EXAM 1- HUSSEIN
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONLY BASED ON SG
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Describe the Lytic cycle of viruses/bacteriophages:
what happens to the host?
host’s membrane is damaged, cytoplasm leaks out
host cell RAPIDLY dies, releases virus particles
Describe the Lysogenic cycle of viruses/bacteriophages:
what happens to the host?
what does the virus to the host?
what period does the viral infection enter during this period?
host cell is NOT killed immediately—> instead is occupied by the virus
virus uses host as a “factory” for replicated viral genes
viral infection enters “latent” period during this process
What virus leads to mononucleosis and Burkitt lymphoma?
EBV/ HHV-4
OVERACTIVE immune response to EBV leads to ________________.
a. mononucleosis
b. Burkitt lymphoma
a
WEAK immune response to EBV leads to ________________.
a. mononucleosis
b. Burkitt lymphoma
b
CMV or cytomegalovirus or HHV-5 leads to WHAT consequences in fetuses?
disease? s/sx?
fetuses:
CMV disease
disease ranges from no defects to CYTOMEGALIC INCLUSION DISEASE
sym: jaundice, CNS damage
CMV or cytomegalovirus or HHV-5 leads to WHAT consequences in HIV/ AIDS pts.?
________ most common opportunistic infection in HIV
disease? leads to?
HIV/AIDs:
CMV retinitis (most COMMON opportunistic infection in HIV)
leads to: retinal detachment, blindness
Adenovirus can lead to what syndromes?
acute hemorrhagic cystitis
pharyngitis
usually w/ pink eye
pink eye (conjunctivitis)
Acute hemorrhagic cystitis caused by adenovirus is most common in what group of people?
boys
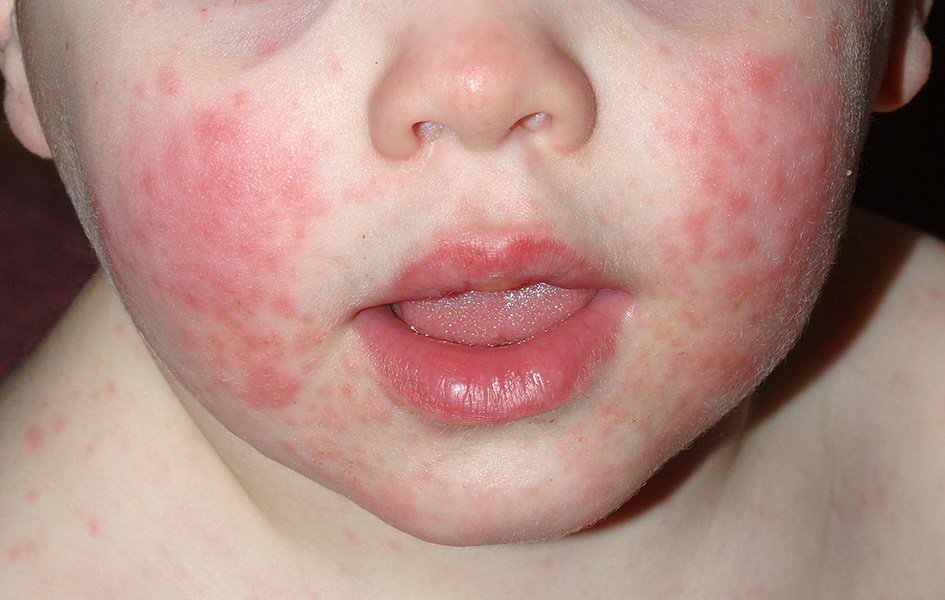
Parvovirus B19 usually infects what age group?
pediatrics/kids
Parvovirus B19 usually causes what fever? what symptoms?
slapped cheek fever
sym:
lacy body rash
facial rash
ALL DNA viruses replicate where?
What is the 1 exception to this?
ALL DNA viruses, replication occurs in the NUCLEUS
EXCEPTION: pox virus—> replication occurs in the CYTOPLASM
What are the modes of infection for HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)?
asymptomatic shedding
direct contact
SEXUAL CONTACT
birth
chewing
What is the major symptom of HPV?
WARTS!!!!!!!!
common warts
genital warts
CONDYLOMA ACUMINATUM (cauliflower-like wart)
HPV can lead to what kind of cancer? vaccine?
HPV can lead to CERIVCAL CANCER
vaccine: HPV vaccine (Gardasil)
usually given to young girls

Chickenpox is caused by what virus?
Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV) or HHV-3
How does chickenpox compare in young vs. old pts.?
which is there tx for?
when do children get vaccinated?
which age is the virus more severe in?
young
no tx, only support
children vaccinated after 12m (live, attenuated)
old
MORE SEVERE IN ADULTS
tx is antivirals
Chickenpox can reactivate later in life and this is called…
shingles or zoster
What is Shingles (Zoster)?
severe pain where?
limited to where?
severe pain in the nerve precedes lesions
limited to 1 DERMATOME (aka rash is limited to the skin supplied by that nerve, compared to chicken pox which is all over your body)
Chicken pox causes lesions that can break open and allow what bacteria to invade and cause secondary infections?
What can this infection lead to?
bacteria: S. pyrogenes (GAS)
S. pyrogenes infection can lead to NECROTIZING FASCIITIS
What are arboviruses?
what are arthropods?
infects who?
transmits virus from ______
“arthropod borne virus”
arthropods= mosquitos, ticks, sandflies, etc.
infects vertebrates and invertebrates
transmits virus from SALIVARY GLAND in the arthropod

ONLY _________ can transfer arboviruses from human-human.
MOSQUITOS

What is the vector for St. Louis encephalitis?
Culex mosquito

When does St. Louis encephalitis occur primarily?
a. late summer, early fall
b. early spring, late summer
c. late winter, early spring
d. only in the winter
a
What are symptoms of St. Louis encephalitis?
mild illness
severe illness
mild: fever, headache
severe: neck stiffness, convulsions, spastic paralysis
aseptic meningitis, severe encephalitis
How is HIV transmitted?
How is HIV NOT TRANSMITTED?
modes of transmission
blood, blood products (ex: needle drug injection)
sexual intercourse (semen, vaginal secretions)
vertical infection (mom—>baby)
iatrogenic (means HIV infections caused by medical interventions including unsafe procedures, contaminated blood, etc.)
Ex: healthcare prof reusing needles
NO TRANSMISSION BY CAUSAL CONTACT OR FECAL-ORAL ROUTE!!!!!!!!

How is polio transmitted?
person to person like fecal-oral
What are the different forms of polio? paralysis?
asymptomatic
symptomatic (muscle weakness, paralysis)
paralysis type:
spinal polio
bulbar polio
bulbospinal polio
What are 2 available vaccines for polio?
Which is preferred?
Which is live? killed?
Which is PO? injectable?
2 VACCINES: SABIN AND SALK
Sabin- live attenuated, oral, best
Sulk- killed, injectable
What symptom is commonly associated with yellow fever virus and hepatitis? why?
JAUNDICE!!!!
bc these viruses mess with the liver
Common vector of yellow fever?
mosquitoooooooo

Rhabdovirus aka rabies is transmitted how?
via infected saliva through BITE of rabid animals
dogs, raccoons, foxes, bats
How does the rabies virus reach the CNS?
travels along nerve fibers
What is the tx for rabies?
symptoms present
if suspected immediately after bite
IF SYMPTOMS ARE PRESENT—> TOO LATE—> NO TX
If suspected, immediately after bite
Post-exposure prophylaxis:
1 dose of human rabies immunoglobulin (HRIG)
Vaccination with the killed virus vaccine: 5 doses of rabies vaccine (On day 1, 3, 7, 14, 28)
What is the name of the antibody used for rabies tx?
HRIG or human rabies immunoglobulin
When is vaccination used for rabies?
in high risk groups
used in pre/post-exposure prophylaxis
What are the symptoms of Measles?
3 C’s—> cough, coryza, conjunctivitis
coryza- cold, acute rhinitis
Koplik spots (looks like salt grains in mouth)
rash (maculopapular rash from ears down)
What is a rare, but serious complication of measles?
subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (chronic CNS degenerative disease)
How is measles transmitted? (not in pp, but on his study guide)
Airbourne respiratory droplets
direct contact with contaminated sources
Rubella can cause serious teratogenic consequences in the _________ trimester.
a. first
b. second
c. third
d. fourth
a.
What are the teratogenic consequences that can be caused by rubella? s/sx?
CONGENITAL RUBELLA SYNDROME
group of physical abnormalities
sym: rash, low birth weight, heart abnormalities, visual problems, bulging fontanel MICROCEPHALY, PDA
How is the Hanta virus transmitted?
rodent feces/mouse droppings

Where in the US, is the Hanta virus most commonly seen?
Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah
What symptoms are commonly seen with ebola? is it deadly? most commonly found where?
Sym: BLLEDING EVERYWHERE (HEMORRHAGE)
vomiting blood
bloody urine
Deadly (>50% death rate)
mostly seen in Africa
What virus is the primary cause of pneumonia in CHILDREN?
RSV
What virus is main cause of primary viral pneumonia and secondary bacterial pneumonia?
Influenza A
List all the viruses that can be transmitted SEXUALLY:
HPV
HSV-1, HSV-2, CMV/HHV-5 (herpes)
HAV, HBV, HCV (hepatitis A-C)
HIV
List the viruses that are oncogenic:
EBV, HBV, HCV, HTLV, HPV
For each virus that is oncogenic, list the cancer it causes:
EBV—> Burkitt Lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lymphoma, thymic carcinoma
HBV and HCV—> primary hepatocellular carcinoma
HTLV—> “human T cell leukemia virus”—> leukemia/lymphoma
HPV—> cervical cancer
For + stranded and - stranded RNA viruses what enzymes (if any), are required for each?
+ stranded: NO RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE REQUIRED inside the virus
- stranded: YES, NEEDS RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE inside the virus
What is the strategy of replication used by + and - stranded RNA viruses?
RNA—> RNA
What is the infectivity ALONE of + stranded RNA and - stranded RNA?
+ stranded: INFECTIVE ALONE
- stranded: NON-INFECTIVE ALONE
What is the MOA of Acyclovir and Ganciclovir? What is required for its conversion from prodrug to active form?
What are the uses for these antivirals?
MOA: inhibits viral DNA replication
prodrug that requires viral THYMIDINE KINASE for activation
Uses: genital herpes and cold sores
Which of the following is a PROTEASE inhibitor?
a. Ritonavir
b. Amantadine
c. Oseltamivir
d. Zanamivir
a
What is HAART and what does it stand for?
stands for “Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy”
it is a cocktail of 2 or more different classes of anti-HIV drugs
What is the MOA of Amantadine? What virus does it target?
MOA: blocks the M2 ion channel
specific for type A influenza aka the FLU
(think: Amantadine—> Influenza A, M2)
Which antiviral drug is teratogenic?
Amantadine
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and Zanamivir (Relenza) belong to what class? MOA? Which viruses?
Neuraminidase Inhibitors
MOA: inhibit neuraminidase on influenza A AND B
Oseltamivir/Tamiflu can be used for tx and prevention. What is indication for treatment?
In pts. >1 given orally to tx uncomplicated infection in 1st 48 hrs
Zanamivir/Relenza can be used for tx and prevention. What is indication for treatment?
In pts. >5 given by inhalation to treat infection in the 1st 48hrs of symptoms
What animal prion disease occurs in sheep?
scrapie
What is the effect of UV light in scrapies?
not effective—>since prion diseases DONT have DNA/RNA, UV light is not very effective
Kuru is mainly transmitted how?
cannibalism in humans
What is an animal prion disease that occurs in cattle?
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
Which of the following is associated with consuming beef products with Bovie Spongiform Encephalopathy?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
b
Which of the following is an inherited disease that is genetically DOMINANT?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
a
Which of the following is associated with an age of onset in YOUNGER INDIVIDUALS (~28)?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
b
Which of the following is associated with an age of onset in OLDER ADULTS (60-68)?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
a
Which of the following is associated a slower progression and death occurs within 13-14 months after diagnosis?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
b
Which of the following is associated a faster progression and death occurs within 4-5 months after diagnosis?
a. CJD
b. vCJD
a
What are symptoms seen with CJD?
cognitive impairment
involuntary muscle movement
In CJD, the CSF contains ______________ protein, which is associated with prion disease.
14-3-3
What is a rare genetic disorder that is inherited, a prion disease, and affects the brain and CNS to cause severe insomnia, memory loss, and muscle twitching?
familial fatal insomnia
Familial fatal insomnia occurs because of a mutation in _______gene.
PRNP
How is active immunity acquired?
through natural infection or by vaccine
Active immunization results in _______________.
a. short and long term immunity
b. permanent, long lasting immunity
c. short, rapid term protection
b. permanent, long lasting immunity
What is responsible for the long-term effects of vaccination?
memory cells
List examples of passive immunization:
Hepatitis A
treatMENT of exotoxin diseases (tetanus, diptheria, botulism)
A conjugative vaccine is _____________ + _______________.
polysaccharide + protein carrier
Which of the following is a conjugative vaccine:
a. Haemophilus Influenzae Vaccine (Hib)
b. Tetanus toxoid vaccine (TT)
c. Inactivated polio vaccine (IPV)
d. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR)
a- Hib VACCINE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
What is the tetanus vaccine?
a. Conjugate vaccine
b. Live attenuated vaccine
c. Toxoid Vaccine
d. mRNA vaccine
c. toxoid vaccine