New Nation-Articles of Confederation & Constitution 24-25
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Articles of Confederation
a plan for a loose union of the states under the authority of Congress.
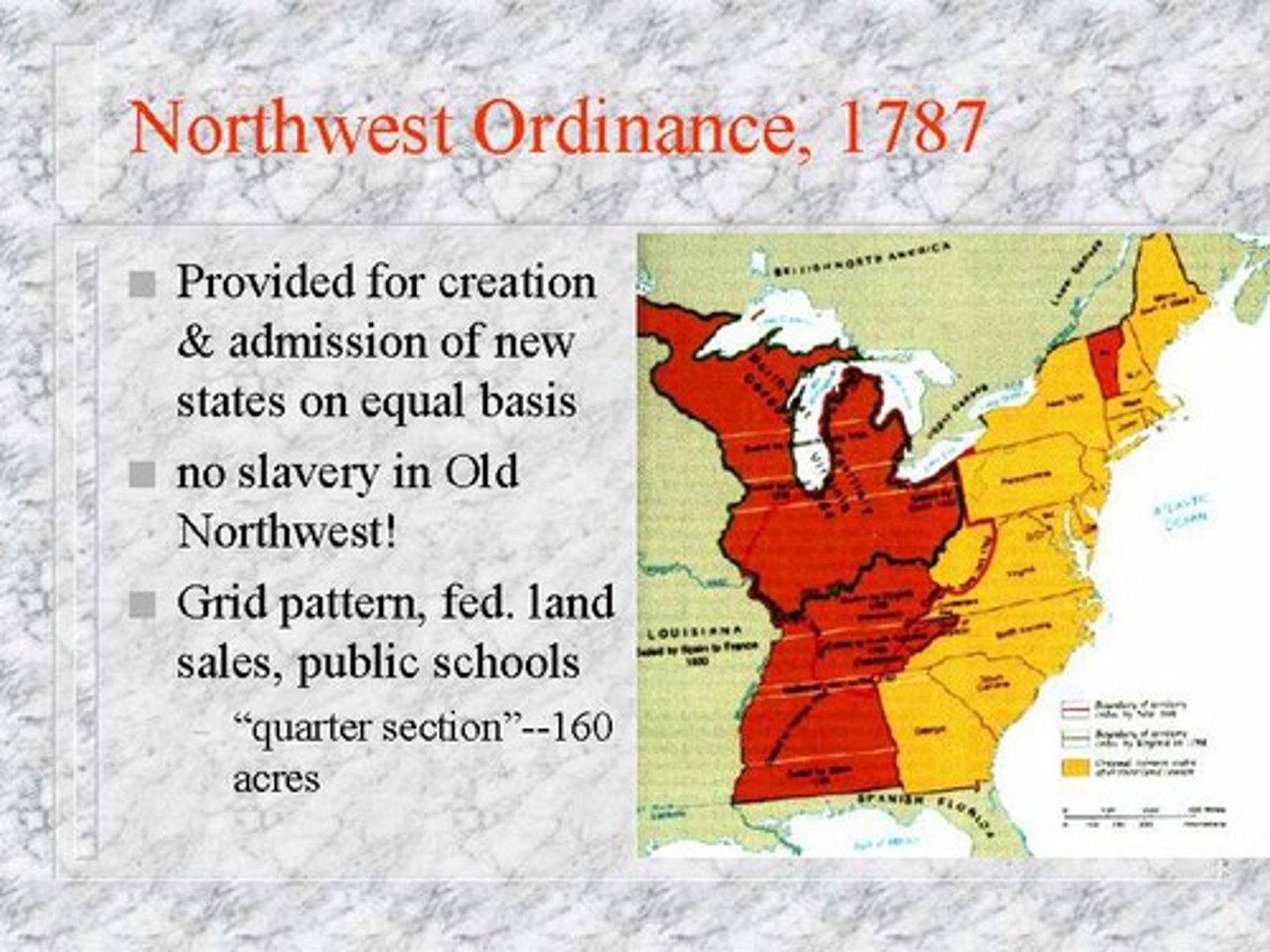
Northwest Ordinance
In 1785 the Congress passed the _________________ _______________ which provided the basis for governing much of the western territory. It outlined the qualifications a territory needed to meet in order to become a state.
commerce
Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress could not regulate ________________ or trade between the states.

legislative branch
This branch of government makes the laws. In the United States, we call this branch Congress.

chief executive, president
Under the Articles of Confederation, there was no ________ _________________ or _______________ to enforce laws.

taxes
Under the Articles of Confederation, The US could not collect __________; which meant they could not make revenue or money.
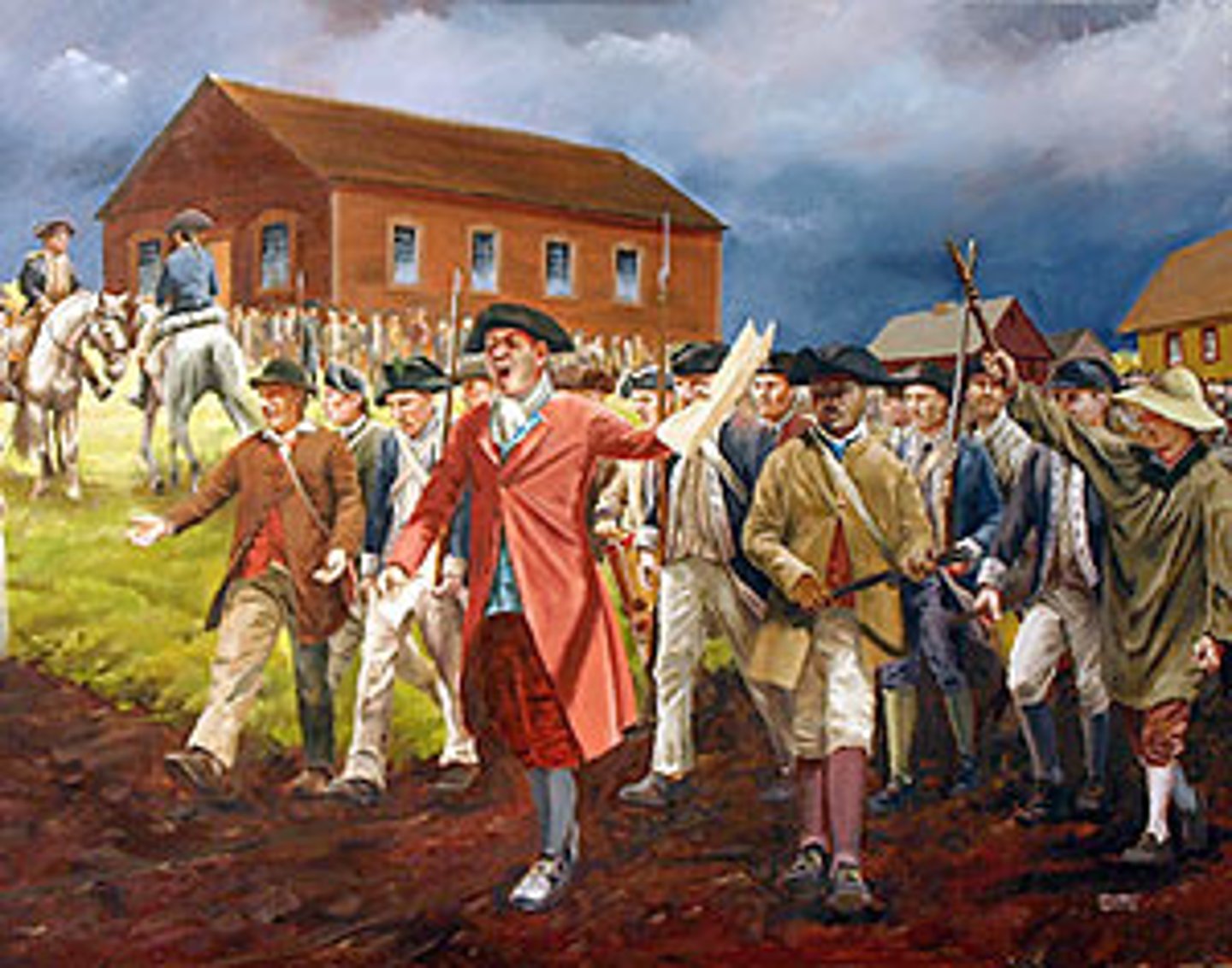
Daniel Shays
Taxes were raised in Massachusetts, so _______ _____ and the farmers closed down several courthouses and attempted to seize weapons and march on Boston.
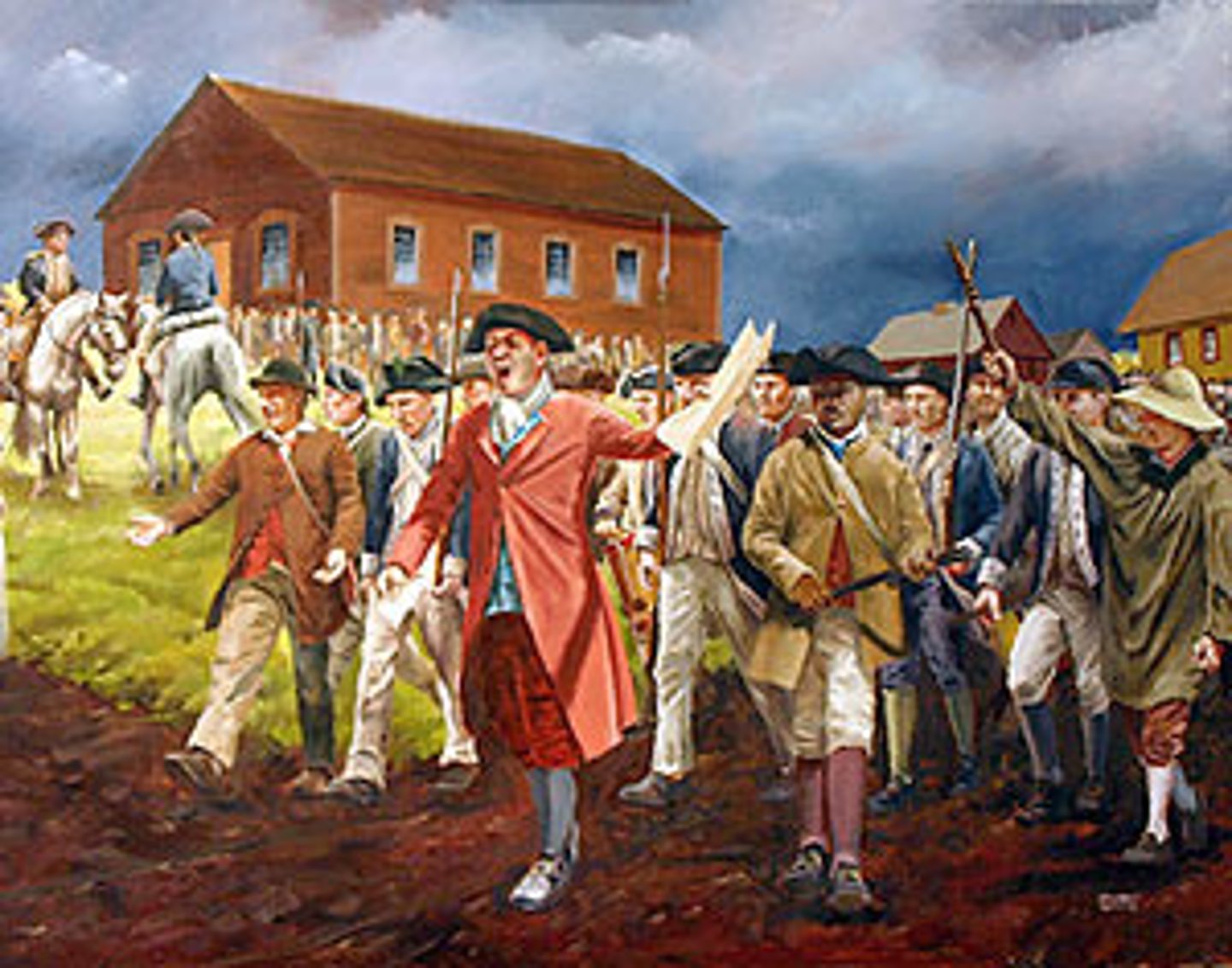

Shays's Rebellion
Anti-tax rebellion in Massachusetts that attempted to seize weapons and march on Boston. The rebellion was put down, but many Americans knew they needed to fix their government after the rebellion.

Constitutional Convention
In 1787, delegates from all the states met in Philadelphia to discuss altering the Articles of Confederation. They eventually replaced the Articles of Confederation with the United States Constitution.
United States Constitution
This replaced the Articles of Confederation
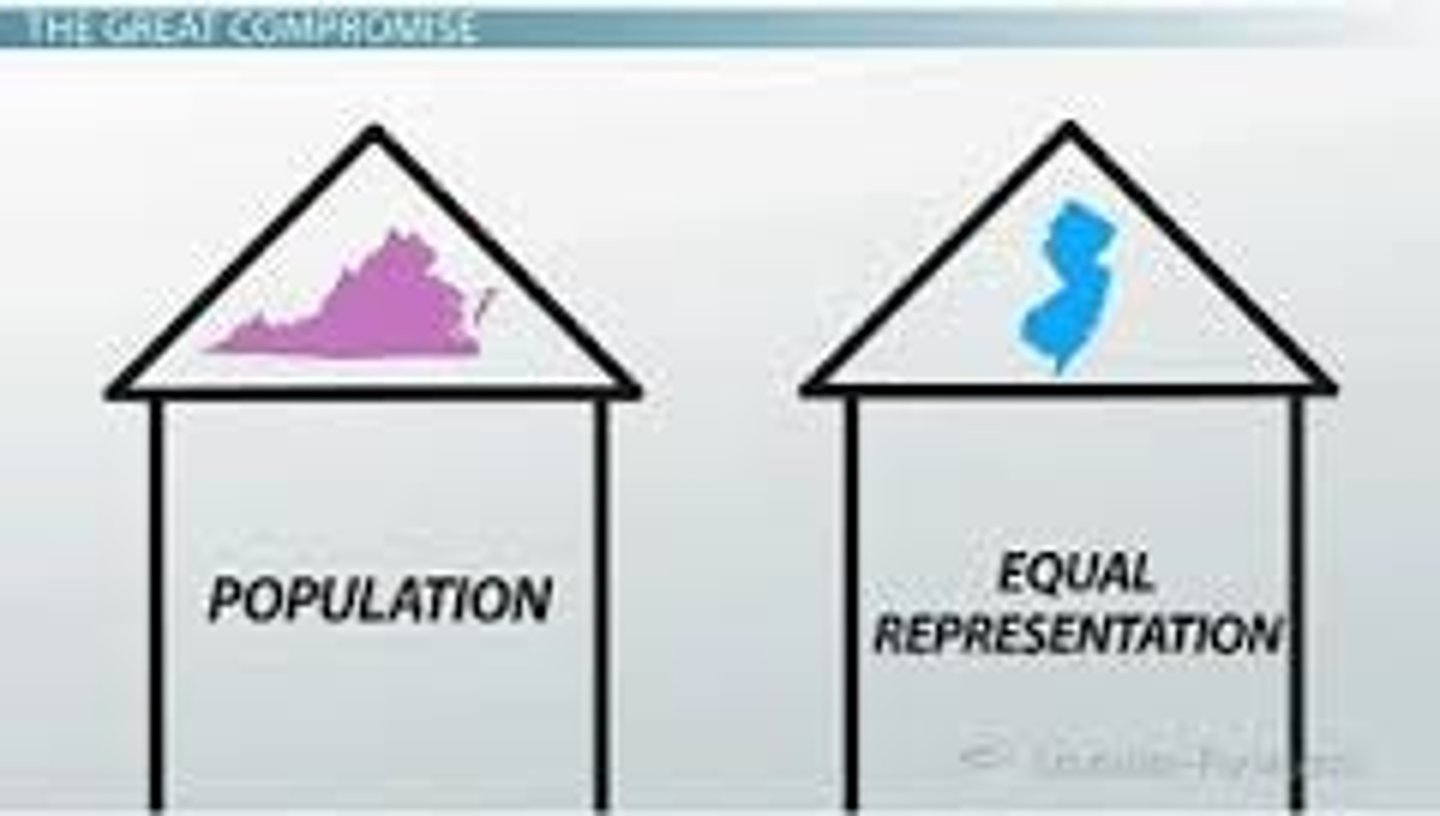
Virginia Plan
A proposal that the legislature of the United States should be based on a state's population. Under the ____________ ______, larger states would have more people in the legislature.
New Jersey Plan
Smaller states opposed the Virginia Plan. They wanted each state to receive equal representation in Congress, no matter their size.
Bicameral Legislature
A two house legislature; in the United States, our Congress is made up of the House of Representatives and the Senate.
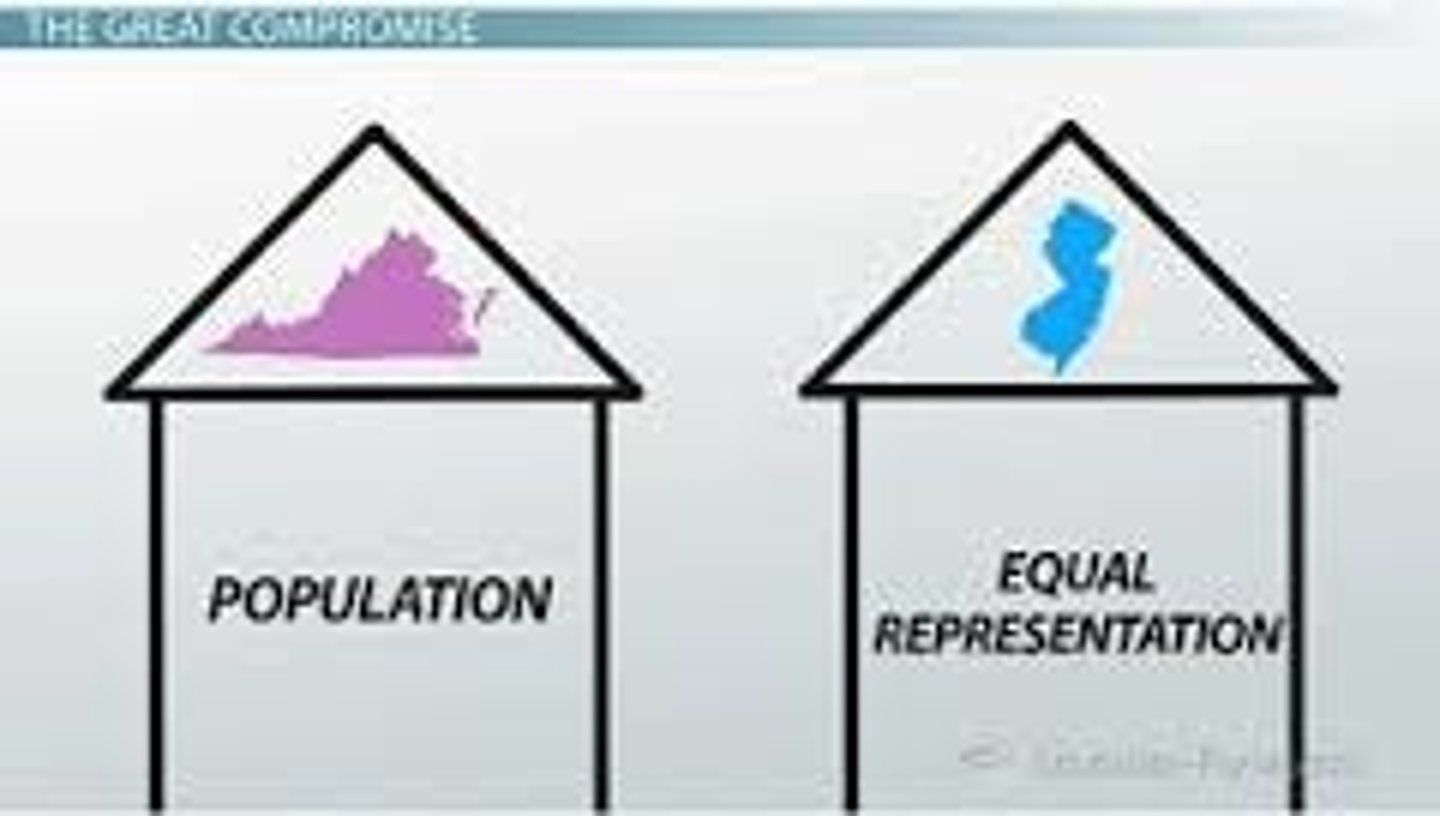
Great Compromise
This plan was also known as the Connecticut Compromise. The US Congress would consist of two houses: The House of Representatives would be based on a state's size (Virginia Plan). The Senate would be based on equal representation (New Jersey Plan).
House of Representatives
In this house of Congress, representation is based on a state's population.
Senate
In this house of Congress, representation is based on equality. Each state, no matter its' size, has 2 representatives.
Three-Fifths Compromise
every five enslaved people would count as three freed people.

popular sovereignty
The new constitution was based on _________ _____________ or rule by the people.
Federalists
Supporters of the U.S. Constitution at the time the states were contemplating its adoption.
Anti-Federalists
Opponents of the American Constitution at the time when the states were contemplating its adoption.
Alexander Hamilton's Financial Plan
raise money through taxes, create a national bank, and promote protective tariffs

Federalists Paper
The Federalist Papers are a series of 85 articles advocating the ratification of the United States Constitution. Signifiicance: The Federalist papers were written by renowned Federalists such as Hamilton, Madison and John Jay.

Judicial review
The authorities of the supreme court to strike down unconstitutional laws

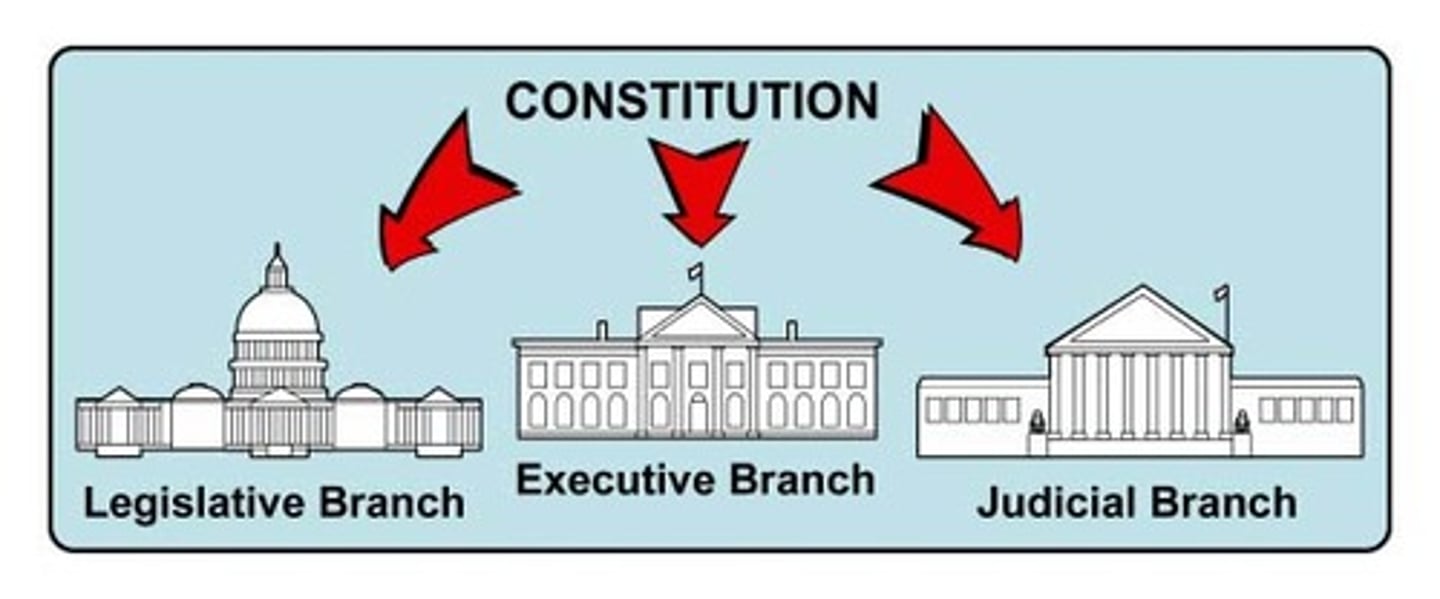
Separation of Powers
dividing the powers of government among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches
Veto
to reject

Great Compromise (Connecticut Compromise)
1787
*Called for a bicameral legislative system in which the House of Representatives would be based on population and the Senate would have equal representation in Congress
*Combined pieces of the New Jersey Plan, the Virginia Plan, and other proposals
*Included the Three-Fifths Compromise, which counted slaves as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of apportioning representation and called for direct taxation on the states
unicamerial legislature
a legislature with only one house, like the Confederation Congress or the legislature proposed by the New Jersey Plan

Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.

Federalism
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments
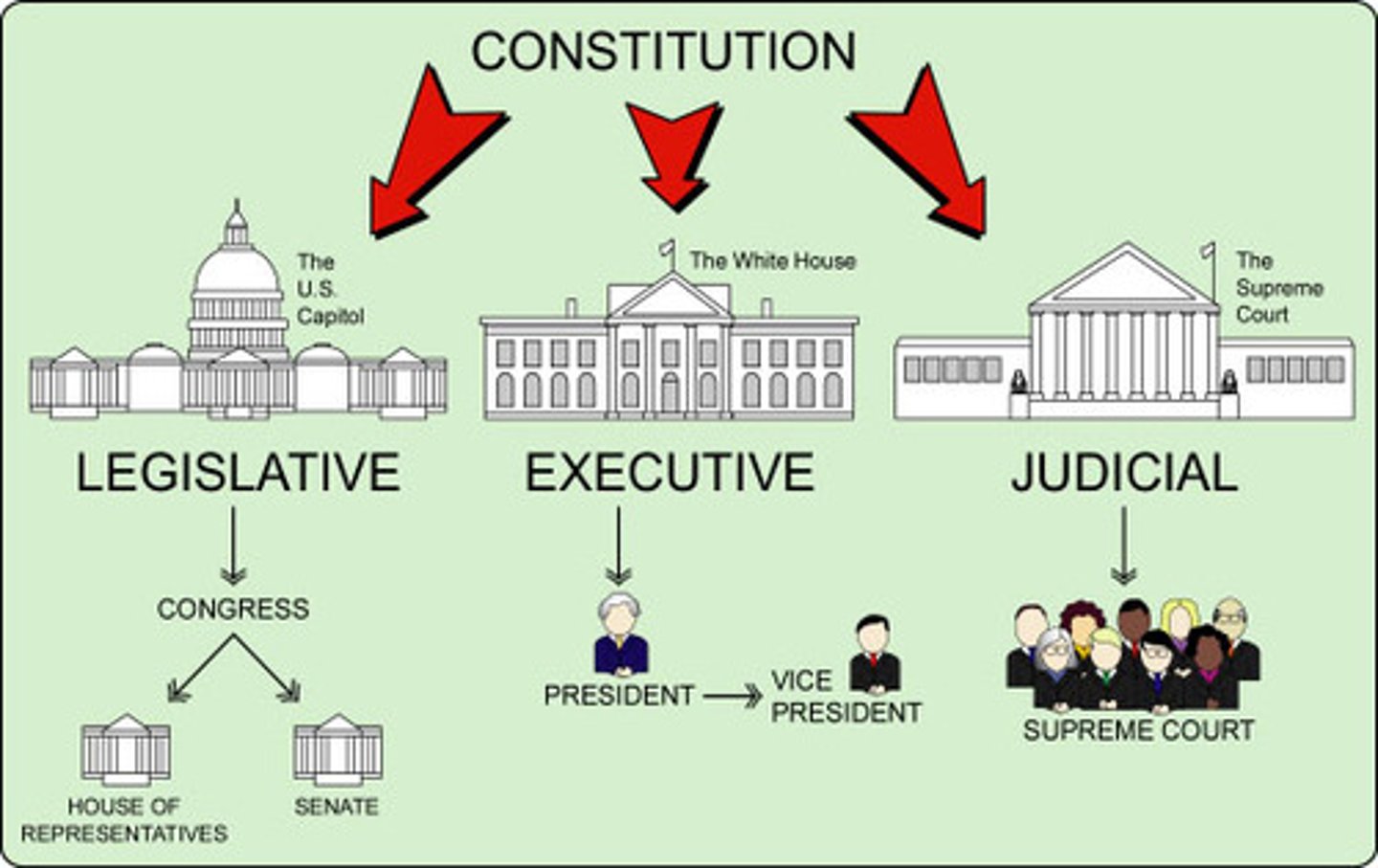
unicameral legislature
One-house legislature
Proclamation of Neutrality
A formal announcement issued by President George Washington on April 22, 1793, declaring the United States a neutral nation in the conflict between Great Britain and France.

federalism
Elastic Clause
the part of the Constitution that permits Congress to make any laws "necessary and proper" to carrying out its powers

Federalism
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments
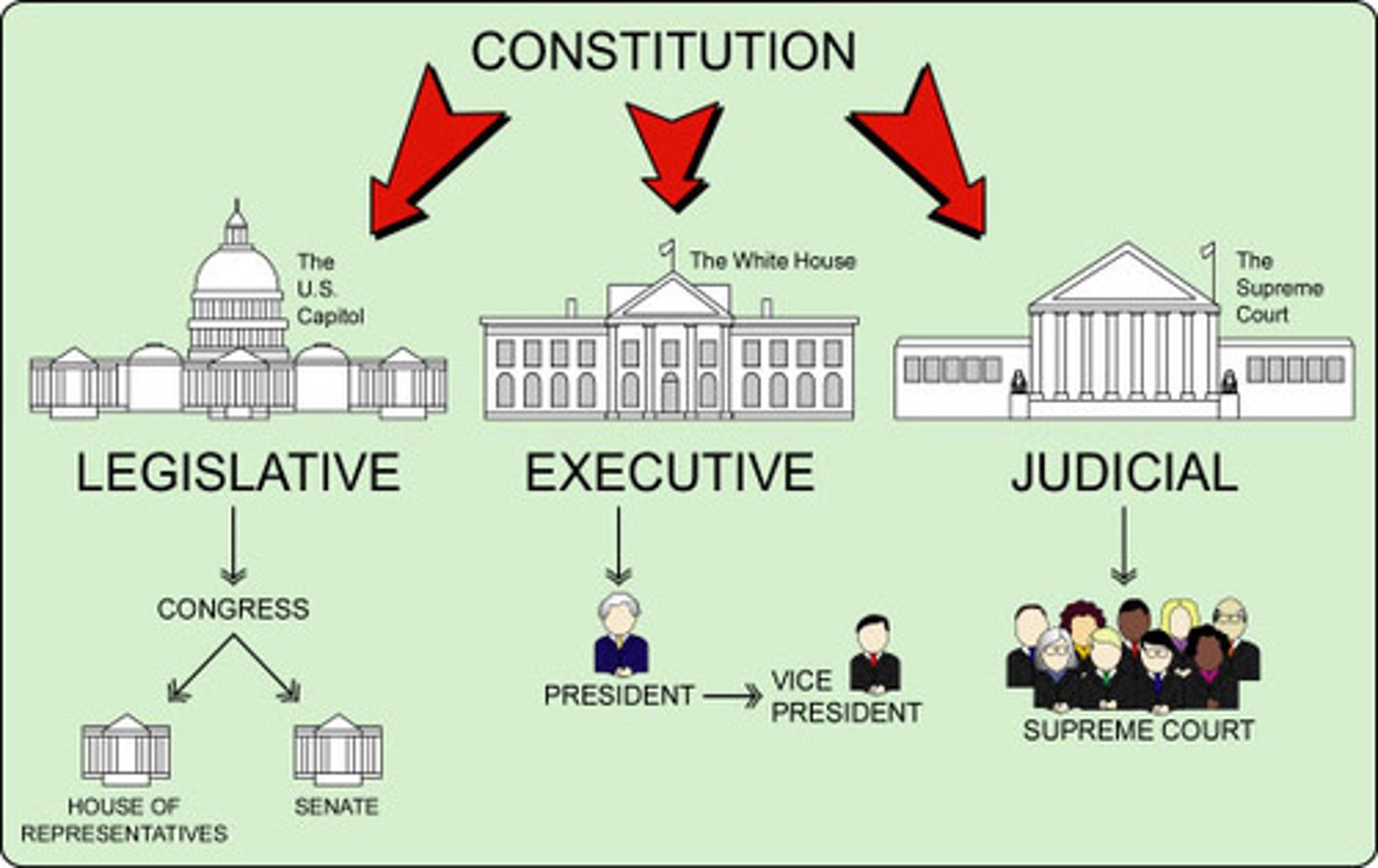
judical review
the power of the Supreme Court to declare laws and actions of local, state, or national governments unconstitutional

supermacy clause
a clause in Article VI that declares the Constitution, acts of Congress, and treaties are the "supreme Law of the Land"
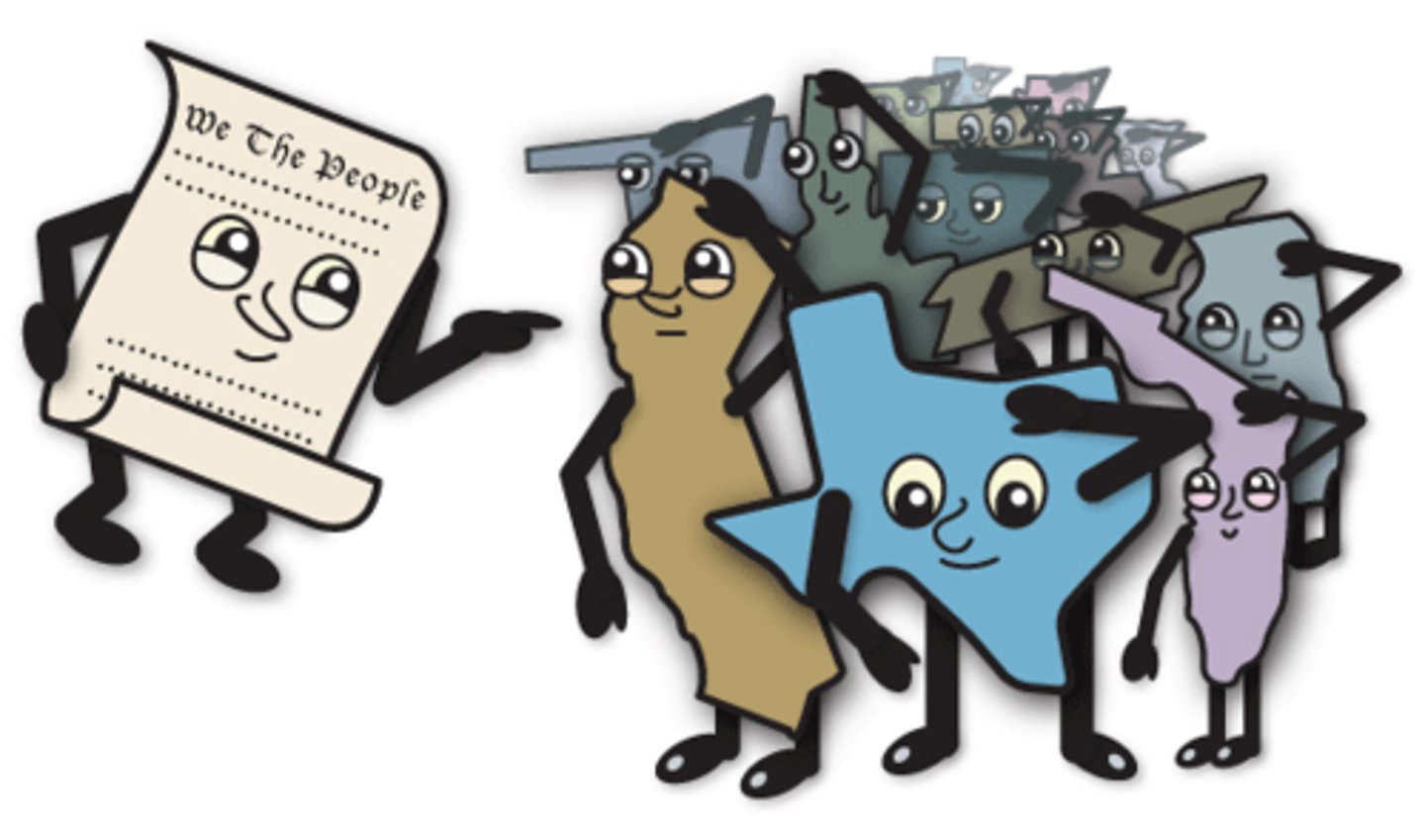
Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.

Federalists
supporters of the Constitution

Anti-Federalists
Opponents of the American Constitution at the time when the states were contemplating its adoption.

Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the Constitution
