Chapter 2: The Balance Sheet
Objective 2.1: Identify financial effects of common business activities that affect the balance sheet.
Making a Balance Sheet
- The three sections of the balance sheet consist of what is in the basic accounting equation:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Stockholders’ Equity
- As a reminder: Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity
Financing and Investing Activities
When starting a company, a key factor is financing, which has two types:
- Debt financing - the money and loans that a business borrows from banks and will repay in the future. A business must repay its debt financing.
- Equity financing - raising money by selling shares to your stockholders or investors. Equity financing is not obligated for a business to repay.
After financing, the next step in for the business to start investing in assets like supplies, equipments, logos, office space, etc.
There are three features in accounting:
1.) Companies documents all activities (loans, purchases, sales)
2.) There is ALWAYS a give and a get in exchanges/transactions
3.) Following the cost principle, a designated dollar amount is chosen (ex: The American dollar)
Transactions and Other Activities
- Companies have external exchanges and internal events
- External exchanges happen between a company and someone. For example, this can be a company selling a product to a customer.
- Internal events involve, within a company, privately utilizing assets to create another asset such as selling a product to get cash.
Objective 2.2: Apply transaction analysis to accounting transactions.
The Accounting Cycle
- The accounting cycle is used to report the financial information of a company.
- Accounting cycles occur day after day, month after month, and year after year.
- Each transaction, which is a business activity that has an affect on the basic accounting equation, is recorded.
- The accounting cycle occurs in the following order:
- Analyze
- Record
- Summarize
- Prepare a Trial Balance
- Report Financial Statements
- After these steps, the cycle starts from the beginning again.
- During the analyzing stage, two ideas must be considered:
- Each transaction involves a duality of effects, meaning it has two effects on the basic accounting equation.
- Assets must ALWAYS equal Liabilities + Stockholders’ Equity
Step 1: Analyze Transactions
- Account titles are given to items that are exchanged, whether they are assets, liabilities, or stockholders’ equity.
- A chart of accounts contains many of the common account titles. Some examples include:
| Assets, Liabilities, or S/E | Account Title |
|---|---|
| Asset | Cash |
| Asset | Equipment |
| Liability | Accounts Payable |
| Liability | Notes Payable |
| Stockholders’ Equity (S/E) | Common Stock |
| Stockholders’ Equity (S/E) | Retained Earnings |
Example Transaction Report:
- A company buys supplies on account for $1,000 (asset increases, liability increases):
| Supplies (+) | Debit $1,000 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable (+) | Credit $1,000 |
- Later, the company will repay the Accounts Payable of $1,000 (liability decreases, asset decreases):
| Accounts Payable (-) | Debit $1,000 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash (-) | Credit $1,000 |
- Exchanges that consists of only promises are not considered to be transactions, therefore they do not need to be reported because they have no effect on the basic accounting equation.
Step 2 and 3: Record and Summarize
Transactions can be recorded using a spreadsheet.
Journal entries are created to record financial effects.
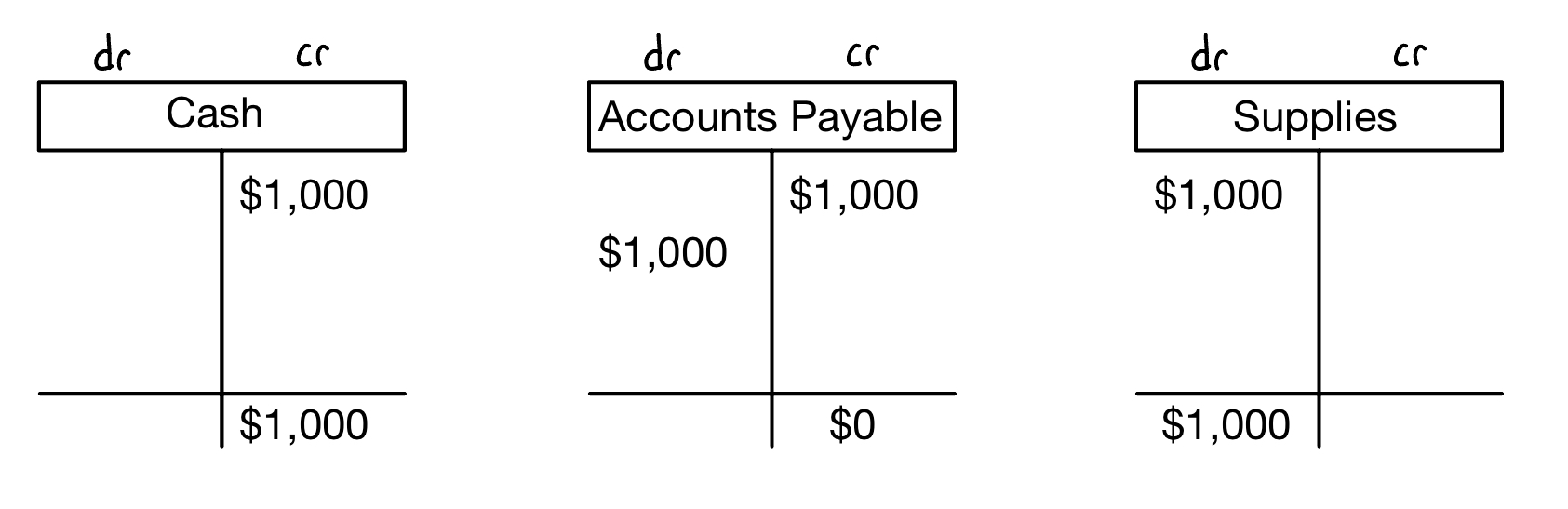
After creating a collect of journal entries, this information is then summarized into ledger accounts (T-accounts)
- A T-account has a spot to put the account name, a spot for debits, a spot for credits, and a spot to put the account’s ending balance
- Debits (dr) are on the left and credit (cr) are on the right.
- An example of T-accounts using the last two examples
Objective 2.3: Use journal entries and ledger accounts (T-accounts) to show how transactions affect the balance sheet.
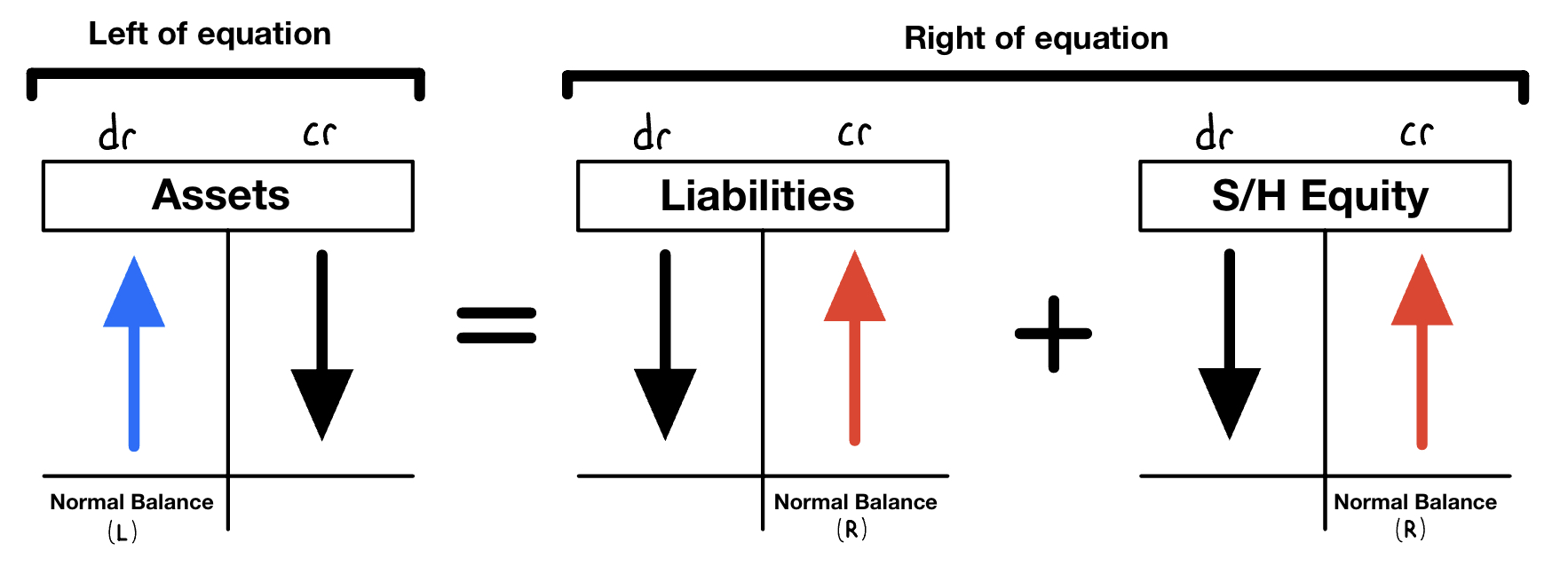
The Debit and Credit Framework
Assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity all have a normal balance, being either a debit or a credit. Their normal balance is the side that makes the account increase.
- Assets have a normal DEBIT balance
- Liabilities have a normal CREDIT balance
- Stockholders’ Equity has a normal CREDIT balance
TIP: An account’s normal balance is on the side it appears in the basic accounting equation
A (left) = L (right) + S/H (right)
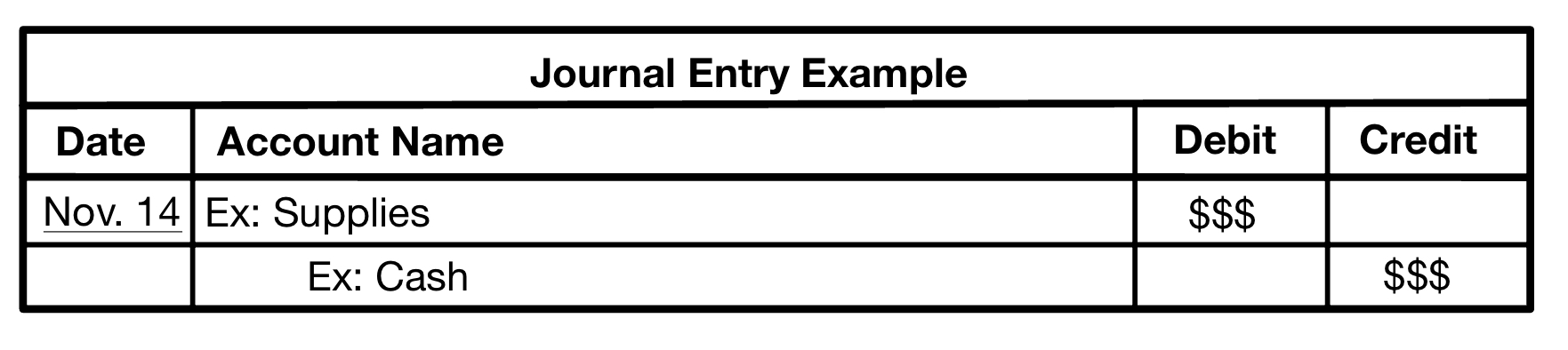
The debit/credit framework is used when making journal entries, which shows how transactions effect accounts.
A journal entry can contain several different accounts and are listed by date in which the transaction occurred.
A journal entry includes:
- The date of a transaction
- The account name
- Debits
- Credits
Objective 2.4: Prepare a trial balance and a classified balance sheet.
Step 4: Preparing the Trial Balance
- A trial balance totals up the debits and credits of each account, but it is considered a draft and not a final.
- A trial balance example would be:
| Account Name | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | $24,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $1,200 | |
| Supplies | $600 | |
| Equipment | $3,500 | |
| Dividends | $100 | |
| Salaries Expense | $3,600 | |
| Utility Expense | $300 | |
| Accounts Payable | $600 | |
| Unearned Revenue | $4,000 | |
| Common Stock | $20,000 | |
| Service Revenue | $9,500 |
- Total of Debits = $34,100
- Total of Credits = $34,100
- Debits = Credits ($34,100 = $34,100)
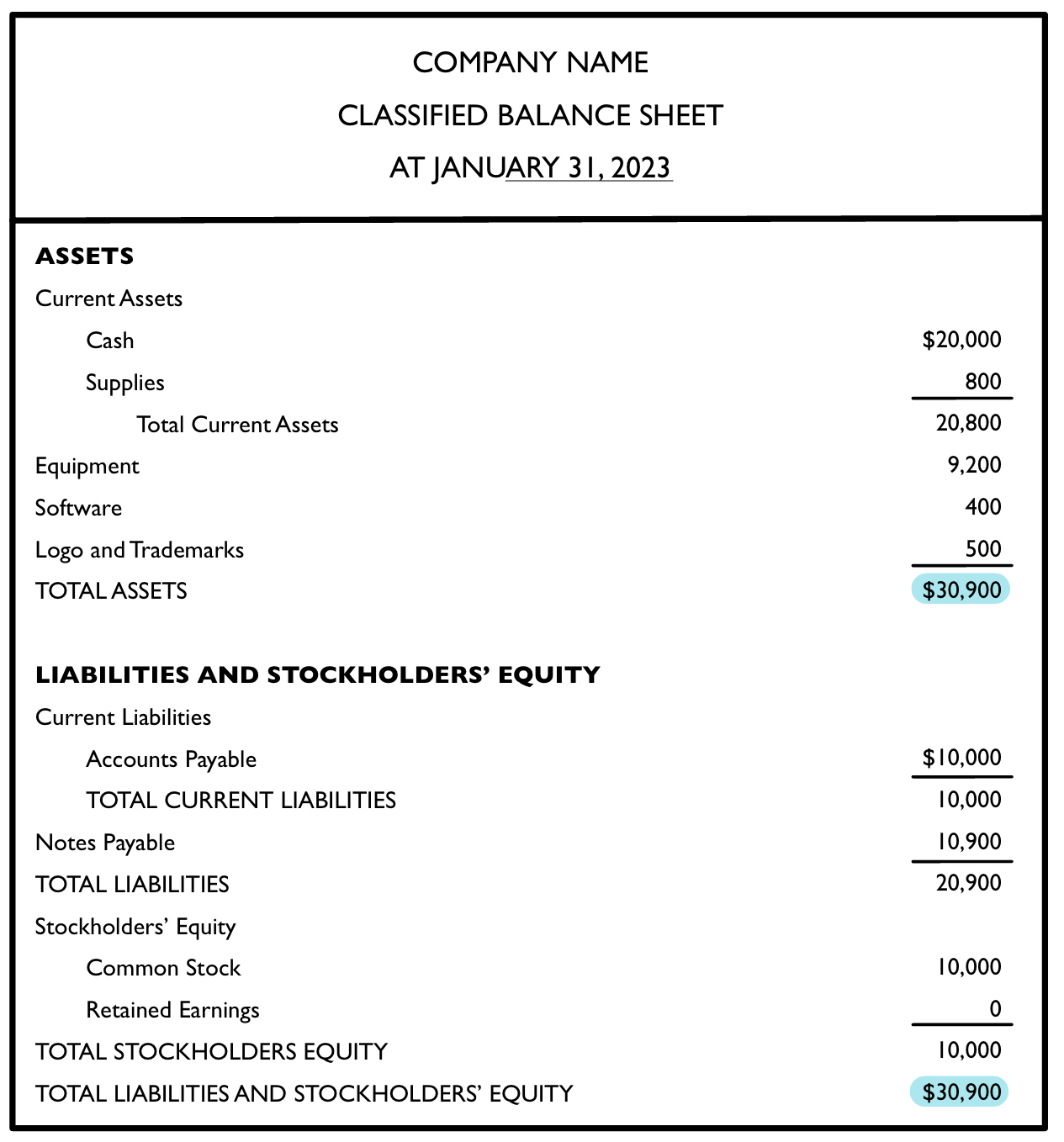
Step 5: Preparing a Classified Balance Sheet
The classified balance sheet is the final after creating the draft and has a different format from the trial balance:
- Assets
- Current Assets
- Total Current Assets
- Other Assets
- Total Assets
- Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity
- Current Liabilities
- Total current liabilities
- Other liabilities
- Total liabilities
- Stockholders’ Equity
- Total Stockholder’s Equity
- Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity
Current vs Non-current
- Current Assets: Aka short term assets, will be used or sold within the year.
- Non-current Assets: Aka long term assets, will not be used or sold within the year.
- Current Liabilities: Aka short term liabilities, will be due and repaid within one year.
- Non-current Liabilities: Aka long term liabilities, will be paid after a year or more.
Objective 2.5: Interpret the balance sheet using the current ratio and an understanding of related concepts.
The Current Ratio
The current ratio provides information on a company’s ability to pay.
You want to have more assets than liabilities.
==Equation to calculate current ratio:==
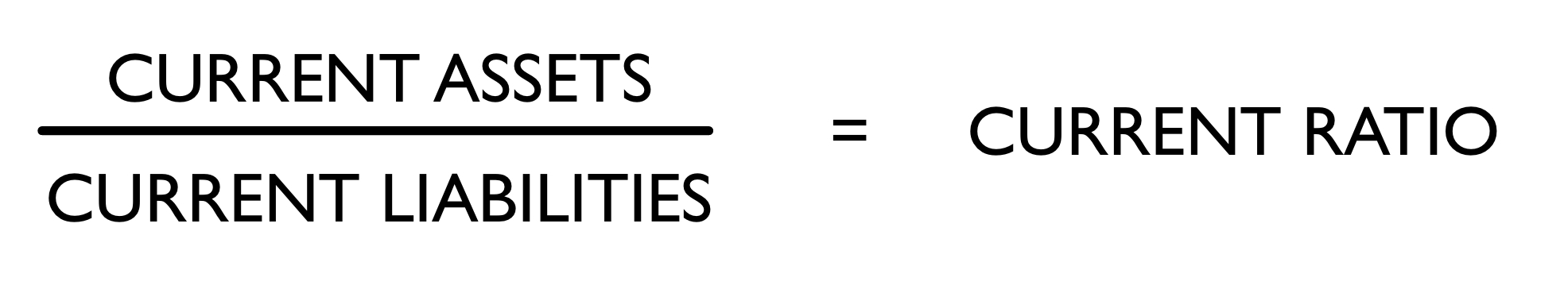
Current ratio example (using classified balance sheet from above)
- Total current assets were $20,800.
- Total current liabilities were $10,000.
- 20,800 ➗ 10,000 = 2.08
- The current ratio = 2.08
Balance Sheet Concepts and Values
- The process of recording and reporting transactions has an effect on:
- What is and is not recorded on the balance:
- Assets like cash, equipment, and supplies can be effected.
- Although ethics, creativity, and vision are not listed, they can still be effected.
- The cost amounts assigned to the recorded items:
- When first recorded, assets and liabilities are recorded at initial cost, following the cost principle.
- If the value of an asset decreases, we adjust the value recorded.