BIS2C - Amoebozoans/Fungi
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
multinucleate body form
body type that forms by karyokinesis (without cytokinesis) OR by fusion of cell membranes
plasmodial slime molds
individual motile, diploid cel that undergoes nuclear division to form a single, enormous multinucleate cell (plasmodium) — cool, moist environment
under harsh conditions, can make a diploid resting stage or meiosis to make spores on fruiting bodies
what happens after spores germinate on plasmodial slime molds?
spores germinate to make swarm cells (can be asexual or fuse to make new diploid cell)
cellular slime molds
ameboid stages are called myxamoebae and are haploid
what happens when food runs out for cellular slime molds?
myxamoebae come together to make “slug” body when a signal is sent out
slug travels to new habitat and turns into a spore-dispersing body with a stalk (spore —> ameobae)
how can myxamoebae reproduce?
binary fission
form cysts that fuse to make diploid stages that then undergo meiosis
slug formation in cellular slime molds
can be made of one genotype or many genotypes
uniclonal slugs travel further but larger slugs travel further
synapomorphy of fungi
absorptive nutrition, chitin in cell walls
why is wood so stable?
cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose make up woody plants
cellulose made of beta 1,4-linked glucose units which is hard to break
hemicellulose tough
lignins are very tough, rigid, and resistant to decay
who can break down cellulose?
termites, cows, horses, koalas can digest cellular with help of unicellular euks and bacteria
ophryoscolex
fungi (using absorptive nutrition)
what composes the fungal body?
fungal body is called mycelium and is composed of many hyphae
features of hyphae
grow only at tips
secrete digestive enzymes at tips, so digest food in environment
why do fairy rings exist?
growing part of fungus (tips of hyphae) secrete digestive enzymes into the environment with many properties
like hydrophobic compounds, nitrogen, mushrooms
brown rot fungi
can break down cellulose and hemicellulose but leaves lignin behind (in conifers)
white rot fungi
breaks down cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin
in all trees
no fungi in the Carboniferous period
peat (partially decayed plant material) = C sink
formed when plants in swamps died; acidified swaps and decreased fungal abundance
bc no fungi, no decomposition of peat and plant matter became fossil fuels
what is a novel use of hyphae in capturing prey
some hyphae form a ring that can swell after absorbing water to capture nematode prey
saprobes
decomposers; fungi are important in nutrient cycling
fungi in composting
they break down cellulose and lignin making more organic material available to bacteria
different species of fungi present during mid and high temperature phases of composting (heat is released during decomposing)
what is the preferred complexity in the food sources for fungi?
prefer intermediate nutrient complexity (like monosaccharides, starch, cellulose)
fungi in bioremediation (mycoremediation)
fungi play important roles in cleaning up polluted sites by targeting pollutants like PCBs)
microsporidia
intracellular parasites with no mitochondria (infect immunocompromised humans)
their spores can invade cells by injecting cytoplasm in host and reproducing there
chytrids
non-monophyletic group that is the only fungal lineage with swimming spores and gametes
play a role in amphibian decline
mycorrhizae
lineage that involved in symbioses with land plants (increases surface area for nutrient absorption in exchange for carbs)
benefits plant gets from mycorrhizae
protection from root pathogens
increased longevity of fine roots
protection from heavy metals in soil
linkages between plants (common mycorrhizal network)
what are the two body forms of fungi?
mycelium (feeding, composed of hyphae)
reproductive fruiting structure (releases spores, often a “mushroom”)
where is the main morphological difference between fungi found?
in their fruiting body
aseptate vs septate hyphae
asepate hyphae do not have septa (walls) that prevent the free flow of cytoplasm
plasmogamy + when it evolved
fusion of cytoplasm
plasmogamy preces karyogamy (evolved before zygomycota)
karyogamy
fusion of two haploid nuclei, resulting in a dikaryon stage
general life cycle of fungi
variable life cycle for fungi
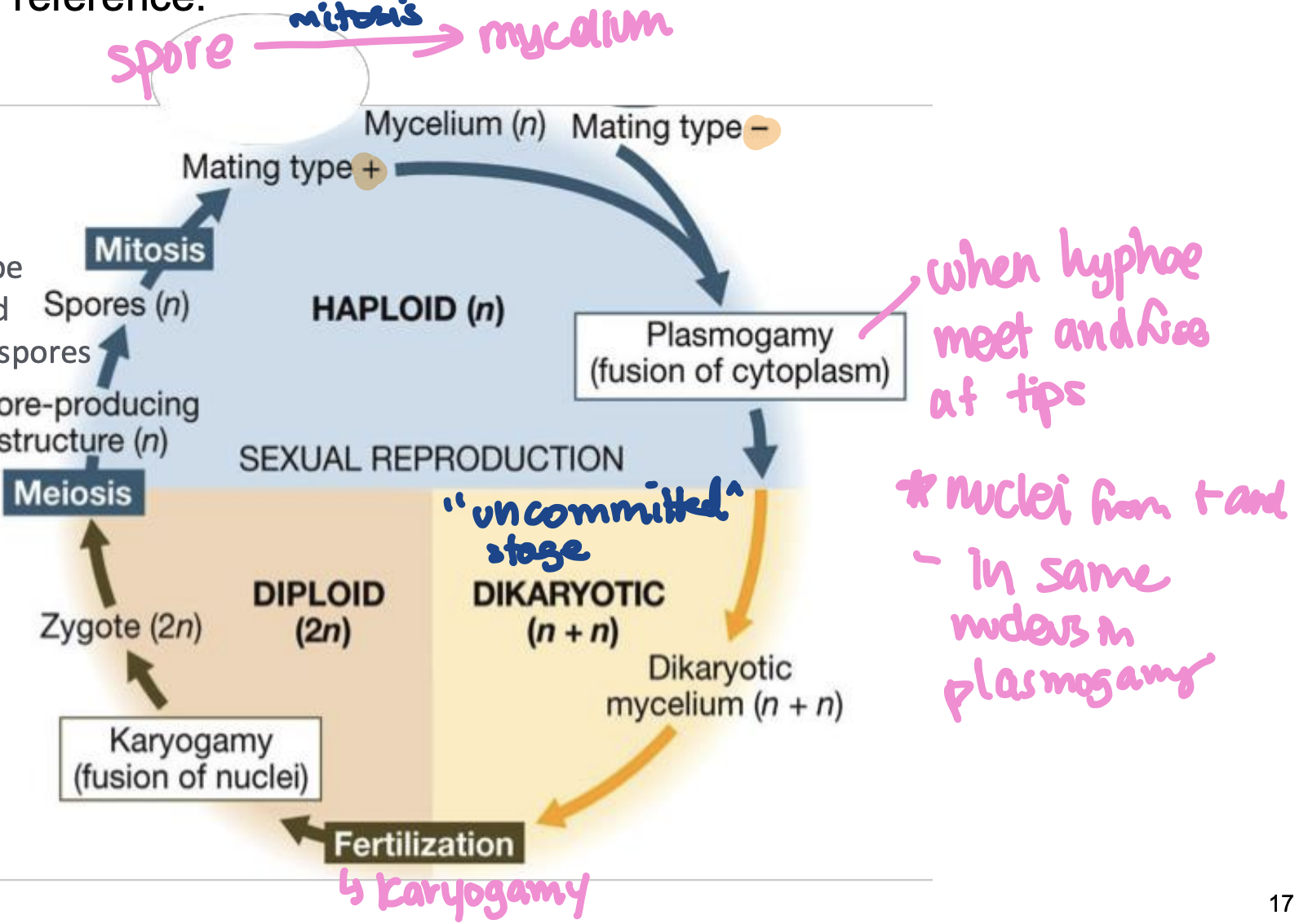
dikaryon
synapomorphy of dikarya
it is:
two, genetically distinct haploid nuclei in each cell
individual cells do not act as gametes (no real gametic stage)
hypal fusion with nuclei acting as gametes
ascomycota
largest group of fungi (2/3 of species) — many yeasts and molds
has ascus (its diagnostic spore structure)
many types of fruiting bodies (many cup-like)
asexual OR sexual reproduction
ascus
sac-like stage with 8 spores (internal spores) called ascospores
ascomycota life cycle
slide 20 lecture 22
fruiting body made of dikaryotic and monokaryotic hyphae
ascomycota fruiting bodies
many shapes, including edibles like morels and truffles
asexual reproduction in fungi
some fungi produce asexually via mitospores (conidia)
pinching off cells at tips of hyphae to start a new mycelium
molds
ascomycetes that lack sexual reproduction in life cycle
only using mitospores
yeasts
unicellular fungi that lack fruiting bodies
ex. are used in making bread and wine (releases CO2)
basidiomycota
2nd largest group of fungi; diagnostic spore structure is basidium (with external looking spores)
which structure on the fruiting body can tell you its a basidiomycota?
gills
basidia and basidiomycota extend out from the surface of a gill
which basidiomycota don’t have fruiting bodies? what example did we discuss in class?
smuts and rusts
ex. huitlacoche (smut fungi) — a delicacy that used in food
examples of enclosed fruiting bodies
puffballs and truffles
evolved several time within basidiomycota and ascomycota (gills in the center)
subterranean fruiting body
probably evolved in response to dry conditions
mostly dispersed by animals (humans dig up truffles)
lichens
symbiosis between ascomycota (the mycobiont) and cyanobacteria or algae (photobiont) with basidiomycete yeast in upper crust protecting lichen with vulpanic acid
fungi are obligated to their photobiont (but not the other way around)
the symbiotic relationship present in lichens
ascomycota gets sugar
provides shelter, moisture, mineral
what forms the body of the lichens?
formed from fungal hyphae
how can reindeer feed on lichens?
have a unique starch called lichenin
reindeer have lichenase to break starch down to glucose
fungi as parasites — plants
have a large econ impact as they are common plant parasites
methyl bromide and fungi
used methyl bromide as a gas fumigant to protect crops from fungi BUT depletes ozone so being phased out
bad for strawberries
rice blast disease
causes lots of loss on rice crop
treatment options limited as fungi spreads quickly and develops resistance
Claviceps
invades grasses like rye
eating infected rye causes St. Anthony’s Fire
St. Anthony’s Fire
burning of limbs associated with severe vasocontriction
but can be used to stop migranes, stop bleeding after childbrith, and treat Parkinson’s
white nose syndrome
caused by Pseudogymnoascus destructans
decimate bats throughout the US as it disrupts hibernation and uses vital fat reserves
Cordyceps
attach to arthropods and take control of their muscles to modify their behavior
makes anthropod into a spore dispersing structure
psilocybin
hallucinogens
competes with serotonin and causes hallucinations
aflatoxin
caused by a fungi that commonly infects food sources and can have lethal effects on animals (like liver cancer)
aflatoxin and soy sauce
close relative of A. flavus, A. oryzae, is used to flavor soy sauce
may be correlated with higher rates of cancer in E/SE Asian countries
disease with inhaled spores
histoplasmosis (caused by inhaling conidia + grows as yeast) and bagpiper’s lung
ringworm
fungal skin infection