intro to alcohols
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
give 2 physical properties of alcohols:
water soluble
higher bpt than alkanes of similar mass due to H bonding between molecules
give the 2 methods for alcohol formation:
hydration of alkenes (or electrophilic addition of alkenes w/ H2SO4)
fermentation - ethanol
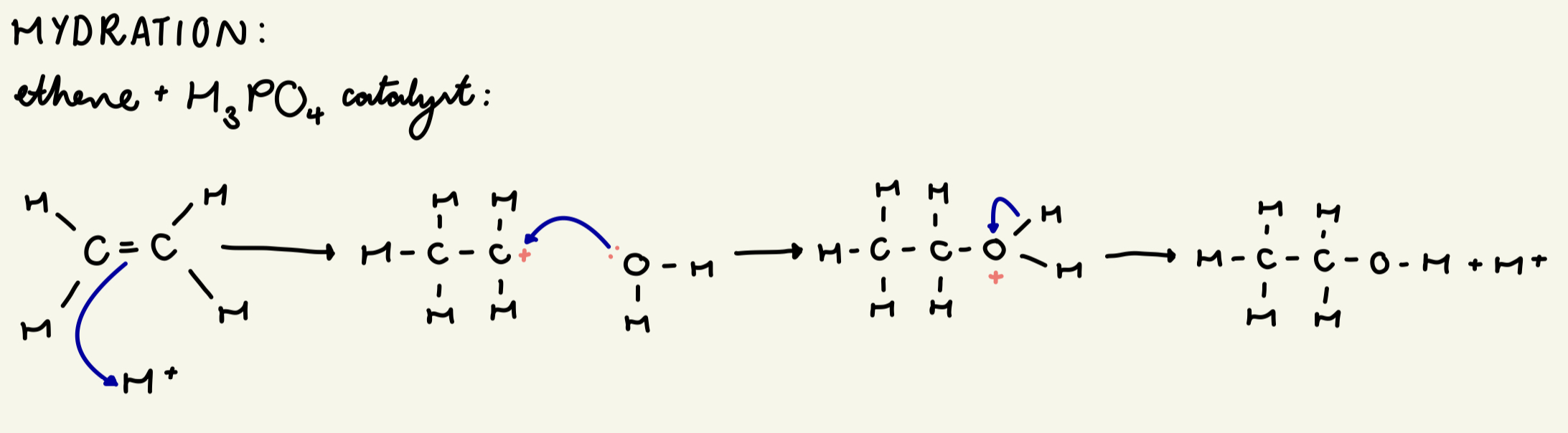
give the conditions required for the hydration of alkenes:
H3PO4 catalyst
60 atm
600 K
often XS ethene - high yield
draw out the mechanism for the hydration of ethene:
give the symbol equation and conditions for fermentation:
C6H12O6 → 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 CO2 - separated by distillation afterwards
anaerobic - to prevent oxidation of ethanol
~ 35oC, yeast - enzymes
what is a biofuel? give one example:
fuels derived from biomass that has recently died
e.g. (bio)ethanol
why are biofuels often described as carbon neutral? why not?
no net emissions of CO2 to the atmosphere
but fossil fuels are needed to make fertilisers/harvest crops etc. so not completely carbon neutral
evaluate the use of biofuels:
strengths:
renewable
carbon-neutral (mostly)
limitations:
land used to grow biofuels is unable to be used for growing food
biofuels in transport - petrol car engines would have to be modified to use fuels w/ high ethanol concs
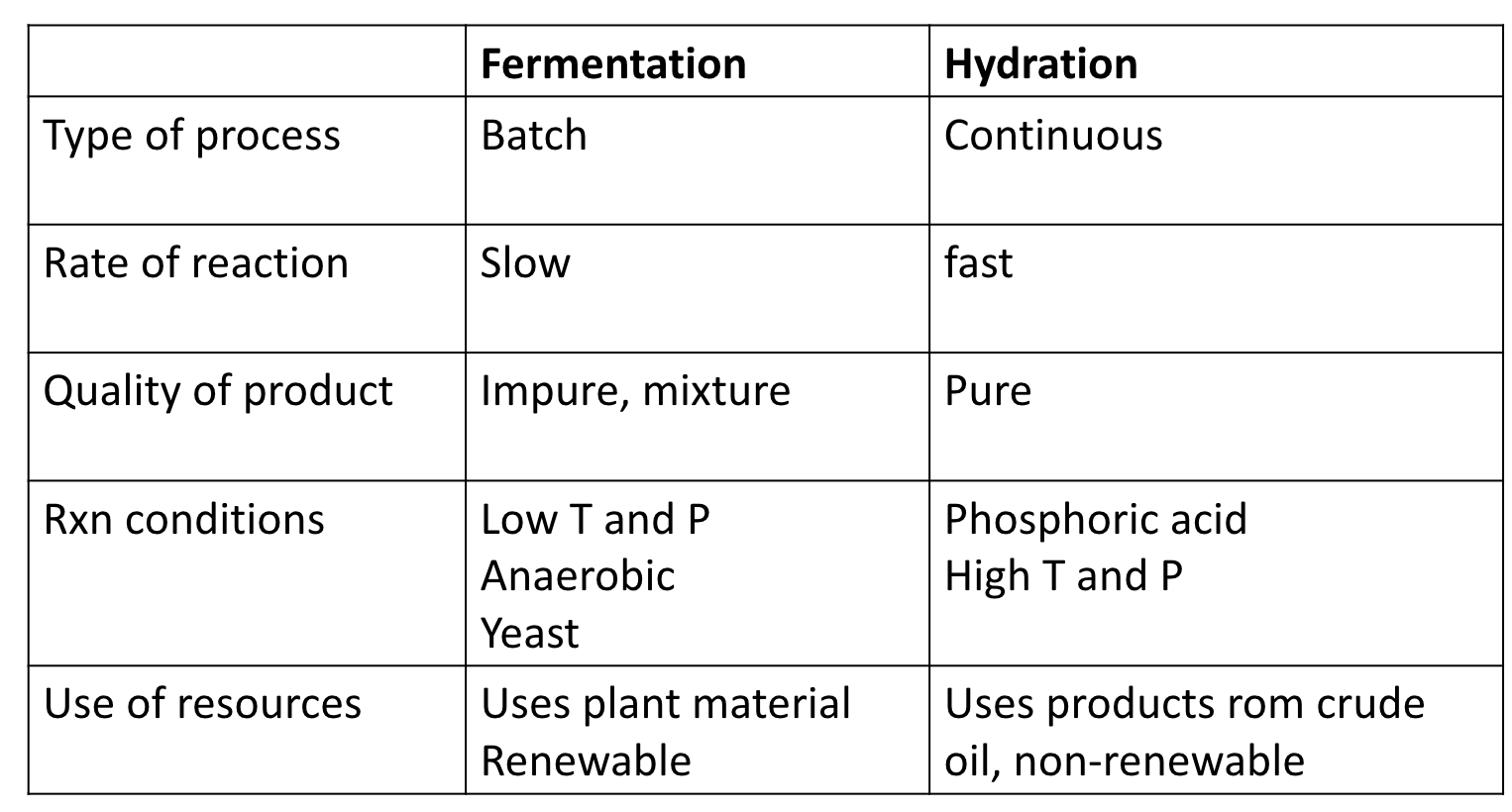
compare the processes of fermentation and hydration: