INT FIN - CH 14 Interest Rate and Currency Swaps
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
The Cost of Debt
The cost of debt consists of the risk-free rate of interest plus the credit risk premium.
Credit Ratings
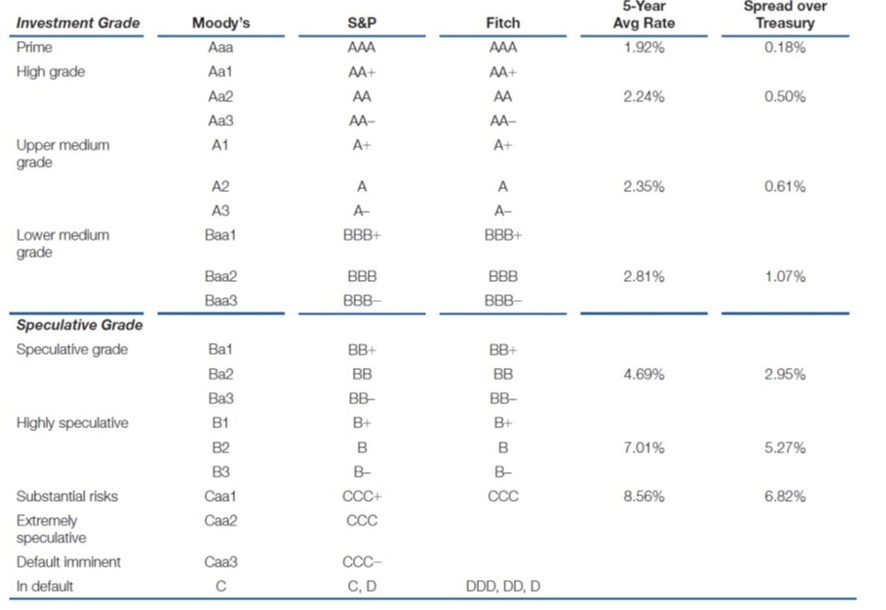
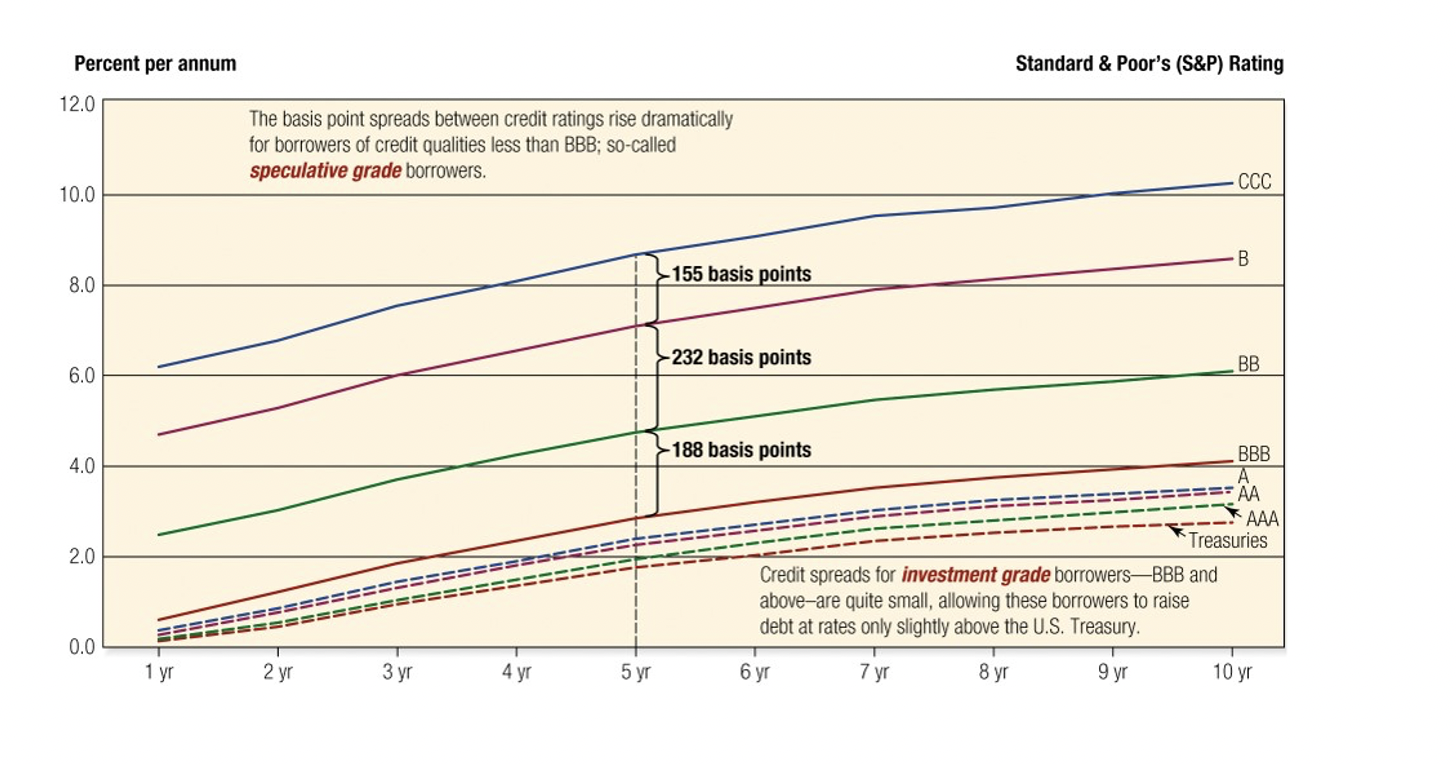
U.S. Corporate Credit Spreads
When you’re near investment grade the spread is relatively narrow
When you get more speculative, the spread increases
Credit risk or roll-over risk
will the credit rating change overtime. Lender reevaluates you when renewing a loan.
the risk the lender will change how they view your (the borrower) creditworthiness at renewal time, and may refuse or increase rates
Repricing risk
The risk that the interest rate you pay (or receive) will change when the contract resets
Managing Debt Cost, Interest Rate and FX Risks
In order to decrease debt cost, better match cash flows, and hedge currency (FX) risks, multinational firms have certain tools available.
•Borrowing and Lending in Eurocurrency Markets
•Interest Rate Swaps
•Currency Swaps
Eurocurrency
Eurocurrency is a time deposit in an international bank located in a country different from the country that issued the currency.
•For example, Eurodollars are deposits of U.S. dollars in banks located outside of the United States, while Eurosterling are deposits of British pound sterling in banks outside of the United Kingdom.
Eurocurrency market
Eurocurrency market is an external banking system that runs parallel to the domestic banking system of the country that issued the currency. Costs are lower, spreads are narrower.
Eurocurrency market operates at the interbank and/or wholesale level, with most transactions being interbank transactions in the amount of $1,000,000 or more.
Alternative Risk-Free Rates (RFRs)
Beginning on January 1, 2022, a new series of reference rates, known collectively as Alternative Risk-Free Rates (R F Rs), went into effect for the various Eurocurrencies.
•These R F Rs are based on overnight wholesale transactions that are unsecured or secured repurchase or “repo” transactions and representative of actual market transactions.
•Representative of risk-free rates, or nearly risk-free rates.
Eurocredits
Eurocredits are short- to medium-term loans of Eurocurrency extended by Eurobanks.
A Eurobank gives out loans in a currency that is NOT the currency of the country the bank is located in.
•Because the loans are often too large for one bank to handle, Eurobanks will band together to form a bank lending syndicate to share the risk.
Credit risk on these loans is greater than on loans to other banks in the interbank market.
Interest rate on Eurocredits must compensate the bank for the added credit risk.
Single-currency interest rate swaps
Same currency. Only the type of interest changes.
interest rate swaps involving swapping interest payments on debt obligations that are denominated in the same currency
cross-currency interest rate swap
Different currencies + different interest payments
one counterparty exchanges the debt service obligations of a bond denominated in one currency for the debt service obligations of the other counterparty that are denominated in another currency.
In a regular interest rate swap:
You do NOT exchange the principal, only the interest payments.
In a cross-currency swap:
You DO exchange the principal at the start and at the end.
Size of the Swap Market

five most common currencies used to denominate interest rate and currency swaps
•U.S. dollar, euro, Japanese yen, the British pound sterling, and the Canadian dollar.
The Swap Bank
Swap bank is a generic term to describe a financial institution that facilitates swaps between counterparties.
Can be international commercial bank, investment bank, merchant bank, or independent operator.
Serves as either a swap broker or swap dealer
swap broker vs swap dealer
•As a broker, the swap bank matches counterparties but does not assume any of the risks of the swap.
•As a dealer, the swap bank stands ready to accept either side of a currency swap, and then later lay it off, or match it with a counterparty.
Swap Market Quotations
Swap banks will tailor the terms of interest rate and currency swaps to customers’ needs.
They also make a market in “plain vanilla” swaps and provide quotes for these and provide current market quotations applicable to counterparties with Aa or Aaa credit ratings.
It is convention for swap banks to quote interest rate swap rates for a currency against a local standard reference in the same currency and currency swap rates against a U S D reference rate.
Plain-Vanilla Swap Strategies
High-credit companies: use swaps to adjust fixed/floating without issuing new debt.
Low-credit companies: use swaps to try to get better rate terms than they would get directly in loan markets.
quality spread differential (QSD).
Necessary condition for a swap is a positive quality spread differential (Q S D).
QSD is the difference between the default-risk premium differential on the fixed-rate debt and the default-risk premium differential on the floating-rate debt. In general, the former is greater than the latter.