Origin of the Universe
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Conditions on Earth that allowed life to begin
1) medium-sized, stable star (sun)
2) planet orbiting 100% in the habitable zone
3) liquid water
4) atmosphere on the planet that traps heat
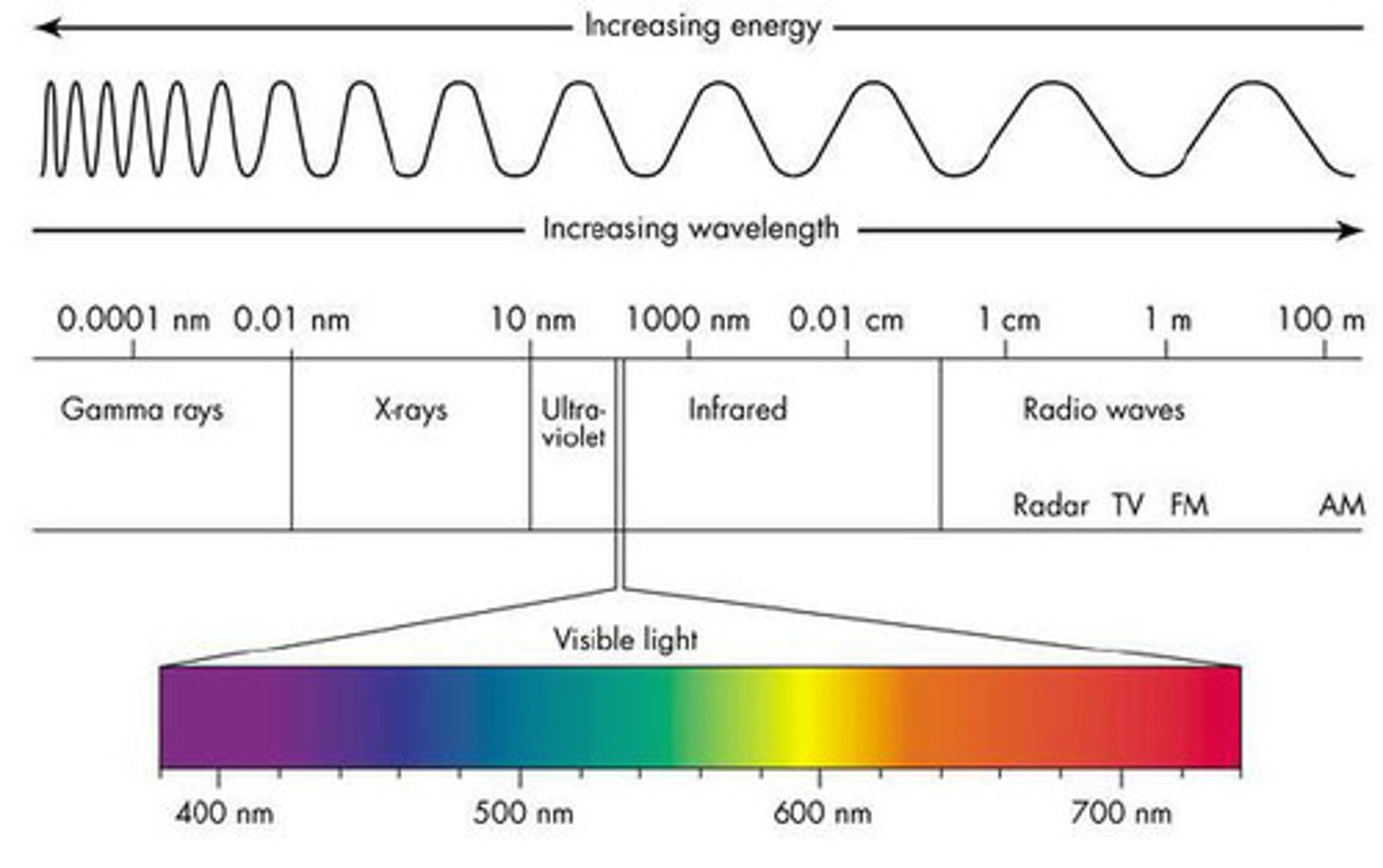
electromagnetic spectrum
All of the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, gamma rays, and microwaves
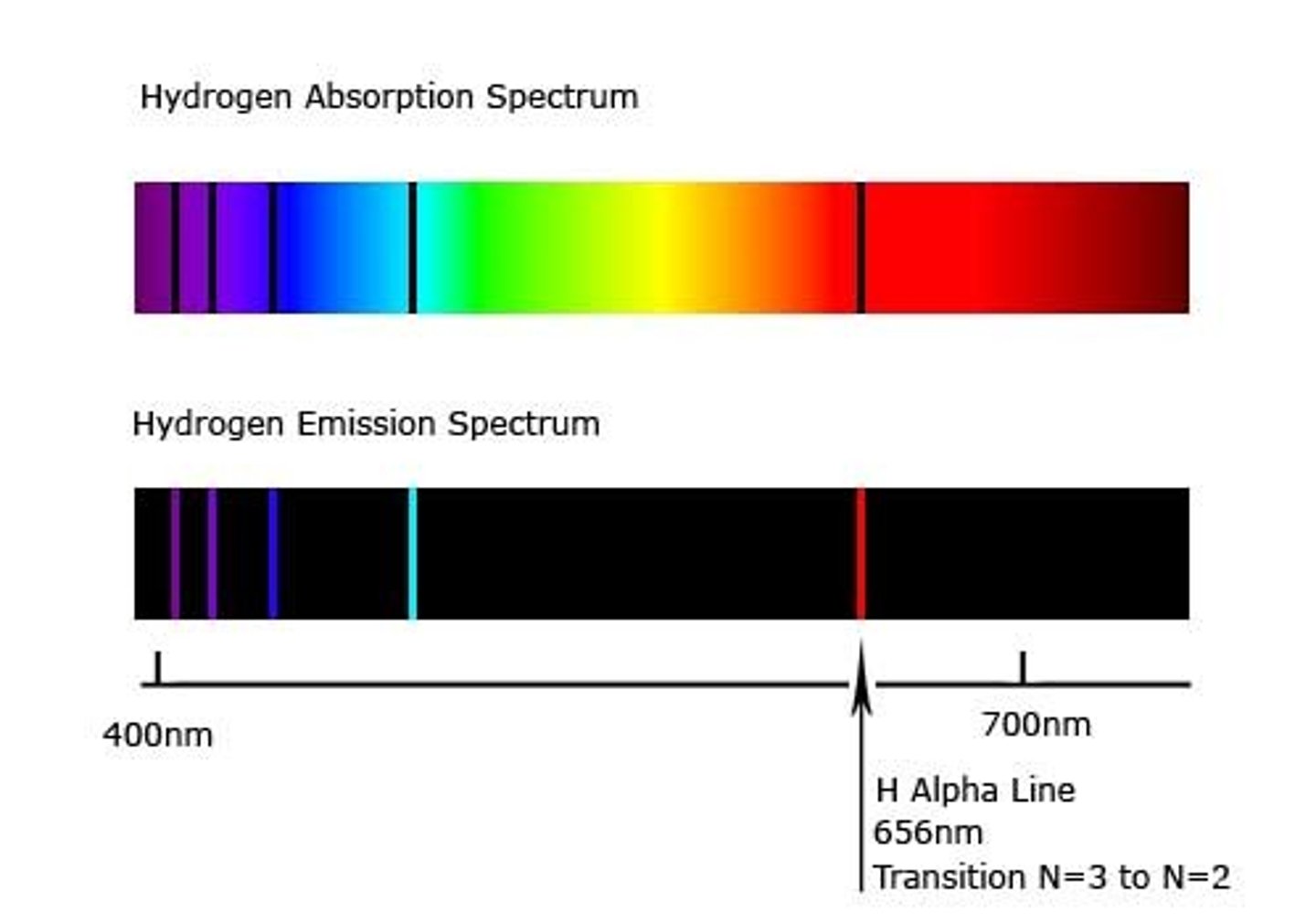
absorption spectrum
a graph plotting a galaxy or star's light absorption versus wavelength
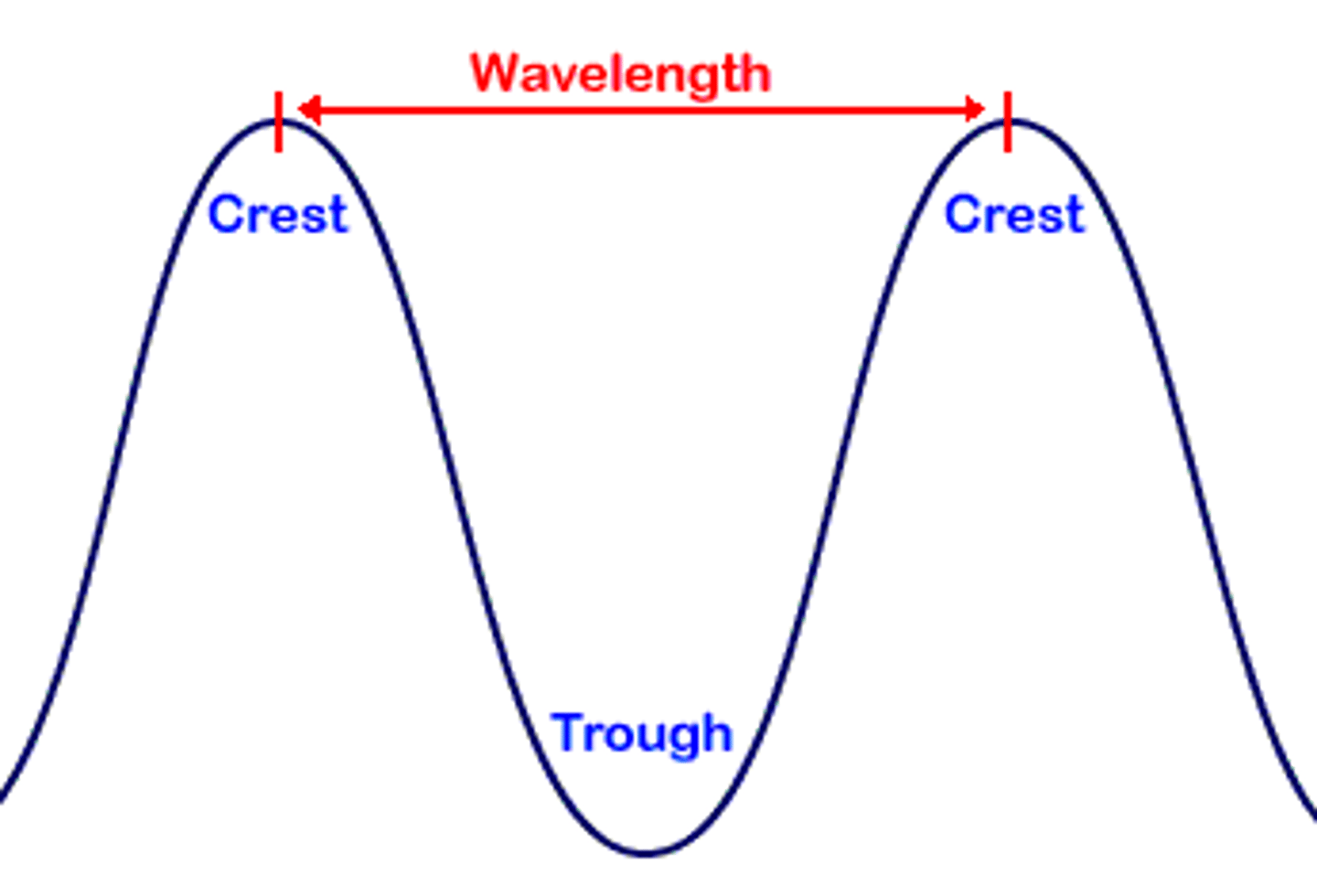
wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves; shorter wavelength = higher energy
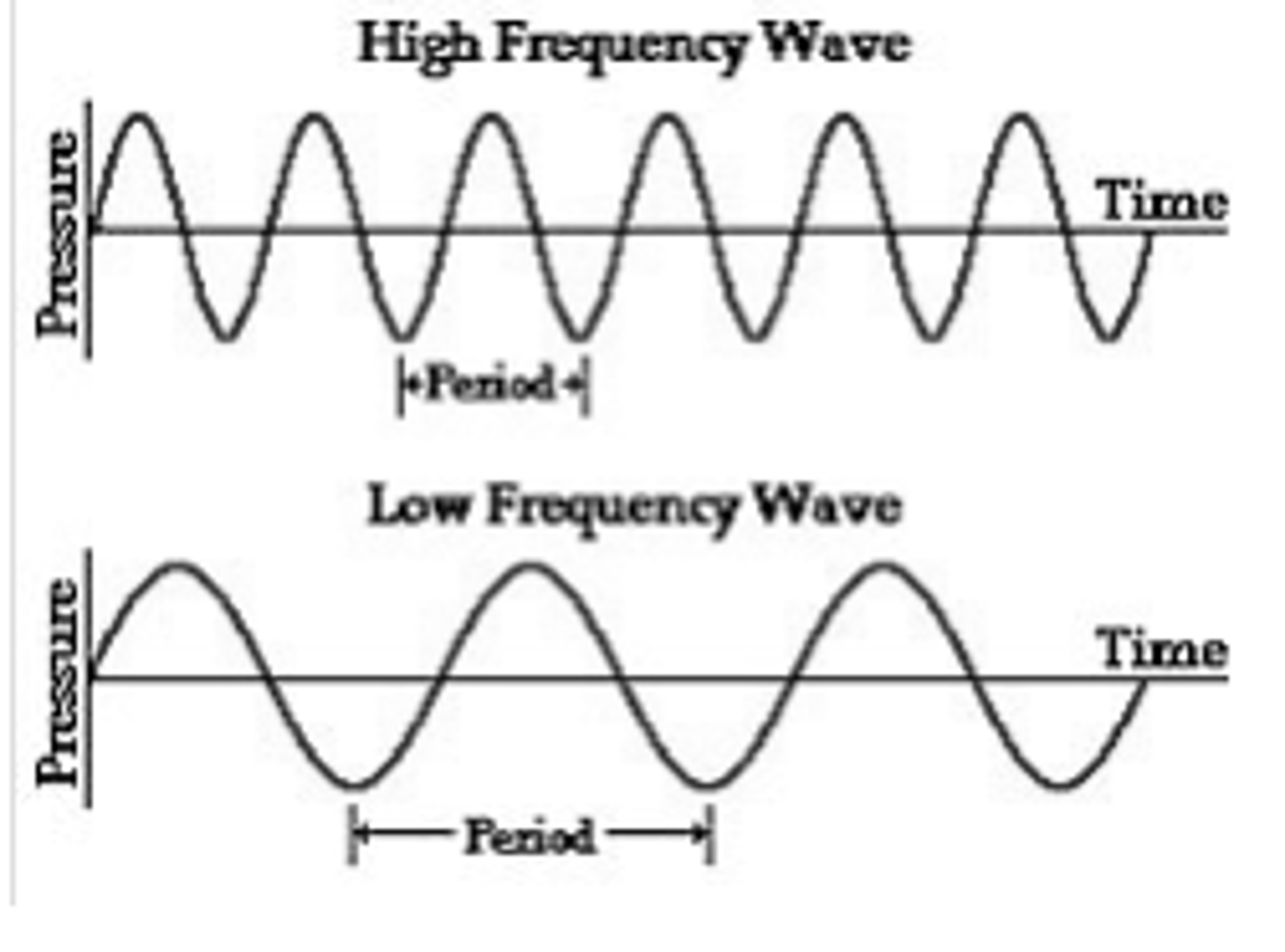
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time; higher frequency = higher energy
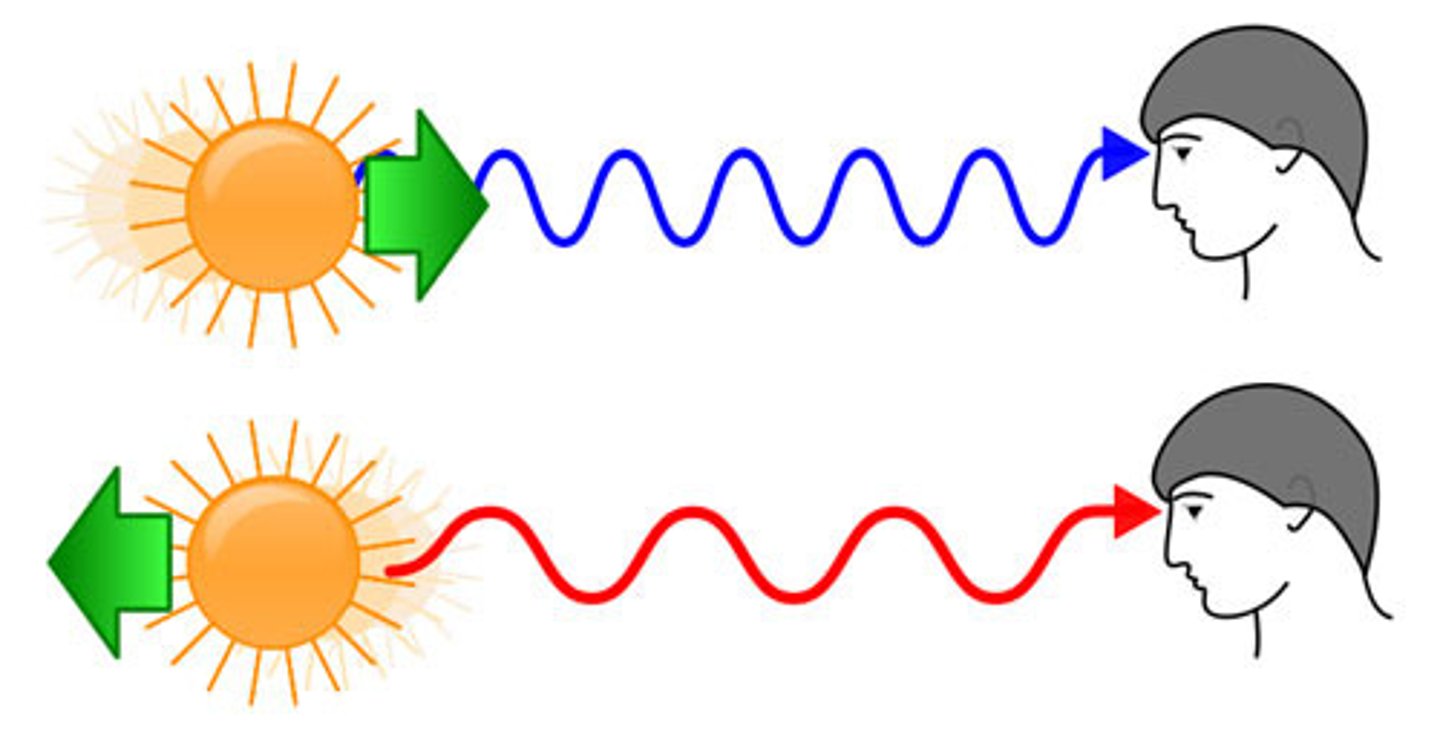
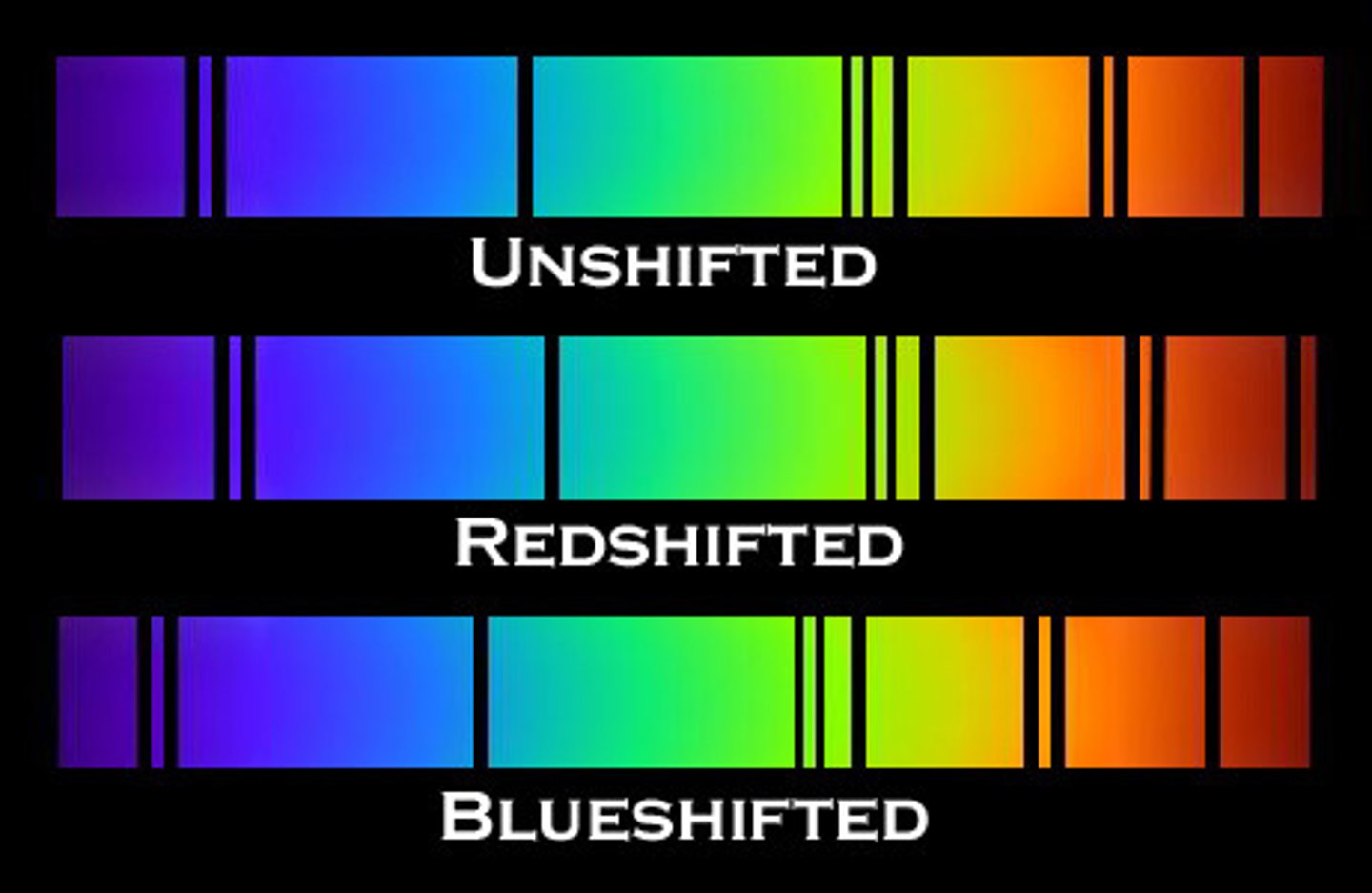
redshift
perceived shift of light to a longer wavelength as the object moves away from observer
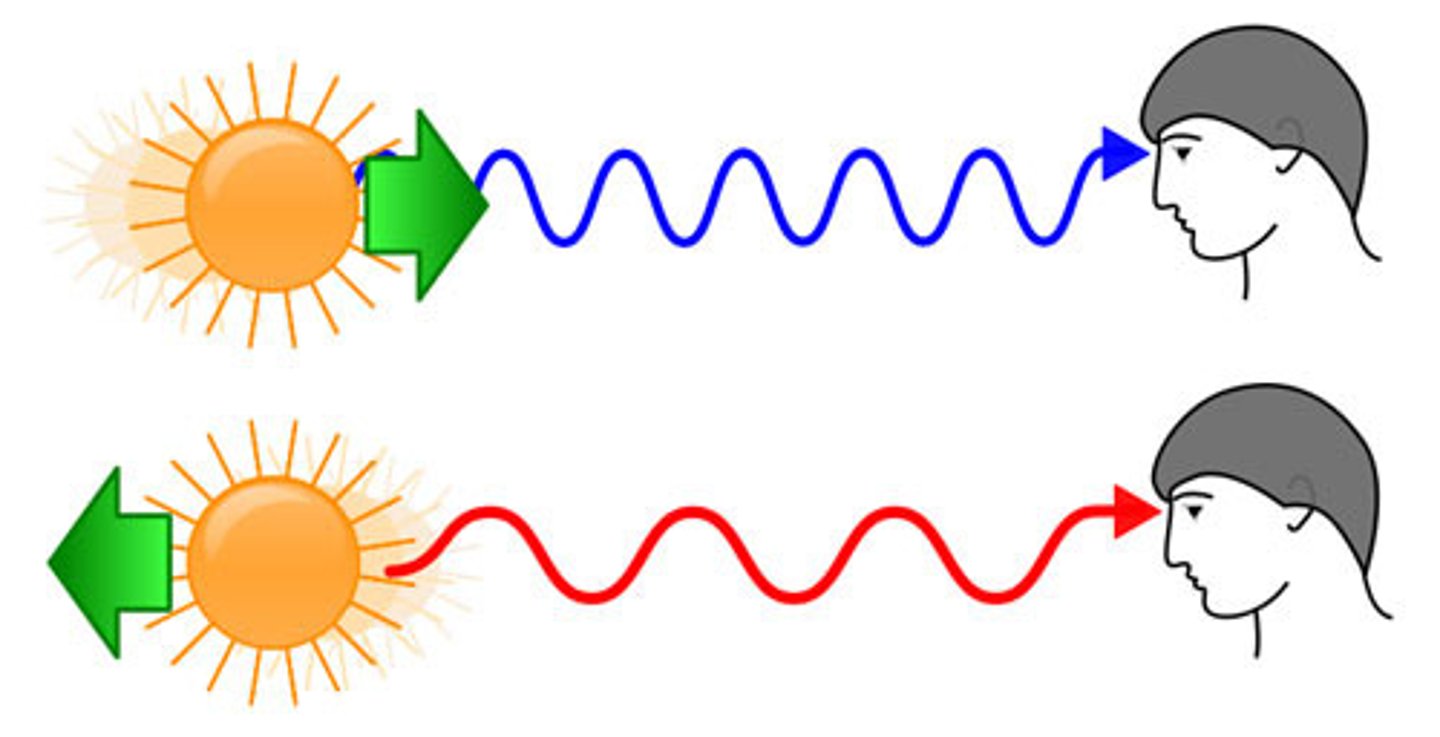
blueshift
perceived shift of light to a shorter wavelength as the object moves toward observer
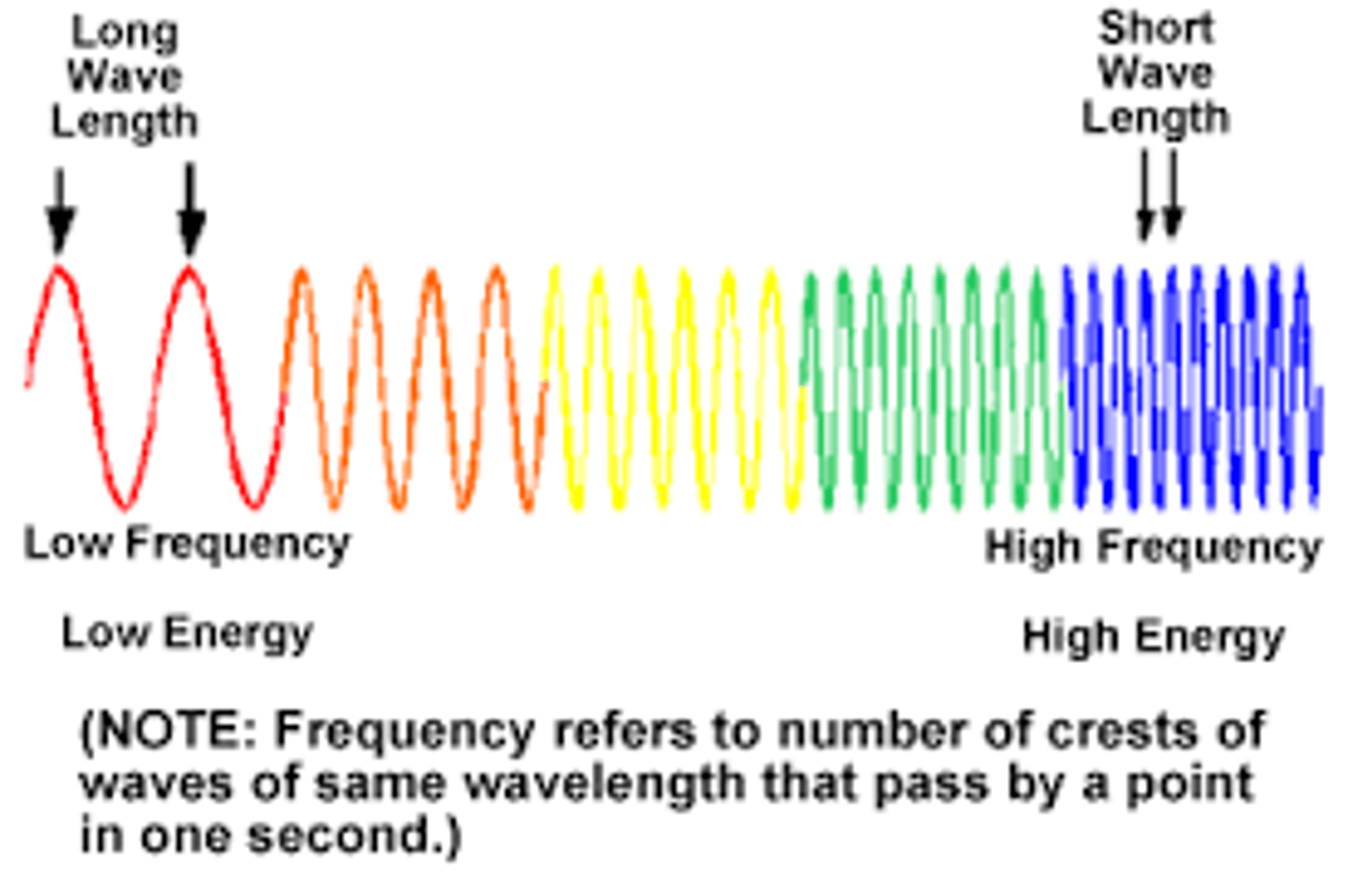
color of visible light with the longest wavelength and lowest energy
red
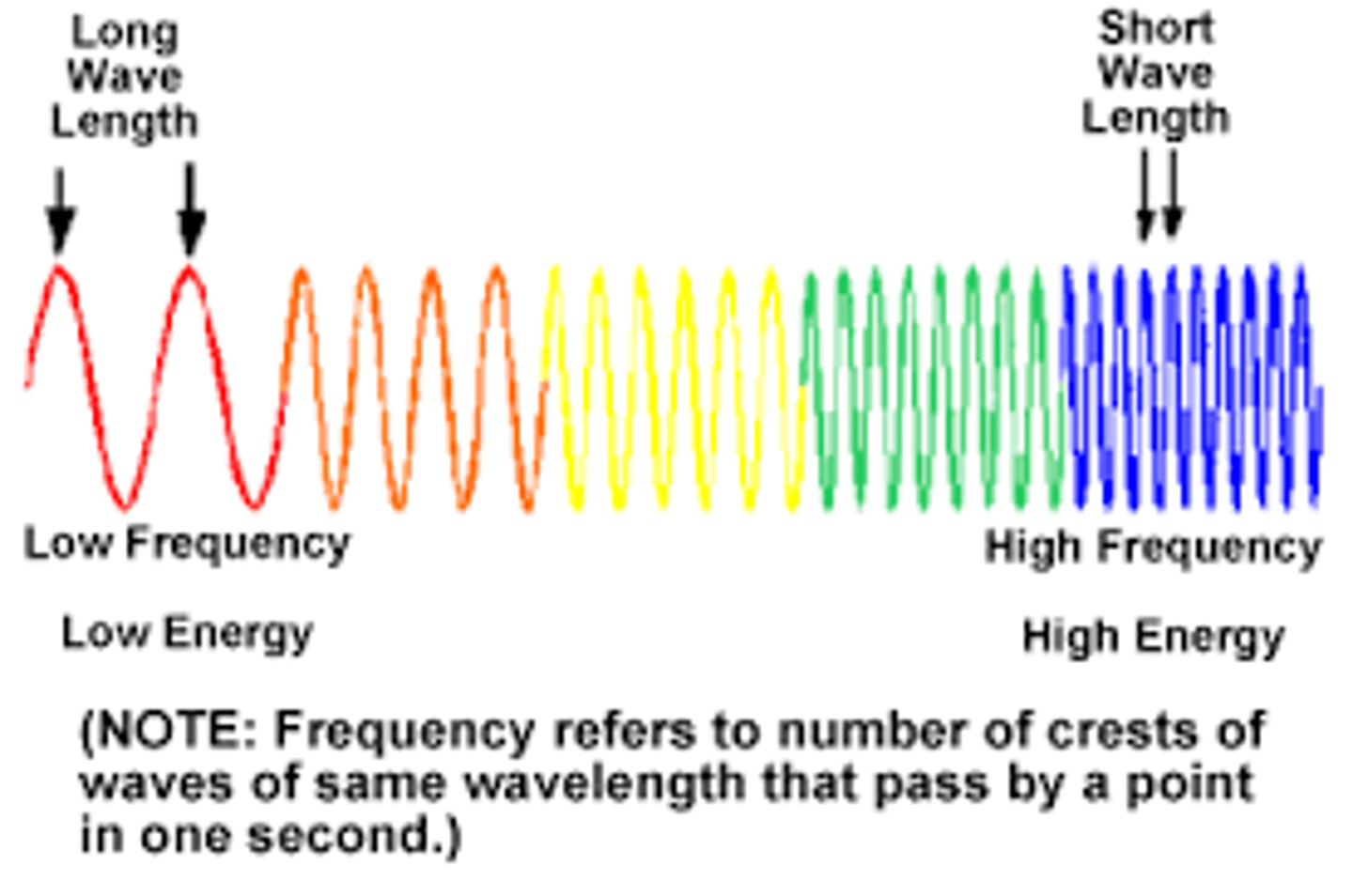
color of visible light with the shortest wavelength and highest energy
blue
most galaxies in the universe are in _______shift
redshift
the universe is ________
expanding
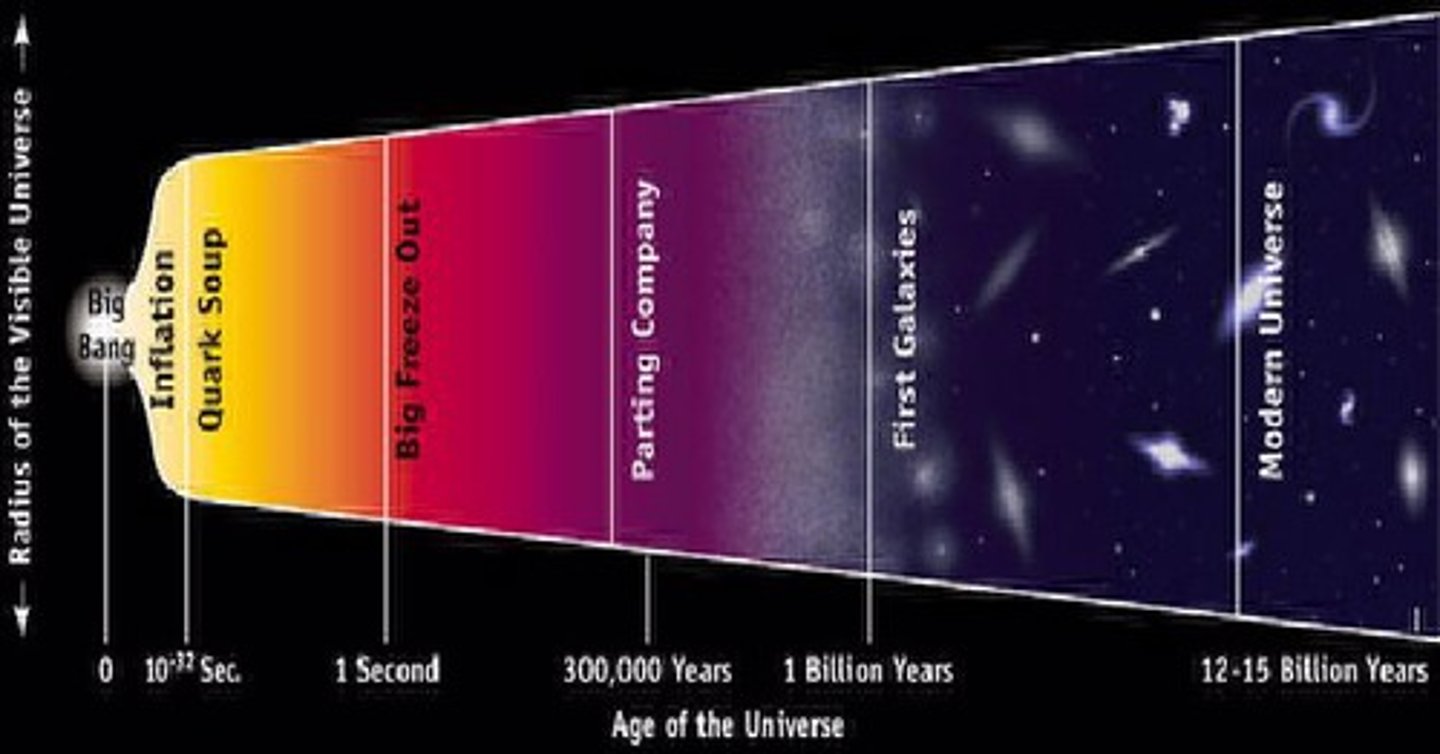
3 pieces of evidence for the expansion of the universe from a small, hot, dense mass
1) most galaxies are in redshift
2) existence of CMB coming from everywhere in the universe
3) ratio of hydrogen to helium (3:1)
Why is redshift evidence for the Big Bang?
If everything is moving away from us now, then logically, rewinding time would show everything getting closer together. The Big Bang theory proposes that if we rewind far enough, all the matter and energy in the universe would be concentrated in a very hot, dense state
Why is CMB evidence for the Big Bang?
The Big Bang theory predicts that the early universe was incredibly hot and filled with light. As the universe expanded and cooled, this light would eventually stretch out to become microwave radiation filling all of space. This faint echo of the hot, early universe is exactly what the CMB is.
Why is the ratio of hydrogen to helium (3:1) evidence for the Big Bang?
The Big Bang theory predicts the conditions that existed in the very early universe would have led to a specific ratio of hydrogen to helium, around 3:1. This prediction is based on the conditions necessary for fusing protons and neutrons into helium nuclei shortly after the Big Bang. This predicted ratio is very close to what we measure in the universe today.
What is the radial-velocity method for detecting planets?
This method detects planets by looking for the wobble of a star caused by a planet's gravity pulling it towards Earth, causing slight blueshift, and away from Earth, causing slight redshift
Drake Equation
a formula for estimating the number of intelligent, technological civilizations in our Galaxy, first suggested by Frank Drake

Gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses and distance apart
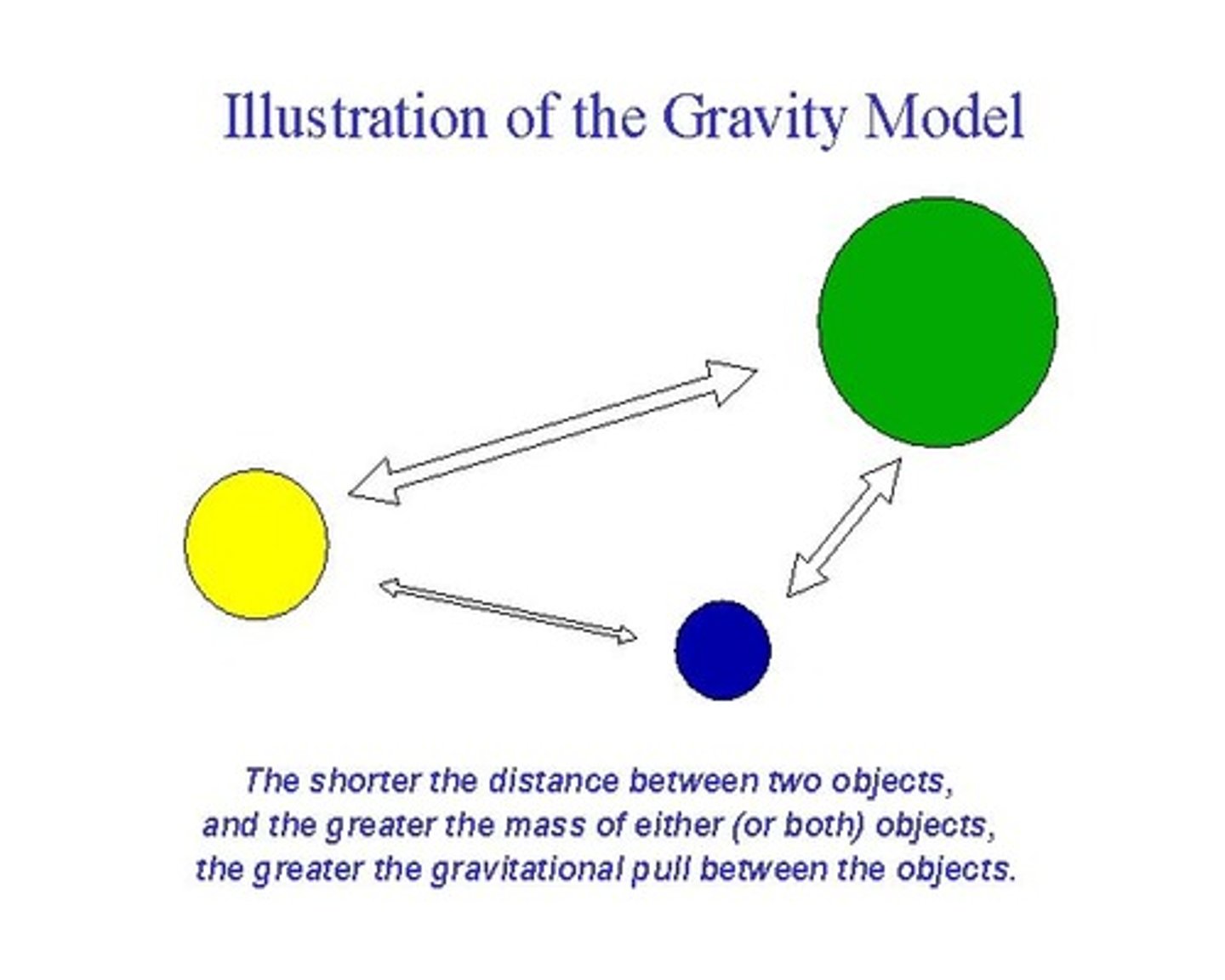
What two factors impact the magnitude of gravitational force?
Mass and distance
HR Diagram
A graph relating the temperature and brightness of stars
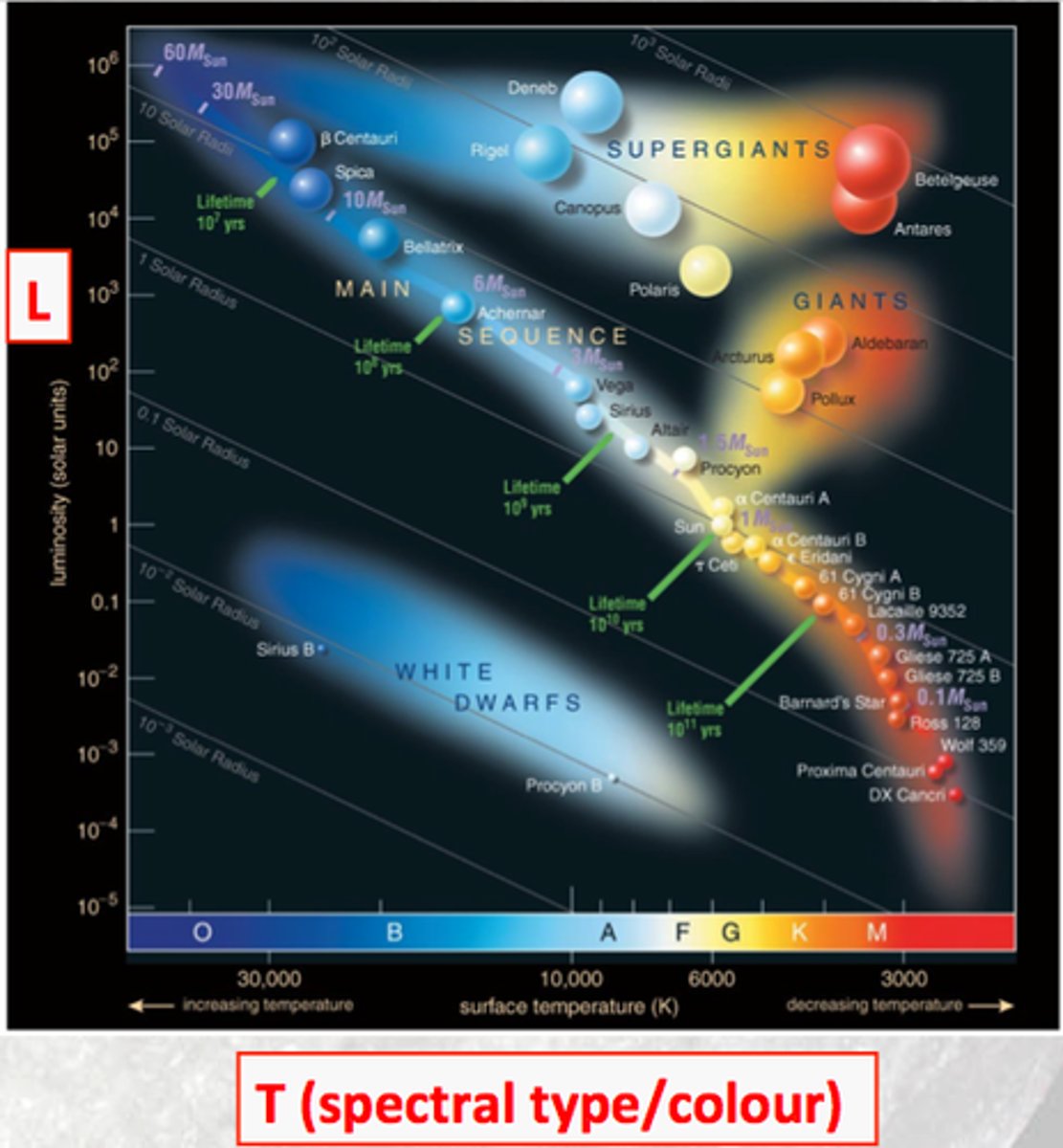
Main Sequence
a diagonal area on an H-R diagram that includes more than 90 percent of all stars; the stage of a star's life when it is most stable and spends the longest time
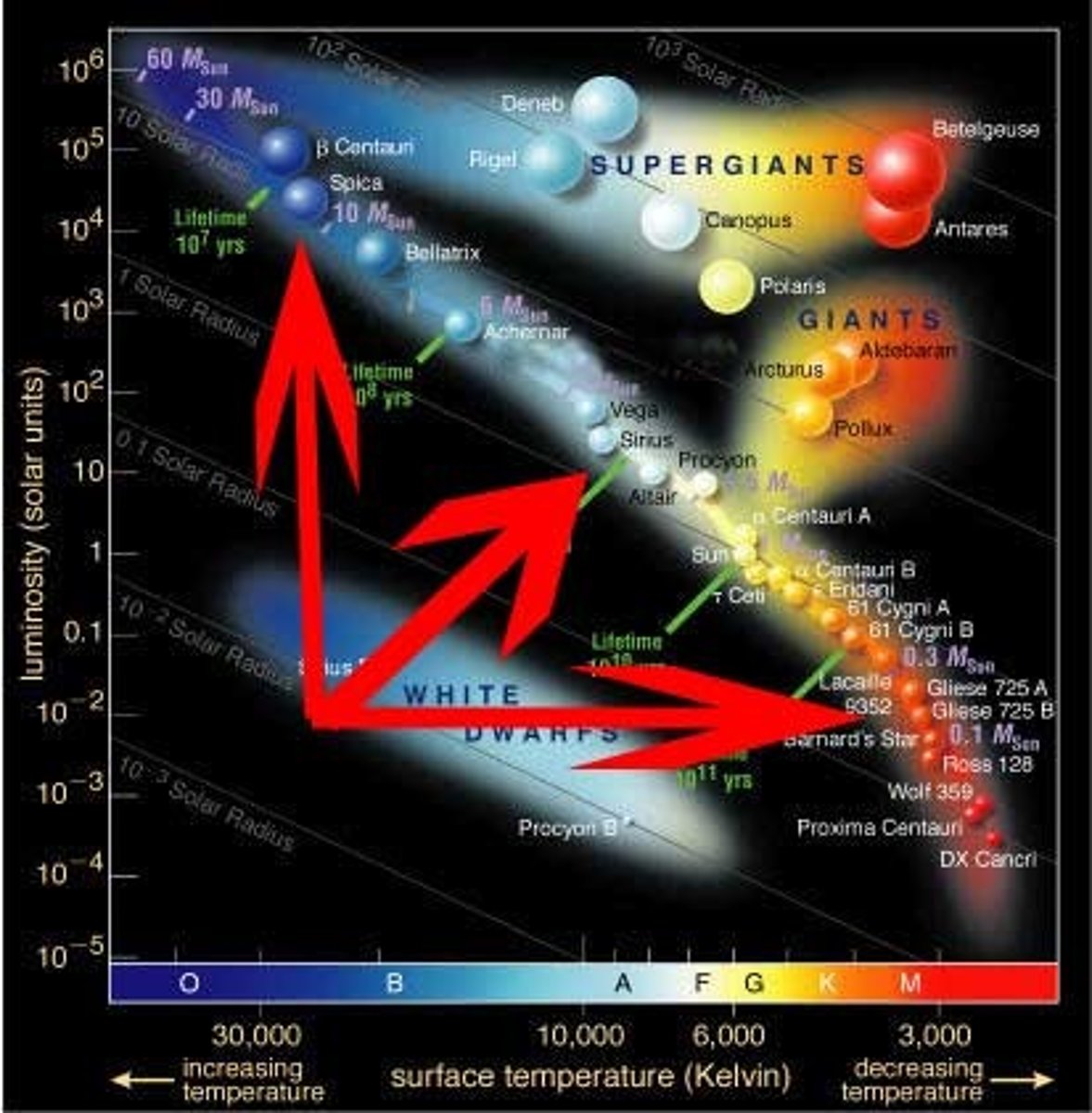
How does the mass of a star relate to its lifespan?
stars with larger masses have shorter lifespans than stars with lower masses
What kind of stars turn into black holes?
The most massive stars (not our sun)
What will our sun eventually become?
A red giant and then a white dwarf
What color are the hottest stars in the main sequence?
blue
What color are the coolest stars in the main sequence?
red
Why does temperature relate to star color?
Hotter stars emit more high-energy, bluer light, while cooler stars emit lower-energy, redder light
In which stage of a star's life is it the most stable?
main sequence
In which stage of a star's life does it spend the longest amount of time?
main sequence
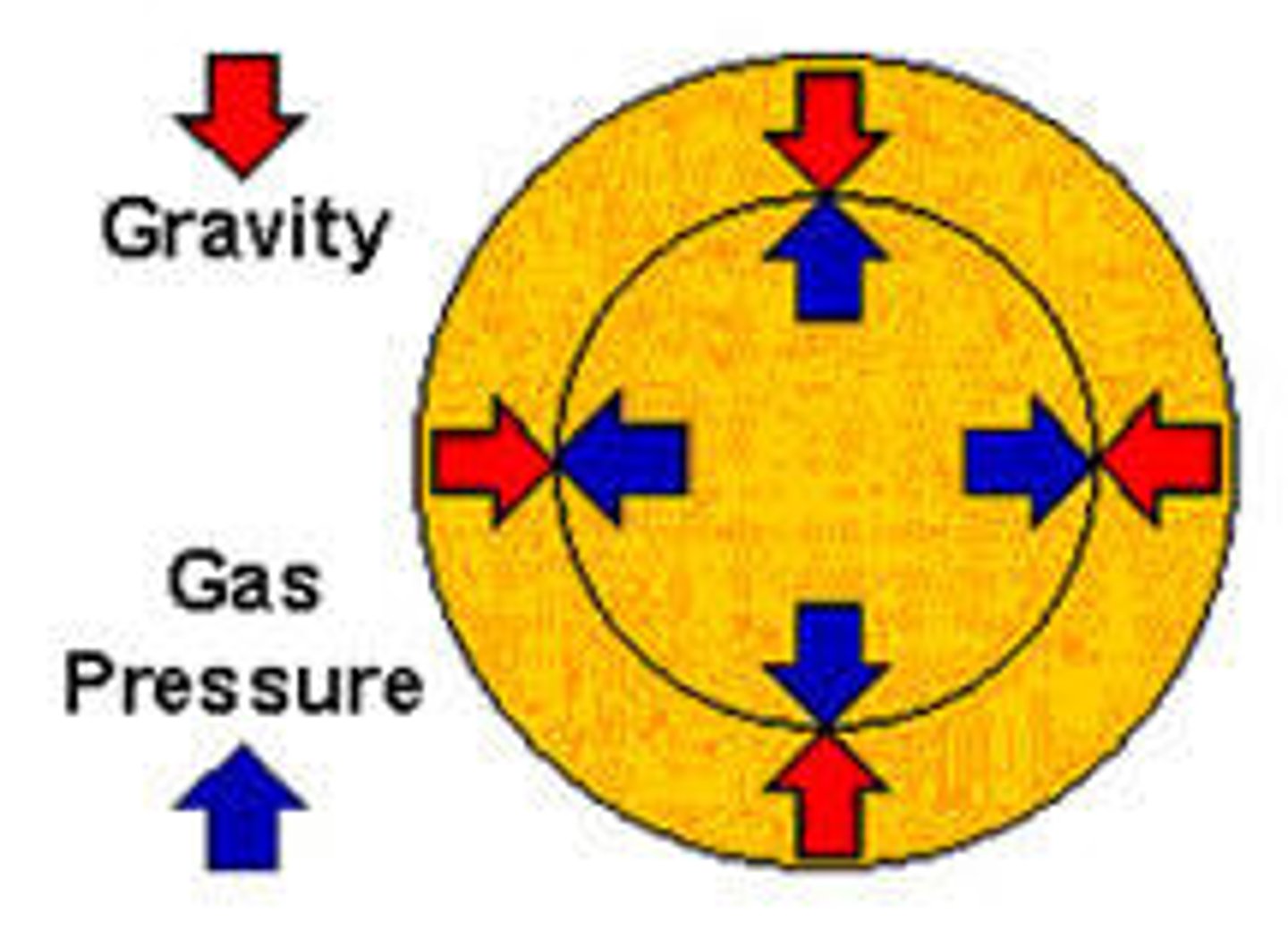
What two major forces are found in stars?
Gravity (pulling in) and nuclear fusion energy (pushing out)
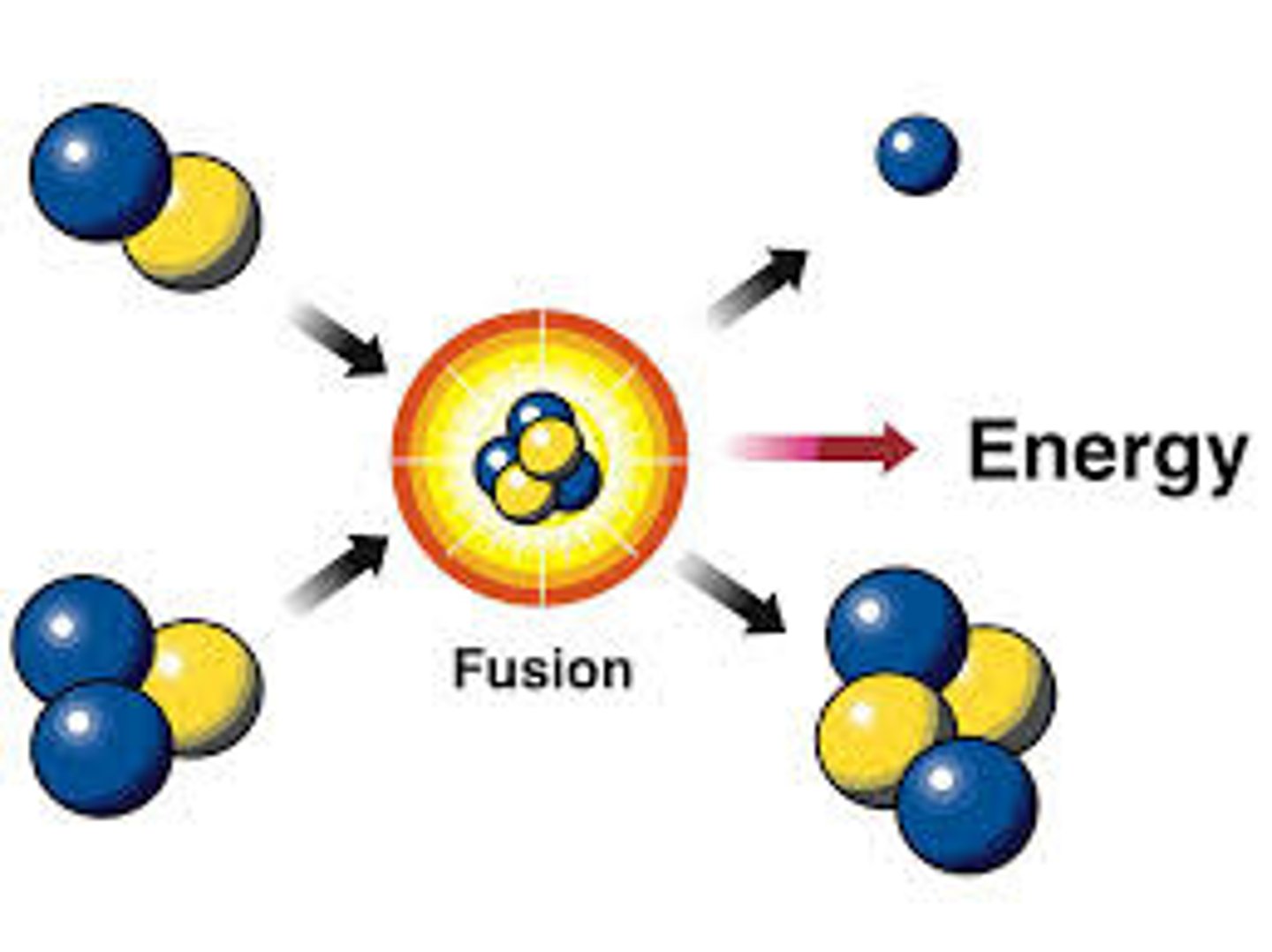
What is nuclear fusion in a star?
the process of combining hydrogen to make the heavier element helium
What happens when the star runs out of hydrogen energy?
As the core shrinks, it gets denser and hotter. This intense heat can trigger the fusion of leftover helium into heavier elements like carbon and oxygen. The star inflates and cools, becoming a red giant. Eventually, fusion ceases altogether and gravity condenses the core into an incredibly dense, small, mass
Why do large mass stars have shorter lifespans?
A massive star's core has a much higher pressure and temperature due to its own gravity. This intense environment fuels a much faster rate of nuclear fusion
Do all stars produce elements as heavy as iron?
No, a star has to have a high enough core temperature, so only very massive stars can fuse elements up to iron.
What is the habitable zone?
the region around a star where water could potentially exist in liquid form
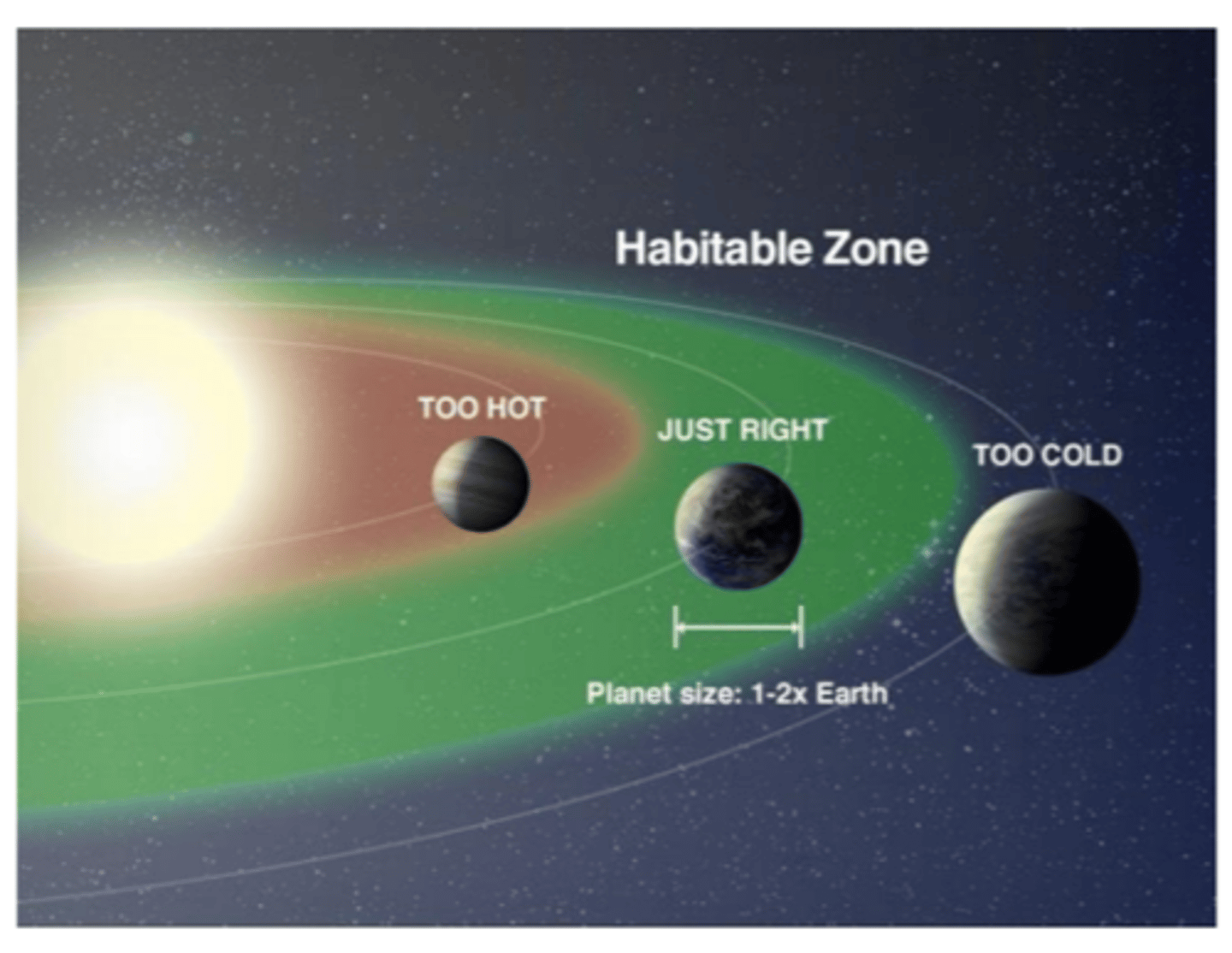
Where is the habitable zone of small mass stars and why is it not ideal for life?
much closer to the star compared to stars like our Sun; this causes orbiting planets to be at risk for frequent solar flares and intense solar radiation