The Meaning of Interest Rates (Chapter 4)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Present value of a simple loan
The current value of a future sum of money or stream of cash flow given a specified rate of return
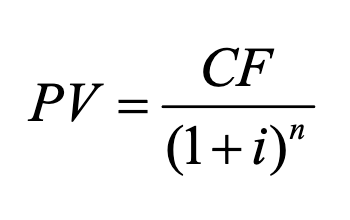
Net present value
The difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a period of time
Yield to Maturity
The interest rate that equates the present value of all cash flow payments received from a debt instrument with its value today (price)
Relationship between price of a coupon bond and ytm
When P = FV, YTM = coupon rate
P and YTM are negatively related
YTM > coupon rate when P < FV
YTM on a consol/perpetuity
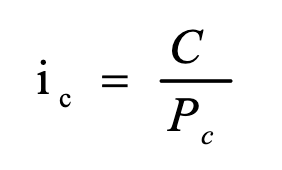
YTM on a discount bond
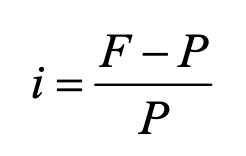
Coupon rate
coupon payment / FV
Current yield
annual coupons / current bond price
Capital Gains Yield
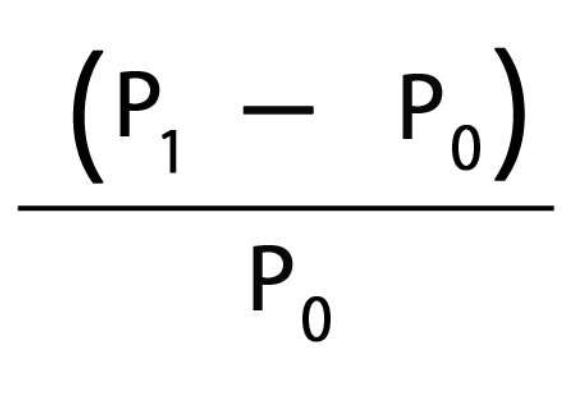
Rate of Return
current yield + rate of capital gain
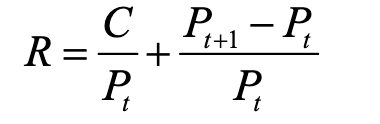
Relationship between interest rates and returns
Return = YTM only if the holding period = time to maturity
Rise in interest rates → fall in bond prices → capital loss IF time to maturity > holding period
The more distant a bond’s maturity, the greater the size of the % price change associated with % interest change
The more distant a bond’s maturity, the lower the rate of return that occurs as a result of an increase in the interest rate
Even if a bond has a substantial initial interest rate, its return can be negative if interest rates rise