Sci 10 Unit A Section 1
Physical Properties
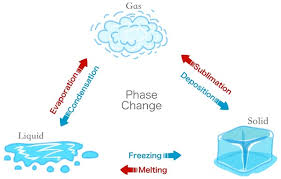
Boiling point or condensation point (evaporation)
Melting or freezing point
Malleability - ability to be beaten or rolled into sheets
Ductility - ability to be stretched
Color
State - solid, liquid, gas
Solubility - ability to dissolve
Crystal formation
Conductivity - ability to conduct heat or electricity
Magnetism
Chemical Properties
Ability to burn
Flash point - temperature needed to ignite a flame
reaction with water
behaviour in air
reaction with acids
reaction to heat
reaction to red and blue litmus
Change of state of matter
Atomic of Theory of Matter
John Dalton - “The billiard ball model”
- Atoms are tiny, indivisible particles of elements
- All elements are composed of atoms
- Atoms of the same element are identical
- Atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds

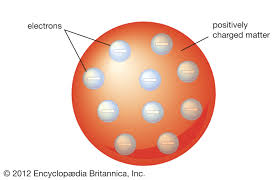
J.J Thompson - “plum pudding model”
Atom consists of one large positive charge and many negative charges inside of it
Experimented with the cathode ray tube
Ernest Rutherford - “planetary or planet model “
Every atom has a small dense positive core named the nucleus
Experimented with gold foil to prove there is a nucleus in a atom
Neils Bohr - electrons are arranged around the nucleus in specific orbits. Electron Shells (2,8,8,2).
Keywords
Physical Properties: describes the physical appearance and composition of a substance
Chemical Properties - describes the reactivity of a substance
Physical Change - change to a substance in which the composition of the substance stays the same. Ex: Ice cream and Ice
It is reversible (melting and freezing)
Chemical Change/Reactions - when two or more materials react and create new materials. Ex: burning wood, baking a cake
The change is irreversible
formation of a new substance with new physical and chemical properties
release or absorption of energy
change in colour
formation of odour
Pure substances - contain only one type of particle and they cannot be broken down into another substance
Element - made up of only type of atom.
Compounds - made of two or more elements
Mixtures - contain two or more pure substances
Homogeneous mixtures - appear to be made up of only one substance (they look the same throughout)
Mechanical Mixture or Heterogeneous mixture - separate components are visible
Suspension - components are in different states.
Colloid - particles of the suspended substances are so small that they cannot be easily separated out from the other substance. Ex: milk