NLE 2 Roman History
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Hannibal
Punic Carthaginian military commander, generally considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Led his army (and elephants!) across the Alps during the 2nd Punic War.
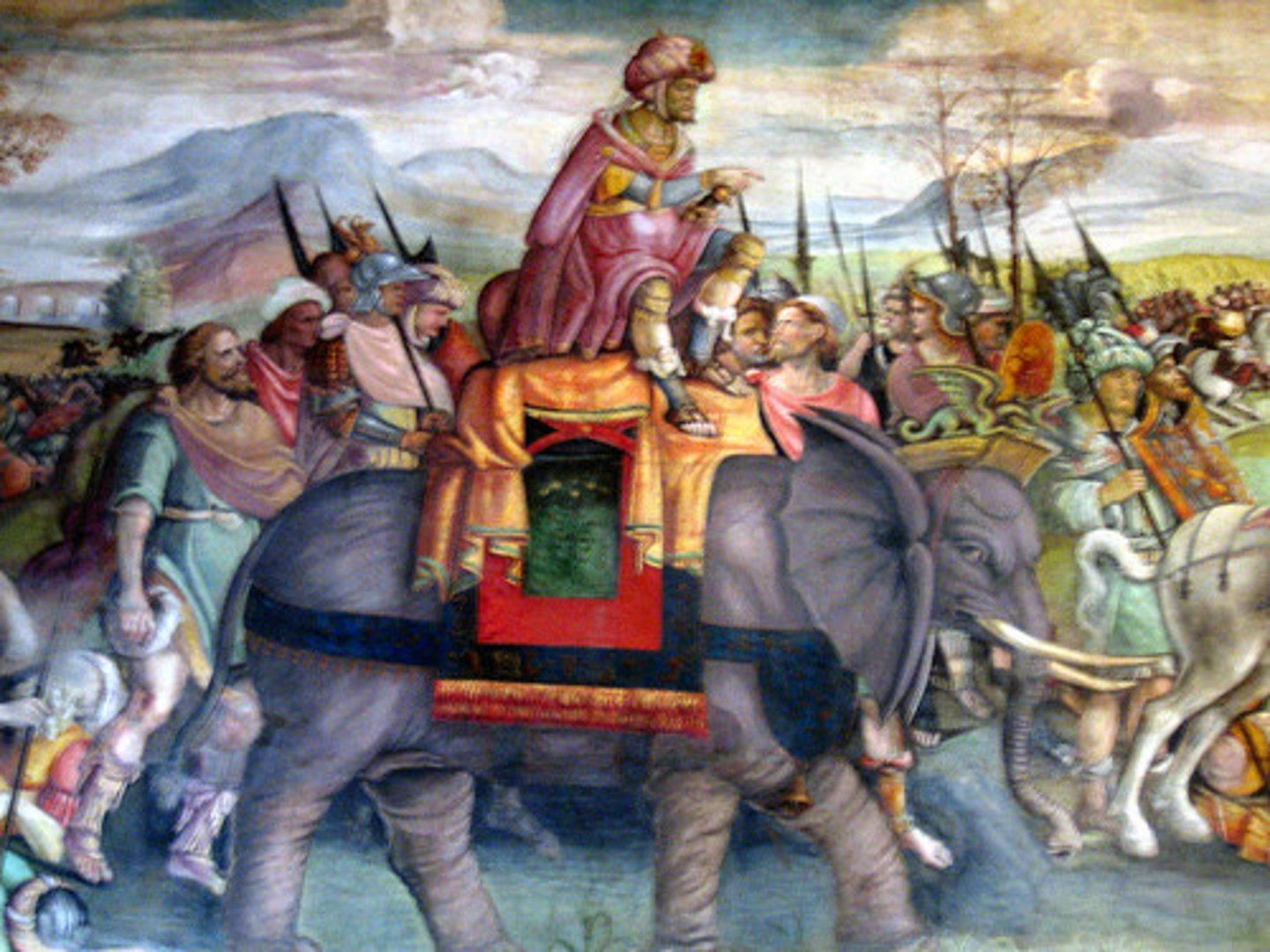

Battle of Cannae
During Second Punic War that took place in 216 BCE in Apulia, Hannibal decisively defeated a larger army of the Roman Republic. It is regarded both as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and as one of the worst defeats in Roman history.

Punic Wars
series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage from 264 to 146 BCE.
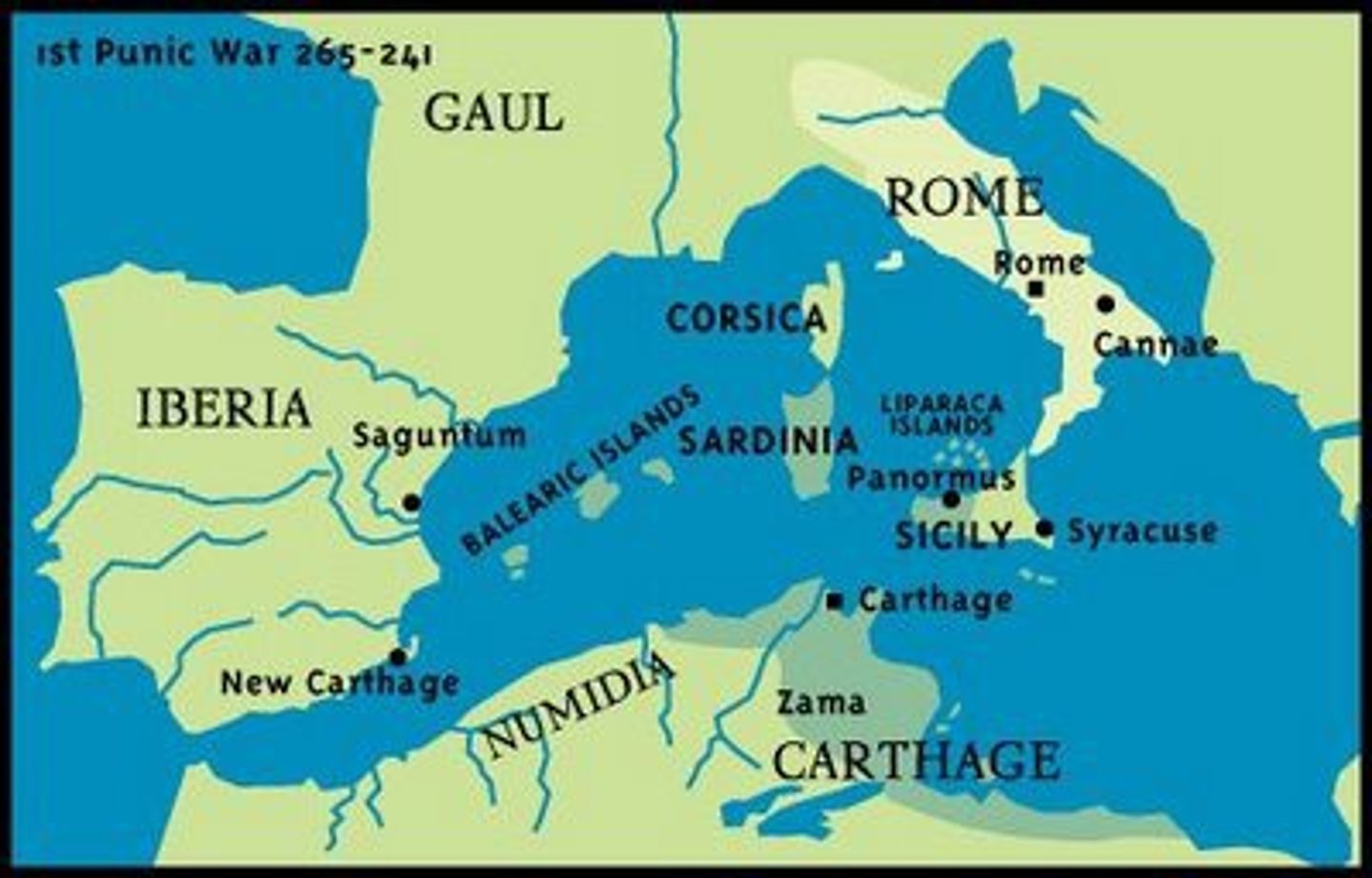
Scipio Africanus
Roman general in the Second Punic War who defeated Hannibal at the final battle of the Second Punic War at Zama. 236-183 BCE.
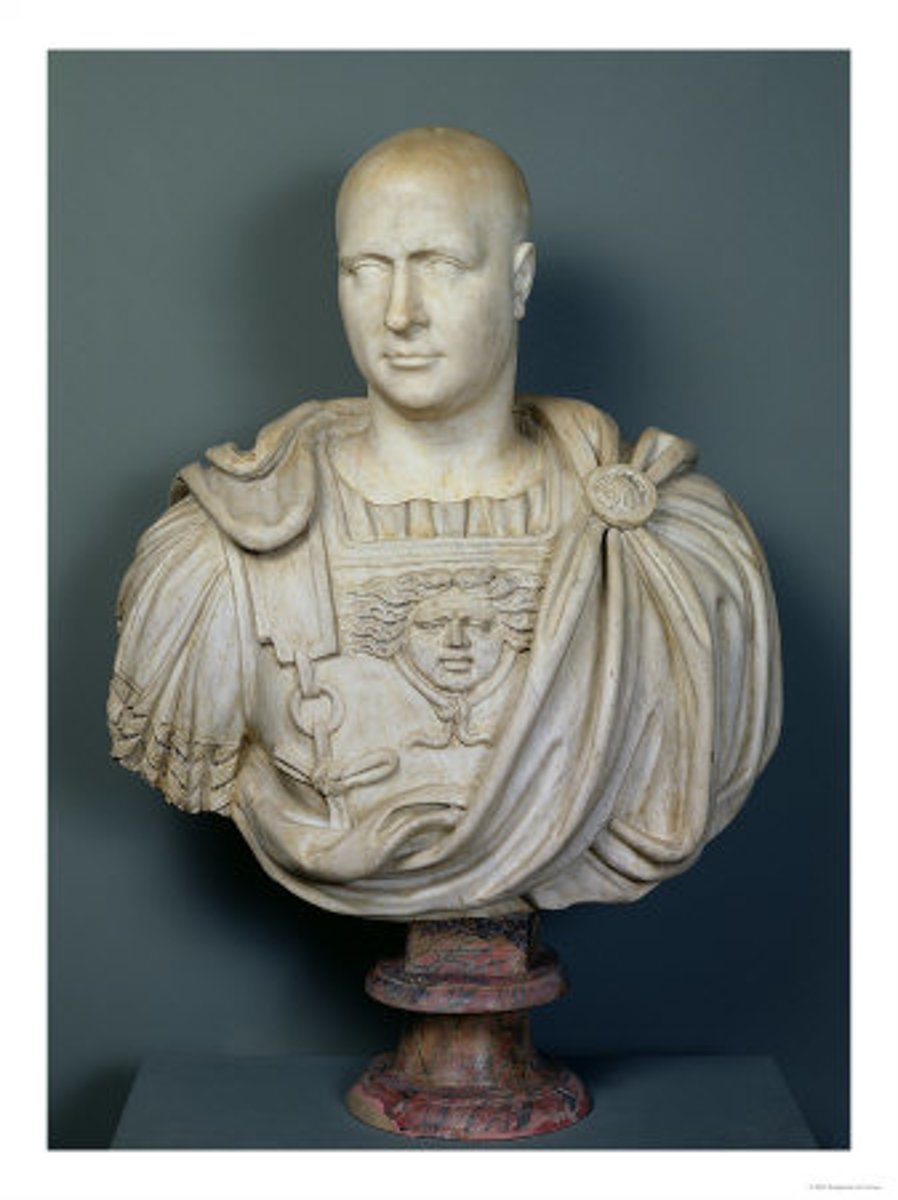

Augustus
First emperor of Rome, ruled from 27 BCE to 14 CE. Defeated Marcus Antonius (Marc Antony) at the Battle of Actium in 31 BCE. Julius Caesar was his great-uncle. As a boy, he was called Octavian and formed an alliance with Marc Antony and Lepidus (the Second Triumvirate) to defeat the assassins of Caesar.
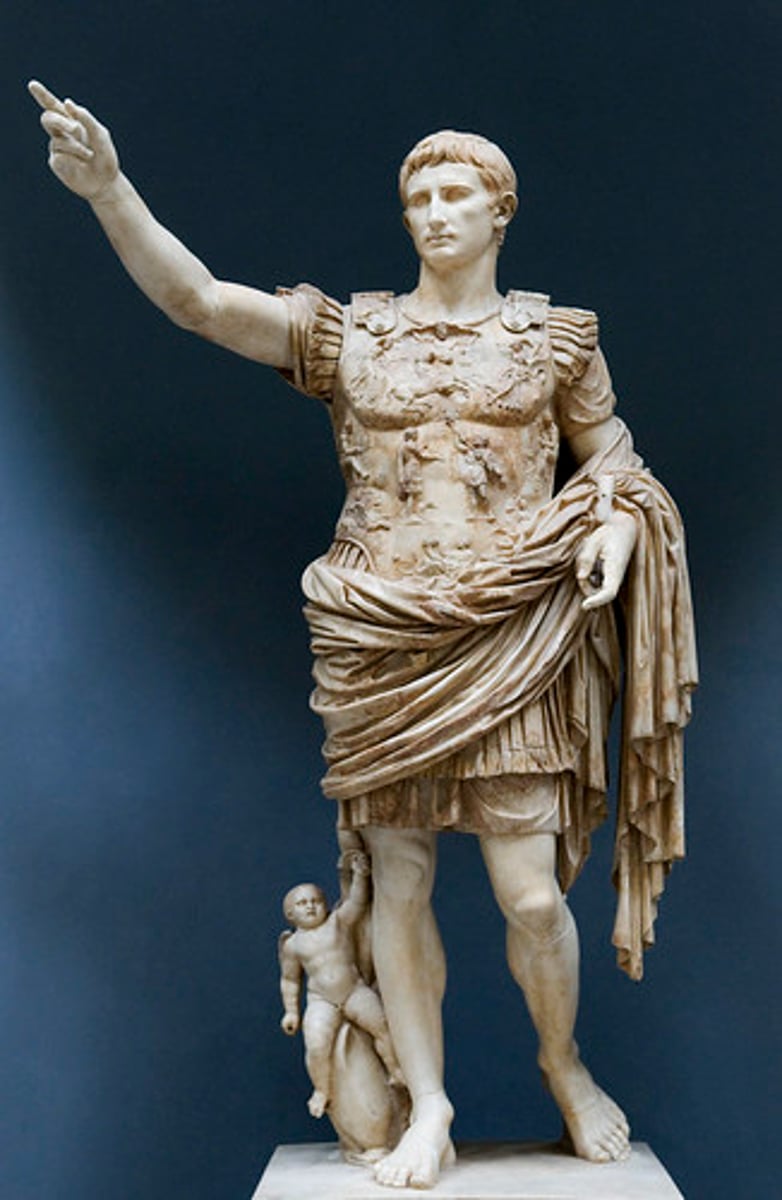

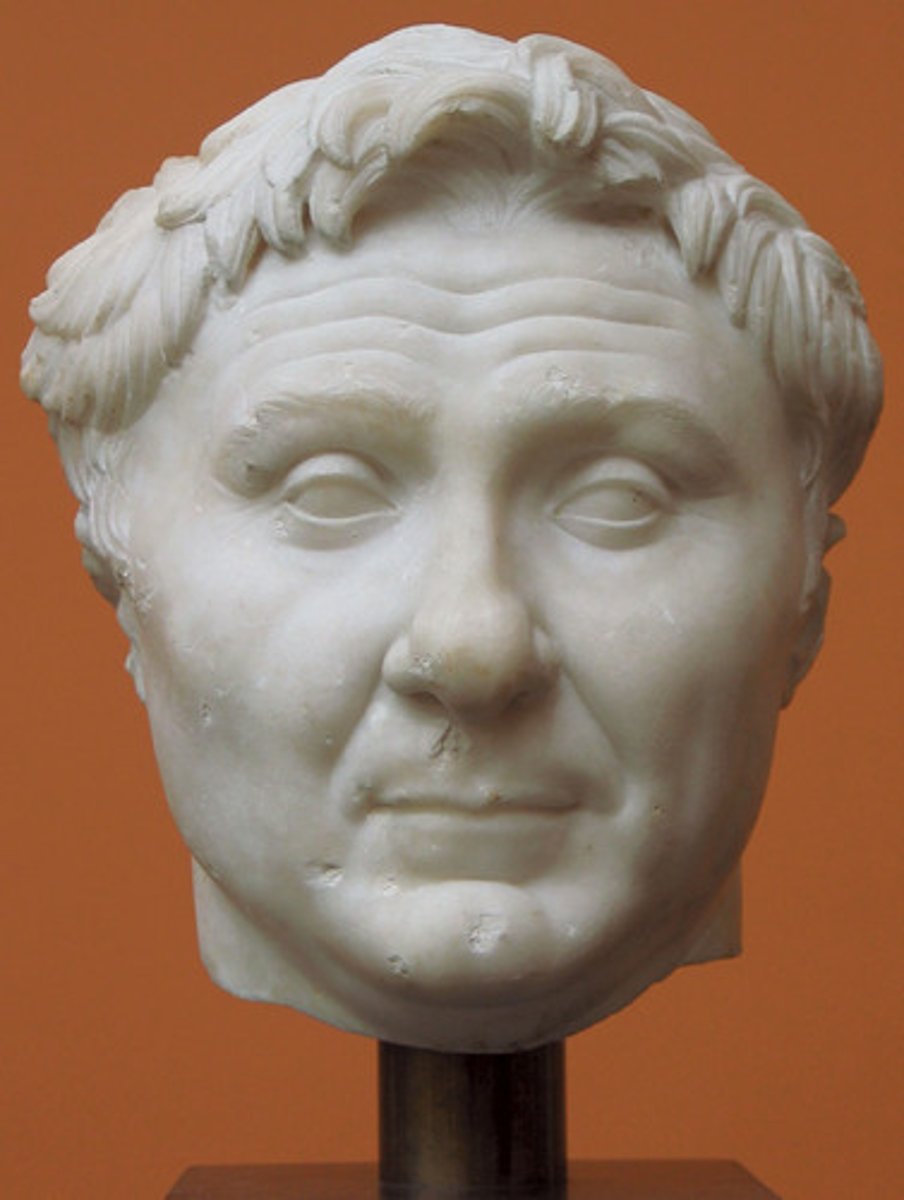
Pompey
A military and political leader of the late Roman Republic, friend and rival of Julius Caesar. Member of the First Triumvirate. Was tasked with ridding the Mediterranean of pirates. 106 - 48 BCE

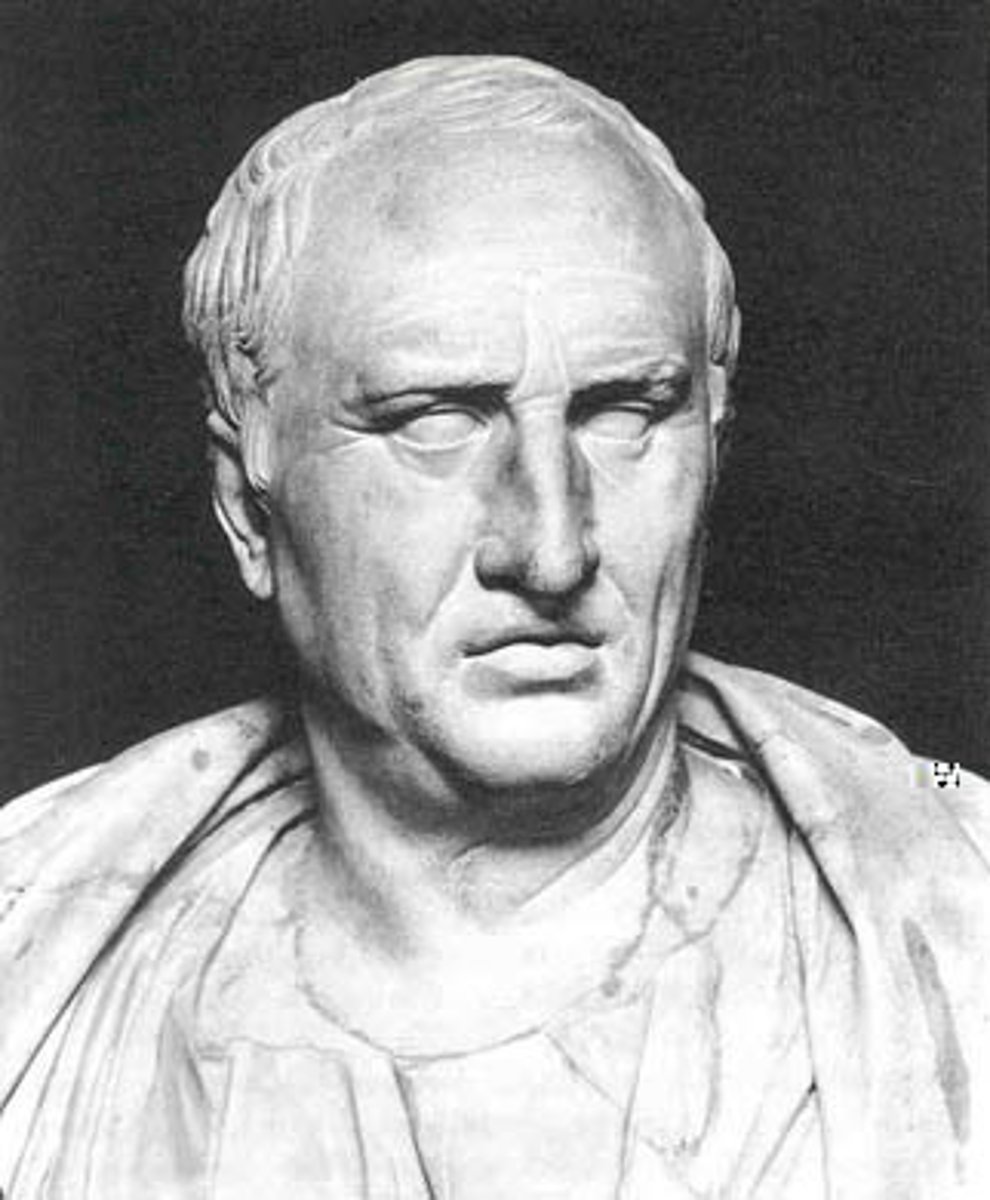
Cicero
A Roman orator, philosopher, politician, lawyer, consul and constitutionalist - widely considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. 106 - 43 BCE

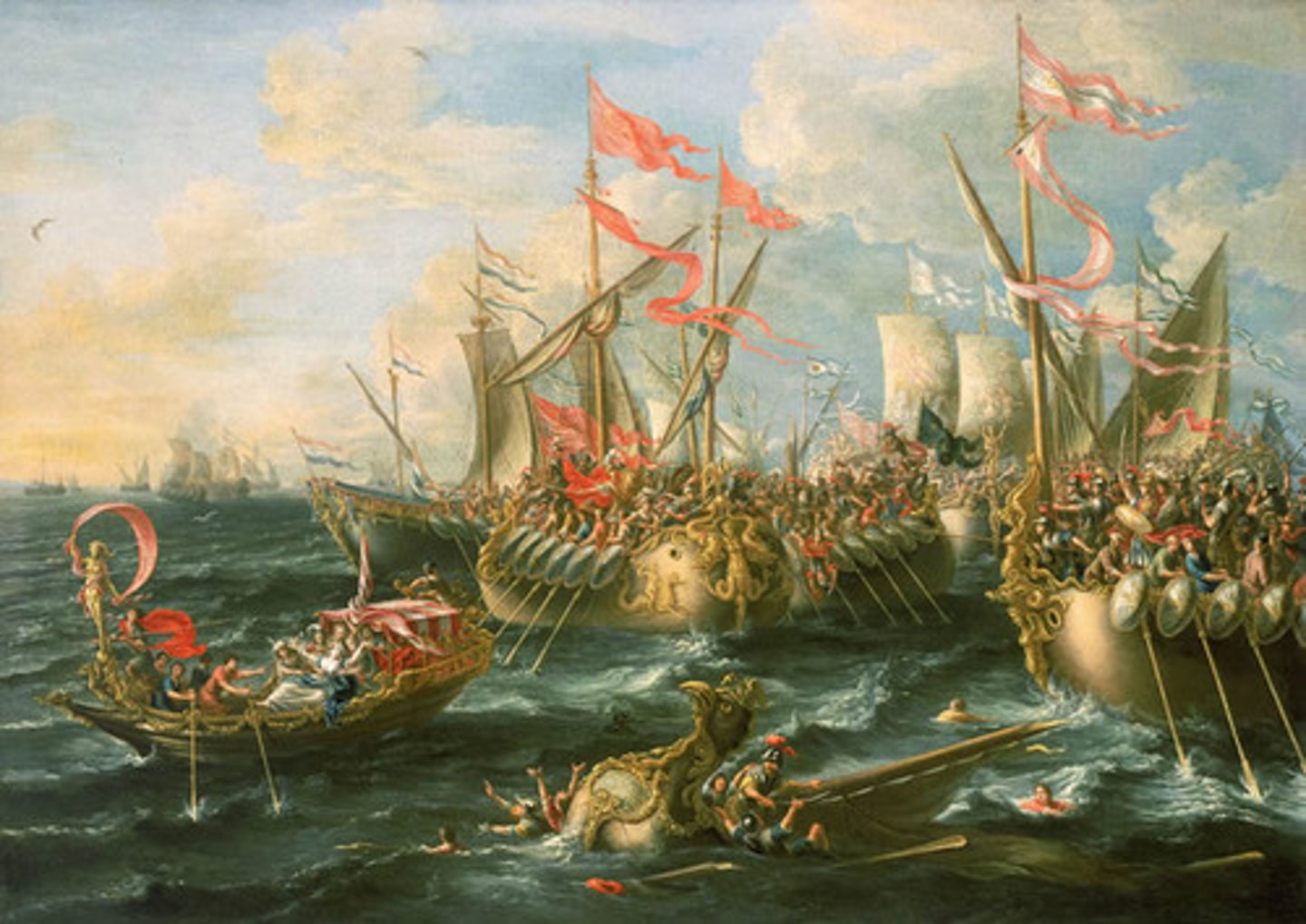
Battle of Actium
a naval engagement between Octavian and the combined forces of Mark Antony and Cleopatra in 31 BCE. Octavian's victory enabled him to consolidate his power over Rome and its dominions.

Nero
Roman Emperor from 54 to 68, and the last in the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Built his Domus Aurea (Golden palace) after a great fire destroyed much of Rome in 64 CE/

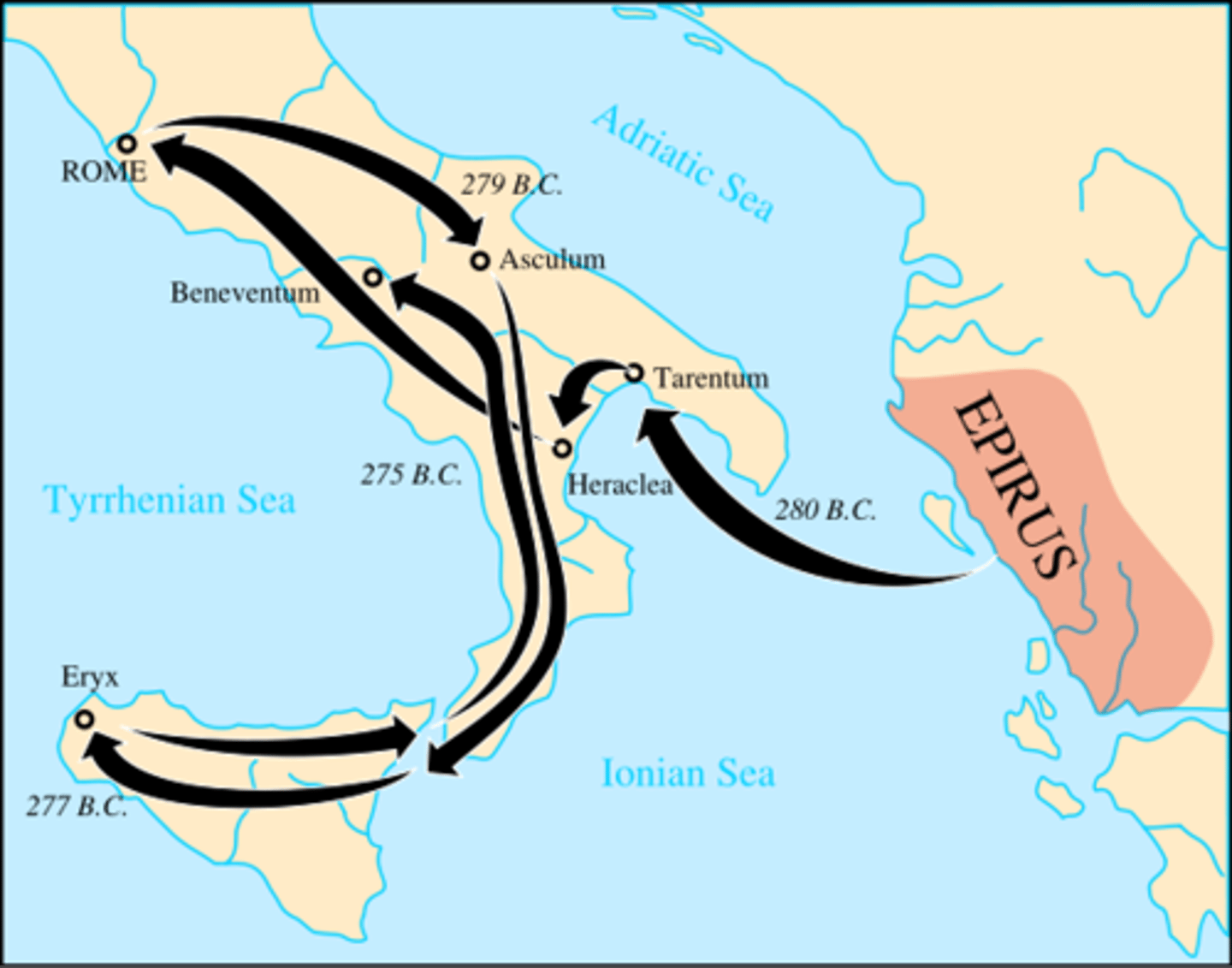
Pyrrhus
Greek general and statesman of the Hellenistic period. He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, Epirus, and Macedon. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome. Some of his battles, though successful, cost him heavy losses, from which the term Pyrrhic victory was coined
Pharsalus
48 BCE at in central Greece, Gaius Julius Caesar and his allies defeated the army of the republic under the command of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus ("Pompey the Great")
Horatius Cocles
Defended the bridge to Rome across the Tiber from Etruscans

Cincinnatus
519-430 BCE, invasion caused him to be called to serve Rome as dictator, an office which he resigned two weeks later, after completing his task of defeating the rival tribes of the Aequians, Sabines, and Volscians.

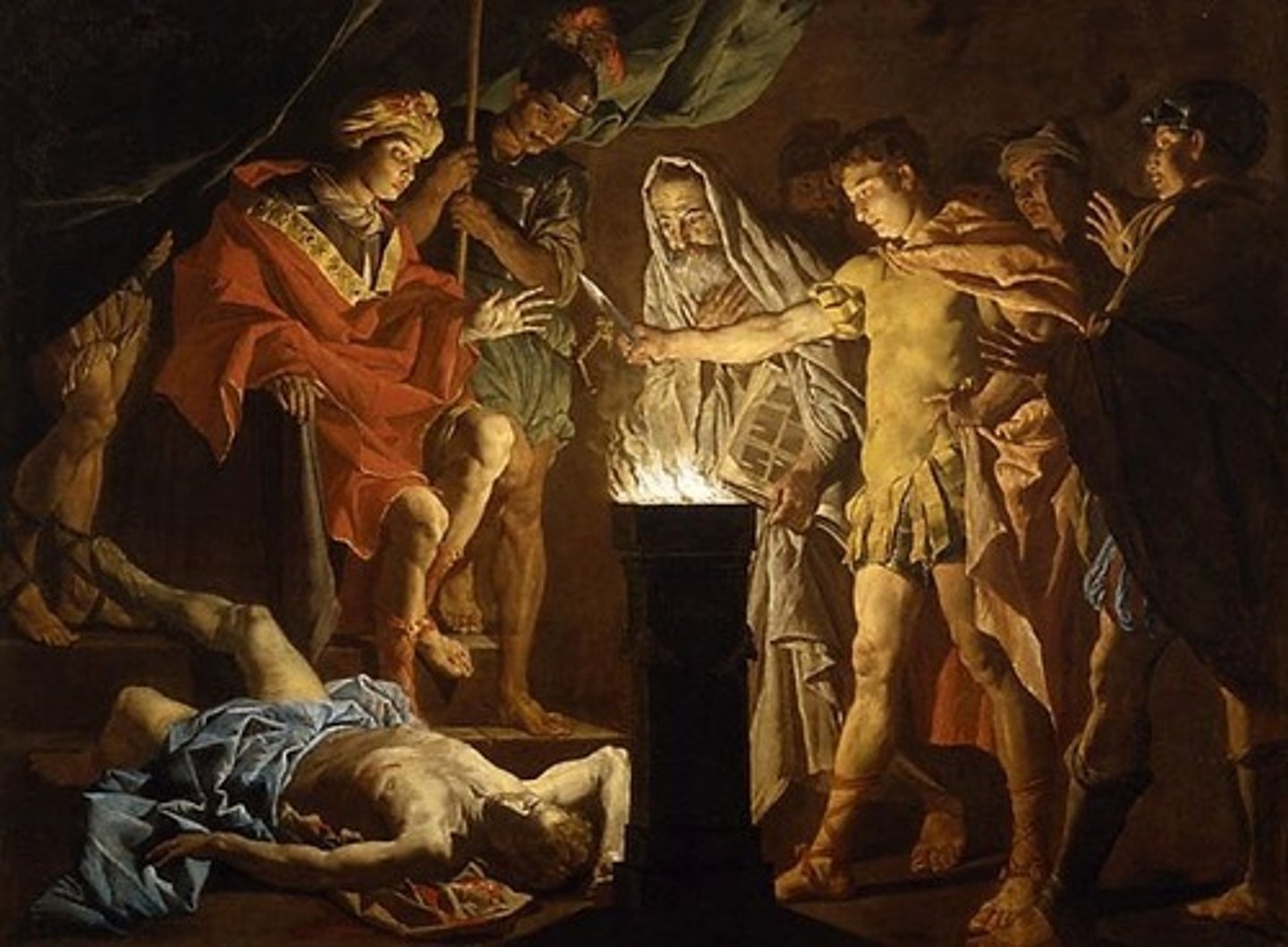
Mucius Scaevola
After being captured by the Etruscans, he thrust his right hand into a fire which was lit for sacrifice and held it there without giving any indication of pain, thereby earning for himself and his descendants the cognomen meaning 'left-handed'.

Julius Caesar
(100 BCE - 15 March 44 BCE) was a Roman statesman, general and notable author of Latin prose. He played a critical role in demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. His victories in the Gallic Wars extended Rome's territory to the English Channel and the Rhine.

Marc Anthony
Roman general, initially allied with Octavian in the Second Triumvirate, but then turned against him. He defeated Brutus and Cassius at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BCE. Octavian defeated him at the Battle of Actium in 31 BCE. Romantically linked with Cleopatra of Egypt.
Spartacus
Thracian gladiator and slave who led a major uprising of slaves against the Roman Republic in 73 BCE (called the Third Servile War), but was defeated by Pompey and Crassus
