Chapter 5
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Alcohols and alkyl halides and an introduction to reactions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
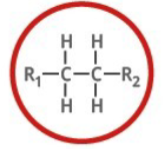
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Alkane
Alkane is what type of functional group
Hydrocarbon
Naming of alkanes
Add: -ane
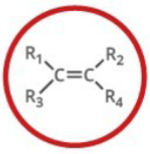
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Alkene
Alkene is what type of functional group?
Hydrocarbons
Naming of alkene:
Add: -ene

Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Alkyne
What functional group is alkyne?
Hydrocarbon
Naming of alkyne
Add: -yne
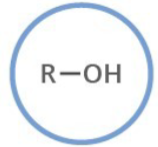
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Alcohol
Generalized abbreviation of alcohol:
ROH
What type of functional group alcohol?
Simple oxygen heteroatomics
Naming of alcohols:
Add: -ol
Generalized abbreviation of alkyl halide:
RCl
Generalized abbreviation of sulfide:
RSR
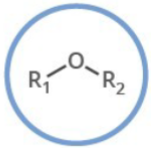
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Ether
Generalized abbreviation of ether:
ROR
What functional group is ether?
Simple oxygen heteroatomics
Naming of ethers:
Add: -oxy - ane
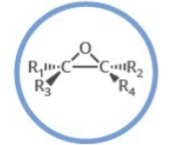
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Epoxide
Generalized abbreviation of amine:
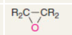
What type of functional group is epoxide?
Simple oxygen heteroatomics
Naming of epoxides:
Add: -ene oxide

Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Haloalkane
What type of functional group is Haloalkane?
Halogen Heteroatomics
Naming of haloalkanes:
Add: halo-
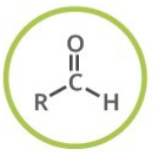
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Aldehyde
Generalized abbreviation of aldehyde:
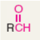
What kind of functional group are aldehydes?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of aldehyde:
Add: -al
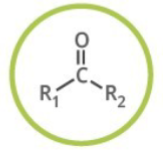
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Ketone
Generalized abbreviation of ketone:

What type of functional group is a ketone?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of ketone
Add: -one
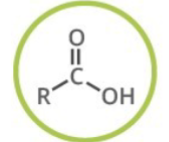
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Carboxylic Acid
Generalized abbreviation of Carboxylic acid:

What type of functional group is carboxylic acid?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of carboxylic acid:
Add: -oic acid
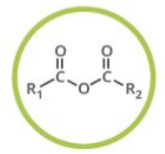
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Acid Anhydride
Generalized abbreviation for acid anhydride

What type of functional group is acid anhydride?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of acid anhydride:
Add: -oic anhydride
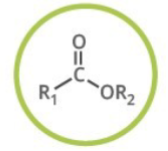
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Ester
Generalized abbreviation for ester

What type of functional group is ester?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of ester:
Add: -yl -oate
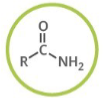
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Amide
Generalized abbreviation for amide
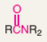
What type of functional group is amide?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of amide:
Add: -amide
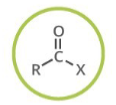
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Acyl Halide
Generalized abbreviation for acyl halide
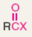
What type of functional group is acyl halide?
Carbonyl Compounds
Naming of acyl halide:
Add: -oyl halide
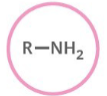
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Amine
Generalized abbreviation of Amine
RNH2
What type of functional group is amine?
Nitrogen-Based
Naming of amine:
Add: -amine

Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Nitrile
Generalized abbreviation of nitrile:
RC(triple bond)N
What type of functional group is nitrile?
Nitrogen-Based
Naming of nitrile:
Add: -nitrile
Generalized abbreviation of nitroalkane:
RNO2
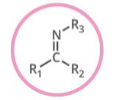
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Imine
What type of functional group is imine?
Nitrogen-Based
Naming of imine:
Add: -imine

Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Isocyanate
What type of functional group is isocyanate?
Nitrogen-Based
Naming of isocyanate:
Add: -yl isocyanate
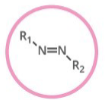
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Azo Compound
What type of functional group is azo compound?
Nitrogen-Based
Naming of azo compound:
Add: azo-
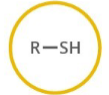
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Thiol
Generalized abbreviation of thiol:
RSH
What type of functional group is thiol?
Sulfur-Based
Naming of thiol:
Add: -thiol
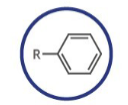
Which functional group is shown? (R = rest of molecule, X = any halogen)
Arene
What type of functional group is arene?
Aromatic
Naming of arene:
add: -yl benzene
IUPAC Nomenclature of Alcohols
Named by identifying the longest straight carbon chain containing the -OH group.
The -ane suffix is replaced with -anol
The location of the -OH group on the chain is designed by a number
What takes priority when numbering the Cs in IUPAC Nomenclature of Alcohols
Alcohol Takes Priority
Halogens has same priority as methyl groups
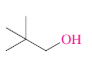
What is the IUPAC name?
2,2-Dimethyl-1-propanol
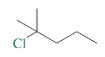
What is the IUPAC name?
2-chloro-2-methylpentane
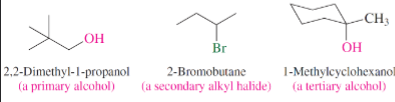
What is the difference between Primary Alcohols, Secondary Alcohols, and Tertiary Alcohols
Primary - The C connected to the alcohol is connected to 1 other carbon
Secondary - The C connected to the alcohol is connected to 2 other carbons
Tertiary - The C connected to the alcohol is connected to 3 other carbons
Alcohol and alkyl halide boiling point increase with
Stronger van der Waals forces
Dipole-dipole
Dipole / induced-dipole
Induced-dipole / induced-dipole
Other than intermolecular forces what effects the boiling point of alcohols?
Amounts of carbons in the main chain (more carbons higher boiling point)
Branching (increased branching decreased boiling point)
Small alcohol are _ in water
Small alcohols are soluble in water
(Methyl and ethyl are considered small)
Formation of an alkyl halide from an alcohol and hydrogen halide reaction
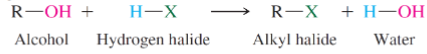
What kinds of alcohol are most reactive toward hydrogen halides
Tertiary most reactive

Hammond’s Postulate
If two states are similar in energy, they are similar in structure
Step of SN1 Reaction with an alcohol as a reactant
Alcohol protonation (OH bonds with H)
Carbocation formation (H2O leaves)
Anion reaction with carbocation
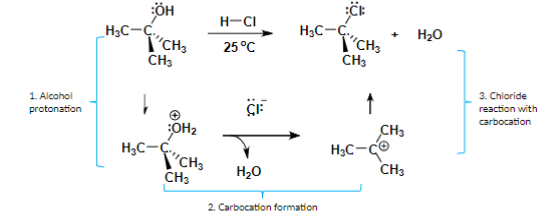
Carbocation
A molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three
bonds
Hybridization of carbocation
sp2 hybridized (molecular geometry is trigonal planar)
pz orbital is empty and perpendicular to the bond
What type of carbocation is the most stabile
tertiary
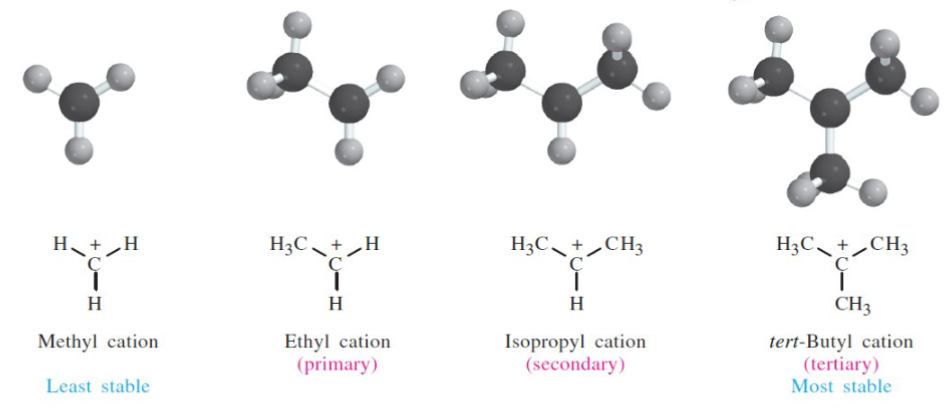
In carbocations: alkyl groups provide _ inductive donation than hydrogens
In carbocations: alkyl groups provide MORE inductive donation than hydrogens
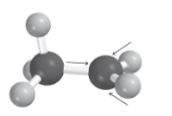
Hyperconjugation
‘Sigma bond to p orbital donation’
3 centers sharing 2 electrons
2 things that stabilize carbocations
inductive donation by alkyl groups along the sigma bond
hyperconjugation, a through space donation of electron density by bonds that are adjacent and parallel to the empty p orbital
SN1 reactions are fastest with what kind of alcohol?
Tertiary (it forms most stable carbocation)
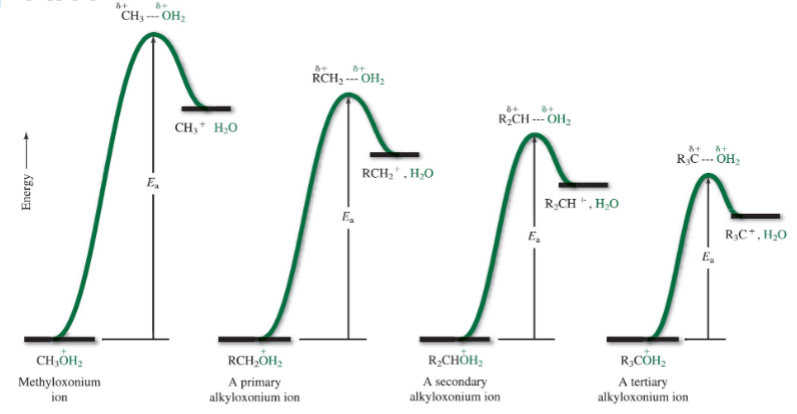
Stereochemistry of SN1 mechanisms
Not stereospecific
(But an SN1 reaction gives products that partially invert. Leading to a mixture
of S and R products generally)
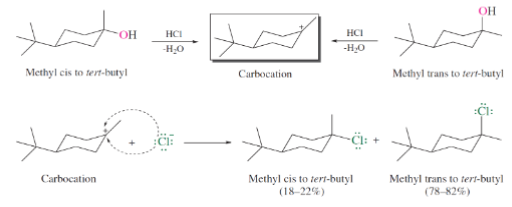
2 types of rearrangements in SN1 mechanism:
Hydride Shift
Methanide Shift (Alkyl Shift)