11th grade Quiz - Carbs & Lipid
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Carbohydrates
Molecules used for short term energy. Consisting of elements: Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
Triglyceride (lipid)
Energy storing molecule made of glycerol & 3 fatty acid chains. Has Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen but NOT in a 1:2:1 ratio
Monosaccharides
The smallest type of carbohydrate. Examples include glucose, fructose, and ribose
Polysaccharides
MANY many sugar (glucose monosaccharides) units put together. Examples include cellulose, starch, and glycogen
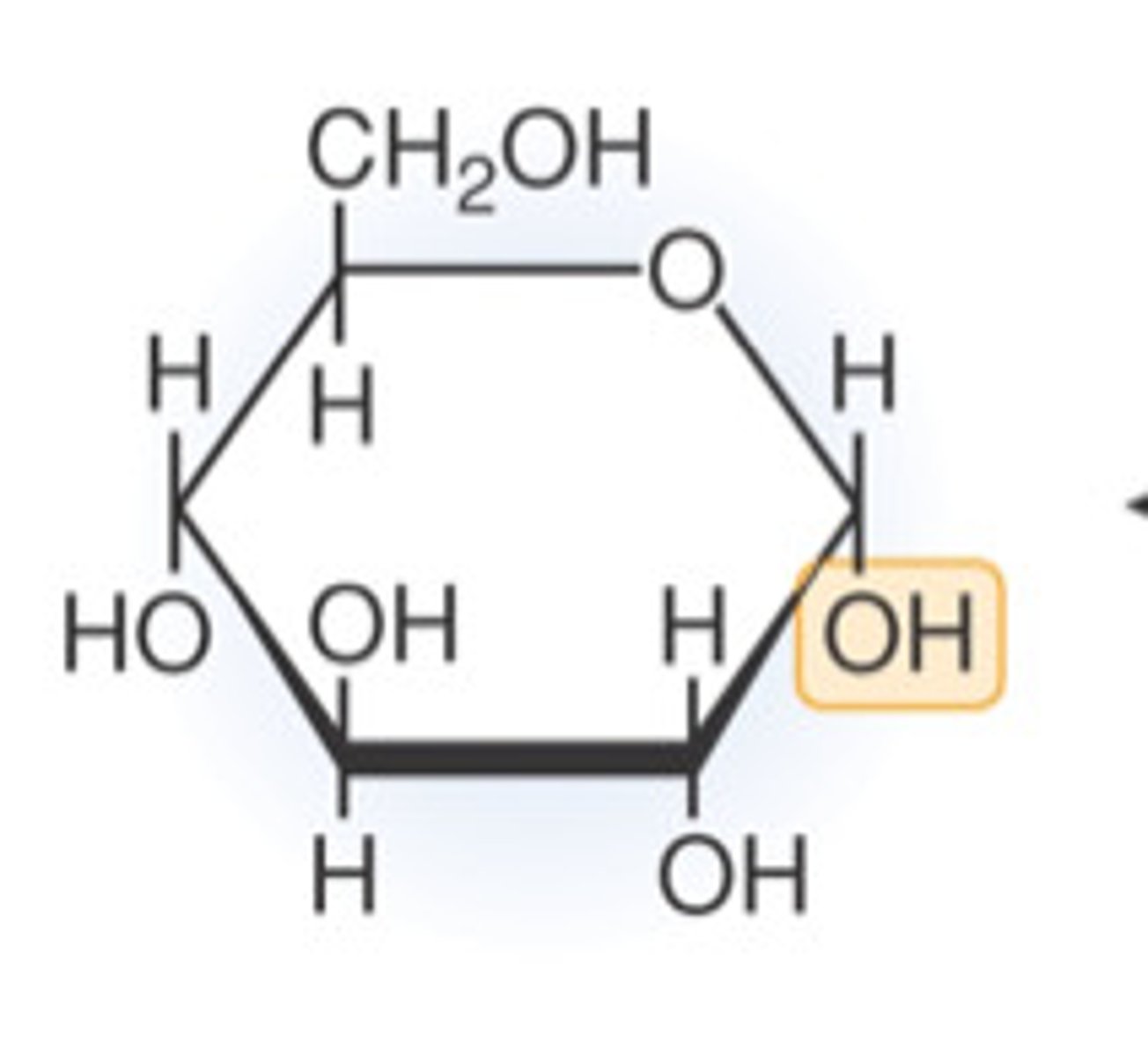
Glucose
What is this?
Monosaccharide
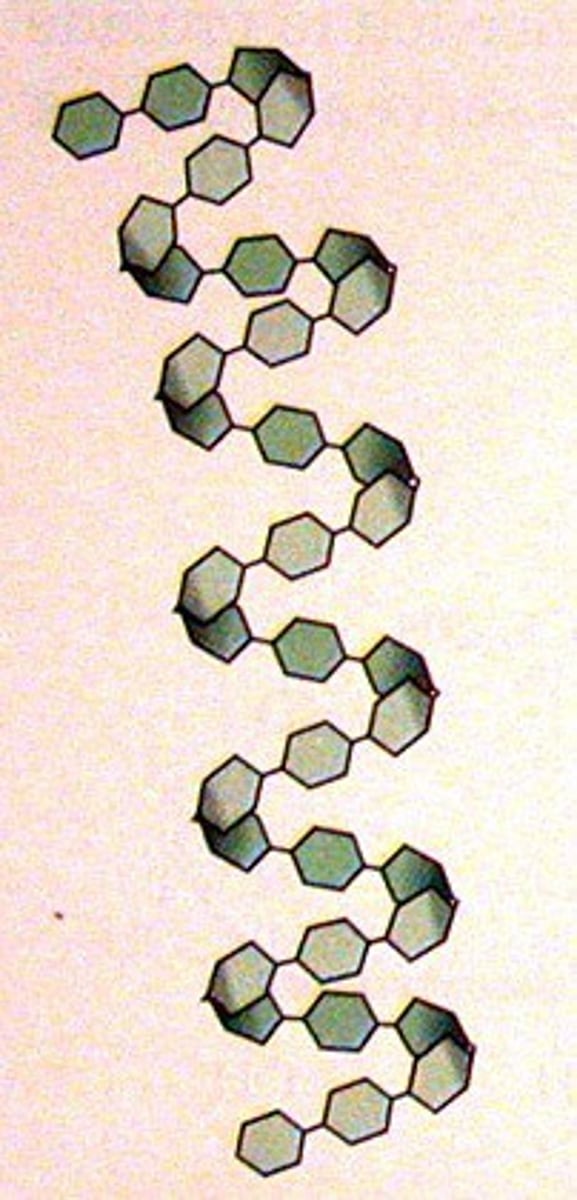
Amylose
What is this?
Alpha glucose connected with 1,4 carbon connections ONLY (no branches). A type of starch made by plants for energy storage.
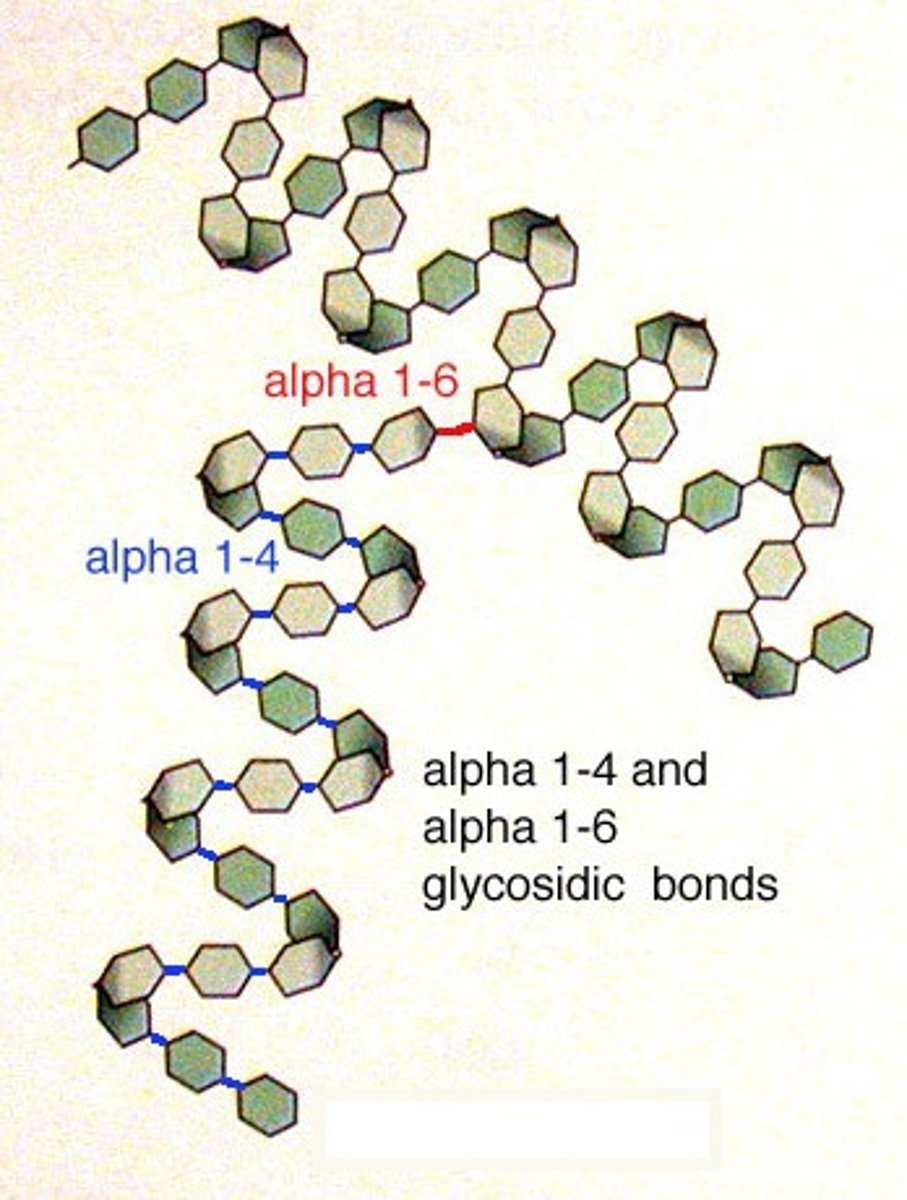
Amylopectin
What is this?
Alpha glucose connected with 1,4 and 1,6 carbon connections (Branched molecule). A type of starch made by plants for energy storage
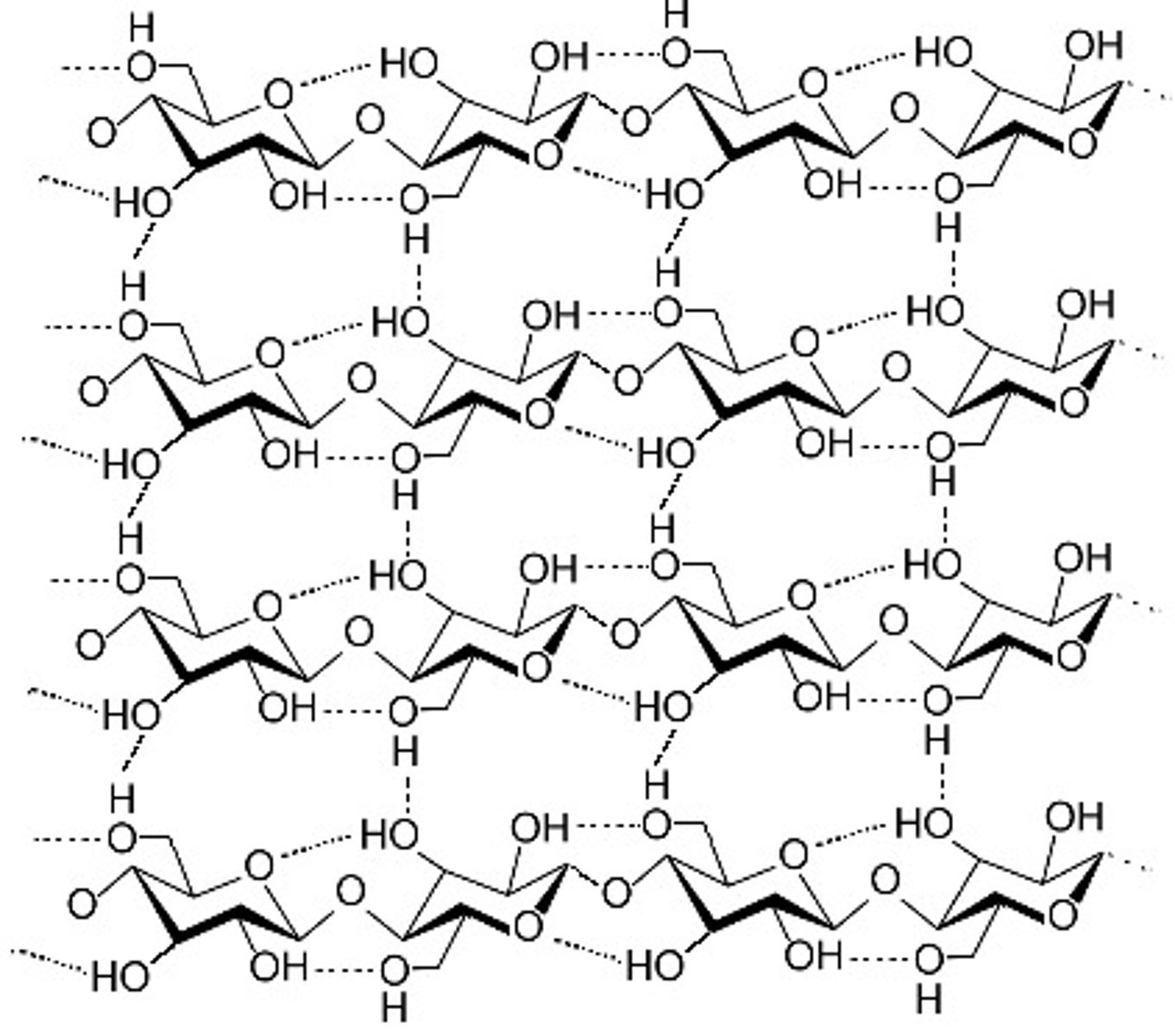
Cellulose
What is this?
Beta glucose connected in 1,4 connections - STRAIGHT CHAINS - very tough / indigestible. Made by plants for the structure of their cell walls
Glycogen
The many branched polysaccharide made by animals when they have too much glucose
Anabolism
Set of metabolic pathways that use energy to create larger molecules by assembling smaller molecules together.
Catabolism
Set of metabolic pathways that break down larger molecules to make smaller molecules, releasing energy.
Condensation Reactions
Anabolic reaction that removes HOH (water) to combine smaller molecules into larger molecules
Hydrolysis Reactions
Catabolic reaction that adds HOH (water) to break apart larger molecules into smaller molecules
Carbon
What element is at the center of all biological molecules (organic chemistry) because of its ability to form 4 covalent bonds?
Function of lipids
Long-term energy, cushion & insulation, and a major component of our cell membranes (phospholipids)
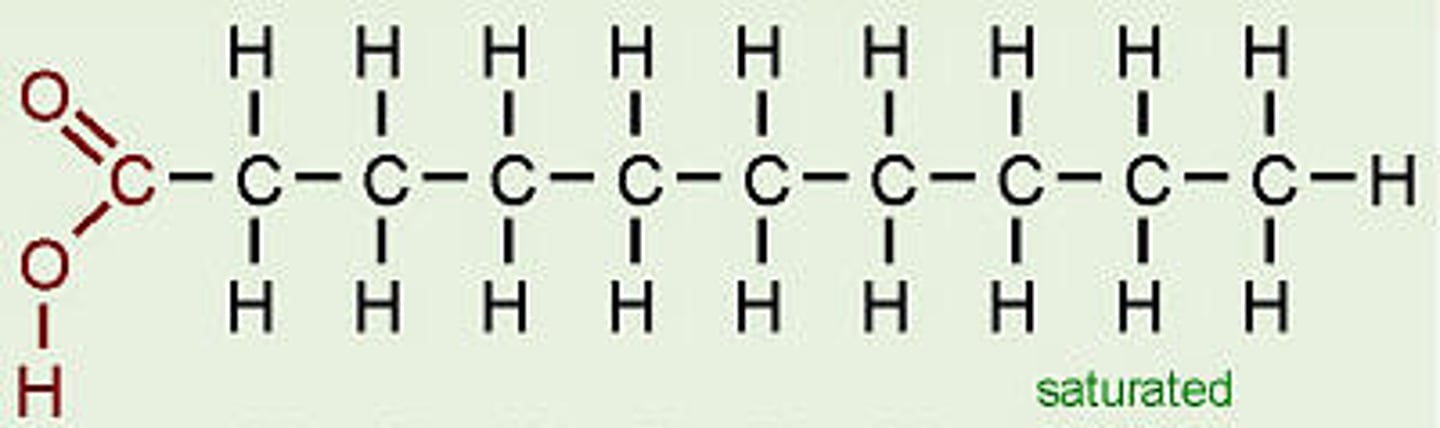
Saturated Fatty Acid
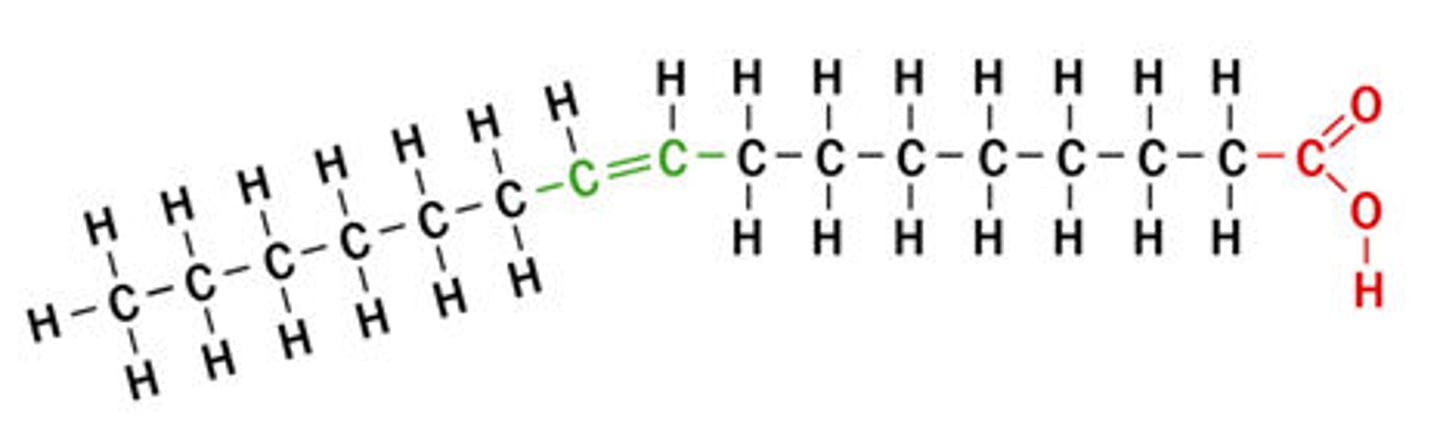
Monounsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid whose molecular structure includes only one double carbon bond.
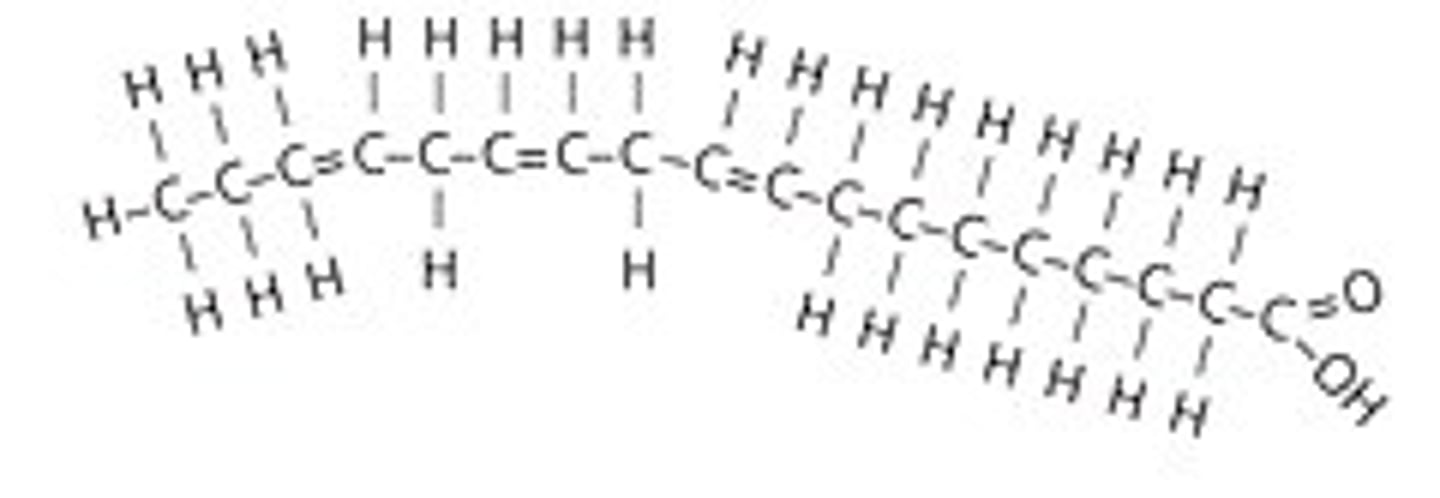
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid containing two or more carbon-carbon double bonds
Triglyceride
A type of lipid that is made up of glycerol with 3 fatty acids attached