CLAVETE CIENCIAS AMBIENTALES
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
Atmosphere
is the gaseous layer that covers the earth and is held near the earth by the force of gravitational attraction.
2
New cards
* Provide the oxygen we breathe
* Protect us from the harmful rays of the Sun
* Regulate temperature
* Protect us from the harmful rays of the Sun
* Regulate temperature
What is the atmosphere’s function?
3
New cards
* Dust
* Ash
* Salt
* Soil
* Smoke
* Ash
* Salt
* Soil
* Smoke
What are some examples of solid particles in the atmosphere?
4
New cards
* Oxygen (20.9%)
* Nitrogen (78.1%)
* Argon and others (0.9%)
* Nitrogen (78.1%)
* Argon and others (0.9%)
What are the elements found in the atmosphere?
5
New cards
* Vapor (gas)
* Small liquid droplets (clouds)
* Ice crystals (clouds)
* Small liquid droplets (clouds)
* Ice crystals (clouds)
What are some examples of liquid particles in the atmosphere?
6
New cards
Atmospheric pressure
measurement of the force with which air molecules collide on the surface
7
New cards
air pressure drops
The further away you get from the Earth’s surface, the more the __________________, since there are fewer gas molecules pushing you around.
8
New cards
Altitude
height of an object above the earth’s surface and sea level
9
New cards
decreases
At higher altitudes, the air pressure
10
New cards
sun
The difference in temperature is caused by the way in which energy is absorbed from the
11
New cards
energy
Some parts of the atmosphere are hot because they contain gasses that absorb the solar energy.
12
New cards
Exosphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Troposphere (top to bottom)
Layers of the atmosphere
13
New cards
tropopause
Boundary between the troposphere, and the stratosphere is called the
14
New cards
turning or changing
In the troposphere “Tropo” means
15
New cards
lowest and thinnest layer
The troposphere is the
16
New cards
90%
The troposphere is _____ of the atmosphere’s mass
17
New cards
Troposphere
the temperature decreases with the altitude
18
New cards
50 C
The top of the Troposphere averages
19
New cards
weather
The troposphere is where the ____________ occurs.
20
New cards
layer or spread out
In the stratosphere “strato” means
21
New cards
dense (less water vapor)
The stratosphere is less
22
New cards
Stratosphere
The temperature increases with the altitude
23
New cards
ozone
The stratosphere contains a high level of
24
New cards
middle and is the middlest layer of the atmosphere
In the mesosphere “meso” means
25
New cards
10km to 50km above the ground
The stratosphere extends from
26
New cards
50km to almost 80 km high
The mesosphere extends from
27
New cards
dense
In the mesosphere gasses are less
28
New cards
mesosphere
temperature decreases as altitude increases
29
New cards
UV radiation
In the mesosphere gasses absorbs very little
30
New cards
meteoroids
The mesosphere protects the earth from
31
New cards
heat
In the thermosphere “thermo” means
32
New cards
80 km, to almost 600 km high.
The thermosphere extends from
33
New cards
Thermosphere
The temperature increases with the altitude
34
New cards
solar energy (UV radiation)
The thermosphere readily aborbs
35
New cards
1,500 C
In the thermosphere the temperature can go as high as
36
New cards
radio waves
The thermosphere reflects
37
New cards
Ionosphere
the sun's energy heats molecules to become ions.
38
New cards
aurora borealis
The ionosphere is known for causing
39
New cards
earth and space
The exosphere is the interface between
40
New cards
hottest layers
The exosphere is one of the
41
New cards
exosphere
In what layer do sattelites orbit?
42
New cards
escape to space
The exosphere is where atoms and molecules can
43
New cards
Electromagnetic Radiation
Form of Energy that exhibits __wave-like__ behavior as it __travels__ through __space__.
44
New cards
Wavelength (λ)
Is the shortest distance between equivalence point on a continuous wave
45
New cards
Frequency (v) *f= cycles/time*
Is the number of waves that pass a given point per second
46
New cards
Amplitude
Is the wave’s height from the origin to a crest
47
New cards
relationship
wavelength and frequency have an indirect
48
New cards
speed (3.00 x 108 m/s) \[c = (λ)(v)\]
All parts of the electromagnetic spectrum travel at the same
49
New cards
colors
* A prism separates sunlight a continuous spectrum of
50
New cards
* Short wavelengths have high frequency
* Long wavelengths have a low frequency
* Long wavelengths have a low frequency
Electromagnetic wave characteristics:
51
New cards
* High frequency waves have high energy
* Low frequency waves have low energy
* Low frequency waves have low energy
Electromagnetic waves & Energy characteristics:
52
New cards
Larger amplitude more energy
Amplitude & Energy characteristics:
53
New cards
Atmospheric radiation
Is the flow of electromagnetic energy between the sun and the Earth’s surface as it is influenced by clouds, aerosols, and gasses in the Earth’s atmosphere.
54
New cards
solar radiation (sunlight) and long-wave (thermal) radiation
The atmospheric radiation includes both
55
New cards
Earth’s atmosphere
Several factors influence the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface and the amount of radiation leaving the
56
New cards
heating of the land surface by sunlight drives the formation of convective clouds
Weather effects
57
New cards
long term changes in the amount of radiation reflected or absorbed by aerosols, clouds, or gasses may change temperature or precipitation patterns
Climate affects
58
New cards
Albedo
Is an expression of the ability of surfaces to reflect sunlight (heat from the sun)
59
New cards
dark
_______ surfaces absorb the rays from the sun (low albedo)
60
New cards
sun rays back to the atmosphere (high albedo)
Light-coloured surfaces return a large part of the
61
New cards
The Stratospheric ozone (good)
* Protects Earth from harmful UV radiation
* Depletion is detrimental to life
* Depletion is detrimental to life
62
New cards
Tropospheric ozone (bad)
ozone is a pollutant
63
New cards
CFC pollution
One of the main effects in ozone depletion is
64
New cards
break down
Radiation from the sun causes the CFCs to
65
New cards
Global Warming
An increase in Earth’s average surface temperature caused by an increase in greenhouse gasses
66
New cards
Greenhouse effect
The trapping of heat by gasses in the atmosphere
67
New cards
* carbon dioxide
* Sulfur dioxide
* Ozone
* CFCs
* Water vapor
* Sulfur dioxide
* Ozone
* CFCs
* Water vapor
Types of greenhouse gasses
68
New cards
energy transference
It is received in the form of radiation (only a small portion reaches Earth)
69
New cards
electromagnetic waves (from infrared to UV)
Radiation is transferred in the form of
70
New cards
heat
When radiation is absorbed it becomes
71
New cards
gasses
The Earth absorbs the energy and transfers it to the lower layers of the atmosphere, heating them and generating convection of
72
New cards
cool air
air particles press together and air sinks
73
New cards
warm air
air particles move apart and air rises
74
New cards
Radiation
A method of heat transferred in the matter of waves.
75
New cards
Convection
* Is when the lower heat rises until the point it gets colder, and by getting colder it goes down so it repeats itself over and over.
* This is a process of redistribution of energy on Earth.
* This is a process of redistribution of energy on Earth.
76
New cards
Conduction
* Is the transfer of heat between substances that are in direct contact with each other. The better the conductor, the more rapidly heat will be transferred.
* Emission of infrared waves that are later absorbed by gasses in the atmosphere
* Emission of infrared waves that are later absorbed by gasses in the atmosphere
77
New cards
Weather ()
__Temporary__ behavior of atmosphere (what’s going on at any certain time)
78
New cards
Climate
Condition of the atmosphere at a particular location over a __long period__ of time (from one month to many millions of years, but generally 30 years)
79
New cards
1. The __SUN__
2. Earth latitudes and altitude
3. The Water __cycle__
4. wind
5. The __Ocean__
What factors affect weather & climate?
80
New cards
latitude
* The area that receives the most direct rays of the Sun (equator, 0) will have the hughes yearly temperatures
* The area that receives the least direct of the sun (poles, 90) will have the lowest yearly temperatures.
* As it increases, average yearly temperatures decreases
* The area that receives the least direct of the sun (poles, 90) will have the lowest yearly temperatures.
* As it increases, average yearly temperatures decreases
81
New cards
percolation
part of the water cycle where water infiltrate through the earth and stores in an aquifer (aquífero)
82
New cards
interception
is the part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the Earth's surface and which subsequently evaporates. (Stores in plants mainly)
83
New cards
Transpiration
also includes transpiration, which is the water movement from the soil to the atmosphere via plants.
84
New cards
Deposition
occurs when water vapor changes state directly from a gas to a solid.
85
New cards
Sublimation
is the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage.
86
New cards
winds
air in motion
87
New cards
* Uneven warming of the Earth
* Air pressure difference
* High pressure = cold
* Low pressure = warm
* Convection and Conduction
* Air pressure difference
* High pressure = cold
* Low pressure = warm
* Convection and Conduction
Why does air move?
88
New cards
direction
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
89
New cards
anemometer
With what instrument do you measure speed or velocity of the winds?
90
New cards
windsock
With what instrument do you measure the strength of winds?
91
New cards
* Earth rotation
* Uneven heating on the planet
* Formation of high and low pressures
* Change in density of air masses
* Uneven heating on the planet
* Formation of high and low pressures
* Change in density of air masses
Factors that affect winds
92
New cards
anticyclone
Air cools - high pressure zone - stability -
93
New cards
cyclone
Air heats up - low pressure zone - instability -
94
New cards
convective cells
The planet occurs in six
95
New cards
cellular convection
Circular patterns caused by air rising and falling are called
96
New cards
wind moves
The more difference in pressure, the faster the
97
New cards
Gustave-Gaspard \*\*\*\*\*\*\*\* (\`1835)
Who created the Coriolis Force?
98
New cards
Coriolis force
The rotation of the Earth affects the movement causing it to travel in a curve instead of in a straight line.
99
New cards
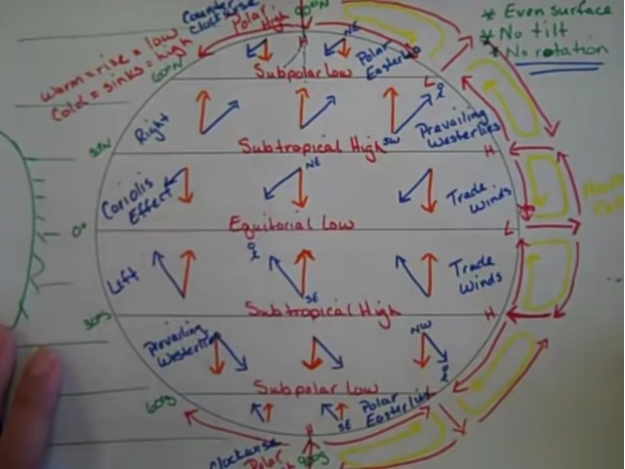
* Polar easterlies
* Trade winds
* Westerlies
* Trade winds
* Westerlies
Types of winds
100
New cards
regional winds
uneven heating of the ground