Calvin Cycle
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
purpose of Calvin cycle
convert Co2 and energy from ATP and NADPH into glucose
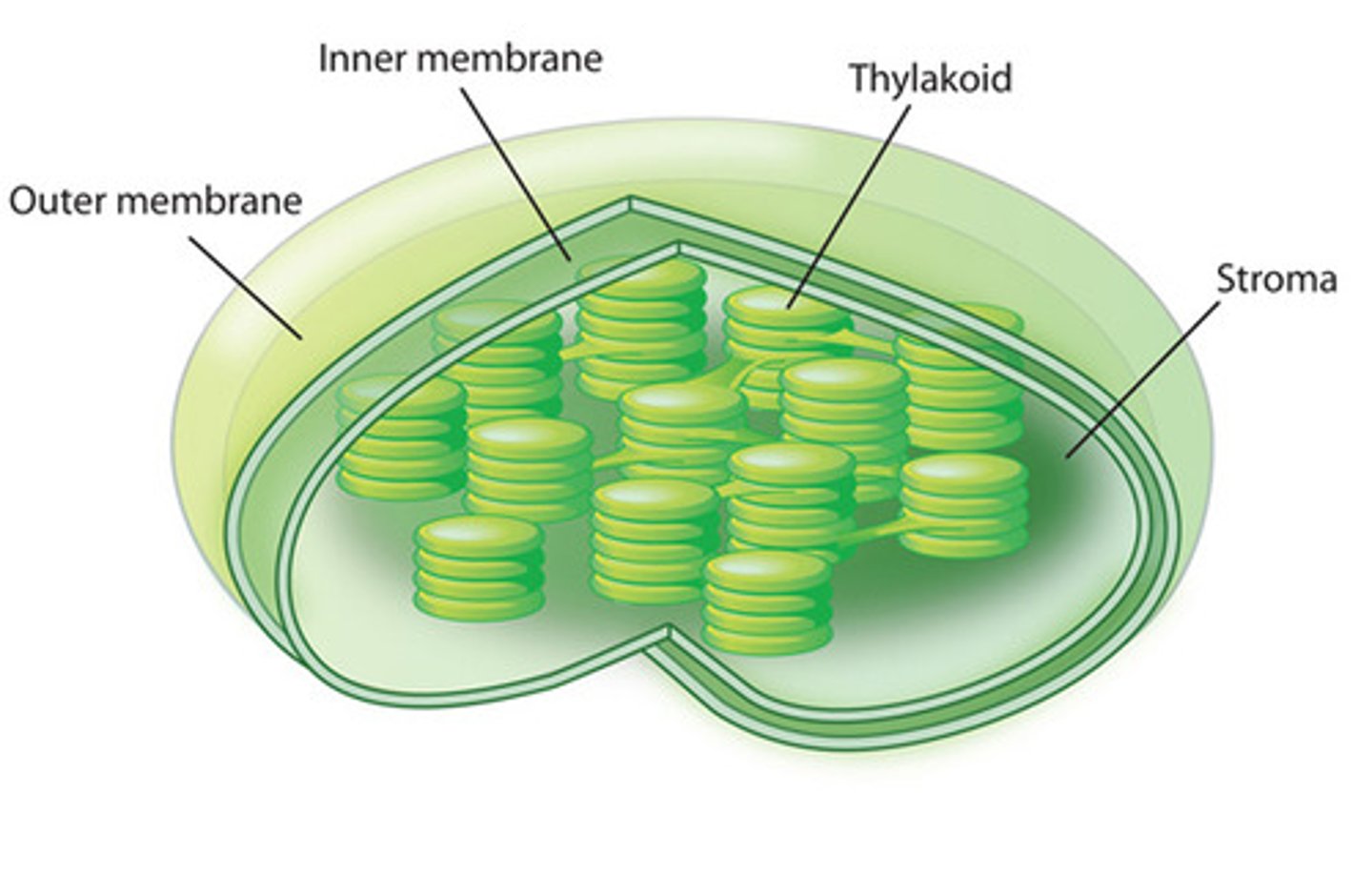
where does the Calvin cycle occur
stroma of the chloroplast
Inputs of Calvin Cycle
CO2, ATP, NADPH
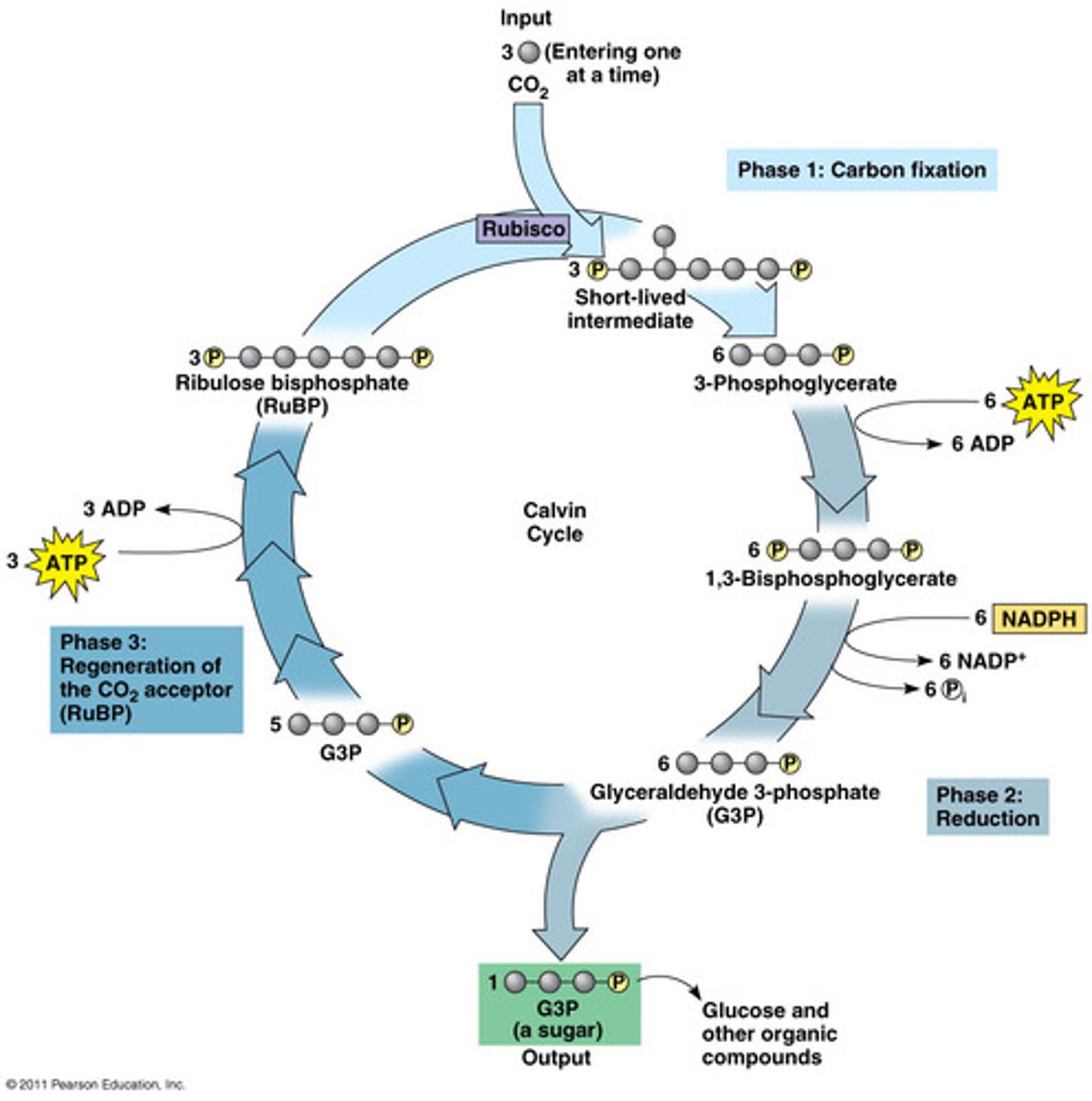
output of Calvin Cycle
glucose, ADP, NADP
Equation for Calvin cycle
6CO2 + 12NADPH + 10H2O + 18ATP →2G3P + 12NADP+ + 18ADP
How does the Calvin cycle create glucose?
using substrates from light-dependent reactions and CO2 in air
the Calvin cycle is...
light independent reactions
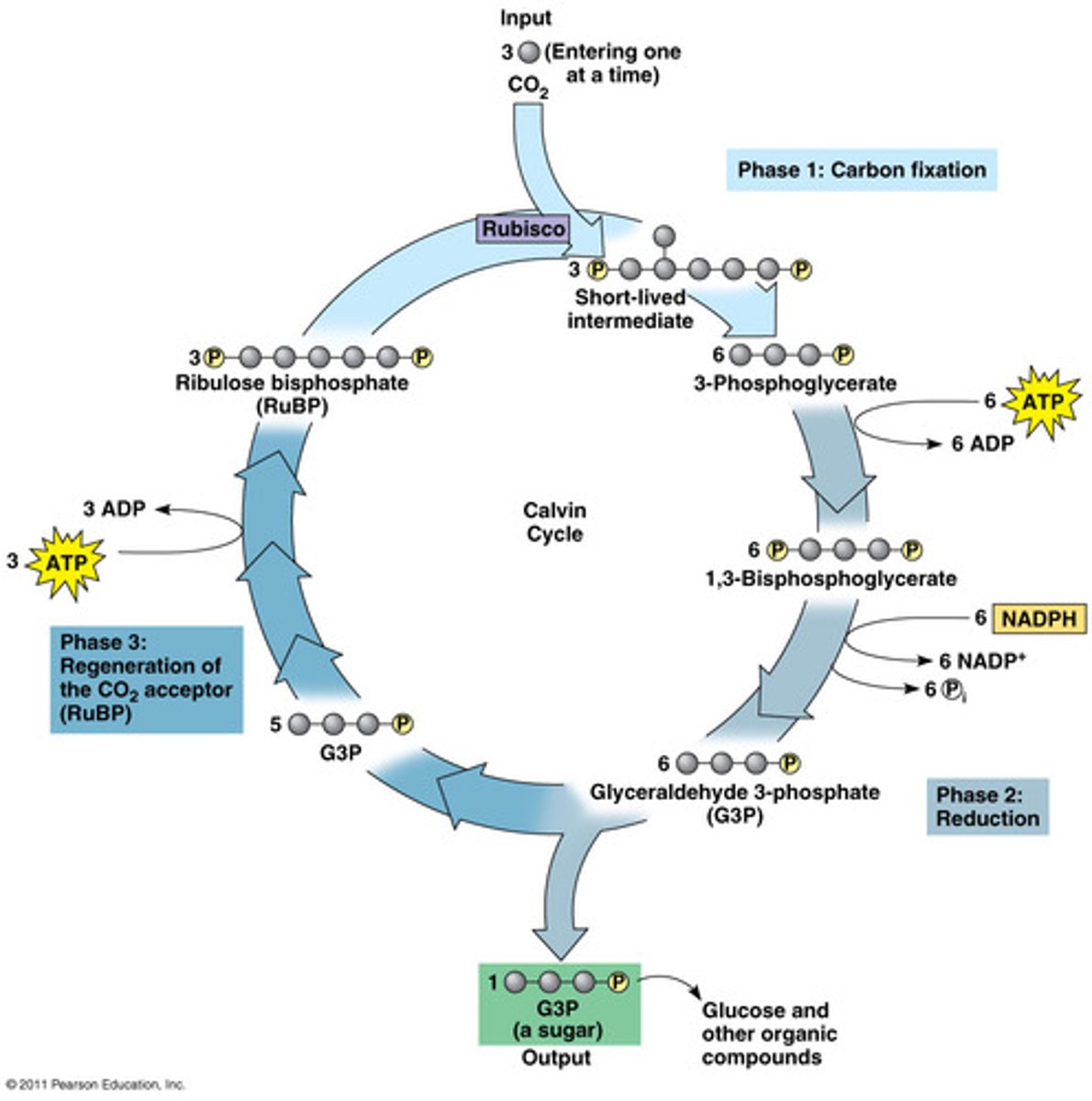
3 phases of calvin cycle
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration
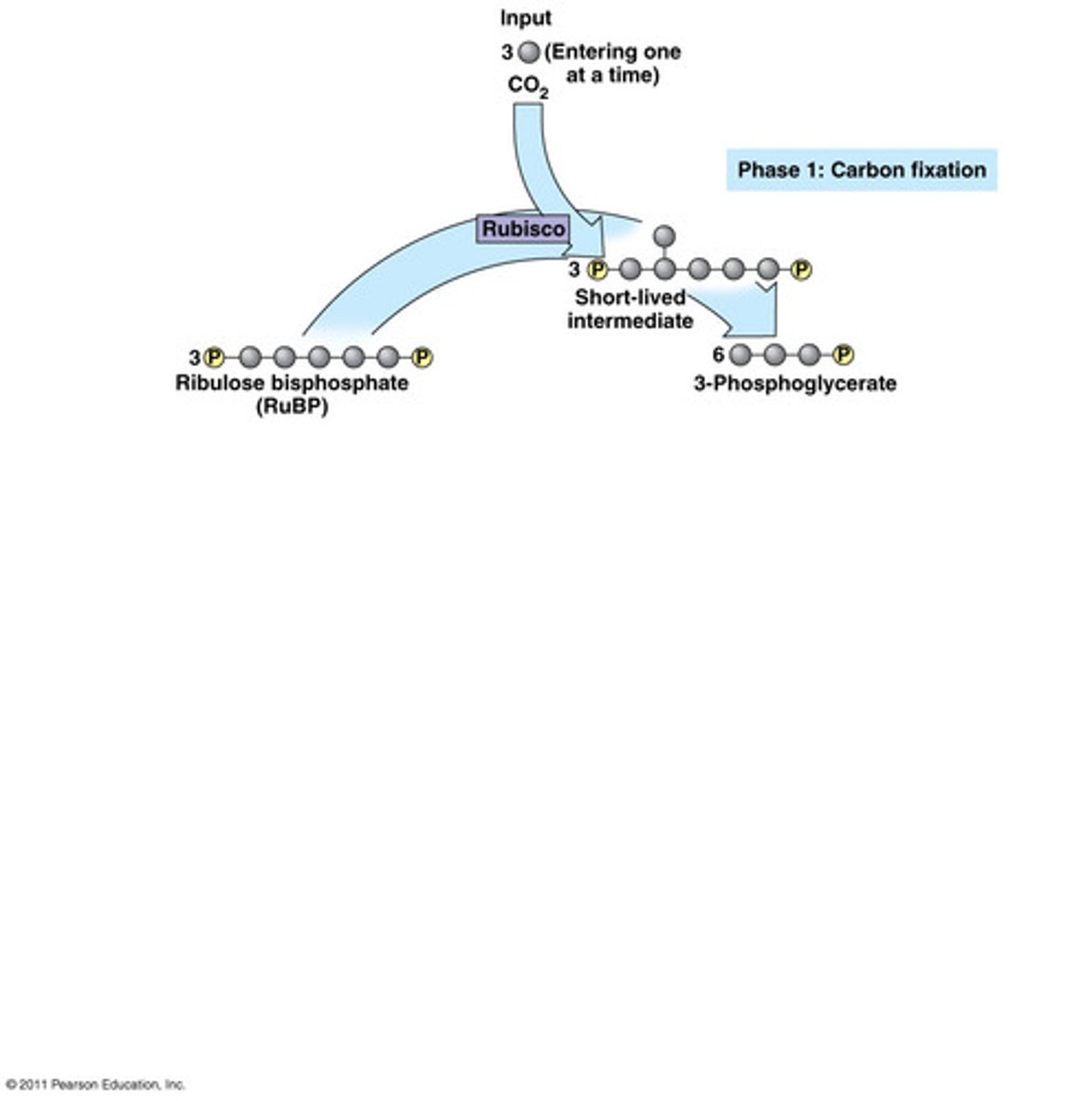
Carbon fixation
CO2 from the atmosphere+ RuBP--> 3 unstable 6-carbon molecules (they break) --> 6 molecules of 3PGA
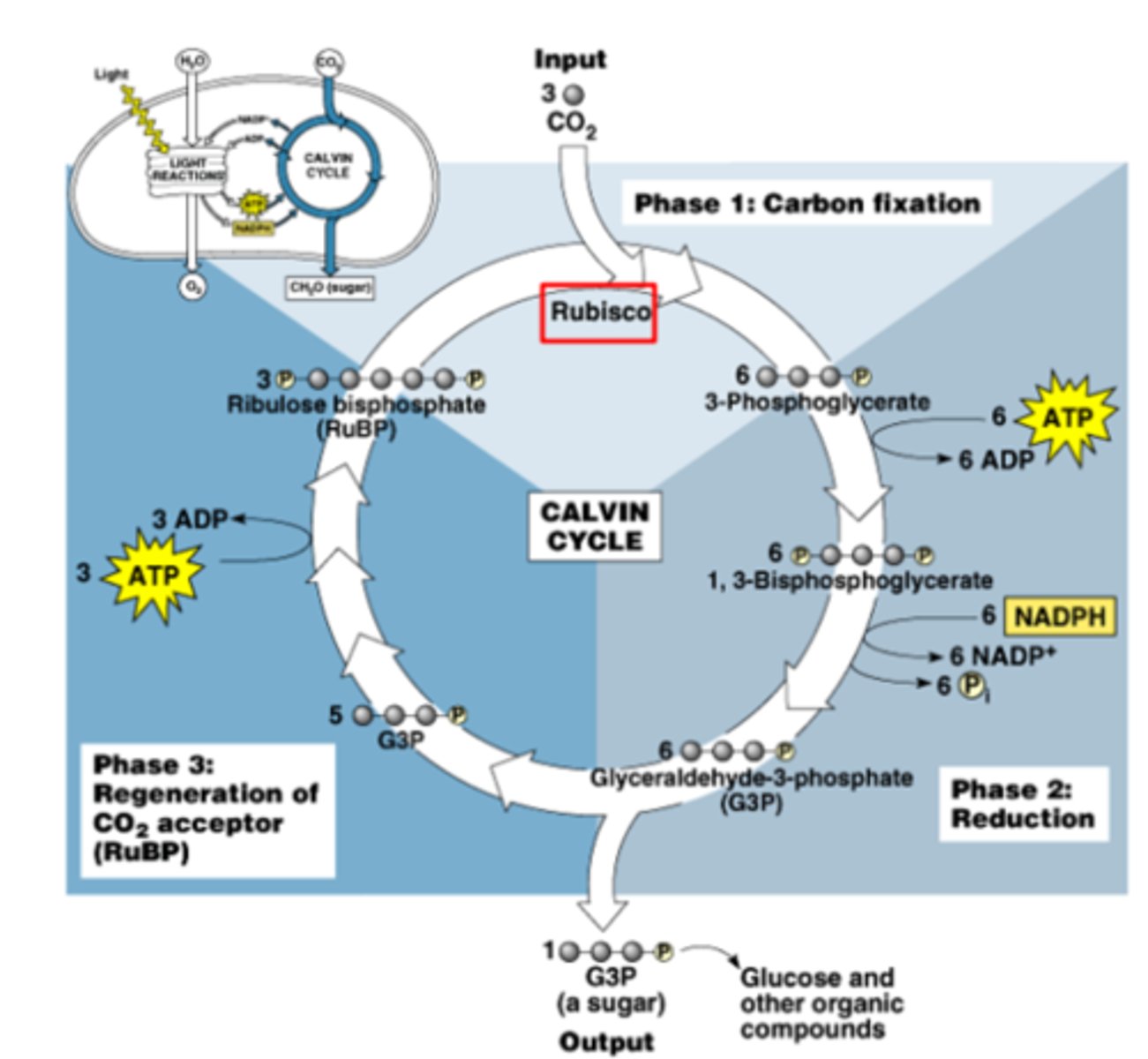
enzyme that catalyzes carbon fixation
Rubisco
first stable intermediate
3-PGA
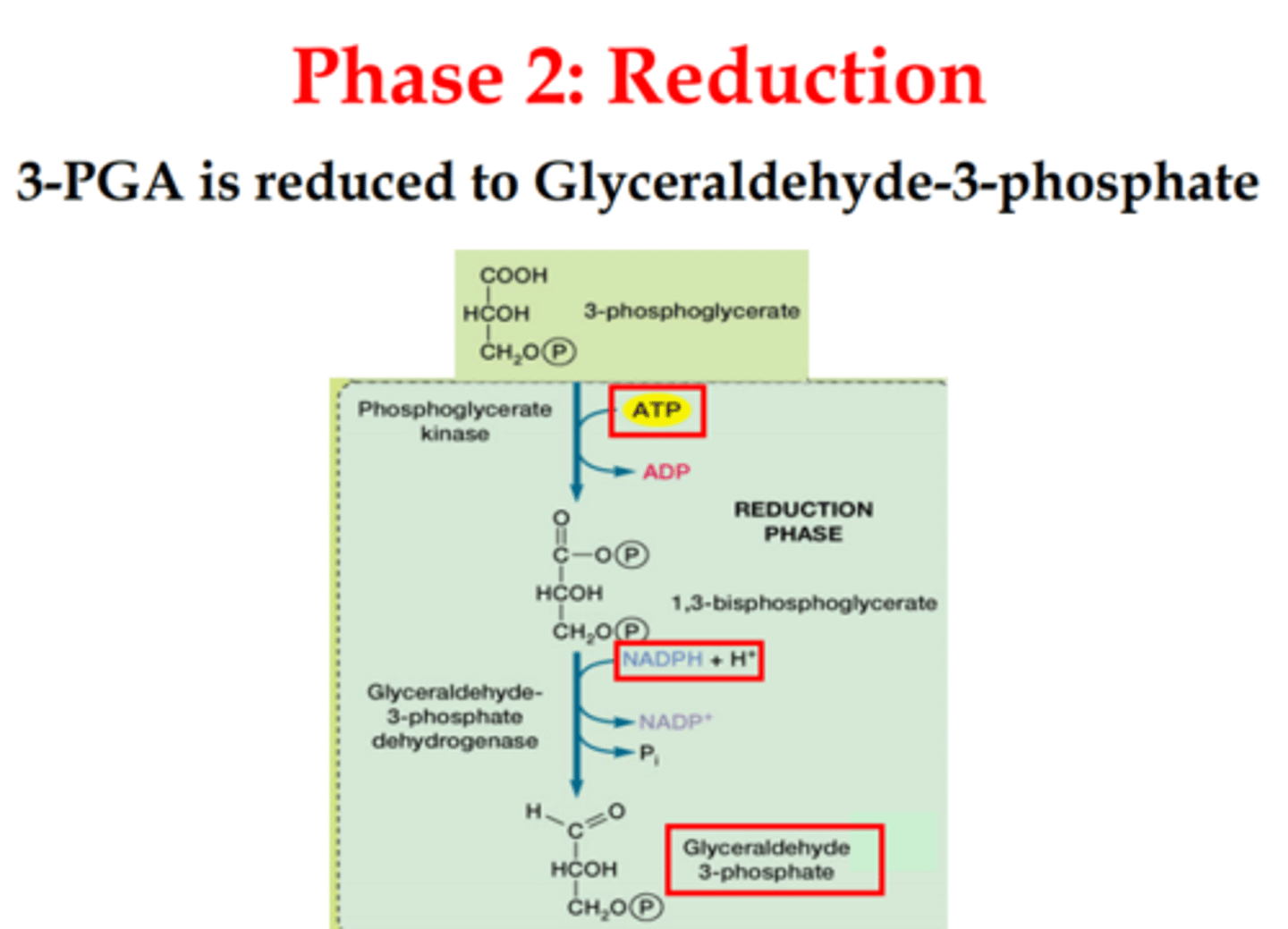
reduction
ATP and NADPH provide energy to convert three 3-PGA --> six G3P
regeneration pt 1
1 G3P exists the cycle (used to make glucose) and 5 remain
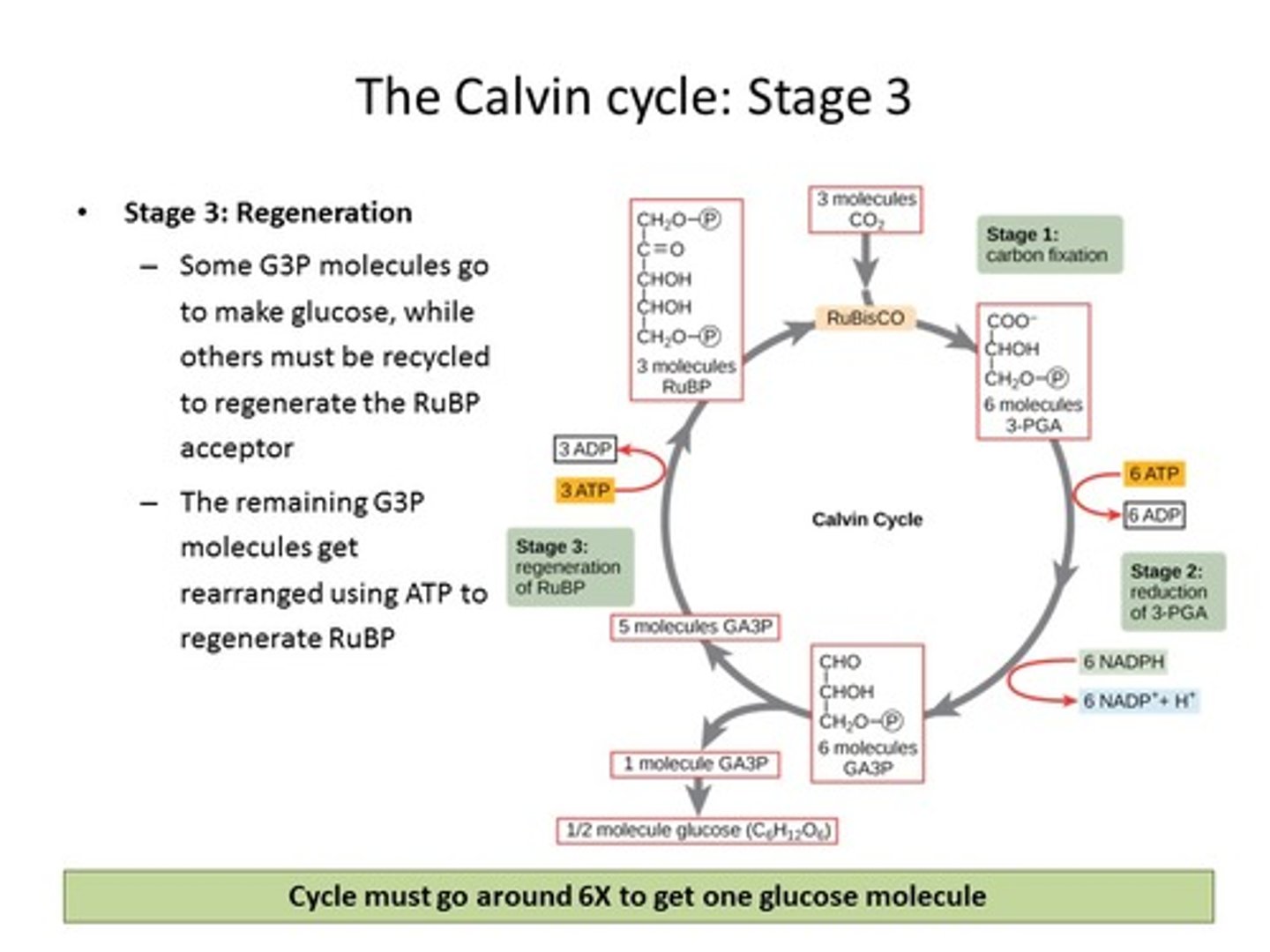
regeneration pt 2
ATP provides energy to rearrange 5 G3P--> 3 RuBP
how many turn of the Calvin cycle make 1 molecule of glucose
6 turns
photorespiration
oxidizing RuBP
rubisco can either reduce CO2 or oxidize RuBP
CO2 and O2 compete for active site of rubisco
C3 plants
only use Calvin Cycle to fix carbon
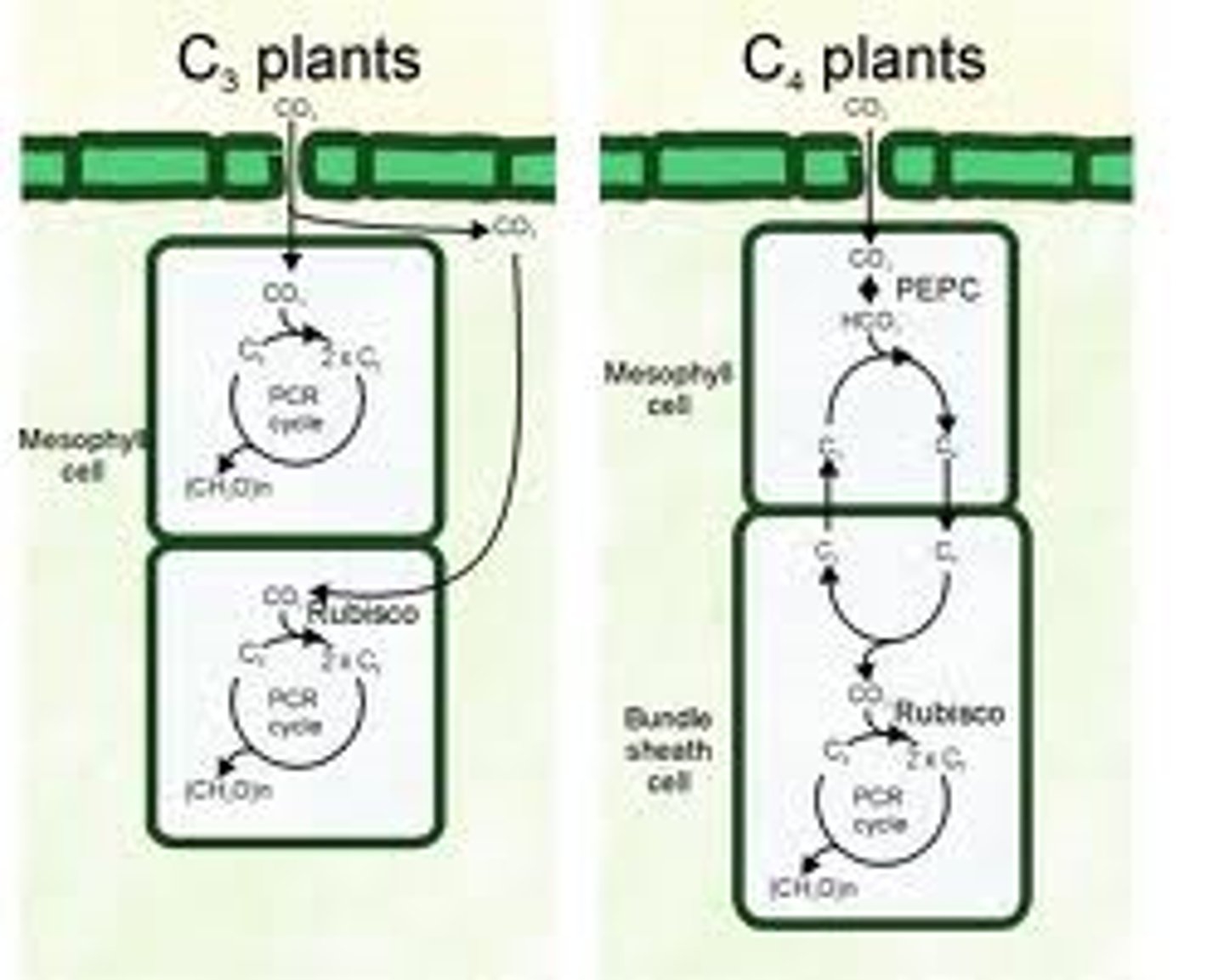
C4 plants
- use Calvin cycle and PEP carboxylase
- allow for storage of CO2
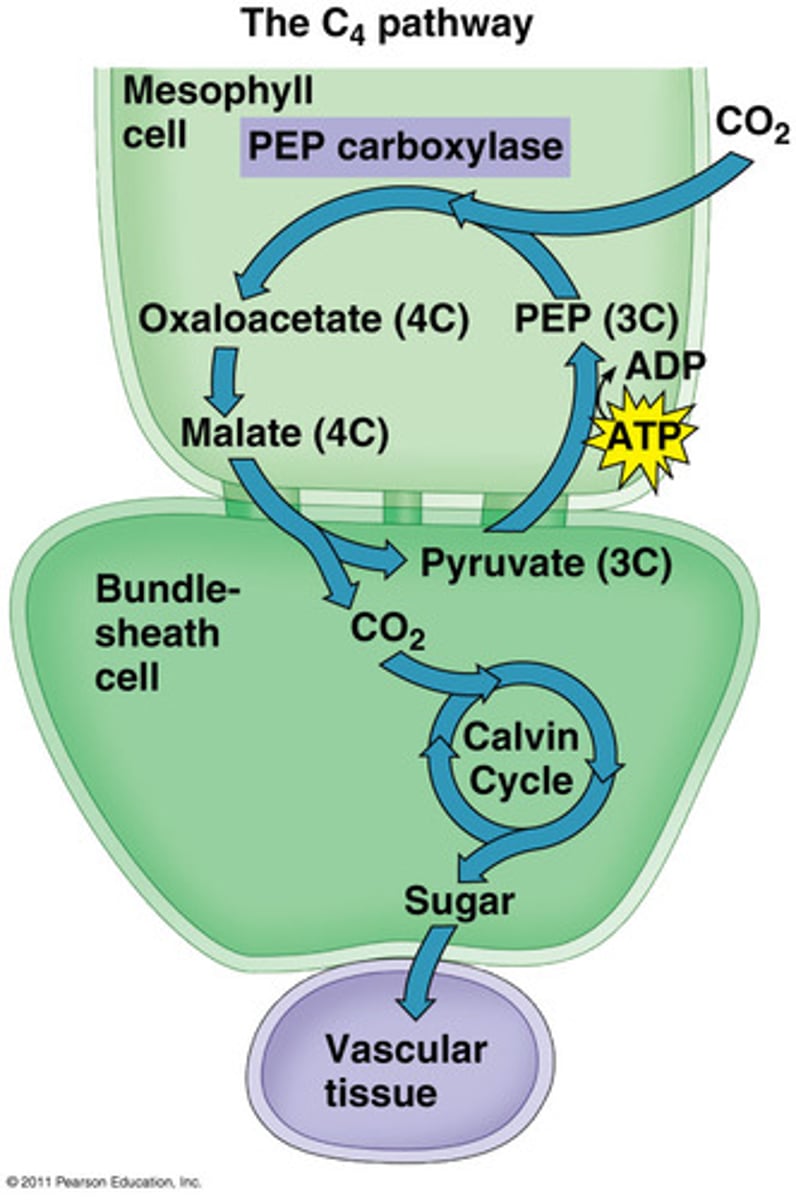
Bundle sheath cells in C4 plants
store CO2 in one cell and decarboxylase in an adjacent cell
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants
- use Calvin cycle and PEP carboxylase
- allows for storage of CO2
stomata of what plants close during the day and open at night?
CAM plants