Psych Brain&Behavior Chapters 2-5 Complete
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Trepanning (trephination)
a surgical intervention in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull (6500 b.c.)
Hippocrates's view of brain
Believed that the brain is the seat of intelligence (460bc-370bc). Key for sensation and perception, disrupted in epilepsy. First person to propose these theories
Rene Descartes
A firm believer that the mind and body exist as separate entities. Dualism
Dualism
The mind and body are two distinct substances and the brain is seen as the tool or medium
Descartes’ Reflex Arc
Proposed one of the earliest models of how the body responds automatically to stimuli without input from the brain
Franz Joseph Gall
(1758–1828) was a German doctor who started phrenology
Phrenology
The study of the conformation (build) of the skull as indicative of mental faculties and traits of character. A pseudoscience.
John Marthyn Harlow
(1819 -1907) American physican attended the surgery for phineas gage
Phineas Gage
a railroad worker whose frontal lobe was penetrated by an iron rod, survived, but he experienced severe personality changes, became very impatient, impulsive, easily disrupted
Pierre Paul Broca
(1824-1880) Physician, did postmortem brain studies of patients his area becomes known to be critical for producing speech, critical in the development of lateralization.
Carl Wernicke
(1849-1905) Physician, did postmortem brain studies of patients his area becomes known to be critical for language comprehension, critical in the development of lateralization.
Lateralization
The specialization of the two brain hemispheres for different functions.
Neuroscience
is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord,
and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders
Neuroscientists
study the function of the nervous system in focus of Molecular level, Cellular level, Functional level, Behavioral level, Evolutionary perspective, Computational, Clinical perspective, Highly interdisciplinary field!
Brain
Controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing,
temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body
Spinal cord
A collection of brain cells running from the base of the brain down the
center of the back
Spinal reflex
Automatic movement without brain input
Anatomical orientation
give clarity and precision when describing locations, pathways, and
relationships. Rostral, Caudal, Dorsal, Ventral, Lateral, Medial.
Neuraxis (neuraxis)
Denotes the direction in which the central nervous system lies, in humans it bends at the brainstem
Spatial Orientation
Refers to the 3D positioning of the brain in space, especially when describing planes and axes.
The frontal or coronal plane
a vertical plane in a medial to lateral direction. Dividing the brain into front and back pieces
The sagittal plane
a plane through the midline of the brain. Dividing the brain into right and left regions
The horizontal plane
plane falls along the horizon. Dividing the brain into top and bottom regions
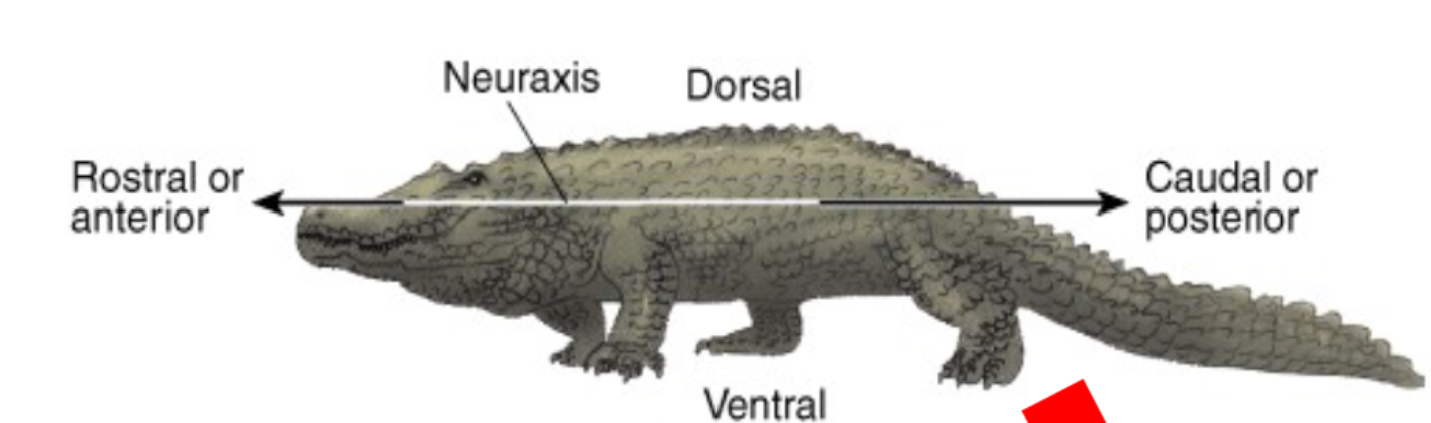
Dorsal
( from Latin dorsum 'back’): refers to the back Anatomical orientation
Ventral
(from Latin venter 'belly’): refers
to the front, or lower side, of an organism Anatomical orientation
Rostral
(from the Latin rostrum, meaning
"beak"): refer to the beak/nose Anatomical orientation
Caudal
(from the Latin cauda, meaning "tail"): refer to the back Anatomical orientation
Lateral
away from the midline Anatomical orientation
Medial
toward the midline Anatomical orientation
Meninges
series of three protective membranes that cover the CNS
Dura mater
Outermost meningeal layer, Thick, tough and fibrous, and Contains venous sinuses that drain blood from the brain
Arachnoid layer
Middle layer, thin, web-like membrane, Acts as a cushioning membrane, Subarachnoid Space, Between arachnoid mater and pia mater, Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Pia mater
Innermost meningeal layer, very thin and delicate, Adheres tightly to the brain’s gyri and sulci
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
a clear, colorless body fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and acts a shock absorber for the brain along with provides buoyancy, delivers nutrients and removes waste products of metabolism and
excess neurotransmitter
Gyri (singular: gyrus):
a distinctive pattern of folds or
bumps of the brain
Sulci (singular: sulcus):
grooves of the brain and form important landmarks that allow us
to separate different part of cerebrum into functional
centers
A lobe of the brain:
a major region of the cerebrum that
is distinguished by anatomical boundaries (sulci) and
specific functions
Frontal lobe
Responsible for high order cognitive
functions (reasoning, planning, decision making),
coordinating voluntary movement
Parietal lobe
Processes sensory information
Temporal lobe
involved in hearing, memory, and
language production and comprehension
Occipital lobe
Primarily responsible for vision
Forebrain
High-order cognition, perception, emotion, memory,
physiological regulation
Gray matter
Information processing, integration, and control, Composed of cell bodies and dendrites of the brain cells, Looks darker
White matter
Communication, information transferring, Composed of nerve fibers (neuronal axons) covered in fat
contents(myelin), Looks lighter
Corpus Callosum
A thick band of white matter that connects the two cerebral hemispheres, Provides a pathway for communication between hemispheres, 10 in (250 mm) in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections
Limbic System
A group of brain structures in the brain that are important for
emotional responses and learning and memory. Consists of Amygdala, Hippocampus, Hypothalamus, Thalamus
Hypothalamus
involved in emotions and drives, vital for
survival, Link between the nervous system and
endocrine system, homeostasis (part of limbic system)
Pituitary gland
Small endocrine gland which releases
hormones and regulates other endocrine
glands, Anterior vs posterior
Thalamus
Egg-shaped structure in the
middle of the brain, sensory relay center of the brain expect for smell
Amygdala
A small, almond-shaped structure inside of
your brain. Emotional learning, Fear learning, Anxiety, Reward processing, Sexual and aggressive behavior
Hippocampus
embedded deep into
temporal lobe, Learning and memory, Memory consolidation, Spatial memory
Basal Ganglia
collection of subcortical gray matter structures
(clusters of neuron cell bodies) responsible for Motor control, Motor learning & habits, Cognitive & emotional roles
Midbrain
Between the forebrain and the hindbrain responsible for sensory information relay and motor control
Hindbrain
Vital functions for survival (breathing, heartbeat), movement coordination. Lowest part of the brain, just above the spinal cord (connects directly with
the spinal cord)
Hindbrain: Pons
allows communication cortex, cerebellum,
and spinal cord and regulates breathing
Hindbrain: Medulla
controls vital autonomic functions (e.i. breathing, heart rate, digestion,
sneezing, and vomiting)
Hindbrain: Cerebellum
involves in balance, posture,
coordination, motor learning
Peripheral nervous system: somatic nervous system
Controlling conscious voluntary movements and relaying sensory
information from the body to the brain, made up of nerves that link the
brain and spinal cord to voluntary or skeletal muscles.
Somatic Nervous System: Cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that control sensation, movement, and autonomic functions of the head, neck,
and some internal organs
Somatic Nervous System : Spinal nerves
Pairs of peripheral nerves that emerge from the spinal cord, Connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Vertebrae
A bony spinal column made of small bones in which the spinal cord is inside
Bell-Magendie Law
Dorsal spinal cord (posterior, afferent) is sensory. Ventral spinal cord (anterior, efferent) is motor control
PNS: Autonomic Nervous system: Sympathetic
Responsible for fight or flight response
PNS: Autonomic Nervous system: Parasympathetic
Responsible for activities that occur when the body is at rest, promoting “rest and digest” activities, conserving energy and supporting routine bodily functions.
PNS: Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary functions of the body (e.i. heart rate, digestion, respiration, and gland activity → without conscious control)
What is the Brain responsible for
Controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing,
temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body
Spinal cord
Spinal cord
A collection of brain cells running from the base of the brain down the
center of the back,
Spinal Reflex
Example: knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal reflex
PNS: Enteric Nervous System
A network of neurons embedded in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract that controls bowel, the brain and ENS connect through the ANS, especially via the vagus nerve. ENS sometimes called the second brain because it uses some of the same chemical messagers as the brain.
Neurons
nerve cells that send messages all over your body to allow you to do everything from breathing to talking, eating, walking, and thinking
Glial cells
support/assist neurons ~85 billion, Different types of these exist
Camillo Golgi (1843 – 1926)
Golgi discovered a method of staining nervous
tissue which enabled to outline of the cells in the
nervous system compared to surrounding
tissues.
Reticular theory
Golgi proposed that the nervous
system was a continuous single network of cells
Santiago Cajal
Considered as a father of modern neuroscience, Came up with the concept called "the neuron doctrine“
the neuron doctrine
the nervous system is made up of discrete individual cells, Neurons are connected indirectly through small gaps (synapse)
Basic Structure of neuron
Soma, Dendrites, Axon and Axon terminals
Soma
Contains the material that the cell needs for the life processes of the cell - Contains nucleus
Dendrites
Branches extensions of a neuron cell body - Serves to receive incoming signals from the other neurons
Axon
carry electrical impulses ‘within’ neuron so that
eventually the signal is propagated to neighboring neurons
Axon terminal
the end of axon, The place where the axon contact with other neurons and pass the signal
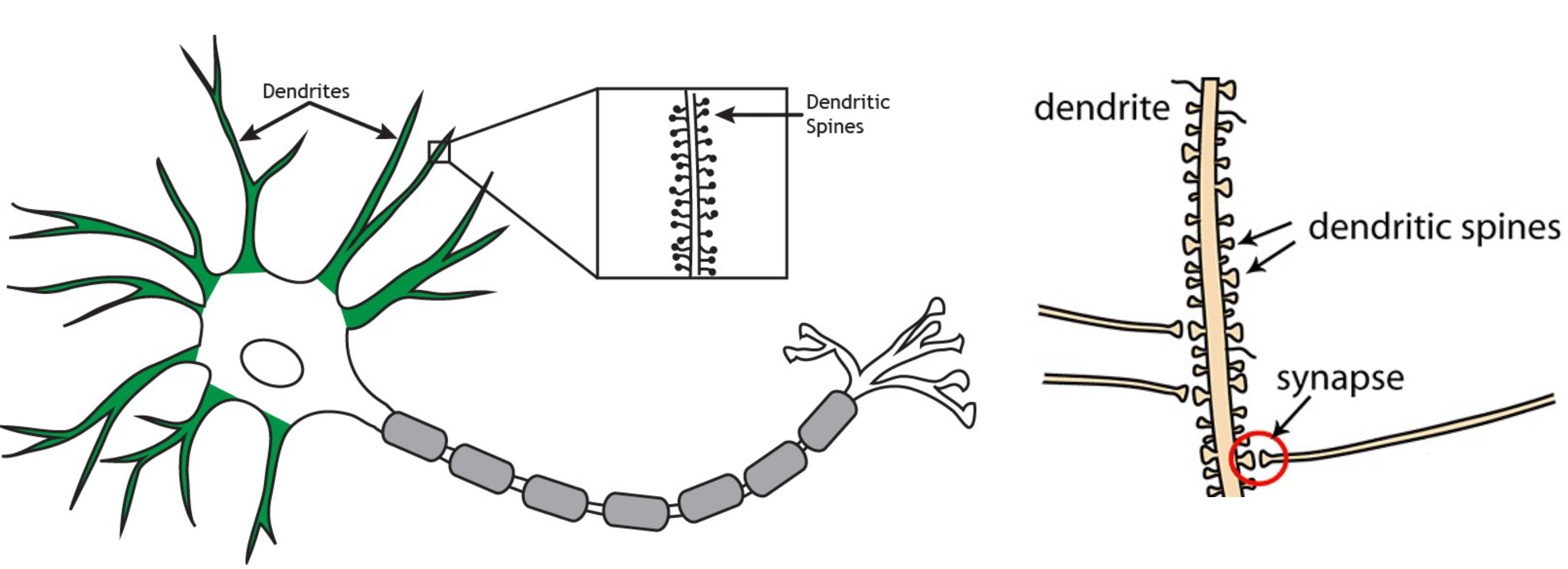
Dendritic spines
Protrusion from a dendrite that greatly increases its surface area and is the usual
point of contact with axons of other cells
Axon hillock
beginning of the axon
Axon collateral
branches projecting from the axon
Presynaptic cell
sends
signals to axon terminal
and propagate
Postsynaptic cell
receives signals from
axon terminal
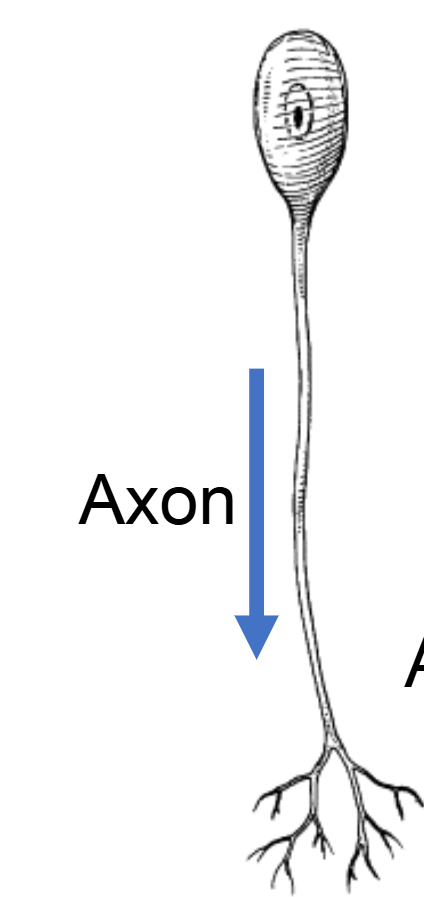
Unipolar Neurons
type of neurons that have (an)
axon(s) but no dendrites
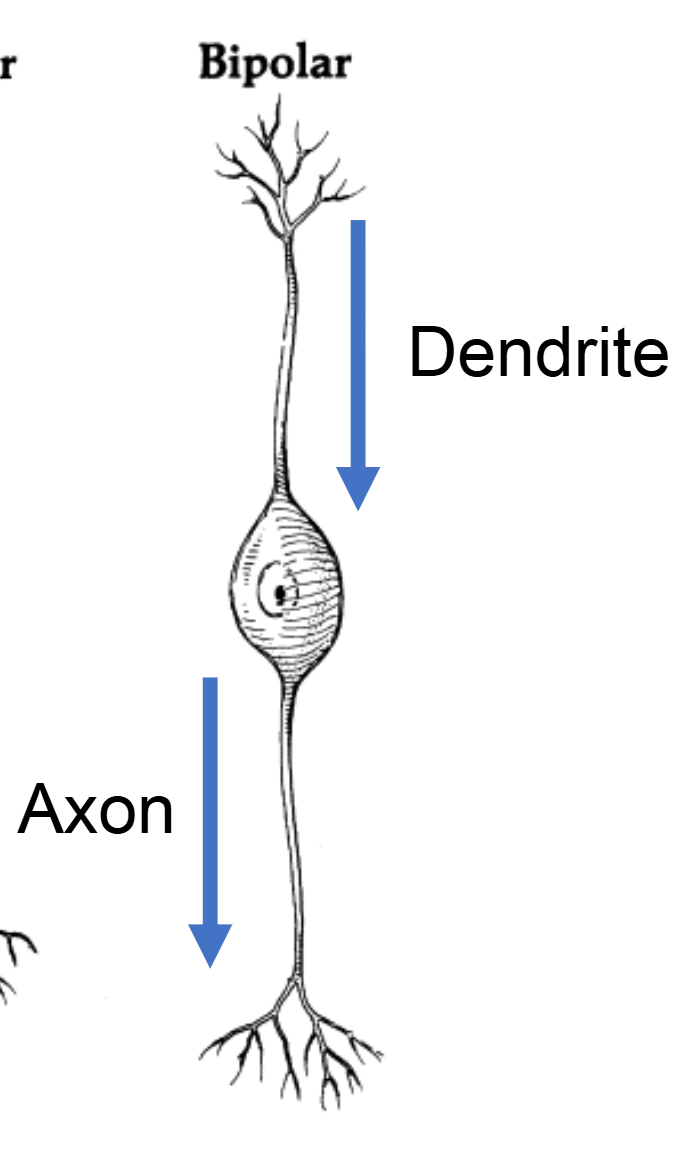
Bipolar Neurons
type of neurons that have one
axon and one dendrite
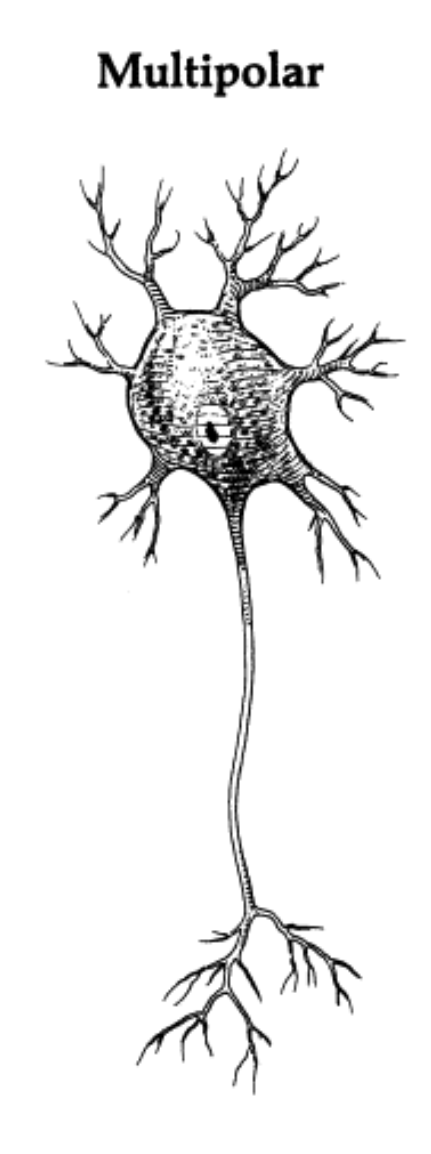
Multipolar Neuron
type of neurons that have 1
axon and many dendrite
Sensory Neuron
Types of neurons that receive sensory information (lights, sounds etc.), bipolar cells.
Motor Neurons
neurons that innervate and control the
muscles, their axon
projects to the outside of the CNS
Interneurons
neurons that connect between brain regions or between neurons, lie between sensory and spinal motor neurons
Cell membranes
serve as barriers and gatekeepers, Separates intracellular and extracellular fluid, Regulates movement of substances into and out of
the cell (most cannot pass), made up of phospholipids.
Soma
Body of neuron, contains nucleus, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum
Cytosol
the liquids found inside cells
Cytoplasm
all materials within a cell membrane
(e.g., organelles, excluding the nucleus)
Nucleus
Cells office containing chromosomes with DNA, goes through gene expression and protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis
Assembly of protein molecules , occurs in the cytoplasm
Transcription
Step in protein synthesis. Because DNA never leave the nucleus to produce the protein in
the cytoplasm..we need someone to copy the genetic
information on the DNA and bring it out!
Translation
Step in protein synthesis. The process of using information
copied into the RNA sequence (mRNA) to
synthesize a protein
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Is made of two linked strands that wind around each other
a twisted ladder-a double helix
Each strand has a backbone =alternating sugar (deoxyribose)
and phosphate groups
Four bases are attached, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) or thymine (T)