PMT 1.3 - Bonding flash cards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is ionic bonding?
What is ionic bonding?
strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions held in a lattice
Give an example of an ionically bonded substance
Give an example of an ionically bonded substance
NaCl (sodium chloride - salt)
How high are ionically bonded substances' bp and mp? Why?
How high are ionically bonded substances' bp and mp? Why?
High - takes lots of energy to overcome strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Do ionic compounds conduct electricity? Why?
Do ionic compounds conduct electricity? Why?
Yes, when molten/in solution as the ions are free to move and carry charge (don't when solid)
What is simple molecular covalent bonding?
What is simple molecular covalent bonding?
Strong covalent bonds between atoms, weak van der Waals forces of attraction between molecules
Are there any lone electrons in simple covalent bonding?
Are there any lone electrons in simple covalent bonding?
No- all involved in bonding
Can simple molecular covalent molecules conduct electricity? why?
Can simple molecular covalent molecules conduct electricity? why?
No - all electrons used in bonding and aren't free to move
Do simple molecular substances have a high/low mpt and bpt? why?
Do simple molecular substances have a high/low mpt and bpt? why?
Low - weak van der Waals forces of attraction between molecules that don't take much energy to overcome (these are overcome rather than covalent bonds)
Describe macromolecular covalent bonding
Describe macromolecular covalent bonding
Lattice of many atoms held together by strong covalent bonds
Do substances with macromolecular covalent bonds have high/low mpt and bpts? why?
Do substances with macromolecular covalent bonds have high/low mpt and bpts? why?
High, as it takes a lot of energy to overcome many strong covalent bonds
Do substances with macromolecular covalent bonds conduct electricity?
Do substances with macromolecular covalent bonds conduct electricity?
Most don't as all electrons are used in bonding
Draw and describe structure of diamond
Draw and describe structure of diamond
3D tetrahedral structure of C atoms, with each C atom bonded to four others
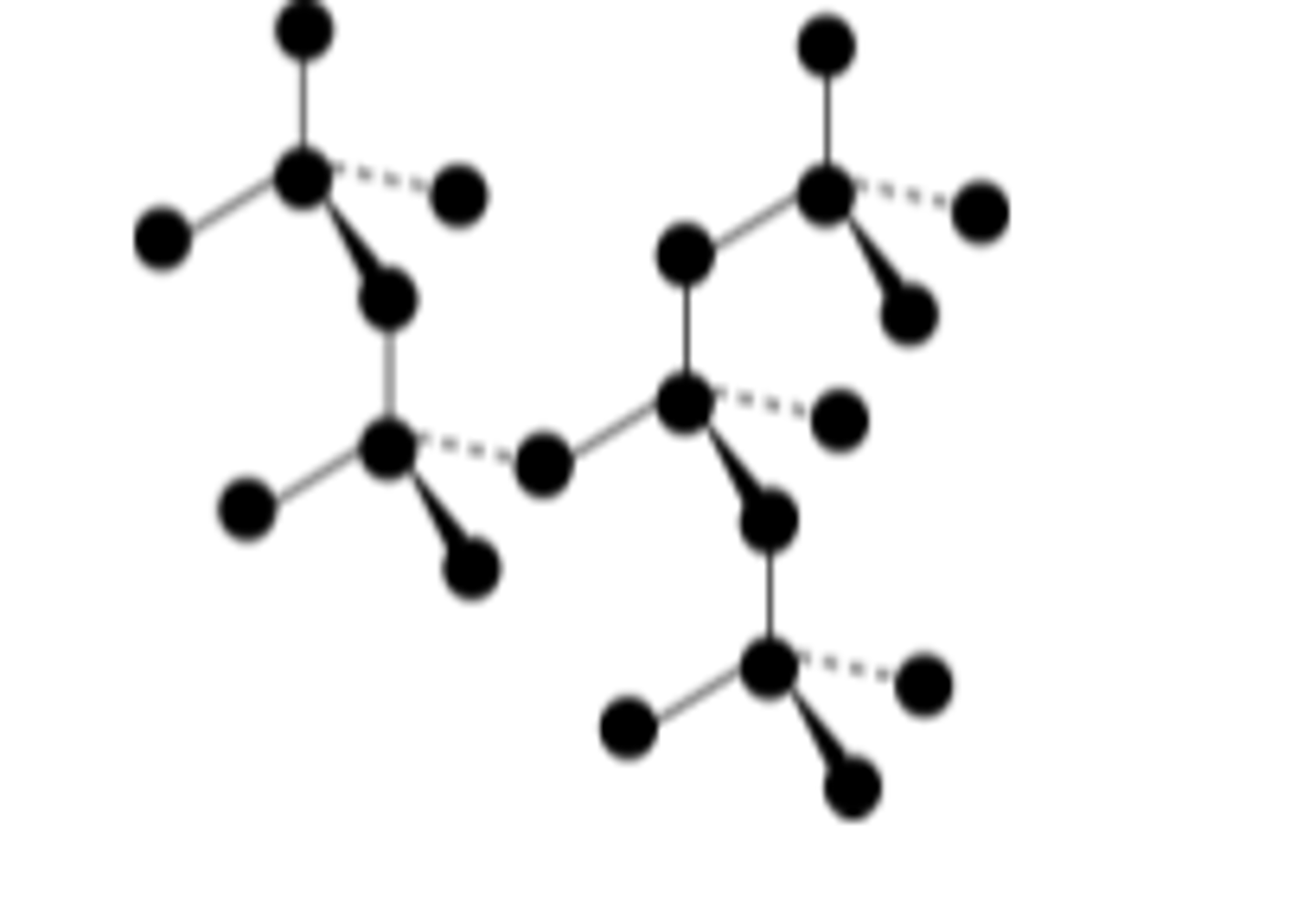
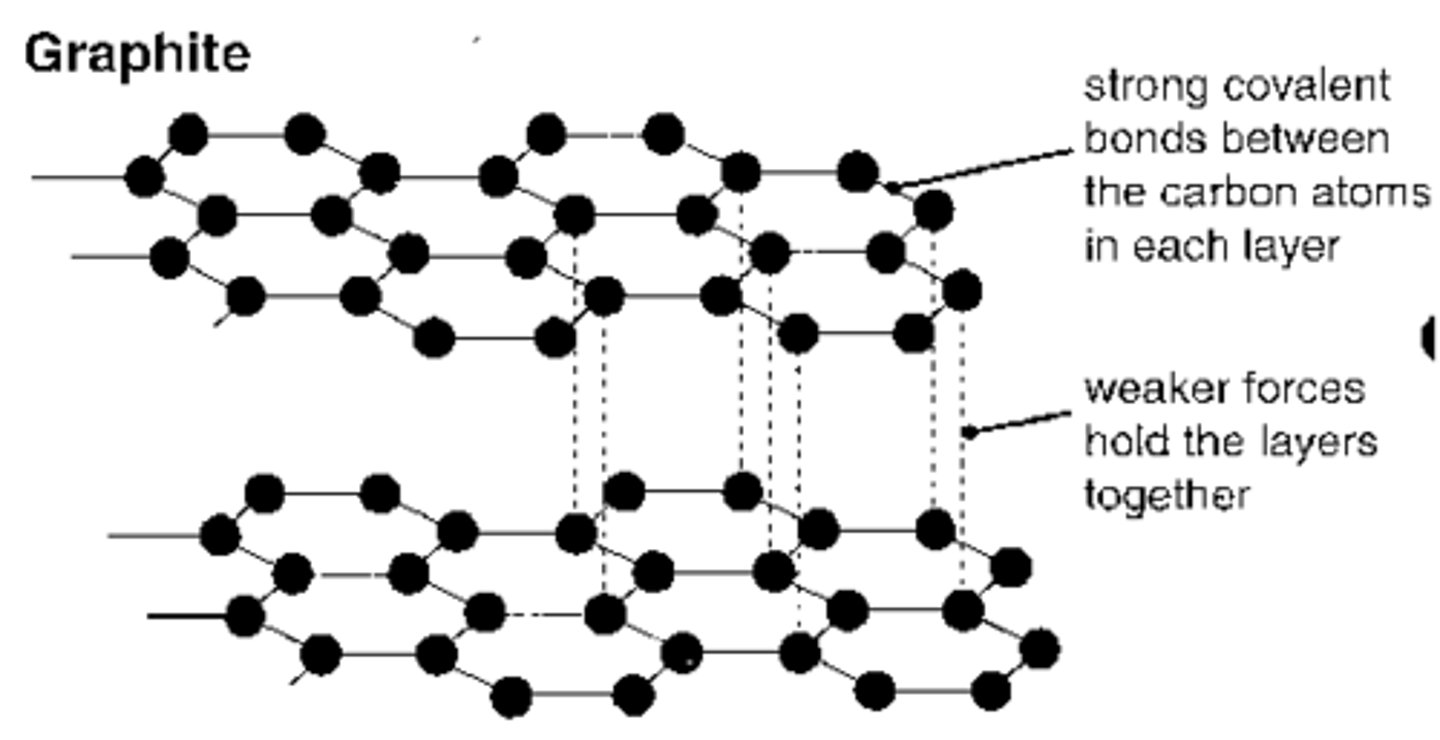
Draw and describe structure of graphite
Similar to diamond - macromolecular covalent - but each C atom is only bonded to 3 others, so it is in layers
Weak van der Waals forces of attraction between layers mean they can slide over each other → soft, slippery
One electron from each carbon is delocalised and can carry charge → conducts electricity
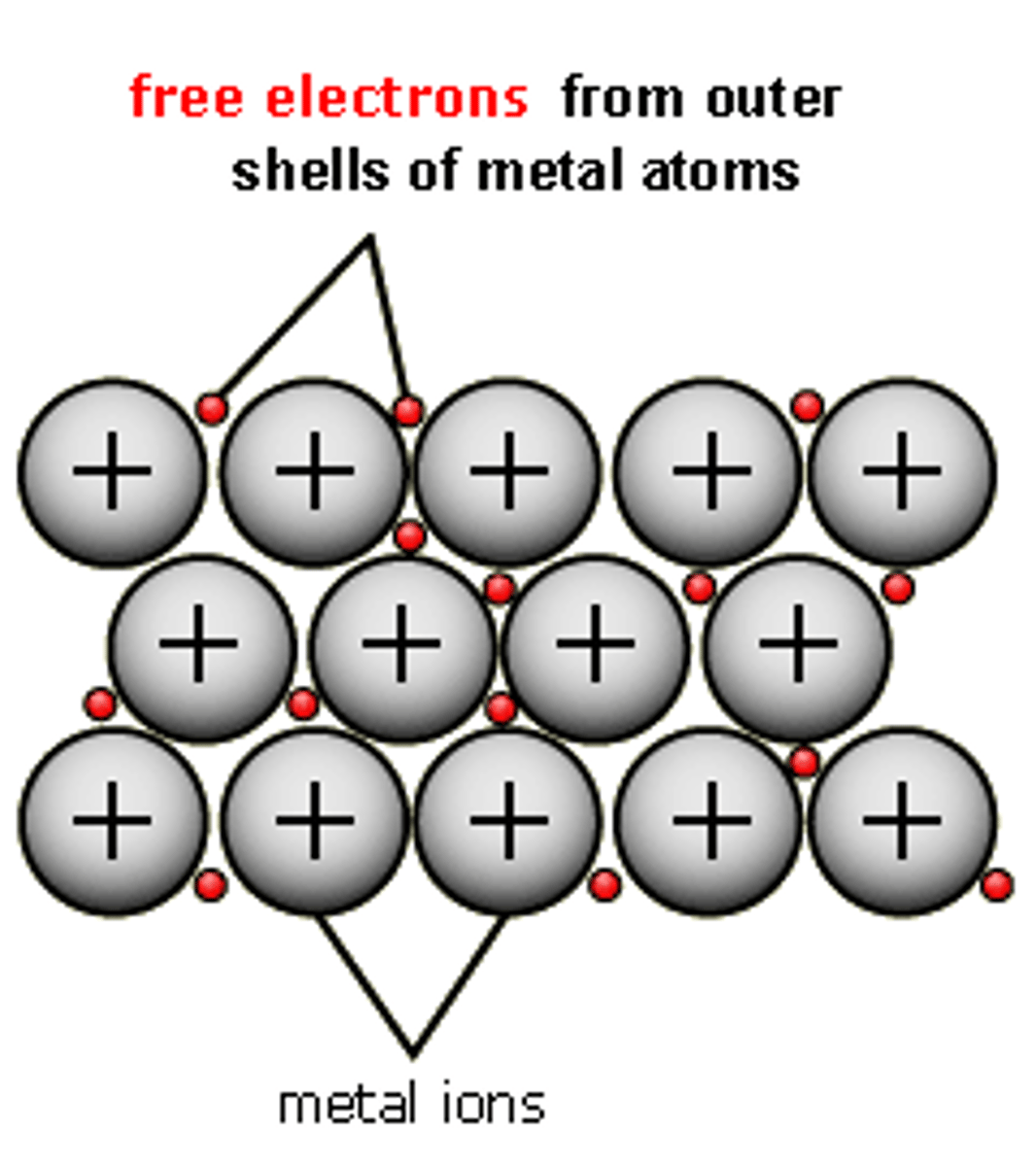
Describe and draw metallic bonding
Describe and draw metallic bonding
Lattice of positive metal ions strongly attracted to a sea of delocalised electrons. Layers can slide over each other - malleable
Do metallic compounds have high/low bpt and mpts? why?
Do metallic compounds have high/low bpt and mpts? why?
High as strong forces of attraction between positive metal ions and negatively charged sea of delocalised electrons
Do metallic compounds conduct electricity? why?
Do metallic compounds conduct electricity? why?
Yes as delocalised outer shell electrons can move throughout the metal to carry charge
How does the strength of metallic bonds change across the periodic table? Why?
How does the strength of metallic bonds change across the periodic table? Why?
Increases → higher Melting and boiling points, stronger
Higher charge on metal ions
More delocalised electrons per ion
Stronger force of attraction between them
Define electronegativity
Define electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract the pair of electrons (the electron density) in a covalent bond
What affects electronegativity? (3)
What affects electronegativity? (3)
Nuclear charge
Atomic radius
Electron shielding
What is the most electronegative element?
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine (4.0 on Pauling's scale) → largest nuclear charge for its electron shielding, small atomic radius
How do you get a nonpolar bond?
How do you get a nonpolar bond?
Both bonding elements have the same electronegativities
When do you get a polar bond?
When do you get a polar bond?
Bonding atoms have different electronegativities
What is the strongest type of inter-molecular force?
What is the strongest type of inter-molecular force?
Hydrogen bonding
What is the weakest type of inter-molecular force?
What is the weakest type of inter-molecular force?
van der Waals forces
Describe van der Waals' forces of attraction.
Describe van der Waals' forces of attraction.
Temporary dipoles are created by the random movement of electrons → induces dipole in neighbouring molecule → temporary induced dipole-dipole attraction aka van der Waals forces of attraction
Are Van der Waals forces greater in smaller or larger molecules?
Are Van der Waals forces greater in smaller or larger molecules?
Larger- more electrons
Describe permanent dipole-dipole attraction
Describe permanent dipole-dipole attraction
Some molecules with polar bonds have permanent dipoles → forces of attraction between those dipoles and those of neighbouring molecules
What conditions are needed for hydrogen bonding to occur?
What conditions are needed for hydrogen bonding to occur?
O-H, N-H or F-H bond, lone pair of electrons on O, F, N
Because O, N and F are highly electronegative, H nucleus is left exposed
Strong force of attraction between H nucleus and Lone pair of electrons on O, N, F
Draw a diagram of hydrogen bonding
Draw a diagram of hydrogen bonding
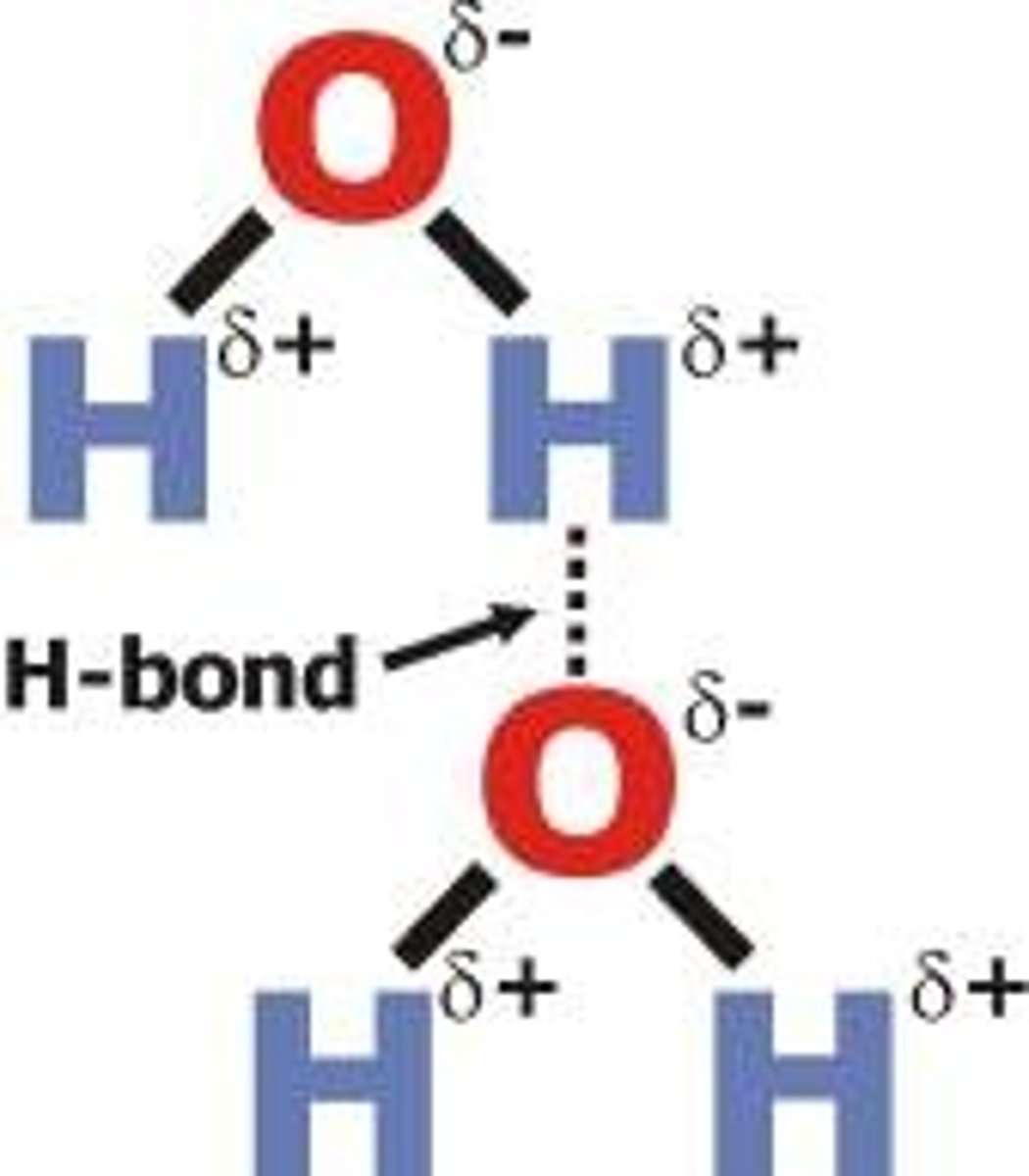
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
In liquid water, hydrogen bonds constantly break and reform as molecules move about
In ice, the hydrogen bonds hold the molecules in fixed positions; this makes them slightly further apart than in liquid water
What is a dative/co-ordinate covalent bond? When is it formed?
What is a dative/co-ordinate covalent bond? When is it formed?
Formed when an electron deficient atom/ion accepts a lone pair of electrons from an atom/ion with a lone pair of electrons (not used in bonding)
Draw the formation of a dative covalent bond in ammonia
Draw the formation of a dative covalent bond in ammonia
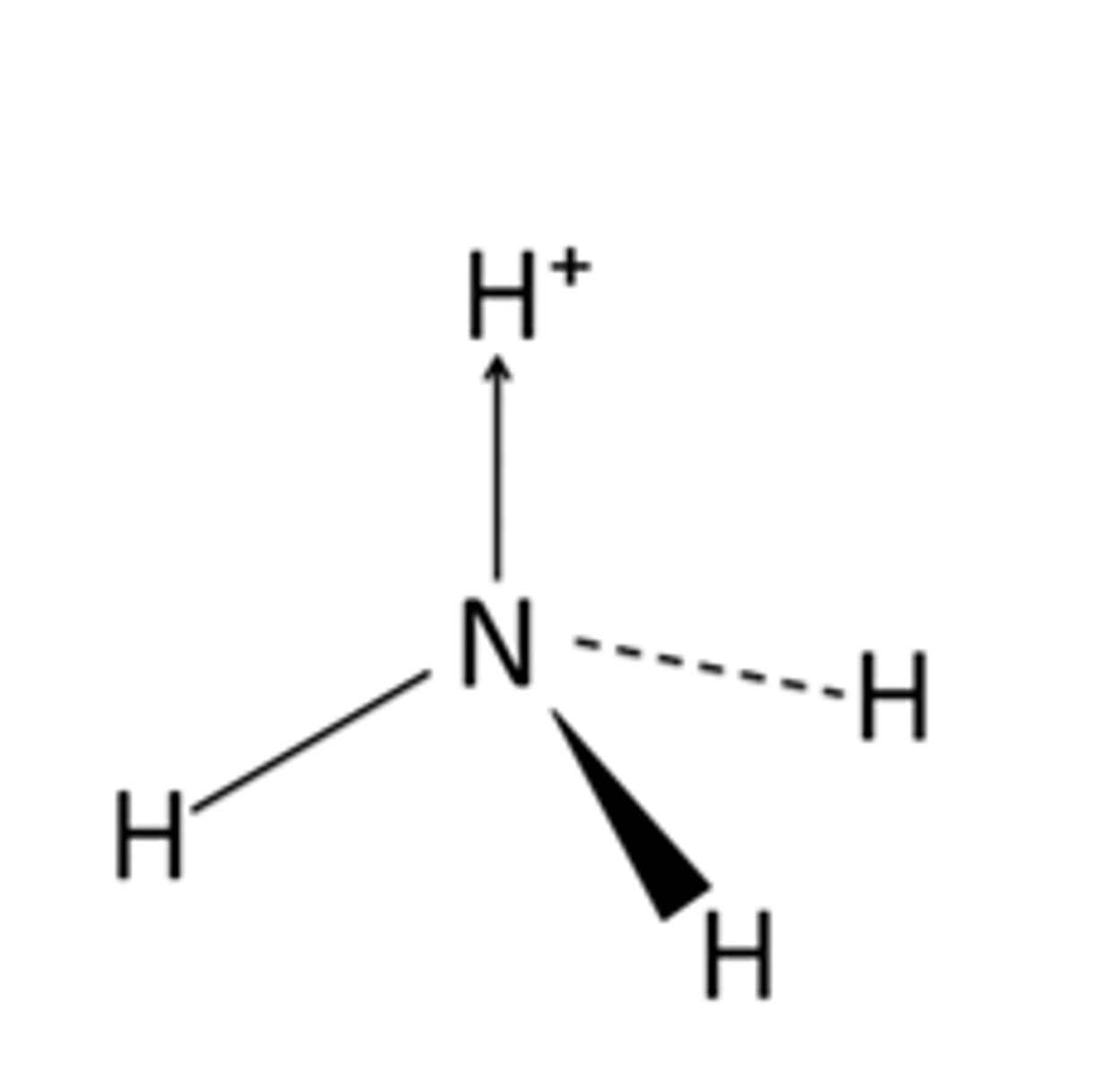
What does the shape of molecules depend on?
What does the shape of molecules depend on?
Number of electrons in the valence shell of the central atom
Number of these electrons which are in bonded or lone pairs
What does the Electron Pair Repulsion Theory state?
What does the Electron Pair Repulsion Theory state?
that electron pairs will take up positions as far away from each other as possible, to minimise the repulsive forces between them
Which experience the most repulsion?
Lone pair-lone pair
Lone pair-bonded pair
Bonded pair- bonded pair
Which experience the most repulsion?
LP-LP repulsion strongest
LP-BP repulsion middle
BP-BP repulsion weakest
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 2 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 2 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Linear
180°

What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 3 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs?
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 3 bonding pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Trigonal planar
120°
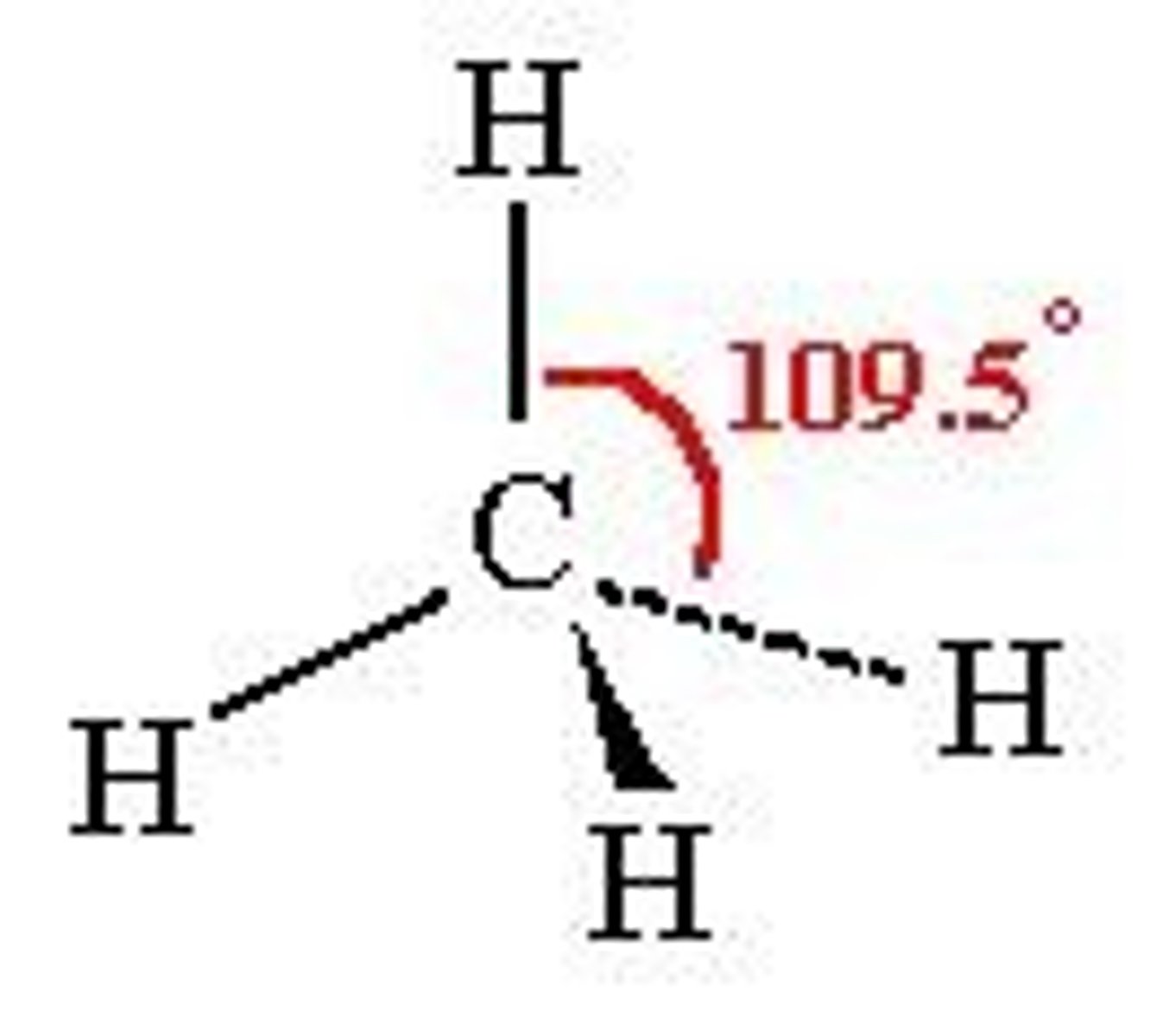
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 4 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 4 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Tetrahedral
109.5°
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 5 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 5 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Trigonal bipyramid
90° and 120°
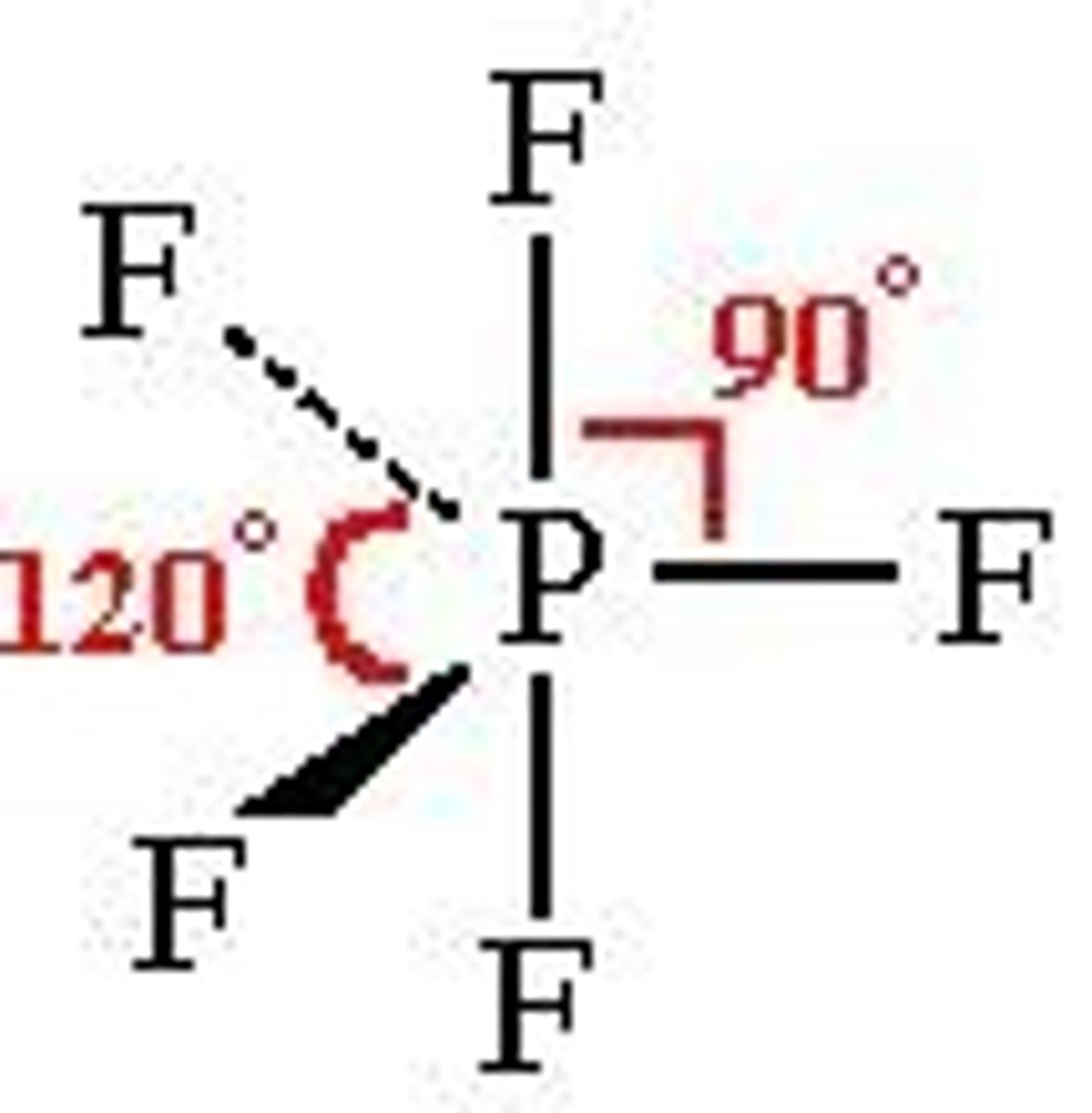
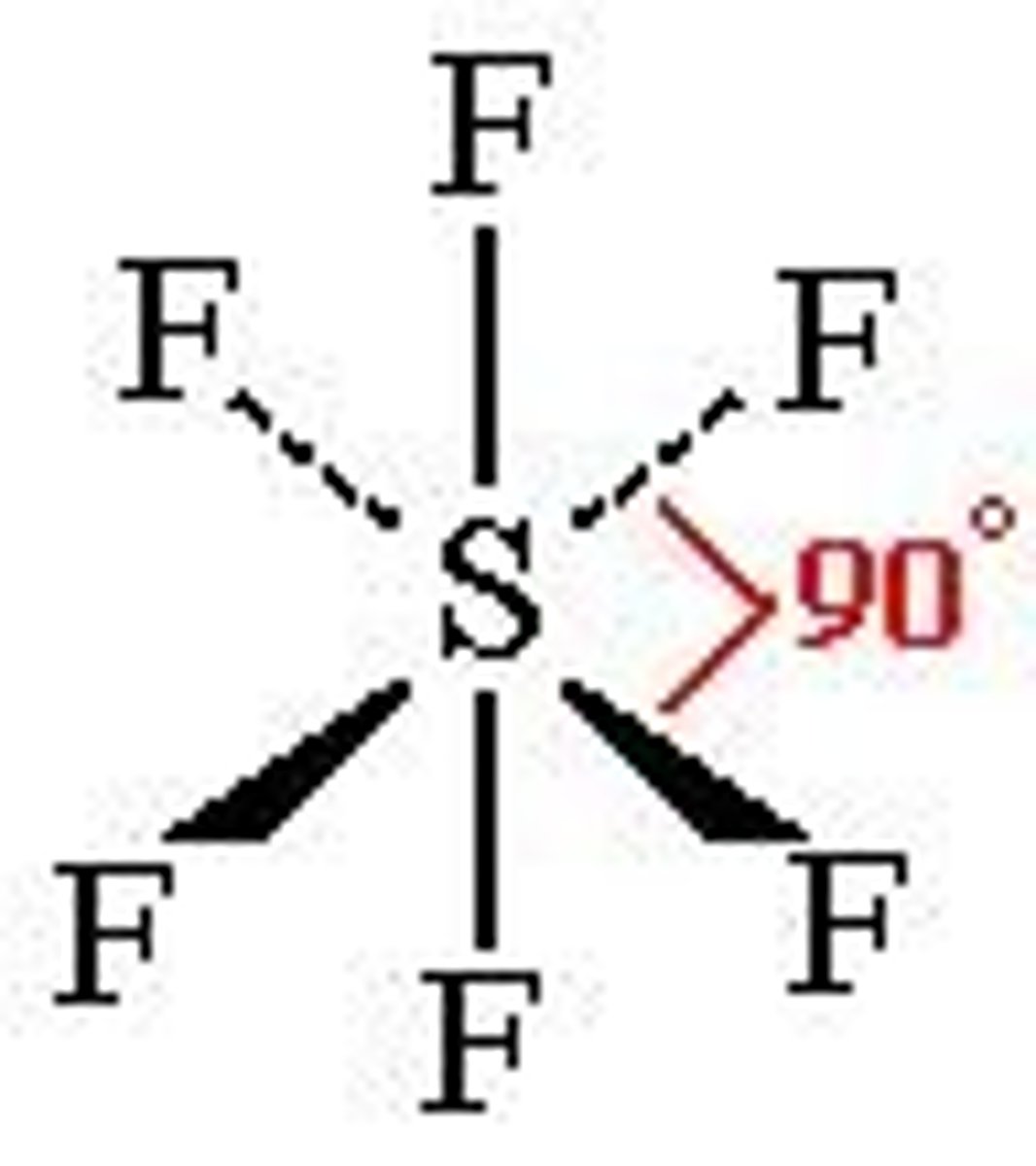
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 6 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
What is the shape, diagram and bond angle in a shape with 6 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
Octahedral
90°