GENETICS EXAM #3: Cancer Genetics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is cancer?
A collection of disorders that share a common feature of uncontrolled cell growth
- In order for cells to become cancerous, they must become resistent to signals that normally inhibit cell growth
Neoplasm/tumor
mass of cells due to uncontrolled cell growth
Tumorigenesis
formation of tumors
Angiogenesis
formation of new blood vessels
Malignant
tumor invades nearby tissues
Metastasis
tumor spread to distant body sites
Benign
tumor does not invade tissue or metastasize
Steps of carcinogenesis (3)
initiation, promotion, progression
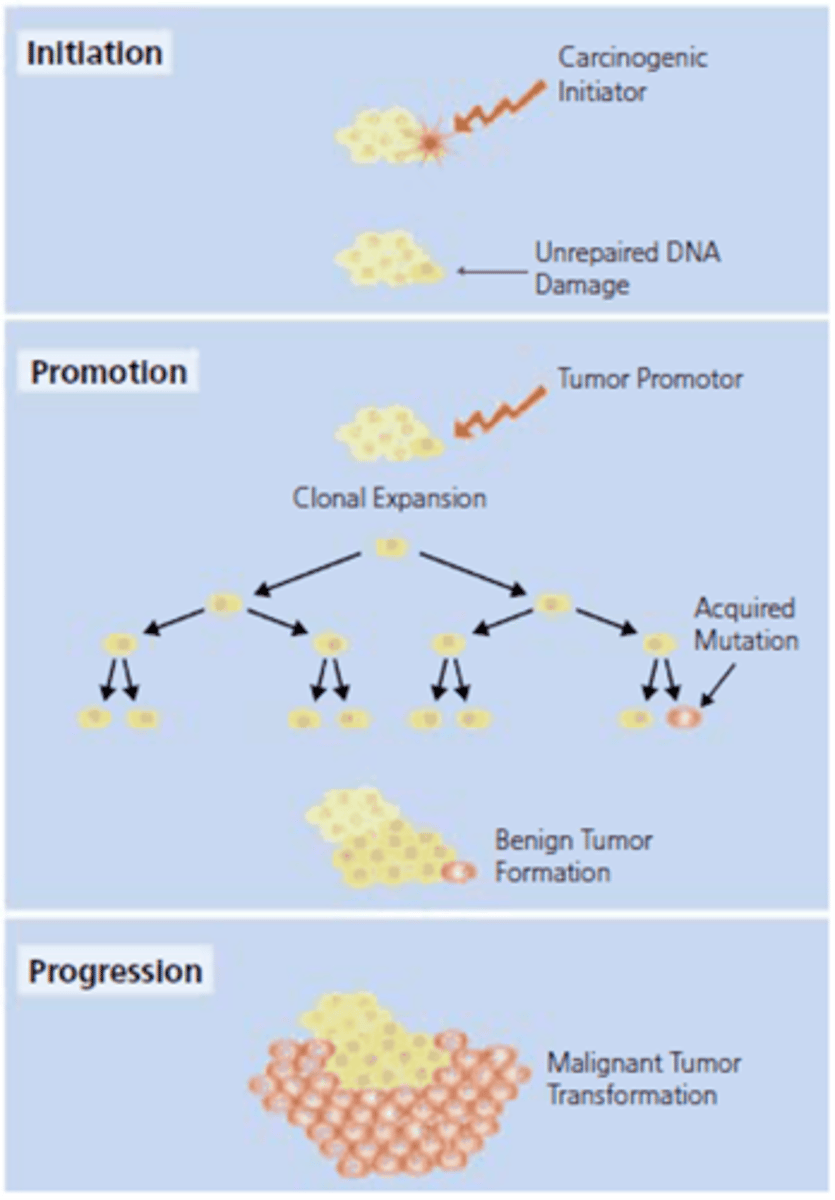
Describe some aspects of carcinogenesis
1. Cells become resistant to signals that normally inhibit growth
2. Cells disable apoptosis
3. A new blood supply is obtained through angiogenesis to nourish the tumor
4. Cancer cells override other inhibitory signals to become
malignant
5. Once malignant, the tumor may metastasize to distant body sites
True or False: A visible tumor will form quickly after the onset of carcinogenesis
False; it may take many years
Carcinoma
cancer of epithelial tissue
Sarcoma
cancer of connective tissue
Lymphoma
cancer of the lymphatic tissue
Glioma
cancer of glial cells of the CNS
Leukemia
cancer of hematopoietic organs
True or False: All cancer is genetic
True; but mutation rates and effects can be modified by environmental factors
Genetically similar populations with different environmental exposures have ____________________ (different, similar) cancer risk
different
Growth Factors
transmit signals from cell to cell
Growth Factor Receptors
on the surface of the cell; bind to GFs
Signal Transduction Molecules
activate a chain of phosphorylation reaction in the cell, targeting and altering activity of different proteins within the cell to communicate with the cell nucleus
Nuclear Transcription Factors
in the nucleus; regulate DNA transcription by interpreting signals to grow, stop growing, and differentiate
Knudson's two hit hypothesis
Both copies have to be defective in same cell to allow tumor to develop
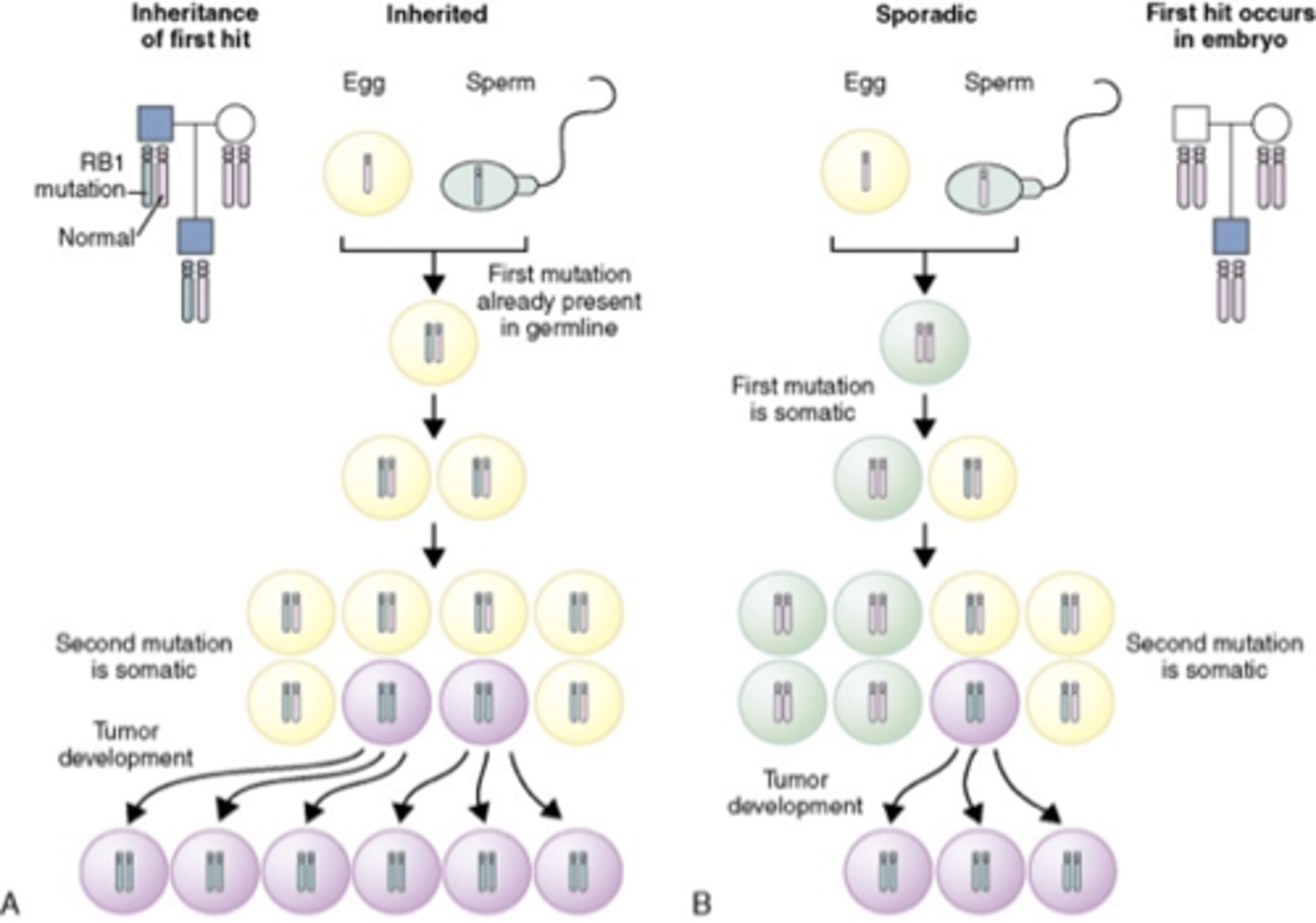
Three classes of cancer genes
- Tumor suppressor genes: inhibit cell growth
- Oncogenes: activate cell growth
- DNA repair genes
Describe tumor suppressor genes
- Control cell division to prevent tumors
- Incomplete penetrance (heterozygous cells do NOT form tumors; require a second hit)
- Mutations in these genes typically lead to loss of function
- Normally block uncontrolled cell growth by participating in pathways that regulate the cell cycle, regulating transcription, or regulating cell-cell interactions
Describe oncogenes
- Originate from proto-oncogenes, which are involved in regulators of normal cell growth
- Mutations lead to an excessively active product that leads to unregulated cell growth and differentiation
- Only a single copy of a mutated gene is required to contribute to the process of tumor progression
- Mutations result in a gain of function of the gene
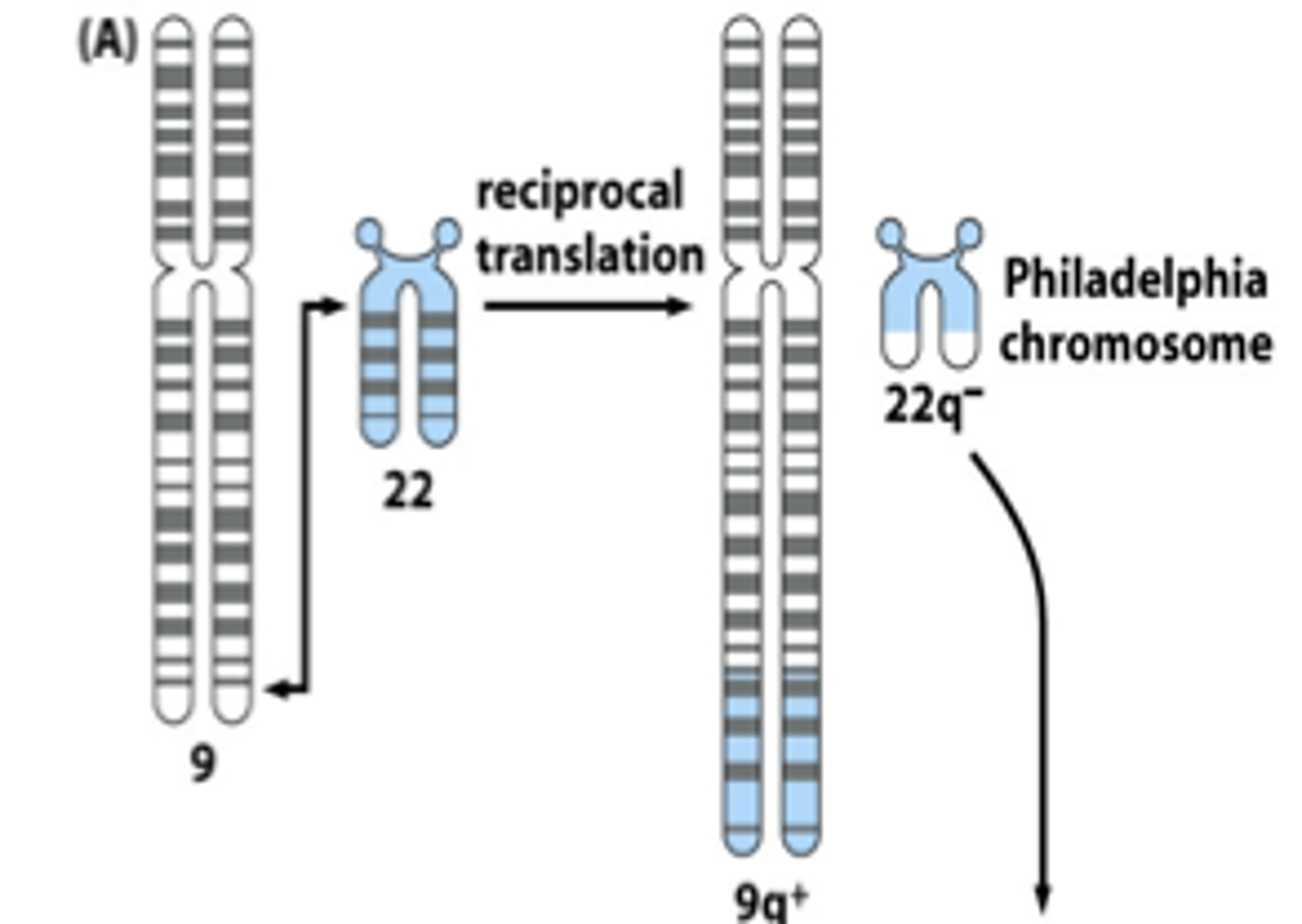
Oncogenes are often activated by...
chromosomal translocation (ex: CML)
Impact of amplification
- Greatly increases level of gene expression
- Influences response to cancer treatment
- Requires higher doses of standard agents or use of an agent specific for the amplified gene's product
- Clinical testing for amplification used to plan therapy
Which tumor is more likely to harbor a germline mutation?
a. Tumor suppressor genes
b. Oncogenes
A
Types of genetic instability in tumor cells
- multiple mutations
- hypermethylation
- hypomethylation
- chromosome breaks
- anueploidy
Instability can be due to defects in _________________ required for _____________________________________.
proteins; accurate cell division or DNA repair
Driver mutations
Mutation in a gene that directly impacts cell growth (through increasing or inhibiting cell signaling) or DNA repair processes
- Initiate the process of carcinogenesis, and can be effective therapeutic targets.
Passenger mutatuions
Additional mutations that occur as a result of a driver mutation, allowing for further progression of a tumor
With each cell division, telomeres _____________________ (shorten, lengthen).
shorten
Tumor cells overcome telomere shortening by activating _____________________, which replaces telomeric segments lost during division and allows _________________ cell division.
telomerase; uninhibited
What percentage of cancers are hereditary?
5-10%
Cancer risk based on FH
- High Risk: hereditary cancer (50% or greater)
- Moderate Risk: familial cancer (multiple relatives with BC at varying ages; not due to a single gene)
- Low Risk: sporadic cancer (one or two relatives with cancer, later ages, different cancers)
True or False: FH is always reliable
False; it's often unreliable
Attributes of sporadic cancer
- Later age of onset (70s or 80s)
- Little or no FH
- Single or unilateral tumors
Attributes of inherited cancer
- Early age of onset (<50)
- Multiple generations with cancer
- Clustering of certain cancers (breast, ovarian)
Inherited cancer genes are usually passed down in an ____________________________ pattern but demonstrates ____________________________________.
autosomal dominant; incomplete penetrance
Individuals inherit ____________________________________, not cancer.
altered cancer susceptibility gene
What is Lynch syndrome?
- Most common cause of inherited colon cancer
- Tumors in proximal (right) colon predominate
- Extracolonic cancers: endometrium, ovary, stomach, urinary tract, small bowel, bile ducts, sebaceous skin tumors
Some criteria for Lynch syndrome
- Colon or endometrial cancer dx <50
- Colon or endometrial cancer dx > 50 if patient has a first degree relative with colon or endometrial cancer at any age
- Patient with more than one primary Lynch syndrome associated cancer
Mutations in __________________________ genes are a feature of Lynch syndrome.
DNA mismatch repair (MMR)
Aside from genetic testing, what are some screening tests for Lynch syndrome?
- Microsatellite instability (MSI)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Management of Lynch syndrome
Colon
- Earlier colonoscopies
- Total abdominal colectomy for colon cancer or multiple adenomes/unresectable polyps
Uterus
- Annual TVU and endometrial aspirate
- Consider TAH/BSO
If someone has Lynch syndrome, what is the chance their brother is also carrying the gene?
50% (b/c it's autosomal dominant)
Testing minors for adult-onset cancer predisposition is generally ________________________________ (recommended, not recommended).
not recommended
Constitutional Mismatch Repair Deficiency Syndrome
- Autosomal recessive
- Individuals with mutations in both alleles of the same MMR gene that causes Lynch syndrome
- Childhood presentation of cancers (hematologic, brain tumors, colon, small bowel, gastric, urologic)
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Estimated penetrance for adenomas >90%
- Risk of extracolonic tumors (upper GI, desmoid, osteoma, thyroid, brain, other)
- Untreated polyposis leads to 100% risk of cancer
MUTYH-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
- Autosomal recessive inheritance
- Almost complete penetrance by age 60 with variable expression
- 1-2% of the population are carriers
- 2 common mutations (Y179C and G382D)
- About 70-80% of mutations
- About 4% of people with MAP will not have the 2 common mutations
True or False: Age of onset of breast cancer is more important than number of women with the disease in a family
True
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer
- Multiple cases of early onset breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Breast and ovarian cancer in the same woman
- Bilateral breast cancer
- Male breast cancer
- Ashkenazi Jewish heritage
BRCA-Positive Management (breast cancer)
- Monthly BSE beginning at age 18
- CBE every 6-12 months starting at age 25 (or 5-10y before the earliest dx in family)
- Annual MRI starting at age 25 (or 5-10y before the earliest dx in family)
- Annual Mammogram and MRI starting at age 30
- Consider chemoprevention (Tamoxifen)
- Consideration of prophylactic mastectomies
BRCA-Positive Management (ovarian cancer)
- Recommend prophylactic BSO between ages 35-40 (consider reproductive desires)
- If delaying BSO: pelvic examination and transvaginal ultrasound with color Doppler imaging every 6 months beginning at age 30-35 (or 5-10 years prior to the earliest dx in the family) with concurrent serum CA-125
- Consider oral contraceptive (discussion of risk/benefit)
Screening, management, and prevention of hereditary cancer
- Options for increased and earlier screening
- Consider preventative surgery
- Consider medications to reduce risk
Screening, management, and prevention of familial cancer
Options for increased screening, tailored to number of diagnoses and ages of diagnosis in the family
Screening, management, and prevention of sporadic cancer
Follow American Cancer Society Guidelines for general population screening
Individual homozygous for mutations in BRCA2 have...
Fanconi Anemia
- Short stature, abnormal skin pigmentation, malformations of thumbs or forearms, hearing loss, developmental delay
- Progressive bone marrow failure
- Adult onset aplastic anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome or AML
- Solid tumors
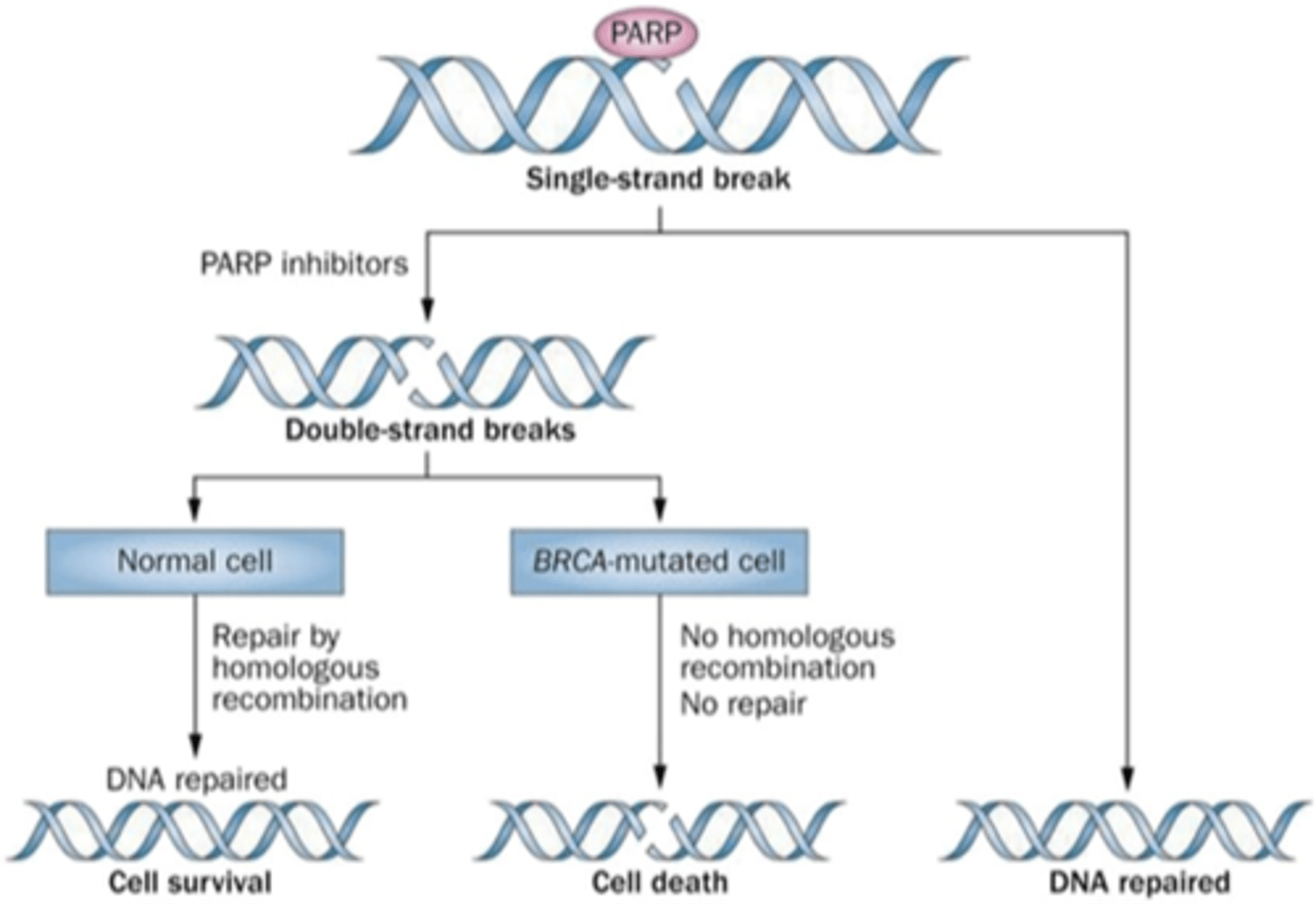
HBOC and PARP inhibitors
Promote cancer cell death by not allowing single strand break to be fixed
PALB2
- Partner And Localizer of BRCA2
- Breast cancer risk around 30-60%
- Pancreatic cancer risk is increased
- Unclear if ovarian cancer risk is increased
- Homozygous mutations also cause Fanconi Anemia
Cowden syndrome (PTEN gene)
Cancer risks:
- Breast 25-50%
- Thyroid 10% (Follicular or papillary)
- Endometrial 6-10%
- Renal cell (Clear cell)
- Colon cancer
- Melanoma ?
Benign lesions
- Hamartomas, thyroid (goiter, adenomas), macrocephaly, lipomas, hemangiomas, AVMs
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Rare hereditary cancer syndrome causing high lifetime risk for cancer
- Early onset breast cancer, bone/soft tissue sarcomas, brain tumors, leukemia, adrenocortical tumors and others
- Multiple cancers often seen in same individual
- Caused by mutations in the TP53 gene
- 50% of affected individuals develop cancer by age 30, and 90% develop cancer by age 70
Familial melanoma
- Genes: CDKN2A and CDK4
- CDKN2A is a tumor suppressor gene – loss of this gene results in loss of p16 activity, which eliminates cell cycle regulation
- CDK4 is a proto-oncogene (mutations lead to a gain of function that down-regulates pRb, resulting in a lack of cell cycle control)
- Mutations in these genes lead to an increased risk of melanoma, moles, and pancreatic cancer
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
- Due to gain of function mutations in the RET proto-oncogene
- Clinical features can include medullary thyroid carcinoma, parathyroid hyperplasia, and pheochromocytoma
- 1-7% of patients with apparently sporadic MTC had a germline RET mutation
- Prophylactic thryoidectomy is recommended prior to 6 years of age
When should genetic testing be considered?
- Significant family cancer history
- Reasonable likelihood of carrying an altered cancer susceptibility gene (affected usually tested first)
- Results will influence medical management
- Patient wants information (empowerment)
Possible results of genetic testing
Positive
Negative
- True negative
- Negative in affected individual
Variant of uncertain significance
- Additional information needed