Mitosis T3 W3
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
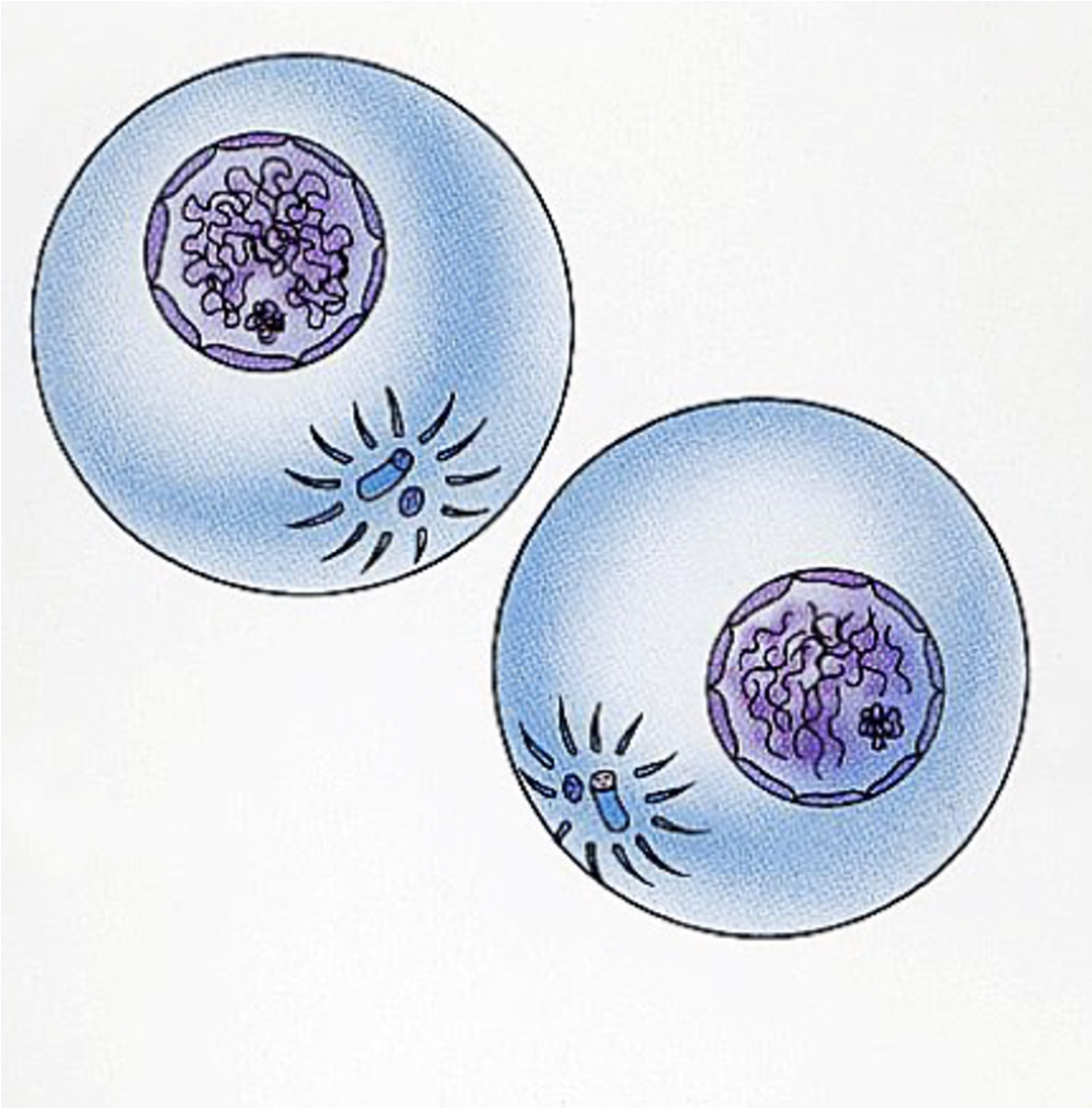
Mitosis defintion
Process of making new cells from existing cells.
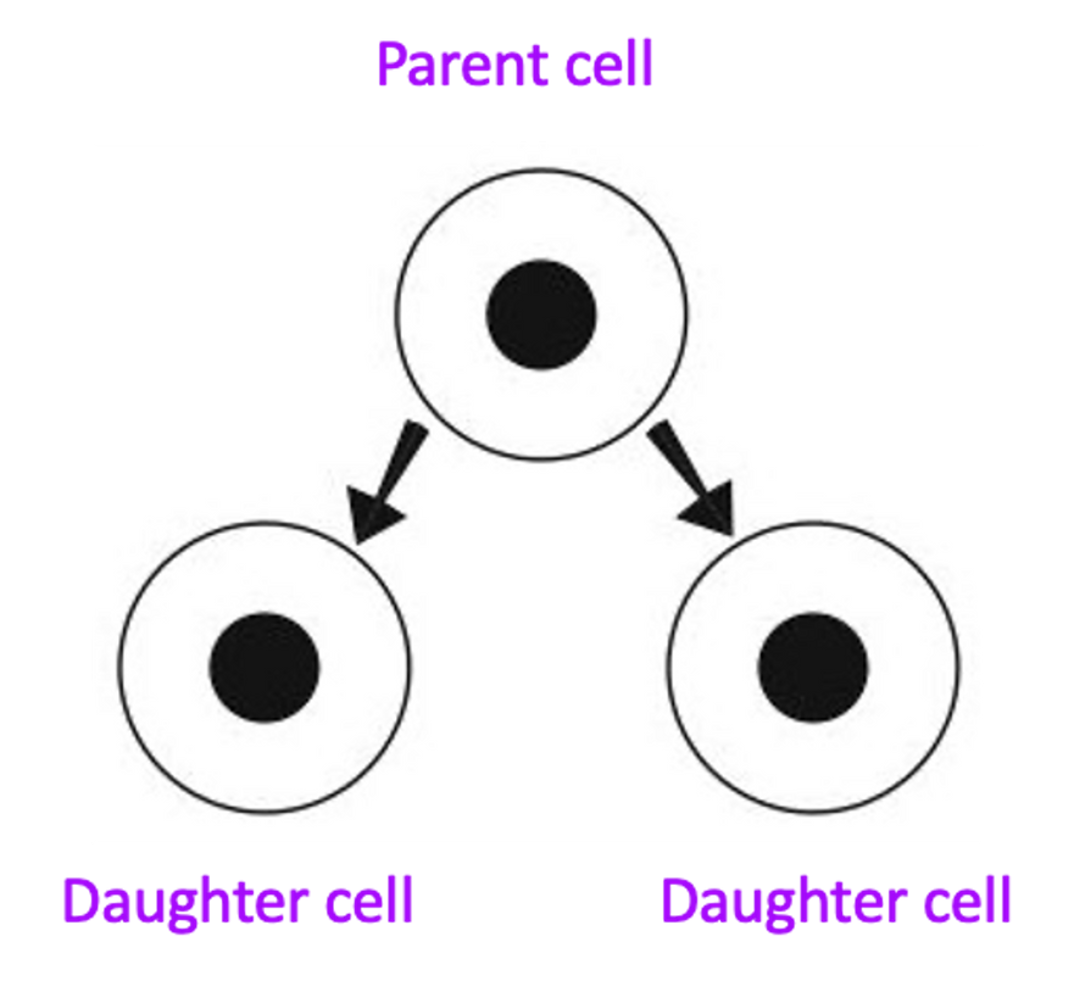
Mitosis purpose
Growth and repair
Where does mitosis occur
Mitosis occurs when body cells, called somatic cells, divide in body tissues.
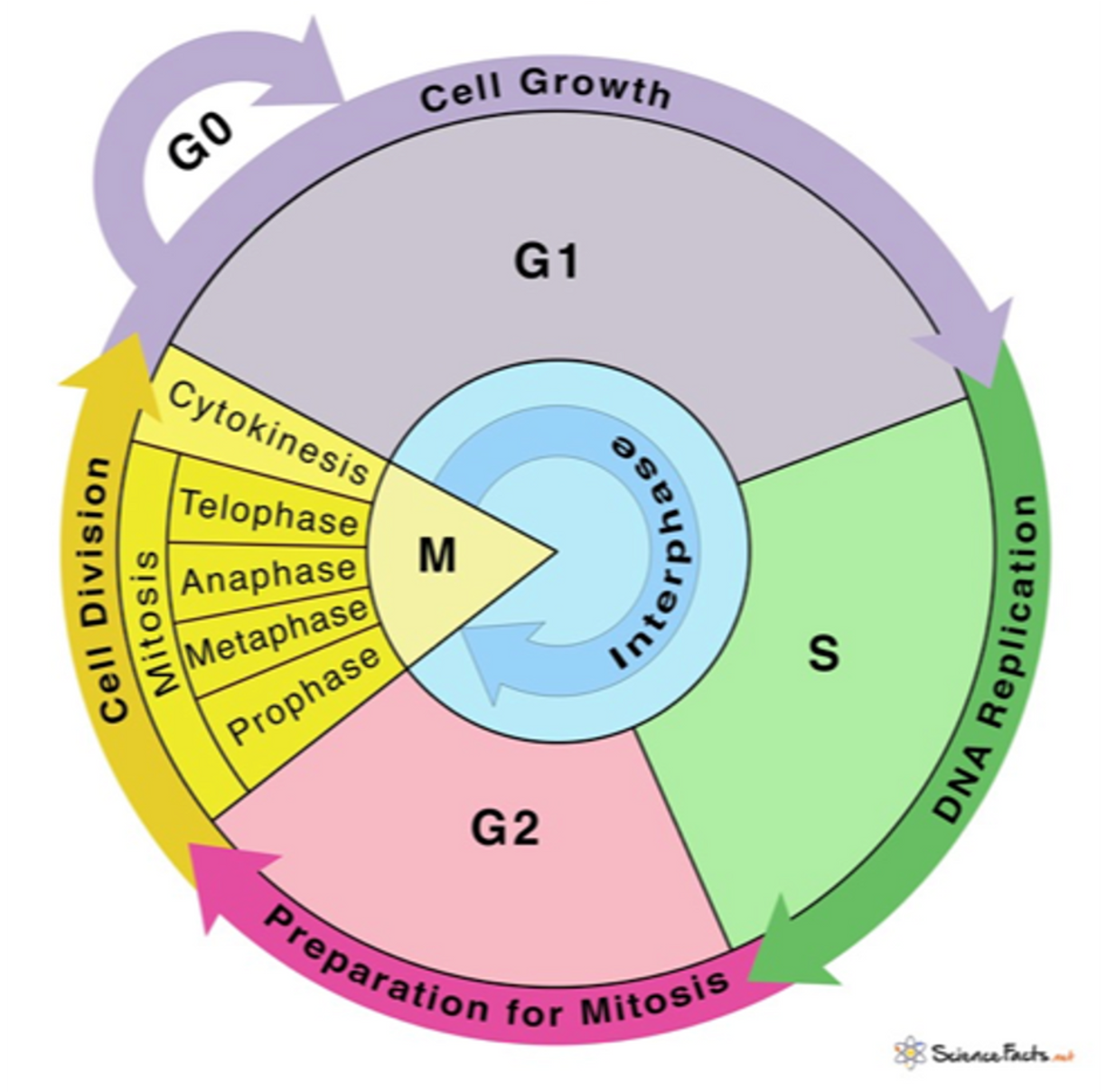
Cell cycle
The events that take place from one cell division to the next are called the cell cycle.
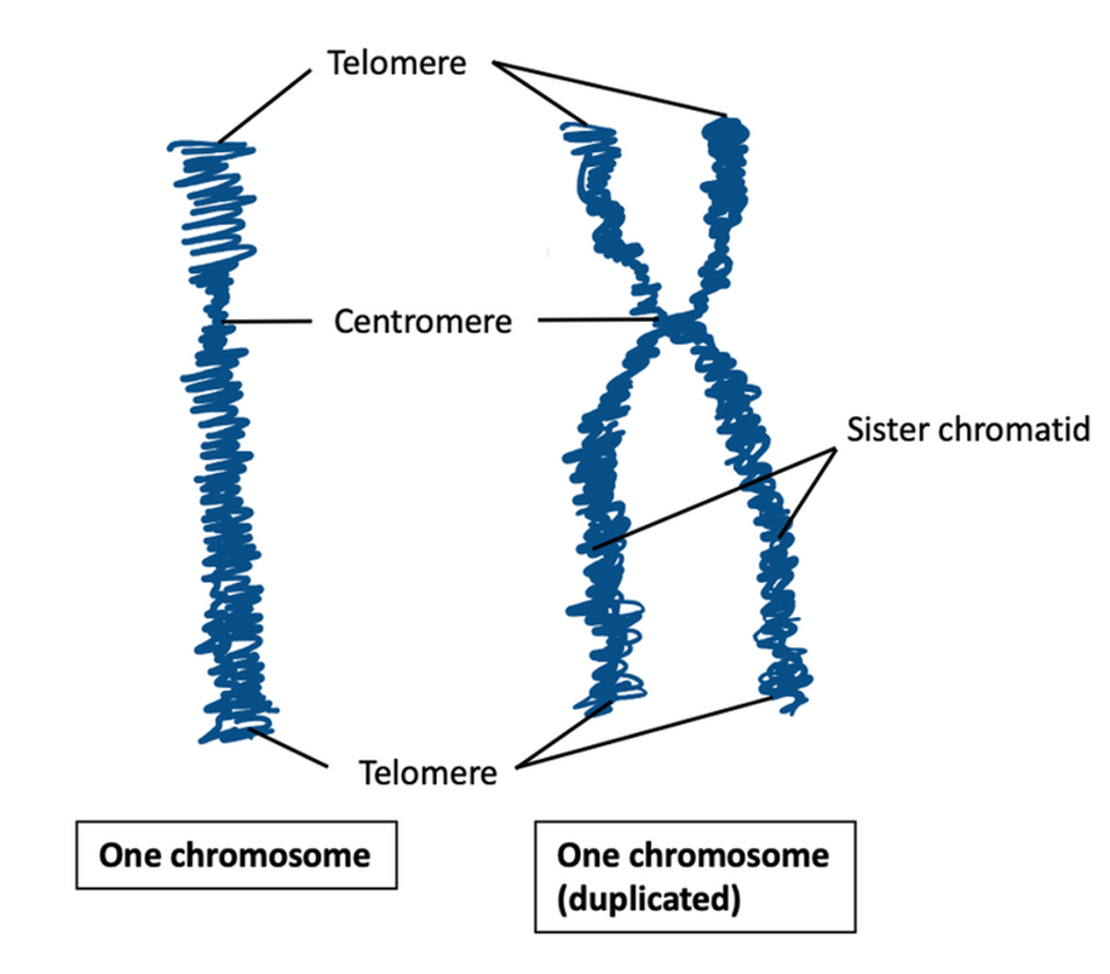
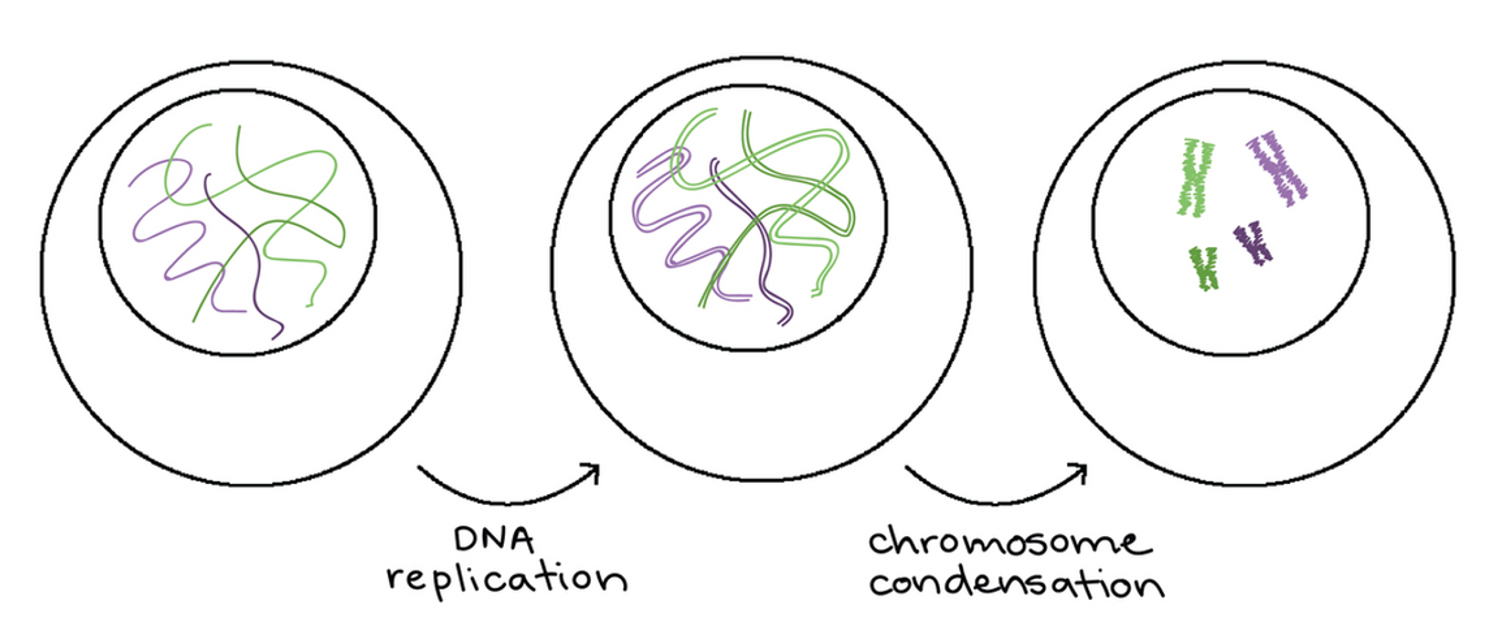
DNA replication
DNA replication occurs producing two copies of each chromosome, called chromatids.
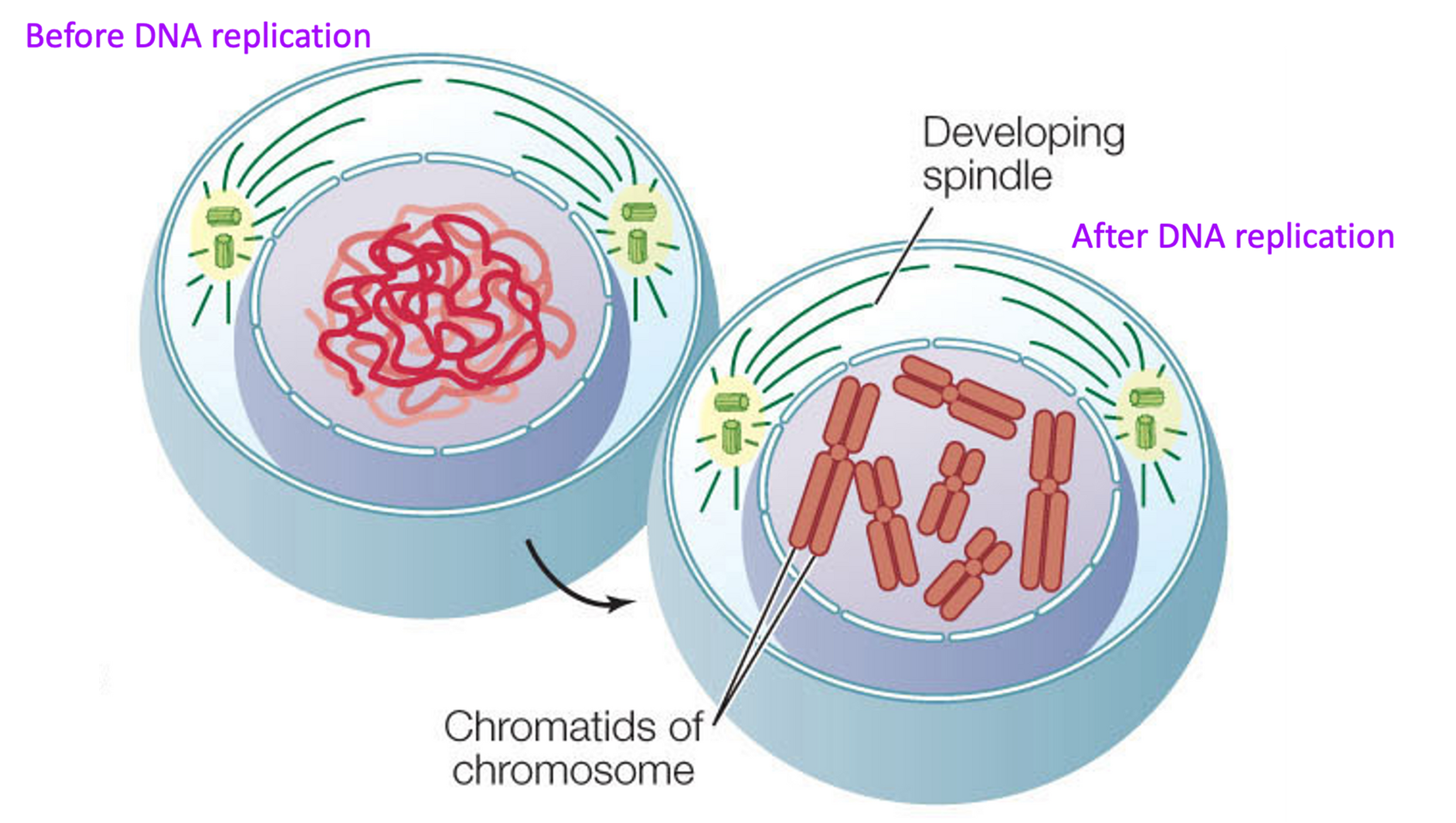
Centromere
Where the chromatids are connected to get a double stranded chromosome
Chromosome condensation diagram
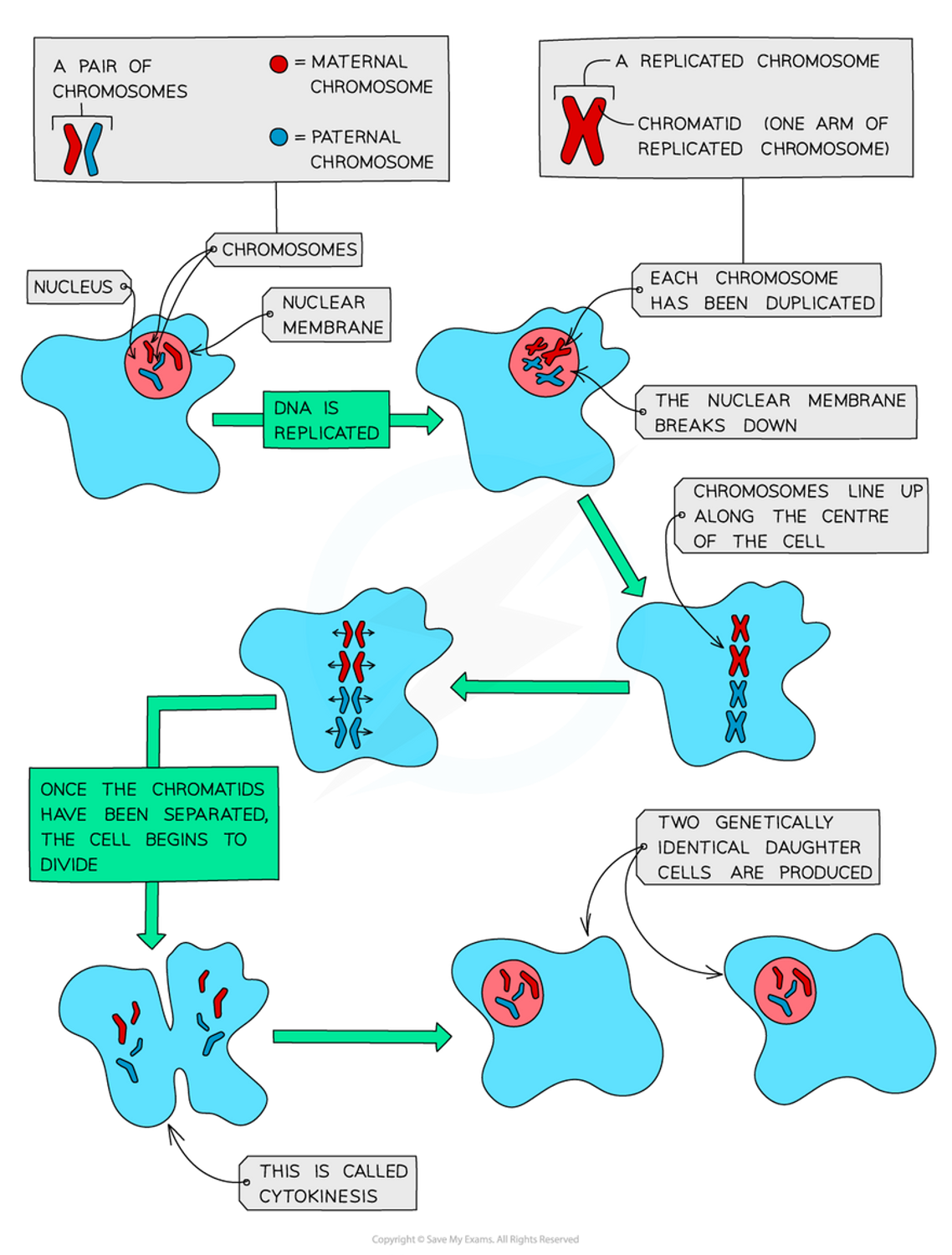
Which phase of the cell cycle does mitosis occur
•Mitosis occurs in the M phase of the cell cycle:
1.Nuclear division – mitosis
2.Cell division – cytokinesis
Nuclear division main phases
4 main phases:
1.Prophase
2.Metaphase
3.Anaphase
4.Telophase
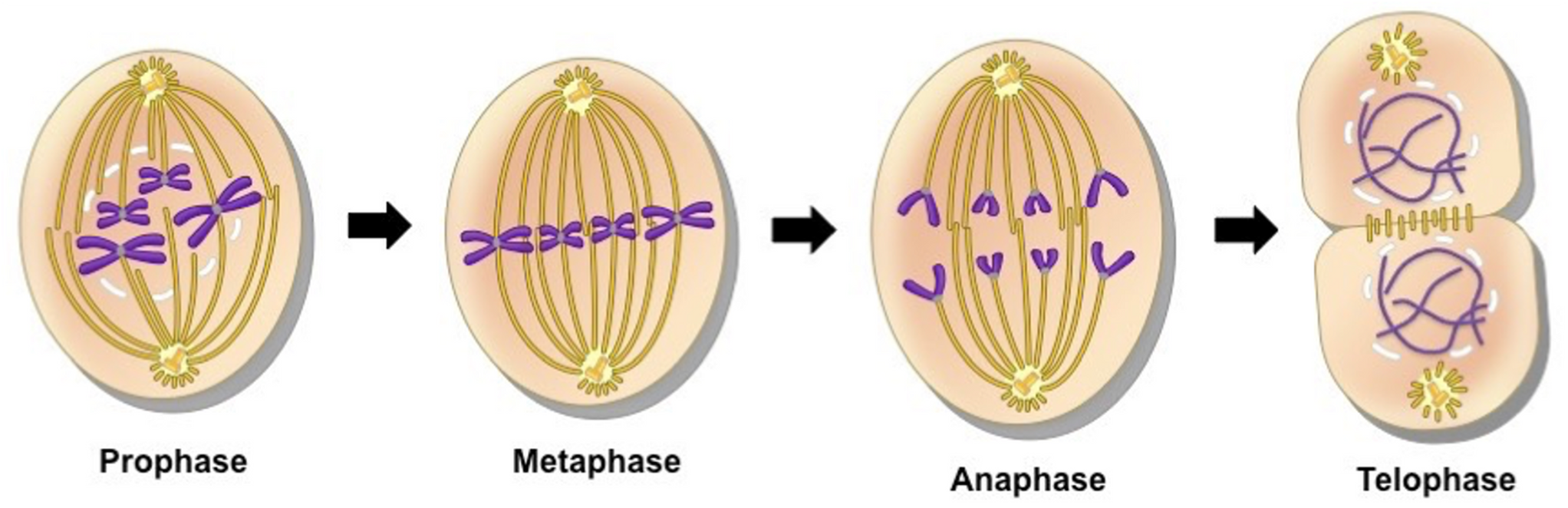
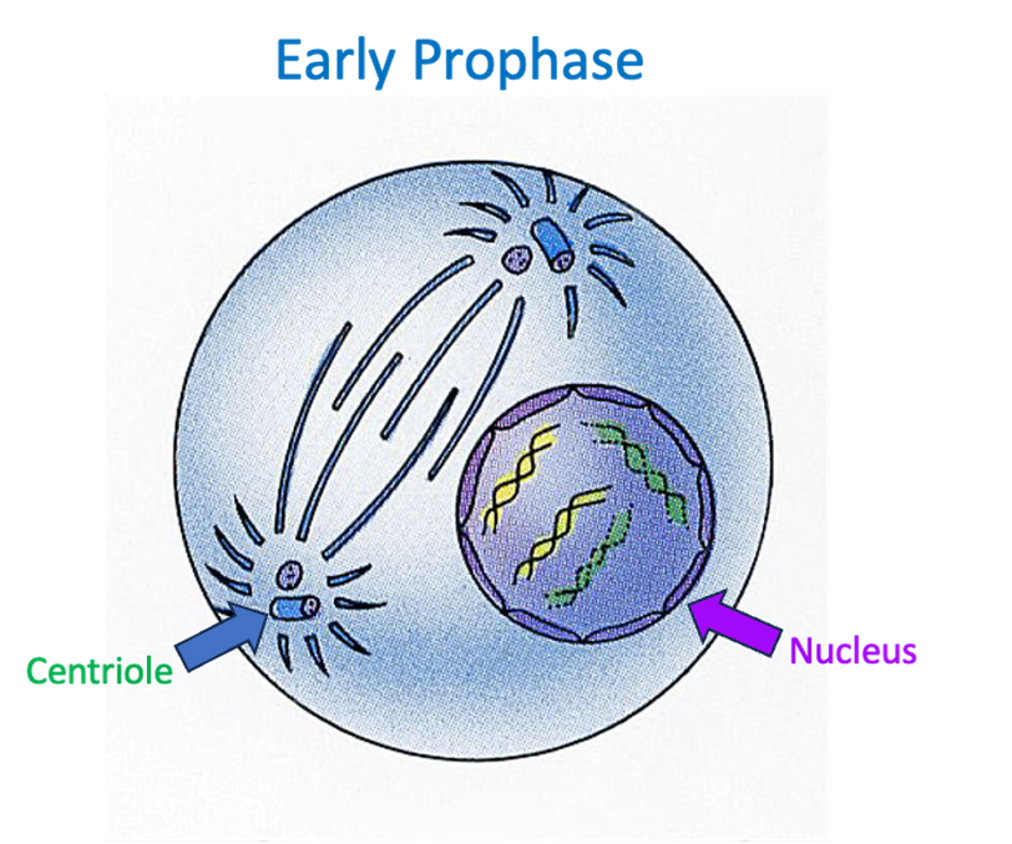
Prophase
•Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell and produce spindle fibres.
•Nuclear membrane breaks down.
•Chromosomes condense and become visible in the cytoplasm of the cell.
•Chromosomes begin migrating to the equator of the cell.
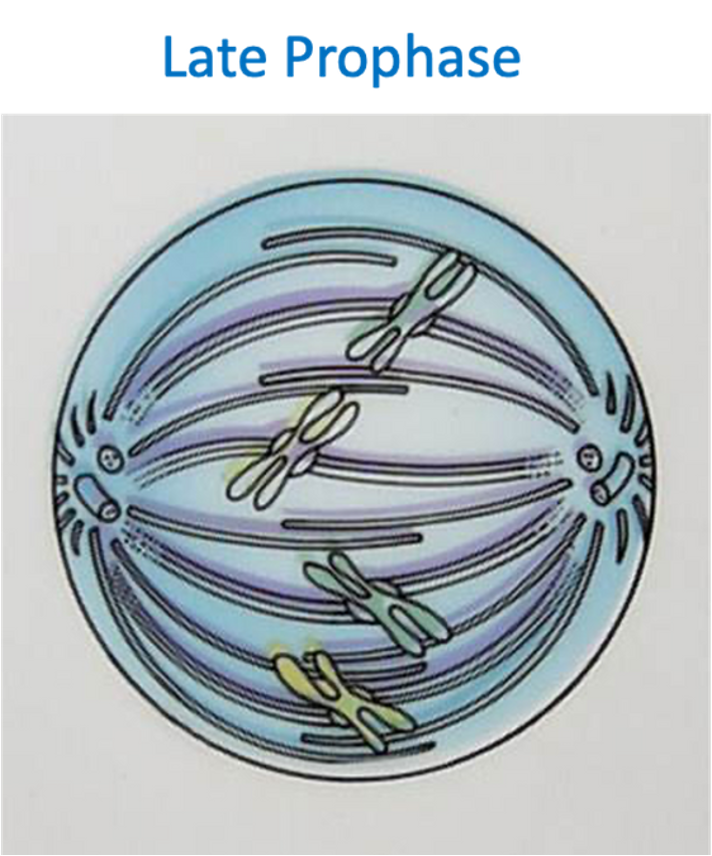
Metaphase
•Chromosomes line up of the equator of the cell head-to-toe.
•Spindle fibres attach to the centromere of each chromosome.
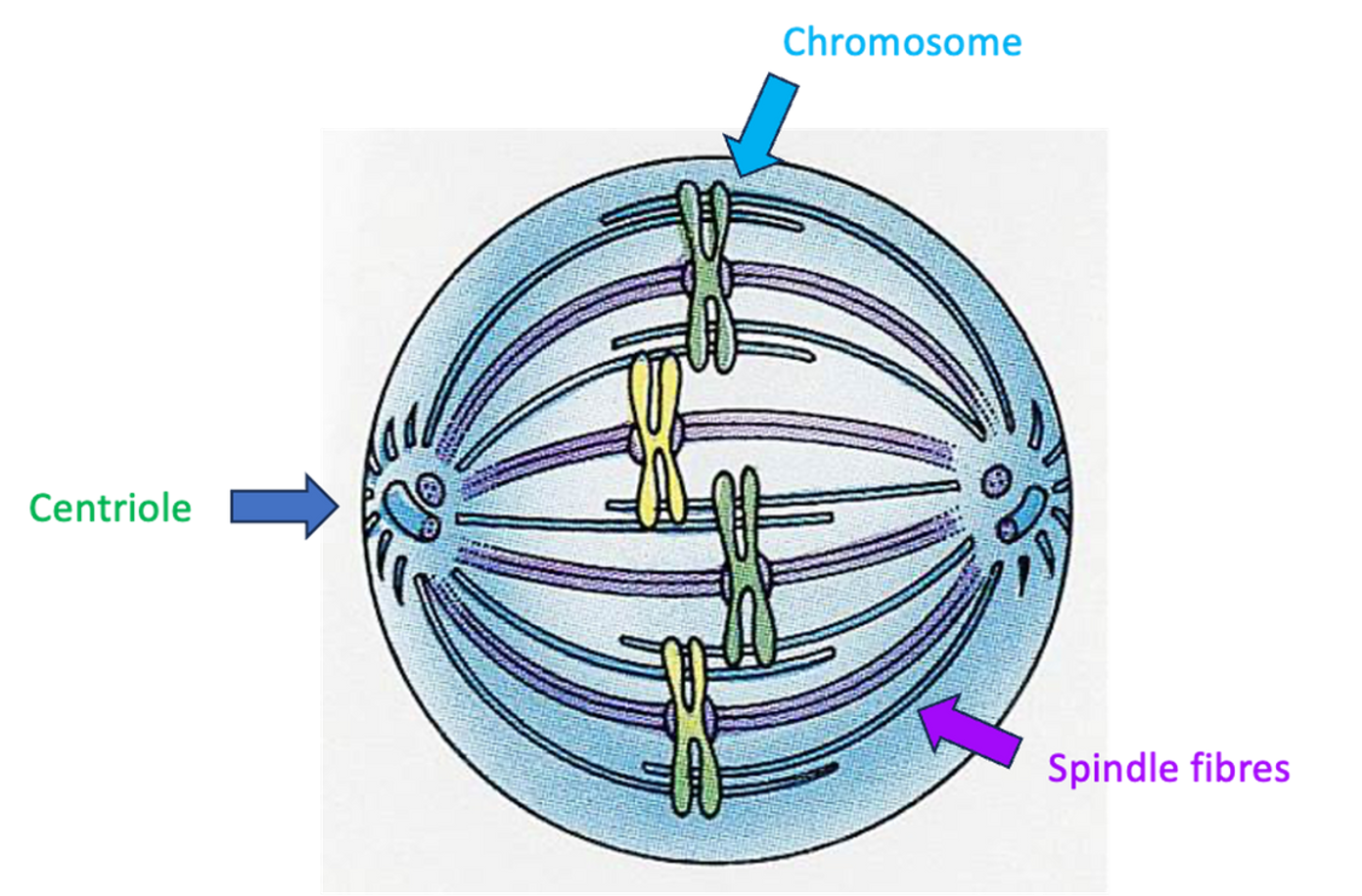
Anaphase
•Spindle fibres contract towards the centrioles.
•The chromosomes are separated at the centromere and the chromatids are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
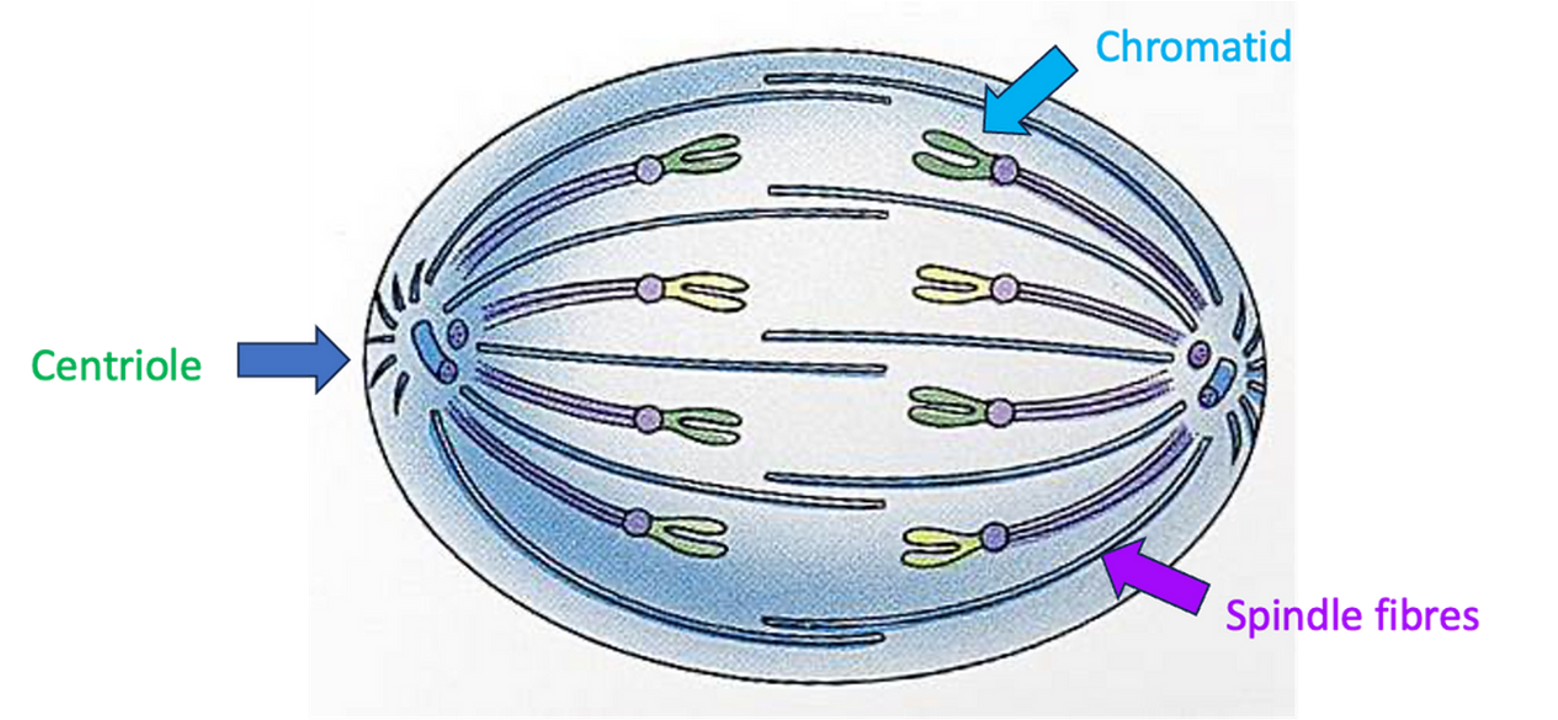
Telophase
•Two nuclear membranes form around each group of chromosomes.
•Spindle fibres break down.
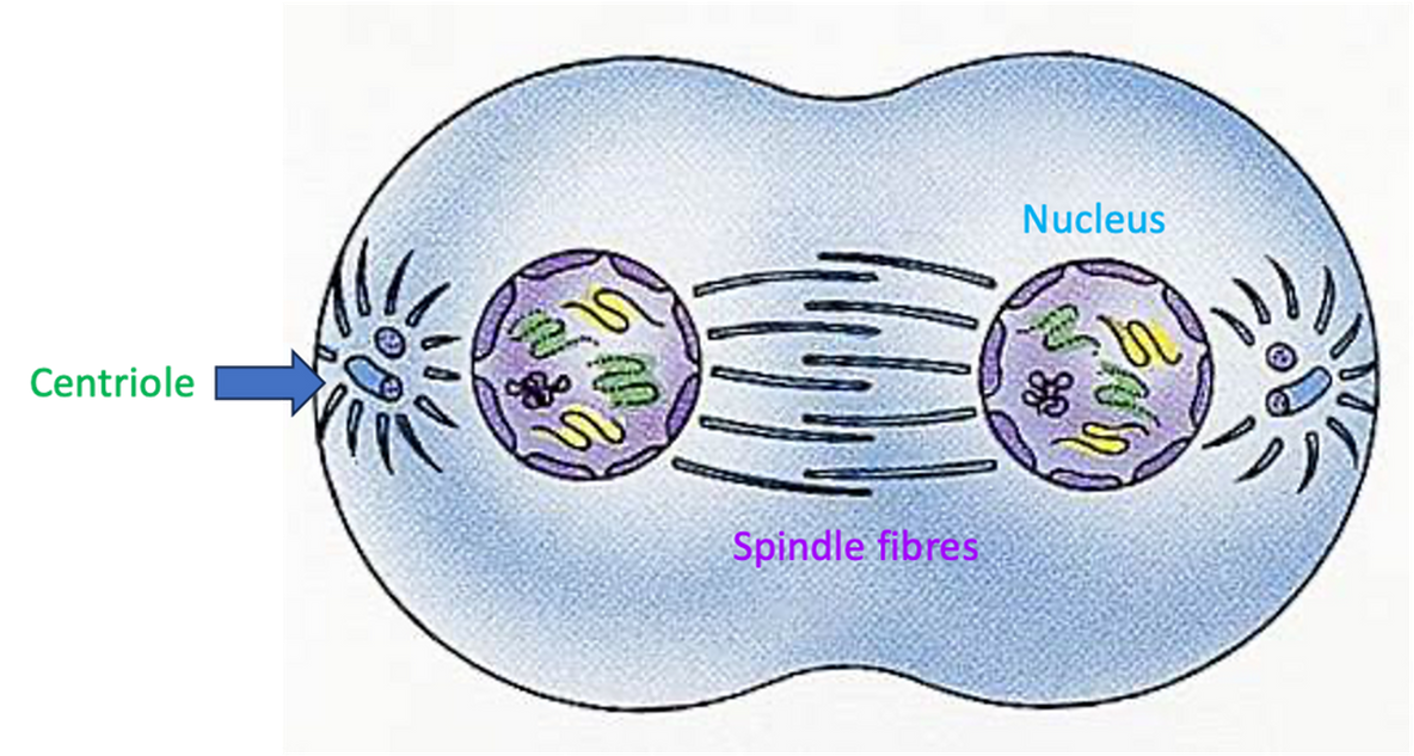
Cytokinises
•The cell membrane and cytoplasm splits into two cells.
•These daughter cells are genetically identical to the original parent cell.
•The daughter cells are diploid cells and they each have 46 chromosomes (chromatin).