Market failure & government intervention 1.3&1.4
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Market failure
when the market fails to allocate scarce resources effectively
causing a loss in social welfare loss
Externalities
the cost or benefit a third party receives from an economic transaction outside of the market mechanism
cigarettes
education
Under provision of public goods
public goods are non rivalry and non excludable
meaning they are underprovided by the private sector due to the freerider problem
street lights
Information gaps
when a buyer or seller doesnt have the full information they need to make a fully informed decision
private costs/benefits
the cost/benefits to the individual participating in the economic activity
private benefits= demand
private costs= supply
social costs/benefits
the costs/benefits of the activity to society as a whole
external costs/ benefit
costs/benefits to a third party not involved in the economic activity
what is a merit good
A good with external benefits
underprovided in he free market
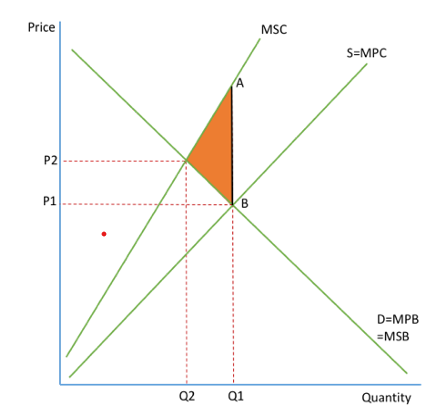
Negative production externalities
occurs when social costs are greater then private costs
market left to operate freely will ignore the external costs involved in producing a good
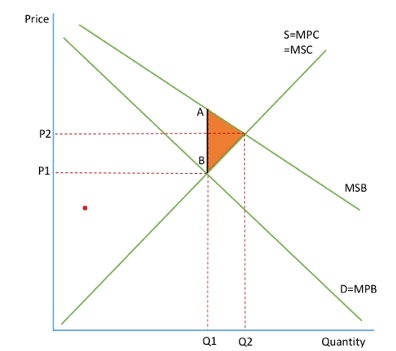
Positive consumption externalities
social benefits are greater then social costs
market is left to its own devices, will produce where MPB=MPC
wont consider the benefits to society so will produce Q1P2
misallocation of resources so there is an under production
healthcare and education
Many externalities are involved with information gaps as people are aware of full implications of their decisions
Government intervention
Governments can intervene to ensure the market considers the external costs and benefits
indirect taxes and subsidies
tradeable pollution permits
provision of the good
provision of information
regualation
Public goods
missing from the free market but offer benefits to society
non rivalry
non excludable
free rider problem
you cannot charge an individual a price for the provision of a non excludable good
a free rider is someone who receives the benefits without paying for it
Private sector producers will not provide public goods to people because they cannot be sure of making a profit
the market would fail and so they are provided by the government and financed through taxation
Symmetrical information
occurs when buyers and sellers have potential ccess to the same information
perfect information
Asymmetric information
when one party has superior knowledge compare to another
usually the seller has more information than the buyer and this means they can take advantage of the other party’s lack of knowledge
what information gaps lead to
market failure
there is a misallocation of resources because people do not buy things that maximise their welfare
consumer demand for a good or producer supply of a good may be too high or too low
economic agents are unable to make rational decisions
eg drugs
government use of indirect taxation
to prevent market failure
fall in supply and increase the costs to individuals
advantages of indirect tax
It internalises the externality- market now produces at the social equilibrium position and social welfare is maximised
raises government revenue- could be used to solve the externality in other ways eg education, may help goods become more elastic
disadvantages of indirect tax
difficult to know the size of the extenality so difficult to target the tax- depends on where the tax is set- government suffers from imperfect information where setting the tax
conflict between gov goal of raising revenue and solving the externality
creation of black market
government use of subsidies
in order to fix information gaps
shift supply curve right- lower cost of production
social welfare is maximised
advantages of subsidies
society reaches the social optimum output and welfare is maximised
encourage small businesses, bring abt equality
disadvantages of subsidies
high opportunity costs
difficult to target
producers can become inefficient
subsidies are difficult to remove
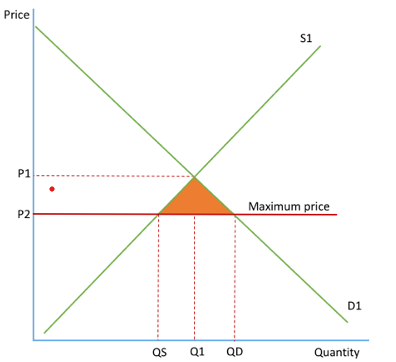
Maximum prices
must be set below current price equilibrium
a legally imposed price for a good that the suppliers cannot charge above
set on good with positive externalities
prevent monopolies from exploiting customers
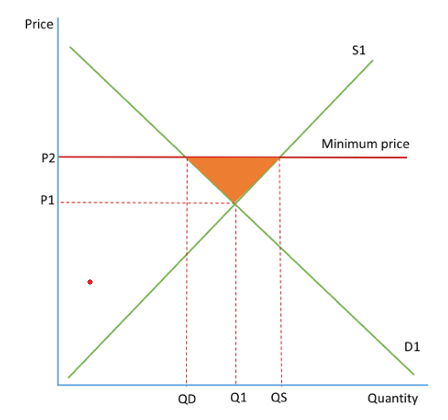
Minimum prices
must be set above current price equilibrium
a legally imposed price at which the price of the good cannot go below
set on goods with negative externalities, the price is raised to the social optimum point and consumption is discouraged
encourage producers to produce goods so can be set on goods with social benefits that are underprovided by the market
advantages of minimum and maximum prices
they can be set where MSB=MSC so allow for soe consideration of externalities and so help to increase social welfare
maximum price- will ensure that goods are affordable
minimum price will ensure that poducers get a fair price
both reduce poverty and increase quality
disadvantages of minimum and maximum prices
is a distortion of price signals and this causes excess supply/demand
excess demand will lead to questions about how to allocate goods and excess supply will lead to questions about what to do with the surplus goods
difficult for the government to know where to set the price
can lead to the creation of the black market
tradable pollution permits
allows the owner to pollute up to a specific amount of pollution and the gov controls how many permits there are so limits the maximum amount of pollution
companies have to buy permits in order to pollute- companies may use greener technology
incentive to cut emissions so maximise profits
advantages of tradeable permits
guaranteed that pollution will fall- maximise social welfare
government raise revenue
encourage efficiency
Disadvantages of tradeable pollution permits
can be expensive to monitor and police
will raise costs for business- higher costs will be past onto consumers
difficult to know how many permits the government should allow
advantages of public goods
corrects market failure by providing important goods with otherwise would not be provided
helps bring abt equality- ensuring everyone has access to basic goods
benefits for the goods them self
disadvantages of public goods
expensive and represents a high opportunity cost for the government
the government may produce combination of goods as consumers can not indicate their prefernece
government may be inefficient as they have no incentive to cut costs
government officials may suffer from corruption and conflicting objectives
eg NHS suffer from severe underfunding
Provision of information
government provides information to allow people to make informed decision
advantages of provision of information
helps consumers act rationally
can make demand more elastic in the long run and so help indirect taxes to become more effective at reducing output
disadvantages of provision of information
can be expensive for the government to do, incurring an opportunity cost
consumers may not listen to the information provided due to irrational behaviour
regulation
governments are able to to impose laws and caps to ensure that levels are set where MSB=MSC or to ensure that companies provide full information on products
ensures firms follow regulation and do not exploit their costumers or take advantage of market position
advantages of regulation
can ensure consideration of externalities, prevent exploitation of consumers and keep consumers fully informed
help to overcome market failure and maximise social welfare
disadvantages of regulation
laws may be expensive for government to monitor- incurring to opportunity cost
dont take into account the different costs of following the laws for different companies
firms may pass on costs to consumers in the form of higher prices
government failure
is when government intervention in the market leads to net welfare loss and a misallocation of resources
the total social costs arising from the intervention are greater than the social benefit
distortion of price signals
some types of gov intervention change price signals in the market and distort the free market mechanism
as a result they keep some companies n business when they are inefficient so the resources should be switched to somewhere else or make consumers pay too much for a good (taxes)
by intervening the gov distorts the mechanism and so resources may be allocated inefficiently
unintended consequences
cause effects which the government did not intend to happen
consumers and producers may react to new policies in unexpected ways and so the policy doesnt have the effect it should
eg the buffer stock scheme in the EU- lead to overproduction and fall in agricultural prices
excessive administration costs
a lot of money that is allocated by the government is actually used up on basic administration costs
the social costs may be higher than social benefits once administration costs are taken into account
governments causing information gaps
it is impractical and impossible for the government to get every piece of information they need