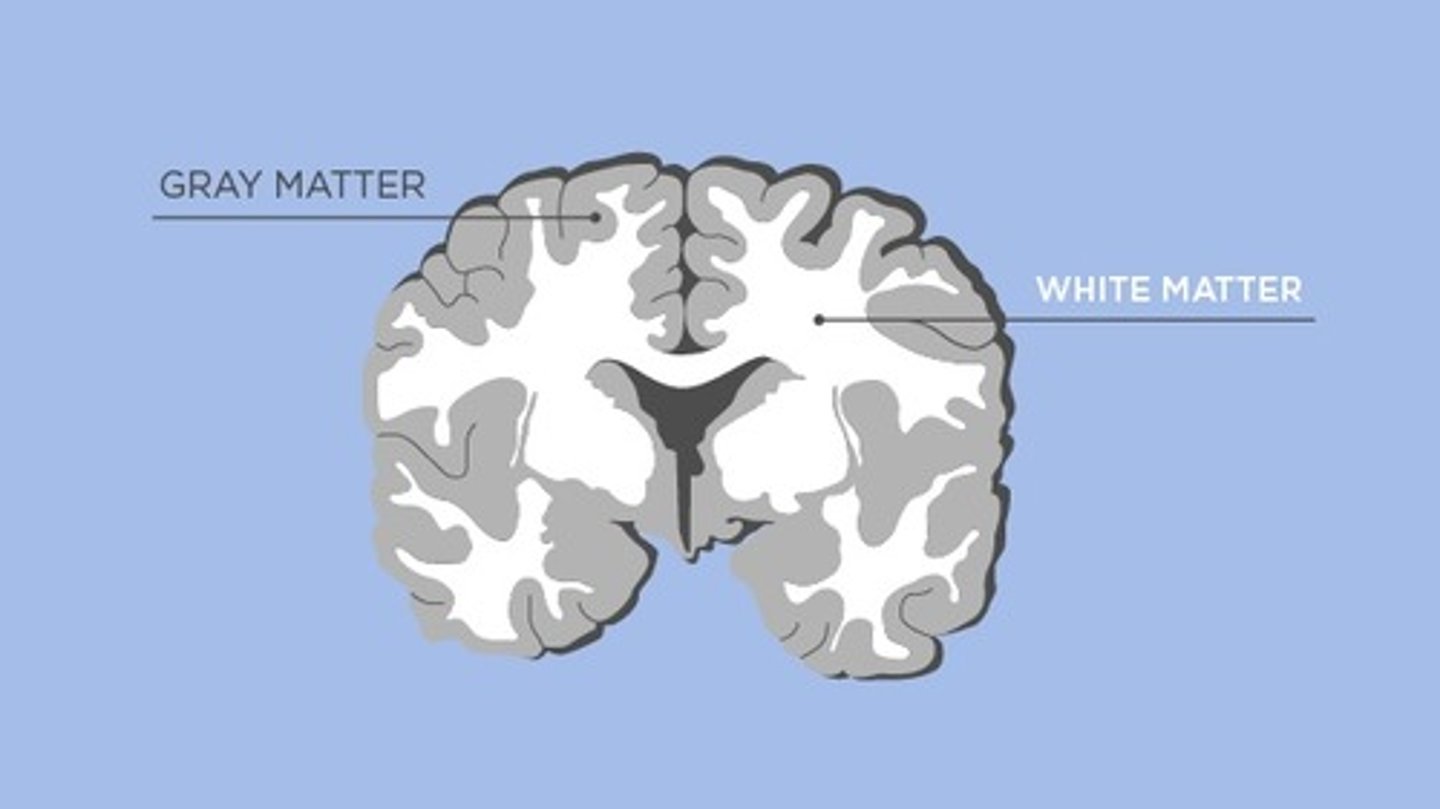
What is grey matter?
cell bodies
what divides the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum
fissurs
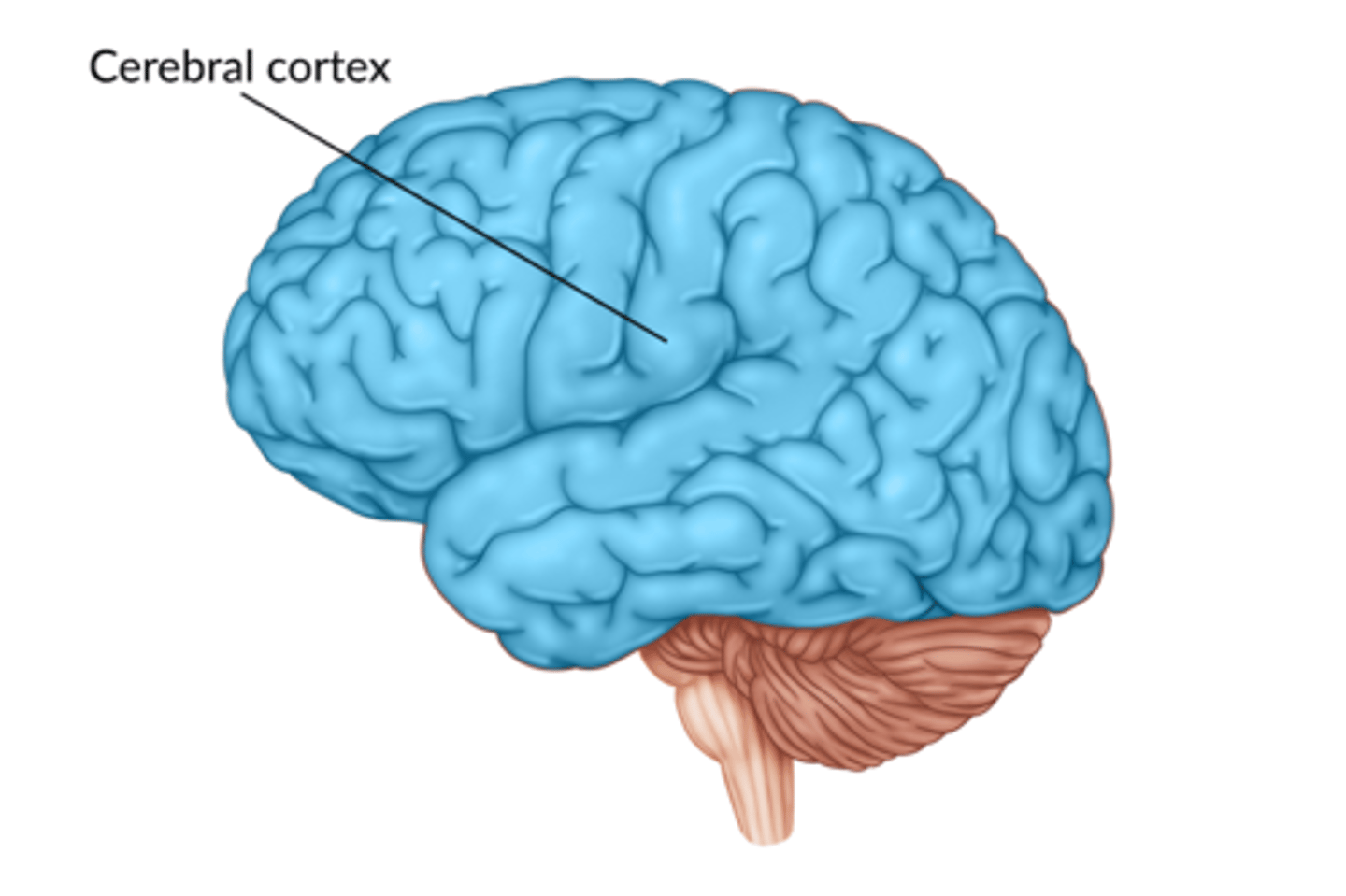
What is the cortex?
outer layer of the brain
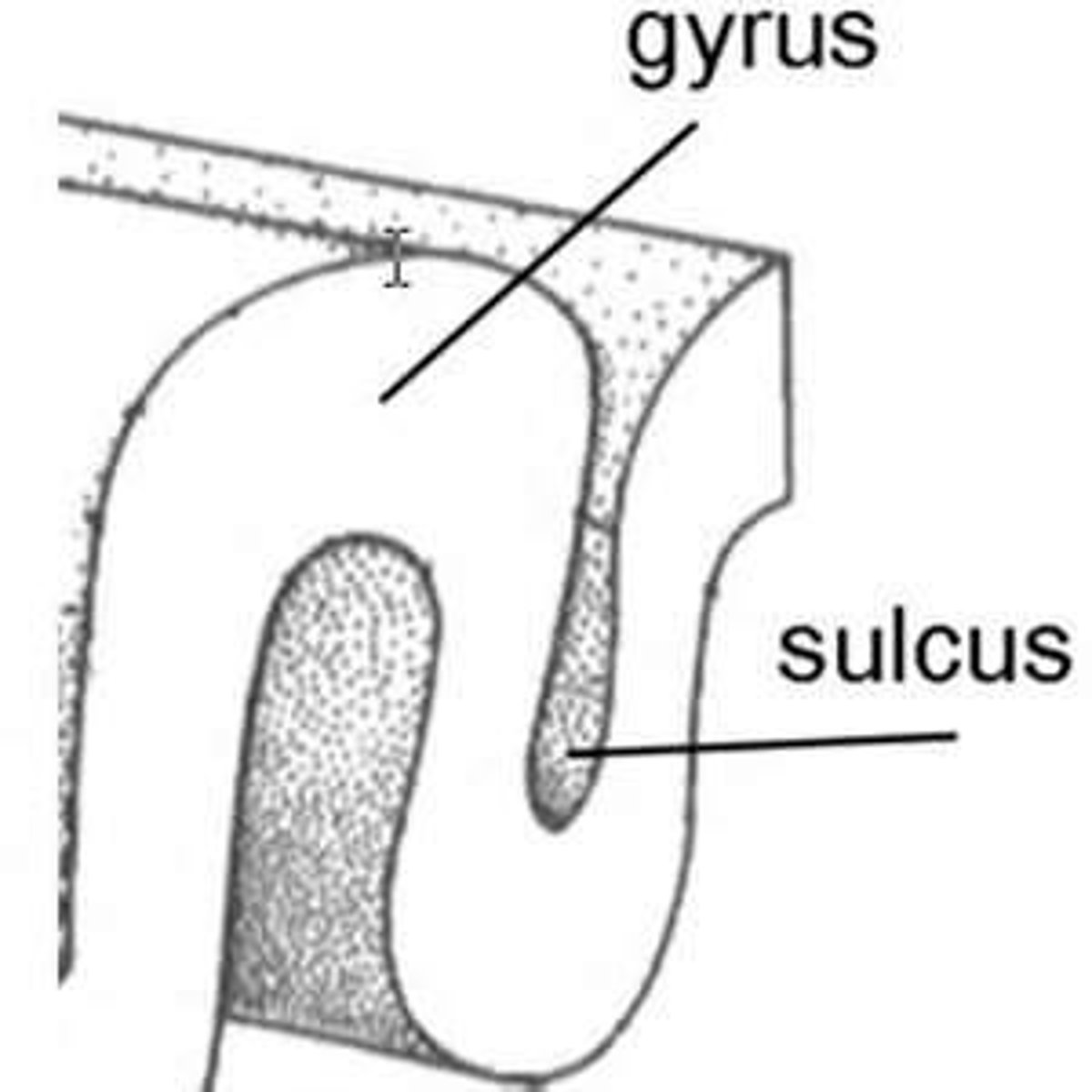
what is gyrus and sulcus
gyrus is the outer ridge of cortex, and sulcus is the inner grooves/depression (sulci connect gyri together)
what are the 5 main lobes of brain
frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, and insula
where is the insula relative to the other lobes
deep to all lobes
what are the 4 tracts of brain
commissural tracts, projection tracts, arcuate fibers, and longitudinal fibers
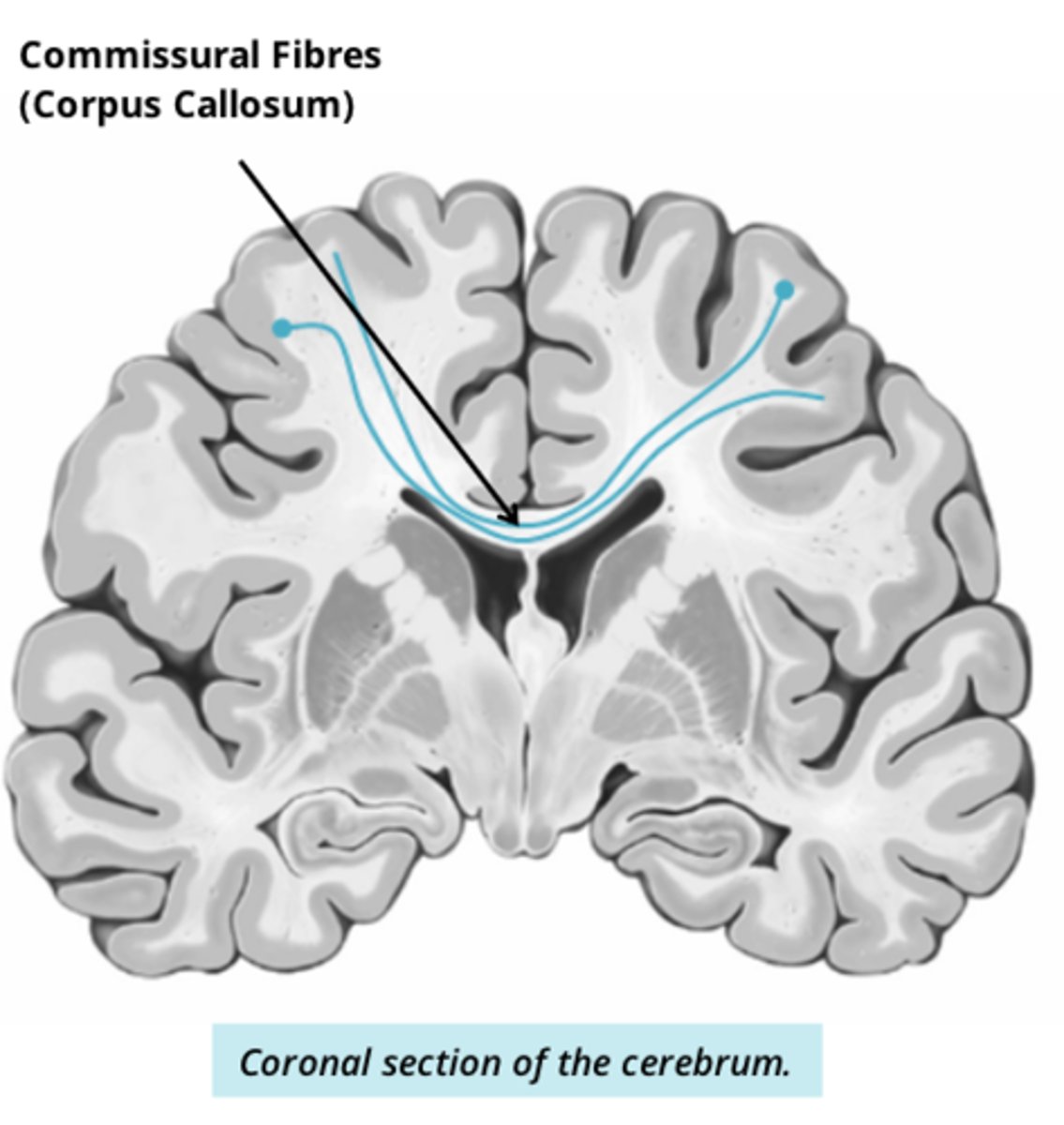
what are commissural tracts
connect L and R hemispheres of cerebrum
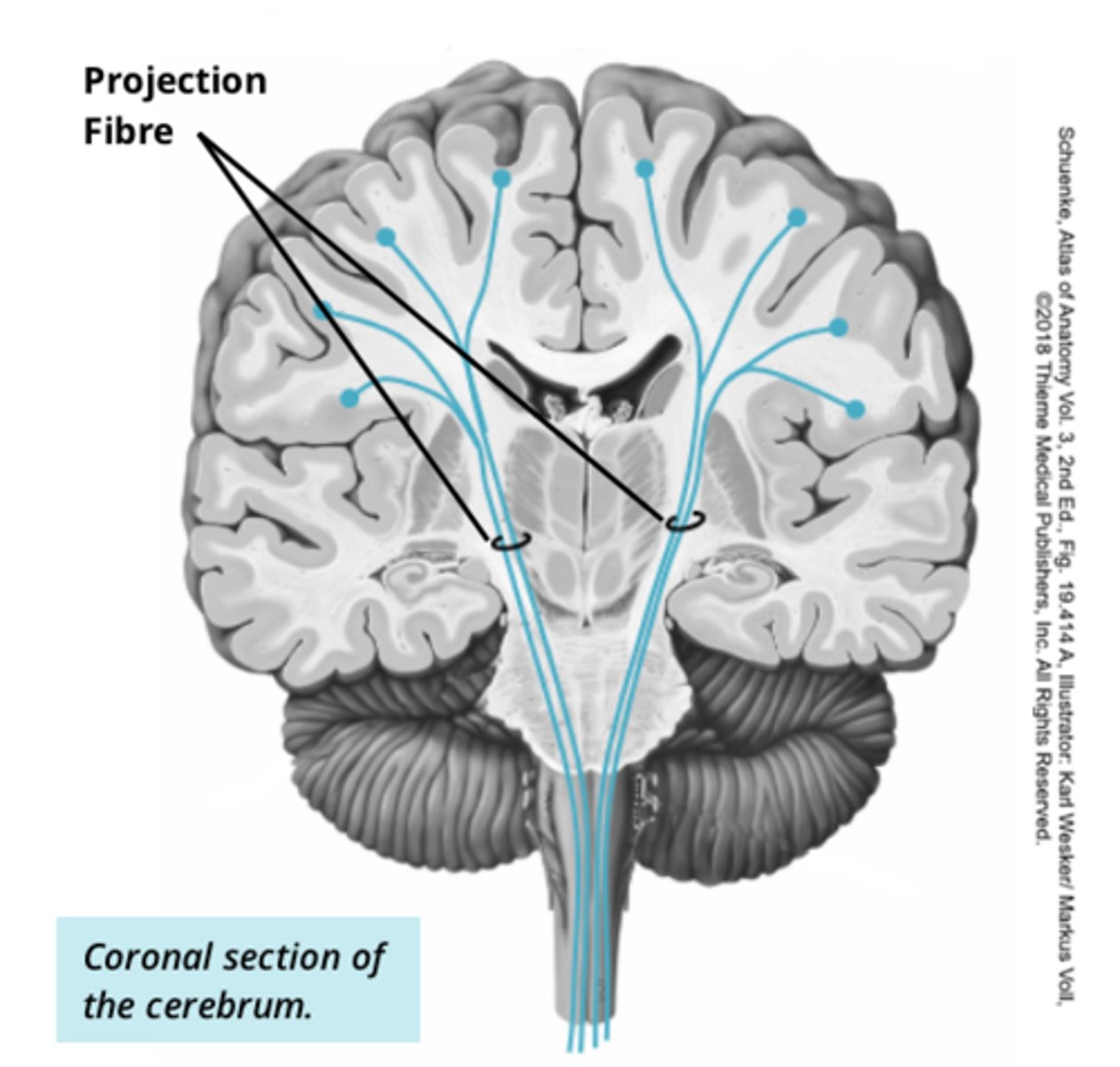
what are projection tracts
carry sensory information form cerebrum to spinal cord (connect cerebrum and spinal cord). Also brings motor signals back up to cortex and deeper grey matter structures
what are arcuate fibers
short tracts connecting neighboring gyri (stay within same lobe)
what are longitudinal fibers
travel through hemispheres ( cross lobes but stay within same hemisphere)
what internal structures does the deeper grey matter include
thalamus, hypothalamus and basal nuclei
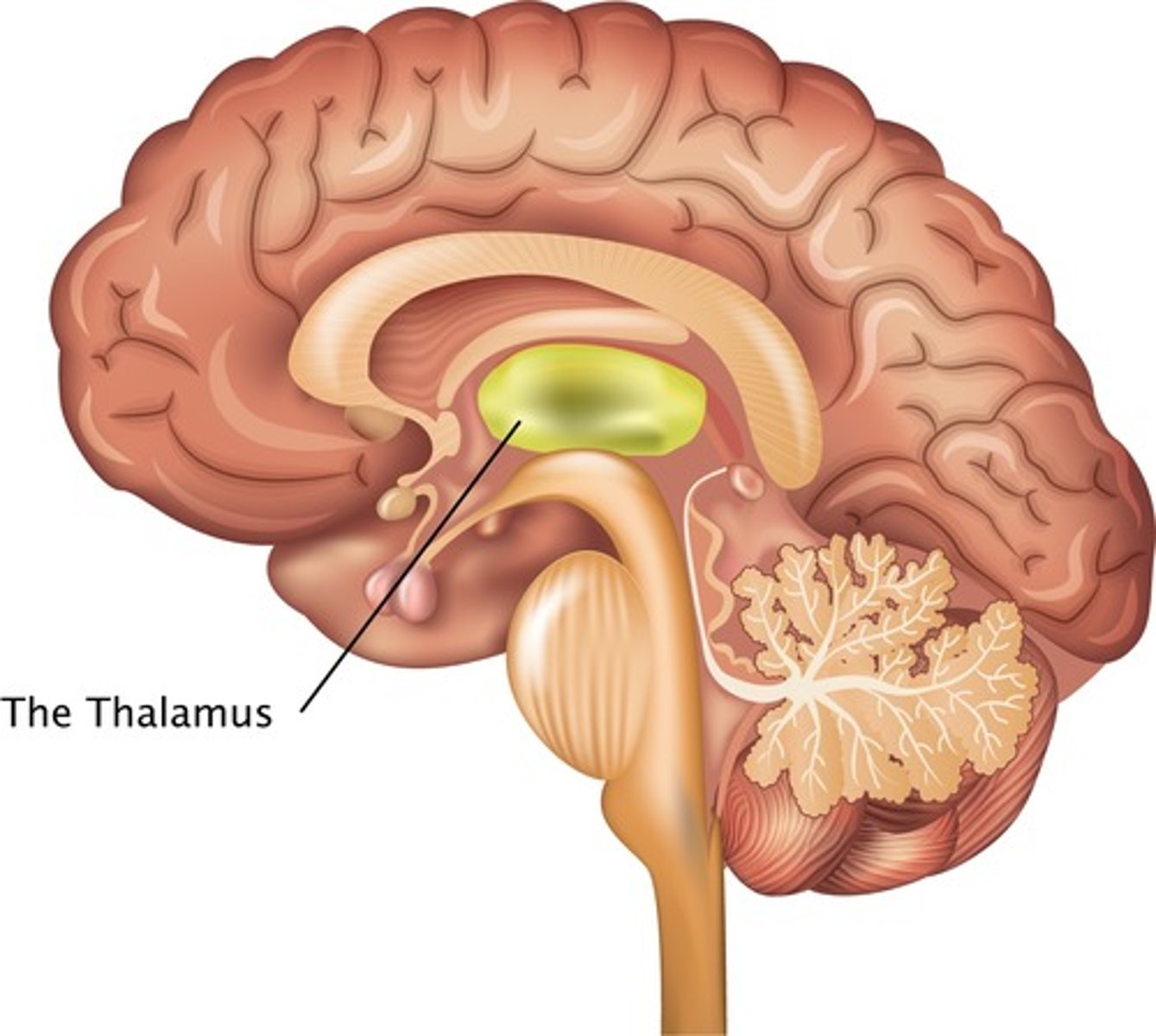
What is the thalamus?
sensory relay station (passes sensory signals to cerebrum)
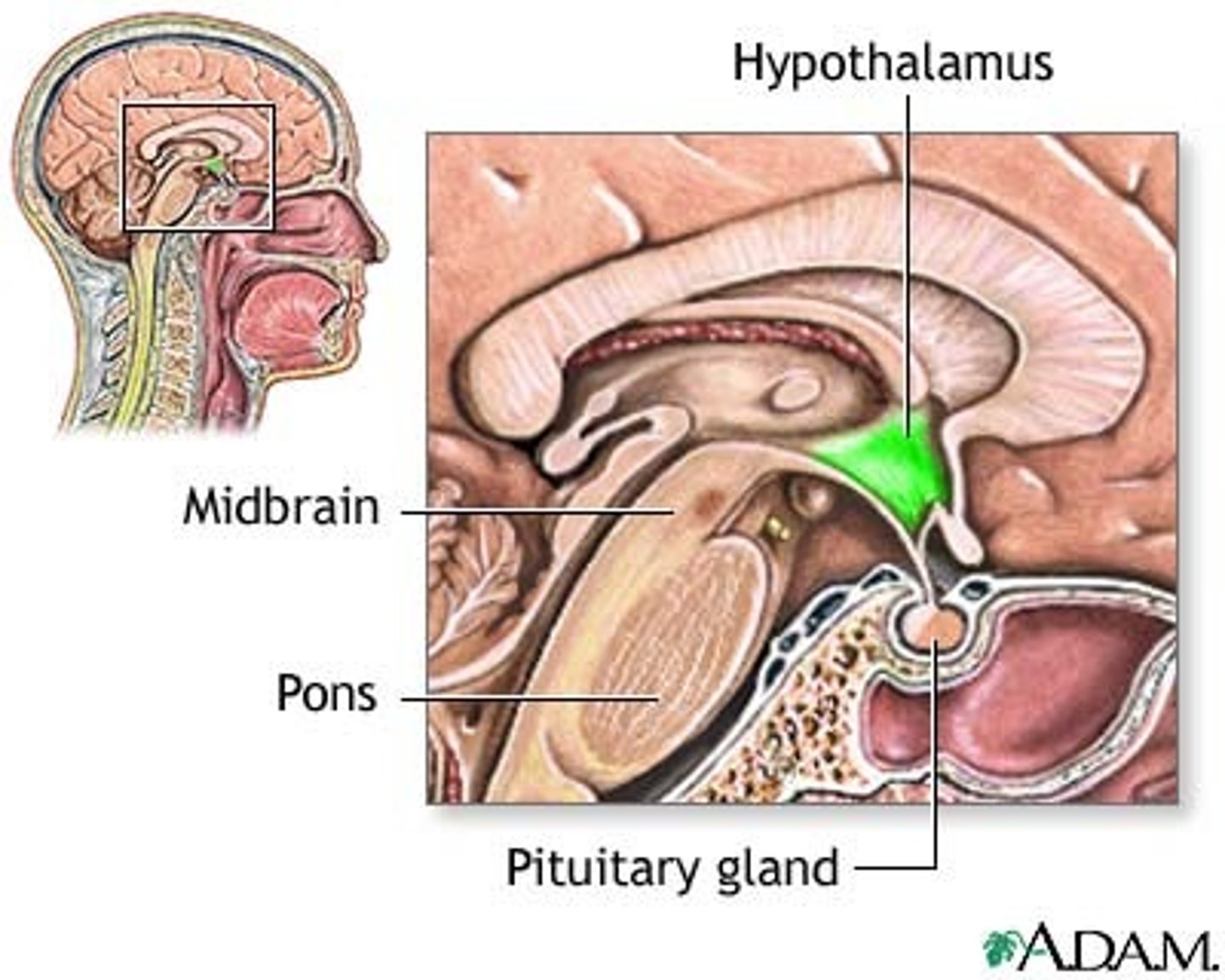
What is the hypothalamus?
controls autonomic nervous system (motor control), and controls endocrine system
what is the basal nuceli
collection of cell bodies, pass voluntary motor signals from cerebrum to other areas of brain and spinal cord
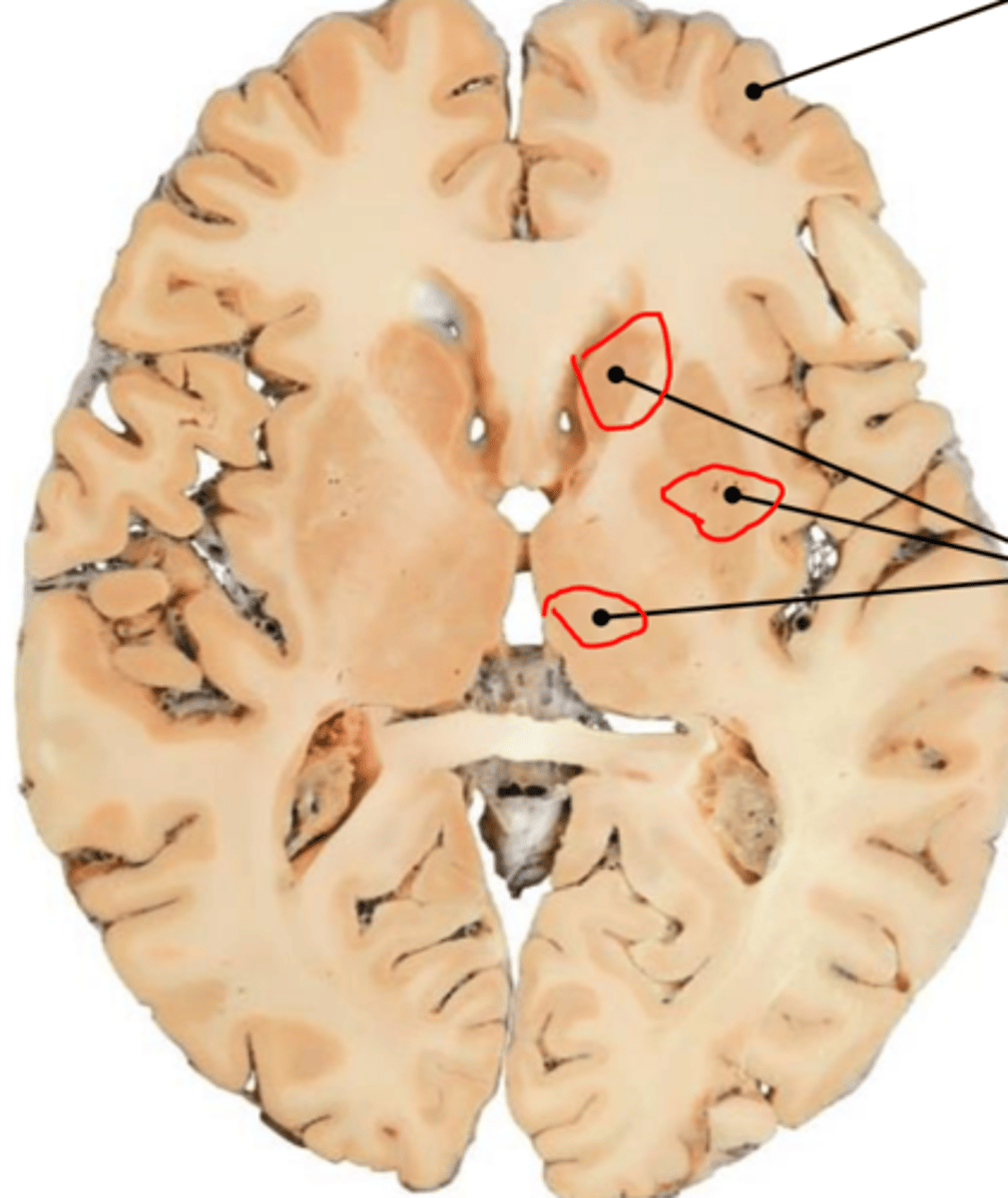
where does parkison disease effect in the brain
basal nuclei
what does the forebrain and hindbrain make up
the brain stem
what 3 structures make up the brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
what is the midbrain responsible for
visual and auditory reflexes, and eye movement
where is the midbrain located
at top of brain stem
what does midbrain connect to
cerebellum
What are the pons responsible for?
regulates breathing and assist in sleep and arousal
where are pons located
between midbrain and medulla oblongata
what is the pons connected to
cerebellum
What is the medulla oblongata responsible for?
regulate HR, BP, and breathing
Where is the medulla oblongata located?
lower part of brain stem
what is the medulla oblongata connected to
cerebellum
how are the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata connected to cerebellum
through peduncles
what are peduncles
bundle of nerve fibers that connect major regions of brain
what does the superior cerebellar peduncle connect
cerebellum to midbrain
what does the middle cerebellar peduncle connect
cerebellum to pons
what does the inferior cerebellar peduncle connect
cerebellum to medulla oblongata
what is the cerebral peduncle
connects cerebrum to brainstem
what is the cerebellum
The cerebellum is the part of the brain associated with voluntary responses (motor actions) (known as little brain)
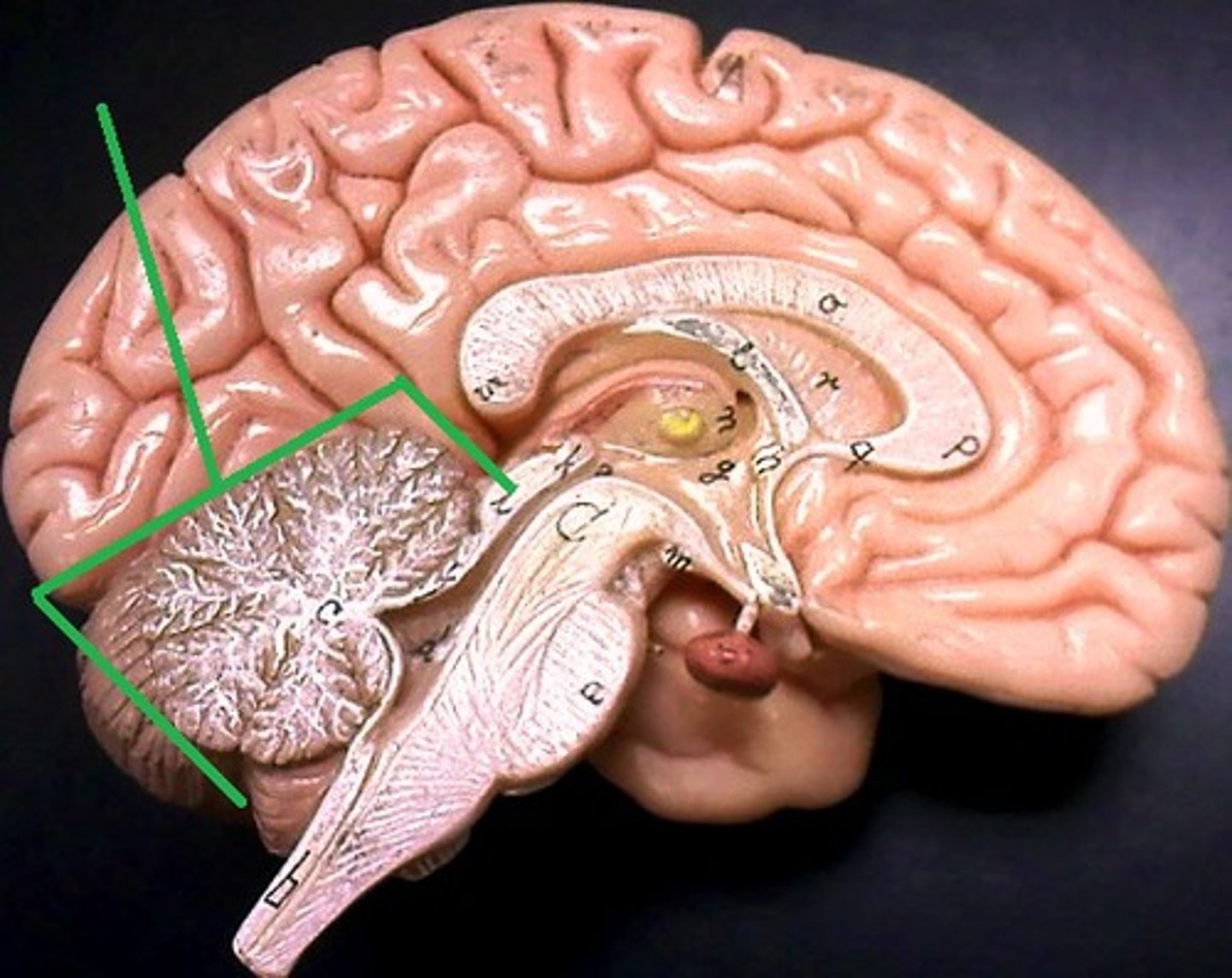
what separates the L and R hemispheres of the cerebellum
the vermis
What is the arbor vitae?
white matter of the cerebellum