The Mughal Empire Key Terms
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Babur (r.1525-30)
The founder of the Mughal Empire, descended from Tamur Lane and Gengis Khan. Battling for territory and control in the Ferghana Valley, he turned his attention to the Punjab region and overtook it from Delhi Sultanate
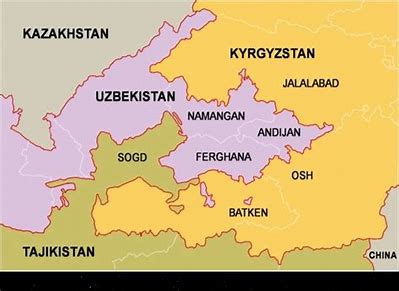
Ferghana Valley
The homeland of Babur, now in Uzbekistan. It was constantly a battle between different princes for control, leading Babur to turn his attention to Punjab
Humayun (1530-1555)
The son of Babur who ruled on and off from 1530-1555, occasionally on the run from Afghans and took shelter in the Safavid Empire in now Iran. Died from falling down a staircase in his library
Akbar (1556-1605)
The most renowned Mughal Emperor, who expanded and consolidated the Empire. He was known for his religious tolerance and curiosity. He moved the capitol between Agra, Fatehpur Sikri, and Lahore
Jahangir (1606-1627)
The rebellious son of Akbar, he revolted during his father’s reign but was eventually confirmed as his successor
Shah Jahan (1628-1658)
The son of Jahangir, he expanded the Mughal Empire and led it to an era of great prosperity but nearly bankrupted it in the process. He also oversaw the creation of the Taj Mahal and the Red Fort and was relatively tolerant to Muslims
Aurangzeb (1658-1707)
The final Mughal Emperor, a devout and conservative Muslim he patronized mosques and expanded the Empire, but his reign led to decentralization after his death
Mansabdari System
A rank system created by Akbar: Mansab (rank), Mansabdar (rank-holder) where the Mansabdar must manage 10-10,000 horses for the emperor. Each mansabdar was given a Jagir, a land grant coordinating with their rank
Divine Faith
Dīn-i Ilāhī, a religious system created by Akbar in 1582. It drew on elements of many different religions: Sufism, Zoroastrianism, and centered around worshipping the sun
Zoroastrianism
A pre-Islamic religion of Iran focusing on the teachings of Zarathustra
Abul Fazal
A writer, historian, and politician who served as the grand vizier of the Mughal Empire from 1579 to 1602, writer of the Akbar Nama
Akbar Nama
A biography and history of the Mughal Empire written in Persian for Akbar in the 1580s. It includes a census of provinces and is one of the first documents to present the idea of a unified Indian Empire
Taj Mahal
The tomb built for Shah Jahan’s wife Mumtaz Mahal in Agra. It contains great architectural diversity, with Indian, Persian, and Islamic stylings
Manuscript Painting
A unique style of miniature painting that evolved during the Mughal Empire, manuscripts were often richly decorated with miniature pictures that praised emperors or illuminated the content of the document
North Indian Classical Music
Music played on instruments such as the veena, sitar, or sarod, with lyrics primarily in Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, or other regional languages
Ottoman Empire
An empire coexisting with the Safavids and Mughals, during the Mughal Empire it encompassed West Asia, North Africa, and Eastern Europe
Safavid Empire
A Persian Empire ruling current Iran from 1501-1736 that began as Sunni Muslim but eventually transitioned the Shiite