ESP231 - UNIT 2: International Trade
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
International trade
"Purchase, sale, or exchange of goods and services across national borders. (thương mại quốc tế)"

Exporting
Sending goods to another country for sale or trade. (xuất khẩu)
Importing
Bringing in goods from another country for sale or trade. (nhập khẩu)
Trade surplus
"A condition that results when the value of a nation's exports is greater than the value of its imports. (thặng dư thương mại)"

Trade deficit
"A condition that results when the value of a country's imports is greater than the value of its exports.(thâm hụt thương mại)"

Mercantilism
"A trade theory which holds that a government can improve the economic well-being of the country by encouraging exports and stifling imports to accumulate wealth. (chủ nghĩa trọng thương)"
Neo-mercantilism
"A modern trade policy of encouraging exports, discouraging imports, controlling capital movement, and centralizing currency decisions. (chủ nghĩa tân trọng thương)"
Theory of absolute advantage
"A trade theory which holds that nations can increase their economic well-being by specialising in goods that they can produce more efficiently than anyone else. (học thuyết lợi thế tuyệt đối)"
Theory of comparative advantage
"A trade theory which holds that nations should produce those goods for which they have the greatest relative advantage. (Học thuyết lợi thế so sánh)"
Factor endowment theory
"A trade theory which holds that nations will produce and export products that use production factors they have in abundance and will import products requiring a large amount of production factors that they lack. (Học thuyết yếu tố dồi dào (Heckscher-Ohlin))"
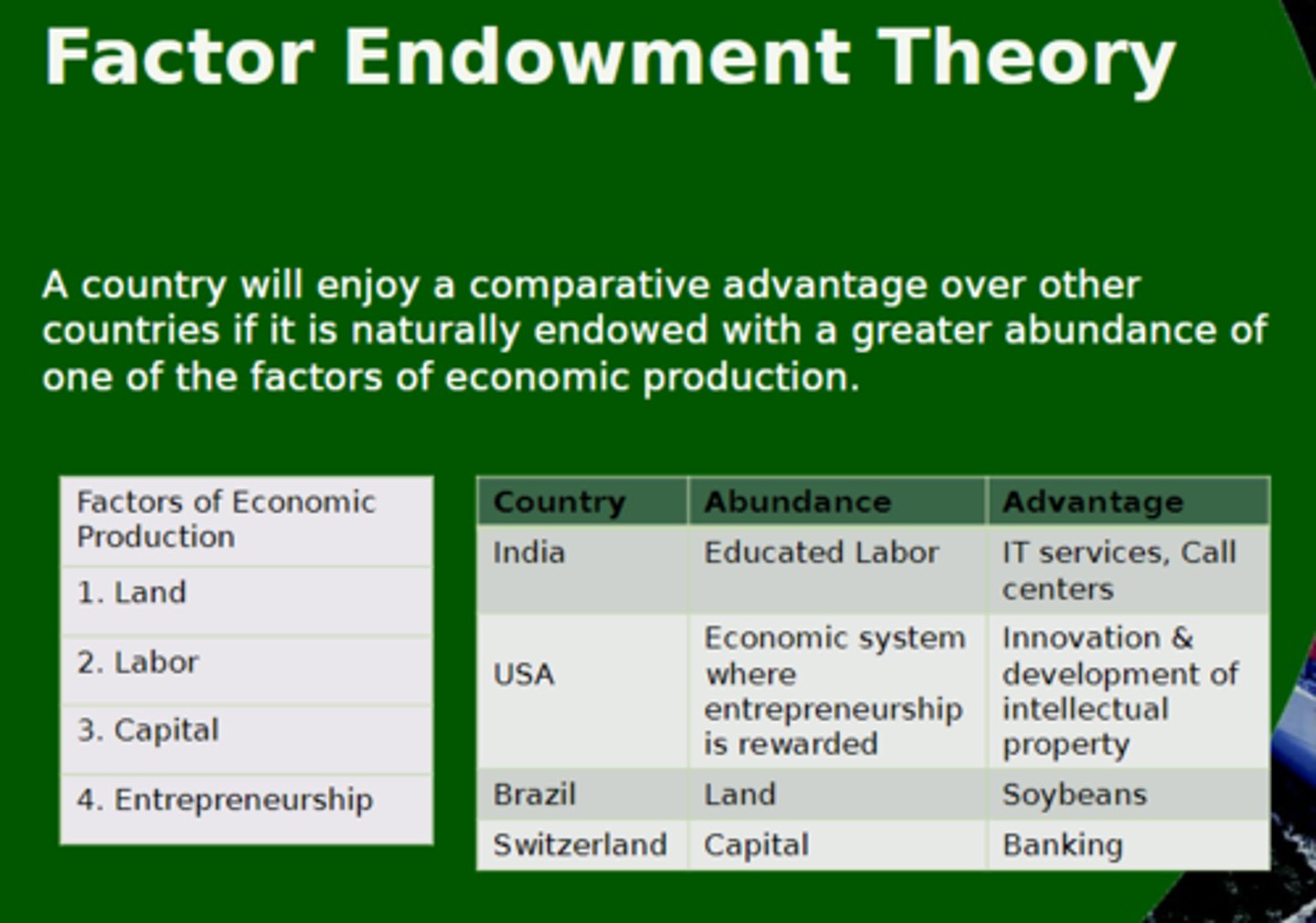
Leontief paradox
A finding which shows that the United States, surprisingly, exports relatively more labour-intensive goods and imports capital-intensive goods.
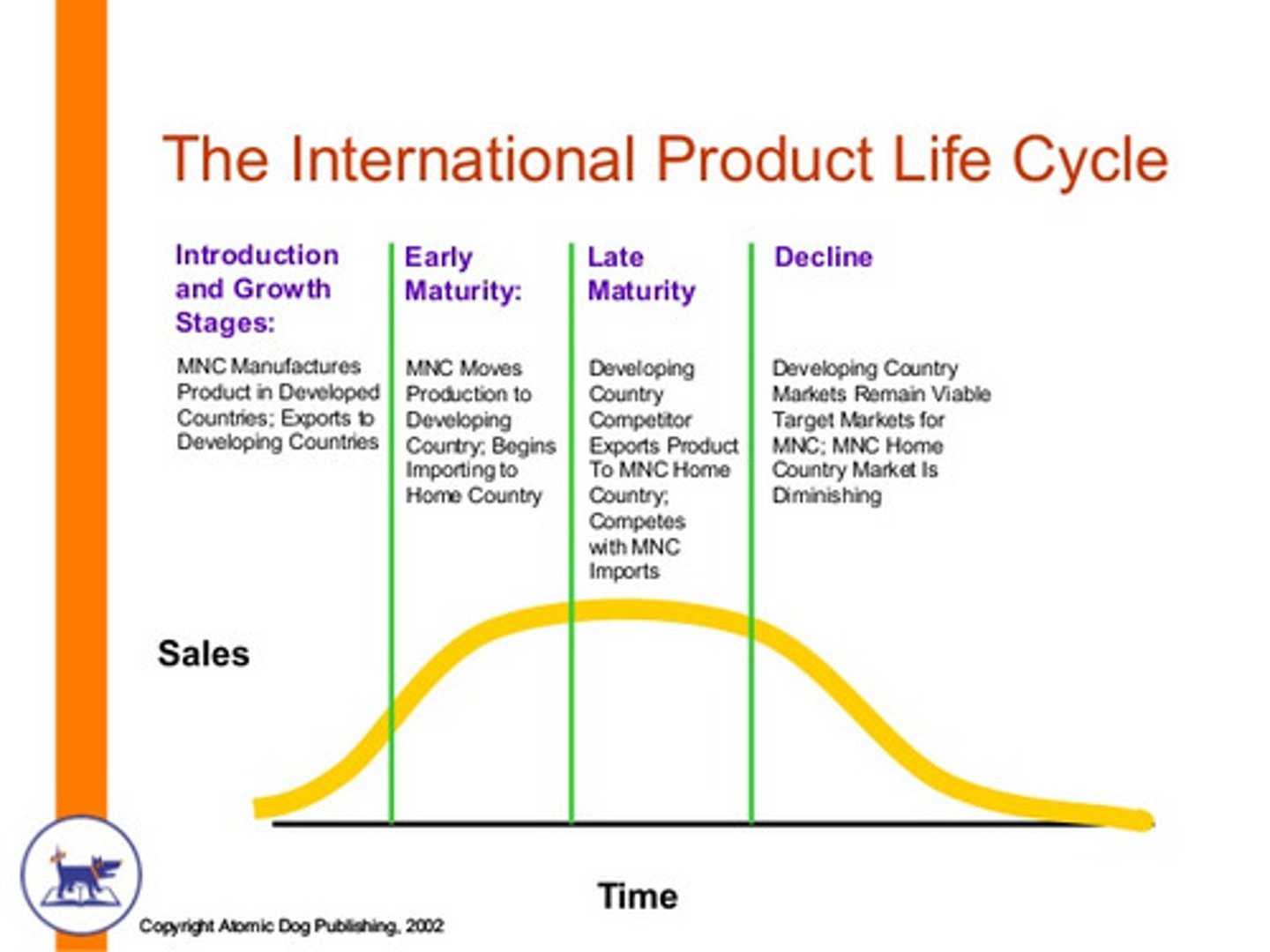
IPLC theory
"A theory explaining the stages of a product's life cycle, where production moves from the inventing country to other nations as the product matures. (Lý thuyết vòng đời sản phẩm quốc tế)"
Embargo
A complete ban on trade (imports and exports) with a particular country. (cấm vận)

Subsidy
Financial assistance to domestic producers in the form of cash payments, low-interest loans, tax breaks, or price supports. (trợ cấp)
Loan guarantee
"A guarantee from a government that it will repay a company's loan if the company defaults on repayment. (Bảo lãnh vay)"
Foreign trade zone (FTZ)
"A designated geographic region in which merchandise is allowed to pass through with lower customs duties and/or fewer customs procedures.

Special government agencies
"Agencies responsible for promoting exports, often organizing trade trips and opening trade offices abroad.
Price-based barriers
"Barriers that add a cost to imported goods, such as tariffs. (Rào cản dựa trên giá)"
Quantity limits
Restrictions on the number of units of a product that can be imported or the market share permitted, often known as quotas.
International price fixing
"An agreement between international firms to fix prices or quantities sold in an effort to control price. This is known as a cartel. - Ấn định giá quốc tế (cartel)"
Financial limits
Restrictions on the flow of currency, such as exchange controls that limit the amount of money that can be taken out of the country.
Foreign investment controls
Limits on foreign direct investment or the transfer/remittance of funds, such as requiring minority ownership positions for foreign investors.
Tariffs
A tax on goods that are shipped internationally, most commonly an import tariff.
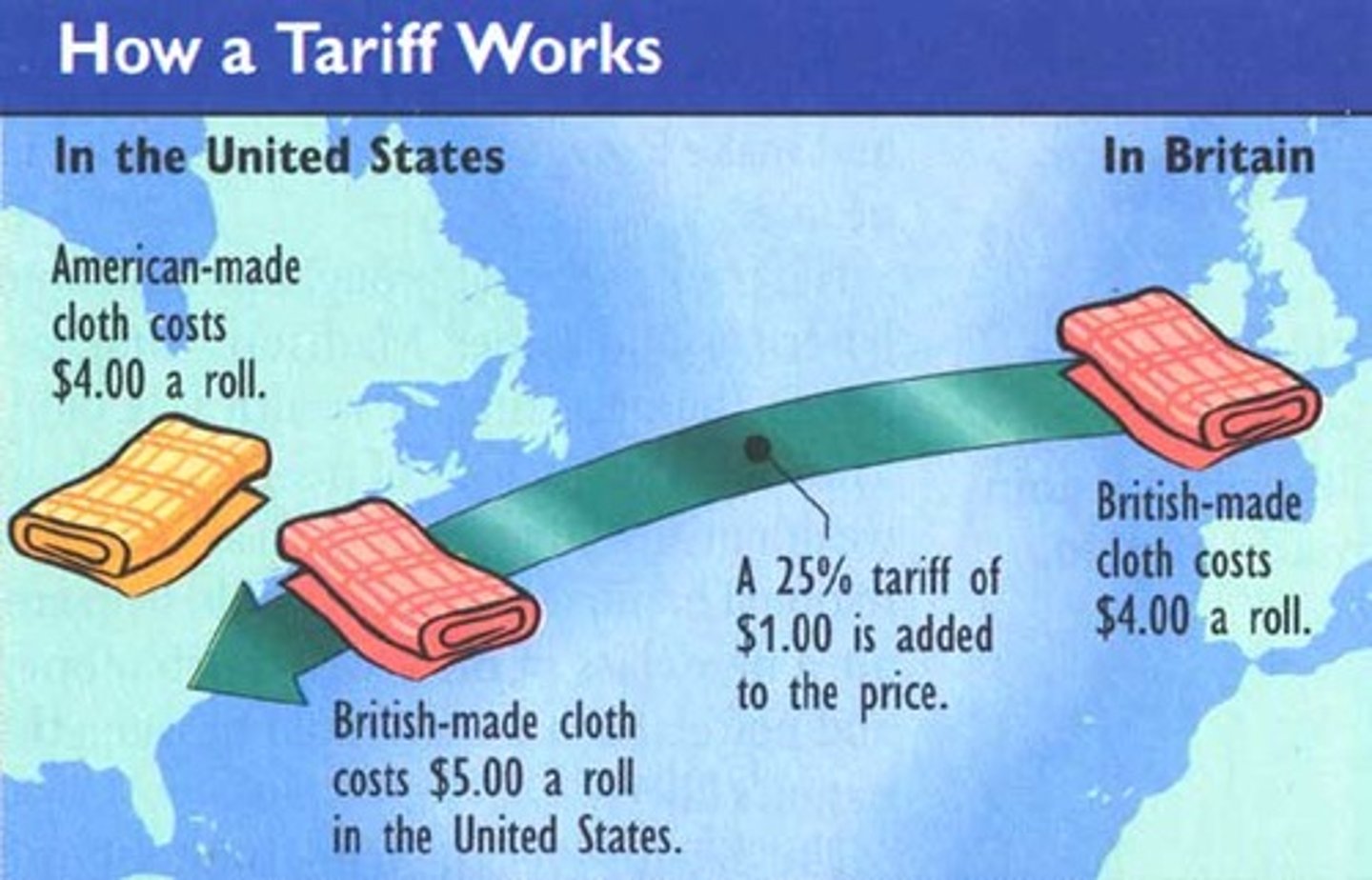
Specific duty / Ad valorem duty
"A specific duty is a tariff based on units ($1 per item). An ad valorem duty is a tariff based on a percentage of the item's value (10% duty).
Dumping
"The selling of imported goods at a price below cost or below the price in the home country (Bán phá giá)"
Quotas
"A restriction on the quantity of a product that can be imported or exported. (Hạn ngạch)"
'Buy national' restrictions
Regulations that require governments to give preference to domestic producers.
Customs valuation
"The process of determining the value of imported goods for the purpose of levying duties. (Trị giá hải quan)"

Technical barriers
Product and process standards (e.g., for health, safety, quality) that can exclude products that do not meet them.
OPEC
"The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, a group of oil-producing nations that seeks to control oil prices and supply. (Tổ chức các nước xuất khẩu dầu mỏ"
LDC (Less Developed Country)
Countries with low levels of industrialization, high poverty rates, and economic vulnerability.
Protectionism
"Protectionism is an economic policy approach that favors preventing the exposure of domestic producers to the rigors of the international market (Chủ nghĩa bảo hộ)"
net barter terms of trade
Refer to the ratio of the unit price of export to the unit price of import
Agreement on Government Procurement (GPA)
An international agreement aimed at opening up government procurement markets to all members, initiated during the Tokyo Round of GATT
Import Tariff
A tax levied on goods shipped into a country, used to raise revenue or protect local industry.
Export Tariff
A tax levied on goods sent out of a country, less common than import tariffs.
Transit Tariff
A tax levied on goods passing through a country.
Compound Duty/Tariff
A tariff consisting of both a specific duty and an ad valorem duty.
Voluntary Export Restraint Agreements
Agreements negotiated to limit exports, used to prevent retaliatory action by importing countries and often circumventing import quota prohibitions
