functional groups
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
which functional groups increase the lipophilicity of drugs?
nonpolar
alkyl groups
phenyl
halogen
ester
hydroxyl groups are …
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
a) strong polar
aliphatic amines are …
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
a) strong polar
tertiary amines have what type of interactions?
dipole-dipole
quaternary amines use what type of interaction?
ionic
charged molecule
carboxylic acid groups are …
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
cyano groups are …
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
nitro groups are ..
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
amide groups are
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
imide groups are
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
sulfonamide groups are
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
ether groups are
a) strong polar
b) weak polar
c) non polar
b) weak polar
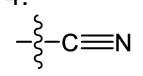
what is this functional group?
cyano/nitrile
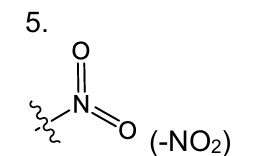
what is this functional group
nitro
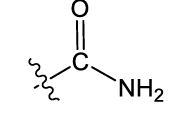
what is this functional group?
amide
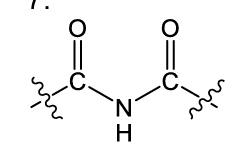
what is this functional group?
imide
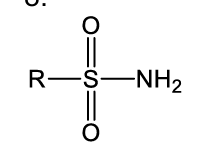
what is this functional group?
sulfonamide
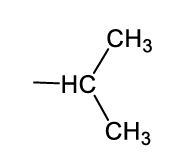
what functional group is this?
iso-propyl
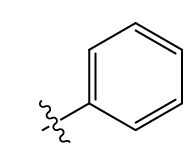
what functional group is this?
phenyl
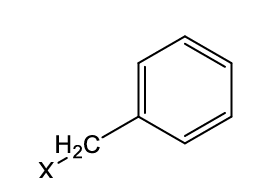
what functional group is this?
benzyl
polar functional groups have good (dissolution/absorption) but poor (dissolution/absorption)
good dissolution
poor absorption through the membrane
highly lipophilic functional groups have good (dissolution/absorption) but poor (dissolution/absorption)
good absorption through membranes
poor dissolution
what are the 4 functional groups that are considered as acidic functional groups (able to ionize in body fluids) ?
carboxylic group
imides
sulfonamides
phenolic
T/F: lower pKa values indicate stronger acidic functional groups
true
what is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pKa = pH + log (proton carrying form/ proton missing form)
what is the pKa range for COOH?
3-5
what is the pKa range for sulfonamide, imide, and phenolic groups?
7-9
what type of amines are very strong polar groups?
primary + secondary
if the drug name is as a salt with sodium or potassium or calcium or lithium, the drug is acidic or basic?
acidic
if the drug name is as a salt with hydrochloride or sulfate or nitrate, the drug is acidic or basic?
basic
if phenobarbital sodium has a pKa of 7.7, at pH 6, it is expected to be
a) 99-100% ionized
b) 90-100% non-ionized
c) 50-90% ionized
d) 10-50% ionized
e) 10-50% non-ionized
b) 90-100% non-ionized
sodium = acidic
non-ionized
10/1 → 10/11 × 100% = 90% unionized
100/1 → 100/101 × 100% = 99.99% unionized
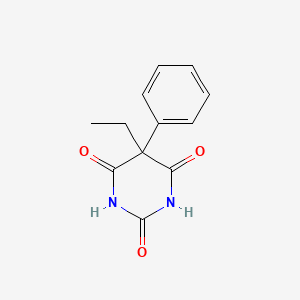
phenobarbital has a pKa of 7. In a pH of 3, is it primarily ionized or unionized?
phenobarbital = acidic because of imide
primarily unionized
what are bases?
donates electrons or accepts protons
lower pKb indicates stronger or weaker base?
stronger
what are the basic functional groups?
aliphatic amines (primary, secondary, tertiary)
pyridine nitrogen
anilino nitrogen
aliphatic amines are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
e) strongly basic
pyridine type nitrogens are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
d) weakly basic
anilino type nitrogens are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
d) weakly basic
what is the pKb range of weakly basic functional groups?
7-9
what is the pKb range of strongly basic functional groups?
3-5
cyano (nitrile) type nitrogens are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
c) neutral
amides are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
c) neutral
pyrroles are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
c) neutral
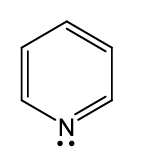
what is the name of this functional group ?
pyridine
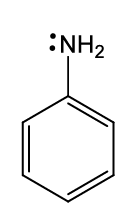
what is the name of this functional group?
aniline
quaternary ammonium nitrogens are are:
a) strongly acidic
b) weakly acidic
c) neutral
d) weakly basic
e) strongly basic
c) neutral
SATA: which of the following nitrogen groups are acidic functional groups?
a) sulfonamides
b) amides
c) imides
d) pyridines
e) pyrroles
a) sulfonamides
c) imides
what equation determines aromaticity?
Huckle’s equation
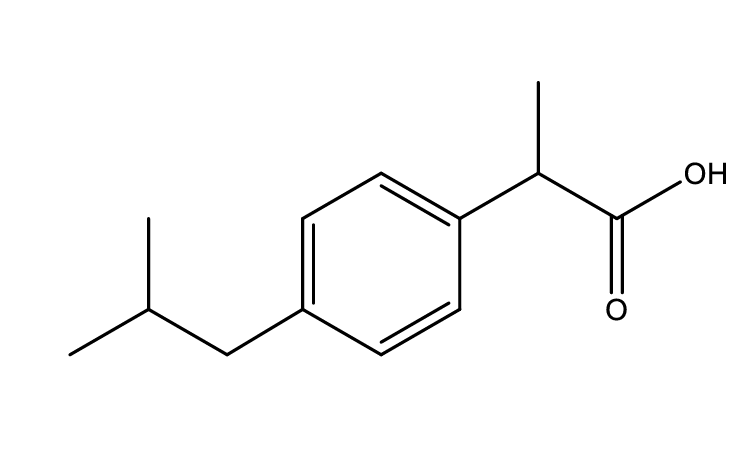
Is this structure acidic, basic, or neutral?
acidic
COOH = strongly acidic
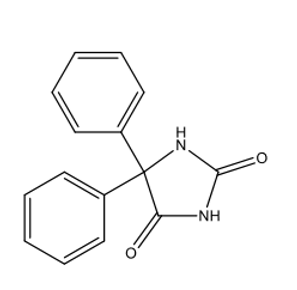
Is this structure acidic, basic, or neutral?
acidic
imide = acidic
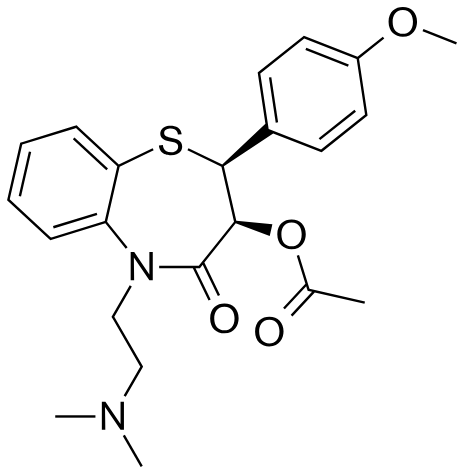
If diltiazem, has a pka value of 7.7, how much of the drug will be available for absorption from the duodenum (pH 6.0)?
a. 0-10%
b. 10-50%
c. 50-90%
e. 99-100%
a. 0-10%
SATA: which of the following are basic nitrogen functional groups?
a) pyridine
b) pyrrole
c) nitrile
d) anilino
e) all of the above
a) pyridine
d) anilino
An aniline has a PKA of 3 and you are in a solution with a pH of 4.6, What percent of the substance will be unionized?
a. 50-90%
b. 99-99.9%
c. 90-99%
d. 50%
c. 90-99%
If the salt form of Phenobarbital is Phenobarbital Sodium, that would mean that Phenobarbital carries a ...
a. positive charge
b. negative charge
c. Neutral charge
b. negative charge
Identify the correct pairs:
i. Amide – Neutral Nitrogen
ii. Carboxylic Acids – polar and non-ionizable
iii. Nitrile – Neutral Nitrogen
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. i only
d. iii only
e. i, ii and iii
b. i and iii
If ibuprofen has a pka of 4.5, how much of it will be dissociated in a pH of 2.5?
a. 99%
b. 99.9%
c. 0.1%
d. 1%
d. 1%
how much do very polar groups increase solubility?
5-6 carbons
how much do weakly polar groups increase solubility?
2-3 carbons
SATA: amides are ..
a) acidic
b) neutral
c) basic
d) very polar
e) weakly polar
f) nonpolar
b) neutral
e) weakly polar
which order of halogens is correct?
a) F>Cl>Br>I
b) Cl>Br>I>F
c) I>Br>Cl>F
d) Br>I>F>Cl
c) I>Br>Cl>F
SATA: sulfonamides are ..
a) acidic
b) neutral
c) basic
d) very polar
e) weakly polar
f) nonpolar
a) acidic
e) weakly polar
SATA: carboxylic acids are ..
a) acidic
b) neutral
c) basic
d) very polar
e) weakly polar
f) nonpolar
a) acidic
e) weakly polar
which type of aliphatic amines are both very polar and basic?
primary and secondary
tertiary = only basic
SATA: cyano (nitriles) are ..
a) acidic
b) neutral
c) basic
d) very polar
e) weakly polar
f) nonpolar
b) neutral
e) weakly polar
why are pyridine nitrogens weaker bases than aliphatic amines?
a) sp2 hybridization
b) sp3 hybridization
c) resonance
d) huckle’s rule
a) sp2 hybridization
larger s orbitals → harder to donate electron as freely
SATA: why are anilino type nitrogens weaker bases than aliphatic amines?
a) sp2 hybridization
b) sp3 hybridization
c) resonance
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
b) sp3 hybridization
c) resonance
why are cyanos neutral?
a) sp hybridization
b) sp2 hybridization
c) resonance
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
a) sp hybridization
50% s
why are amides neutral?
a) adjacent carbonyl group
b) sp2 hybridization
c) resonance
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
a) adjacent carbonyl group
electron withdrawing group
why are pyrrole-like nitrogens neutral?
a) adjacent carbonyl group
b) sp2 hybridization
c) resonance
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
c) resonance
Huckle’s rule for aromaticity
why are quaternary ammonium nitrogens neutral?
a) adjacent carbonyl group
b) sp2 hybridization
c) resonance
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
d) nitrogen has no lone electrons
no lone pair
is morphine sulfate acidic or basic?
basic
list the functional groups in this molecule
ether
ester
tertiary amine
amide
ketone
thioether
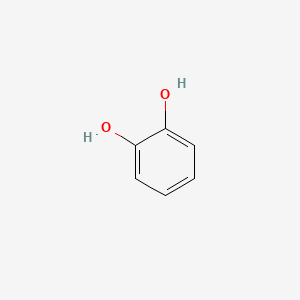
what functional group is this?
catechol
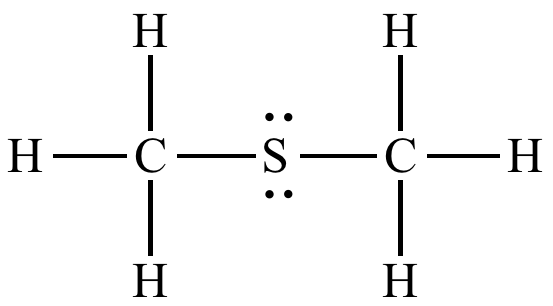
what is this functional group
thioether
An example of a weakly polar group is...
a) Primary Aliphatic Amine
b) Sulfonamide
c) Phenyl
d) Hydroxyl
b) Sulfonamide
T/F: If a drug's pKa is 7.7 and is placed into a solution with a pH of 7.7, the drug will be 50% ionized and 50% unionized.
true
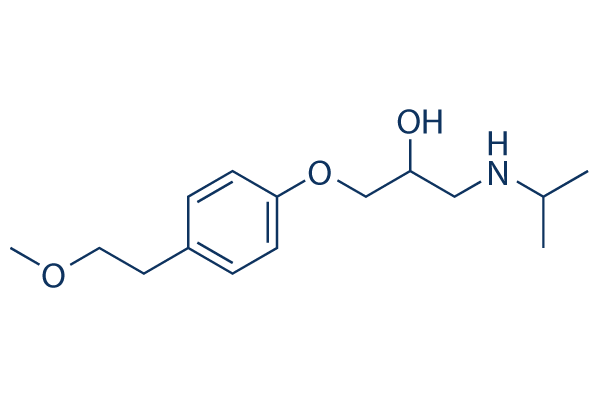
Which of the following functional groups are present in Metoprolol?
a) Ether
b) Tertiary Amine
c) Phenol
d) Ester
a) Ether
Which of the following functional groups with nitrogen is basic (capable
of accepting protons)?
a) Pyrrole
b) Pyridine
c) Imide
d) Amide
b) Pyridine
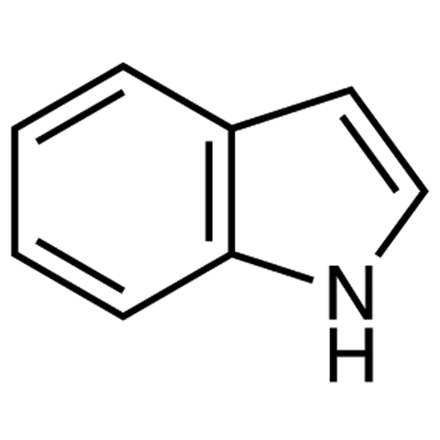
Select the correct pairing of “Common Name/Fused Heterocyclic Rings”
a) Indole/Benzene & Pyrrole
b) Indole/Benzene & 2-Pyrroline
c) Quinoline/Benzene & Pyrrole
d) Oxepine/Pyridine & Imidazole
a) Indole/Benzene & Pyrrole