Exam 3 - Biochemistry
1/467
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Biochem Exam 3 with Dr. Hnatiuk at Cedarville University (BIO-3710)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
468 Terms
Galactosemia
Rare disorder that interferes with the metabolism of galactose; causes vomiting and diarrhea after milk consumption, enlargement of the liver, jaundice, cataracts, lethargy, and delayed neurological development
An inherited deficiency in galactose 1-phosphate uridyl transferase activity
What often causes galactosemia?
Cataract
The clouding of the lens of the eye due to pathological protein aggregation
Aldose reductase catalyzes the reduction of galactose to galactitol in the lens when the transferase is not active. Galactitol is poorly metabolized and accumulates. Water diffuses into the lens to maintain osmotic balance, triggering the formation of cataracts
How are cataracts formed?
Lactase
An enzyme that cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose
Lactobacillus
_____ is one example of an industrially useful anaerobic bacterium.
Control sites
Enzymes catalyzing irreversible reactions in metabolic pathways are _____ _____ that are controlled by allosteric effectors, covalent modification, or regulating transcription.
Hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase
In glycolysis, three enzymes catalyze irreversible reactions:
Contraction
Glycolysis in skeletal muscle provides ATP primarily to power _____.
ATP, AMP
The primary control of muscle glycolysis is the ratio of ____ to ____.
Phosphofructokinase
High levels of ATP allosterically inhibit _____.
AMP
_____ reverses the inhibitory action of ATP.
Increases
Enzyme activity _____ when the ATP/AMP ratio is lowered.
Committed step
The first irreversible reaction unique to the glycolytic pathway
Phosphorylation of F-6P to F-1,6-BP by phosphofructokinase
What is an example of a committed step?
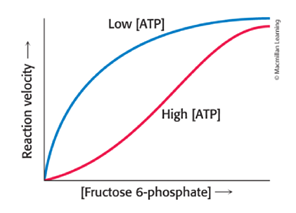
Hyperbolic, sigmoidal
High [ATP] converts the _____ binding curve of F-6P into a _____ one.
pH
A decrease in ___ inhibits phosphofructokinase activity by augmenting the inhibitory effect of ATP (occurs when muscle is functioning anaerobically and producing excessive lactic acid and prevents muscle damage from too much acid).
Because adenylate kinase forms ATP from ADP
Why is ADP not the positive regulator of phosphofructokinase?
Low-energy
AMP serves as the signal for the ____-____ state.
Because in the cell [ATP] > [ADP] > [AMP], meaning small changes in [ATP] result in larger changes in [AMP];
Why does AMP as an allosteric regulator provide sensitive control?
G-6P (its product)
Hexokinase is inhibited by _____ in muscle.
High [G-6P] signals that the cell no longer requires glucose for energy or synthesis of glycogen, which leads to glucose remaining in the blood
How is hexokinase inhibited by its product in muscle?
Because a rise in [F-6P] leads to a rise in [G-6P] as they are in equilibrium
Why does inhibition of phosphofructokinase lead to the inhibition of hexokinase in muscle?
ATP, high
Pyruvate kinase is allosterically inhibited by ____, which slows glycolysis when the energy charge is ____.
Feedforward stimulation (feedforward activation)
Occurs when products of a preceding irreversible step activate the enzyme
When the pace of glycolysis increases, F-1,6-BP activates the kinase
What is an example of feedforward stimulation?
Regulation of Glycolysis in Muscle
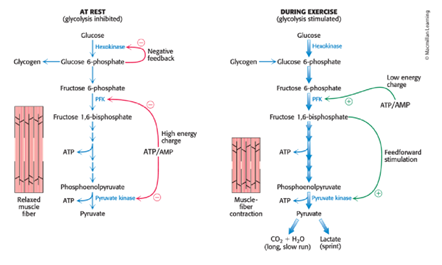
Blood-glucose, reducing power, synthesizes
The liver maintains ____-____ concentration, generates _____ _____ for biosynthesis, and _____ biochemicals.
ATP, ATP
Liver phosphofructokinase can be regulated by _____, although this is not an important metabolic signal as the liver does not experience sudden _____ needs.
pH
Liver phosphofructokinase can be regulated by ____, although this is not an important metabolic signal as the liver does not produce lactate.
Citrate, citric acid cycle
In the liver, phosphofructokinase is inhibited by _____, an early intermediate in the ____ ____ ____, by enhancing the inhibitory effect of ATP.
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP)
In the liver, phosphofructokinase is activated by _____.
Binding of F-2,6-BP increases the affinity of the enzyme for F-6P and diminishes the inhibitory effect of ATP
How is phosphofructokinase activated by F-2,6-BP?
Accelerates
High F-6P (accelerates/decelerates) the synthesis of F-2,6-BP.
G-6P (its product)
In the liver, hexokinase is inhibited by _____.
Glucokinase
A specialized isozyme of hexokinase that provides G-6P for glycogen synthesis and fatty acid formation; not inhibited by G-6P; functions as a monomer, but displays sigmoidal kinetics
Abundant
Glucokinase phosphorylates glucose only when glucose is _____.
The liver-specific glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP) when [glucose] is low
What inhibits glucokinase in the liver?
L type (predominates in the liver) and M type (predominates in muscle and the brain)
What isozymic forms of pyruvate kinase are present in mammals?
ATP, alanine
In the liver, pyruvate kinase is allosterically inhibited by ____ and _____.
Reversible phosphorylation
In the liver, the L form of pyruvate kinase is controlled by _____ _____.
Glucagon-triggered cyclic AMP cascade (when blood-glucose level is low)
What leads to the phosphorylation of pyruvate kinase in the liver, diminishing its activity?
Substrate channeling
Process that facilitates movement of substrates and products between enzymes; increases enzyme efficiency and prevents the release of any toxic intermediates
Gluconeogenesis
The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors; converts pyruvate into glucose; occurs mainly in the liver, with a small amount in the kidney and other tissues; important during starvation and fasting
Lactate, amino acids, glycerol
The major precursors for gluconeogenesis are _____, _____, and _____.
Lactate dehydrogenase
_____ _____ converts lactate into pyruvate.
Glycerol, fatty acids
Triacylglycerol hydrolysis in fat cells yields _____ and ____ ____.
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Glycerol enters either the gluconeogenic or the glycolytic pathway as _____ _____.
The conversion of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone phosphate
The Pathway of Gluconeogenesis
Bypassed
The three irreversible steps in glycolysis must be _____ in gluconeogenesis.
Hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase
What are the three irreversible reactions in glycolysis?
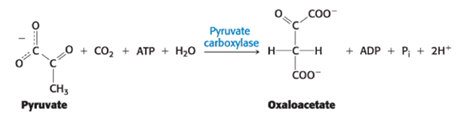
Pyruvate carboxylase
What enzyme catalyzes the carboxylation of pyruvate to oxaloacetate using a molecule of ATP?
Oxaloacetate
The conversion of pyruvate into phosphoenolpyruvate begins with the formation of _____.
Mitochondria, biotin
The conversion of pyruvate into phosphoenolpyruvate occurs in the _____ and requires _____.
Biotin
A covalently attached prosthetic group which serves as the carrier of activated CO2 in the conversion of pyruvate into phosphoenolpyruvate.
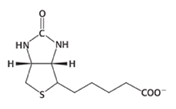
Lys, amide
The carboxylate group of biotin is linked to the epsilon-amino group of a specific ____ residue by an _____ bond.
Three
The carboxylation of pyruvate takes place in _____ stages.
Tetramer, four, four
Pyruvate carboxylase functions as a _____ composed of ____ identical subunits, each of which contains ____ domains.
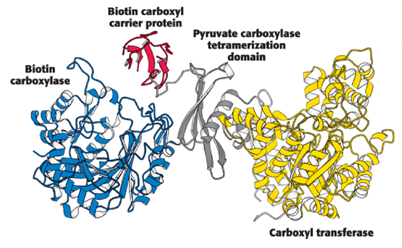
BC, BCCP, CT, and PT
What are the four domains of pyruvate carboxylase?
Biotin carboxylase domain (BC)
Catalyzes the formation of carboxyphosphate and the attachment of CO2 to the biotin carboxyl carrier protein domain (BCCP)
Biotin carboxyl carrier protein domain (BCCP)
Swings to the active site of the carboxyl transferase domain (CT)
Carboxyl transferase domain (CT)
Transfers the CO2 to pyruvate to form oxaloacetate
Pyruvate carboxylase tetramerization domain (PT)
Facilitates the formation of the tetramer and is the binding site for acetyl CoA, a required allosteric activator
Malate dehydrogenase
What enzyme catalyzes the reduction of oxaloacetate to malate?
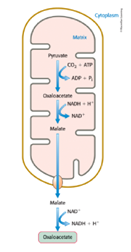
Mitochondria, cytoplasm
Malate is transported from the _____ to the _____ by a cytoplasmic NAD+-linked malate dehydrogenase and reoxidized to oxaloacetate.
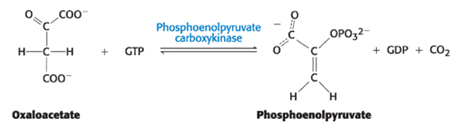
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
What enzyme decarboxylates and phosphorylates oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate?
GTP
What is the phosphoryl donor for the conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate?
The reactions catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
What two reactions bypass the pyruvate kinase reaction in glycolysis?
Reverse, irreversible
Phosphoenolpyruvate is metabolized by the enzymes of glycolysis in the _____ direction until the next _____ step.
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (allosteric enzyme)
What enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate and Pi?
Phosphatase
An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a phosphate to form inorganic phosphate
Whether the phosphate is transferred to water or ADP
What is the difference between kinases and phosphatases?
Liver
The generation of free glucose occurs primarily in the _____.
Lumen
For the generation of free glucose, glucose 6-phosphate is transported into the _____ of the ER.
Glucose 6-phosphatase
What enzyme hydrolyzes glucose 6-phosphate to glucose?
The ER membrane
To what is glucose 6-phosphatase bound?
Glycogen
In most tissues, glucose 6-phosphate is converted into _____ for storage.
Unfavorable (unless it is coupled to favorable reactions)
The formation of glucose from pyruvate is energetically _____.
-48
The Gibbs free energy of gluconeogenesis is ____ kJ/mol.
+90
The Gibbs free energy for the reversal of glycolysis is ____ kJ/mol.
Reactions of gluconeogenesis
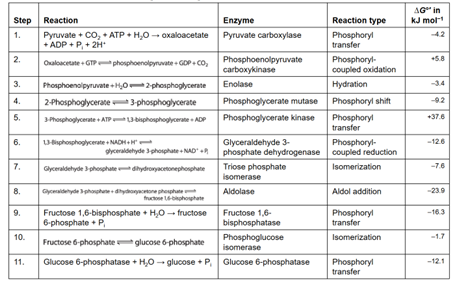
Inactive, active
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are regulated within a cell such that one pathway is relatively ____ whereas the other is highly _____.
When energy or glycolytic intermediates are needed
When does glycolysis predominate over gluconeogenesis?
When there is a surplus of energy and glucose precursors
When does gluconeogenesis predominate over glycolysis?
The interconversion of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and fructose 6-phosphate
What is a key regulation site for glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, phosphofructokinase
When energy is needed AMP inhibits _____ and stimulates _____, which turns on glycolysis and inhibits gluconeogenesis.
Phosphofructokinase, fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
When levels of ATP and citrate are high, ATP and citrate inhibit _____, and the decrease in AMP relieves _____ inhibition, which turns off glycolysis and turns on gluconeogenesis.
Liver
Reciprocal regulation at the interconversion of phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate occurs in the _____.
Allosteric effectors ATP, alanine
Pyruvate kinase is inhibited by _____ _____ _____ and _____.
ADP
Pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase are inhibited by _____.
Acetyl CoA
Pyruvate carboxylase is activated by _____.
Reciprocal regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis in the liver

Blood-glucose
The rates of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are adjusted in the liver to maintain _____ levels.
F-2,6-BP
_____ stimulates phosphofructokinase and inhibits fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase.
Loses, F-6P
When blood glucose is low, F-2,6-BP ____ a phosphoryl group to form _____.
Is not
F-6P (is/is not) an allosteric effector of PFK.
Bifunctional enzyme
Contains two enzymes on a single polypeptide chain
Phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK2), fructose bisphosphatase 2 (FBPase2)
A bifunctional enzyme, containing _____ and _____, determines F-2,6-BP levels.
PFK2 forms F-2,6-BP and FBPase2 degrades F-2,6-BP
What two enzymes regulate F-2,6-BP concentrations?