Business management unit 3
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
The role of finance
finance is needed for starting up a new business, for day to day operations, growth, and to expand the business
Why do firms need capital
To start a business
Day-to-day operations
Growth and expansion
Capital expenditure
Spending on items lasting more than a year
Fixed assests- machinery, land, equipment
Long-term investments
used collateral
Examples- Machinery, technology, vehicles
Revenue expenditure
Revenue expenditure is spending on goods and services that a business uses in the short-term
Money on day to day activities
Examples- Rent, wages, raw materials, insurance, fuel
Otherwise, in the long run a business would be unable to grow and continue operating
internal sources of finance
personal funds- personal savings of owners and risk for owners
Retained profits- Value of profit kept by the business after paying off the tax, interest, and dividends (to the shareholders) to use within the business
Often used for purchasing and/or upgrading fixed assets which will increase returns
advantages- cheap, permanent source, flexible, controlled by owners
Disadvantages- start ups are rarely profitable at first, might be insufficient for expansion, might be used up
Sale of assests- Businesses can sell their unused assets, such as selling old machinery and computer equipments that have been replaced
advantages- no interest or borrowing costs
disadvantage- available to established businesses only
External sources of finance
share capital- money raised from selling shares in a company
Loan
Overdrafts
Grants
Debt factoring
Trade credit- payment made a later stage agreed upon between seller and buyer
Leasing- the lessee pays rental income to hire assets from the lessor, who is the legal owner of the assets.
venture capital- a form of high-risk capital, usually in the form of loans or shares, invested by venture capital firms, usually at the start of a business idea
overdrafts
When a lending institution allows a firm to withdraw more money than it currently has in its account
grants
Funds usually provided by a government, foundation, trust, or other agency to businesses which does not need to be repaid.
subsidies
Financial Assistance granted by a government, NGO, or an individual to support businesses that are in the public interest
loan
Money sourced from financial institutions such as banks, with interest charged on the loan to be repaid
debt factoring
a business sells its invoice to a third party
short-term finance
Day to day running of business
one year or less
examples- overdrafts, trade crediting, debt factoring
medium- term finance
1-5 years
equipment, machinery, vehicles
examples - leasing, grants, loans
long-term finance
expansion of business
5-30 years
examples - loans, share capital
fixed cost
costs of production which have to be paid regardless of output level
Examples- rent, interests, lease payments
independent of output level
semi-variable cost
An element of both fixed and variable costs
Changes when production exceeds a certain level of output
variable cost
cost of production which change in proportion to output level
Examples- raw materials, packaging
direct cost
related to an individual product or to the output of a specific product
Indirect costs
cannot be traced directly to the output of a product
sales volume
the number of products sold
sales revenue = price * quantity
revenue stream
Revenue streams are the sources of revenues or incomes for a company or a business
Firms utilising different sources/methods to generate income
revenue streams examples
Advertising revenue: this is when an organisation is offering advertising space and charges other organisations for posting ads in this space
Royalties/franchisor: royalty payments are made to artists for the use of their artworks or to franchisors for the use of franchise
Sponsorship deals: the way it usually works is sponsor gives you financial support in exchange for an extra advertising space and publicity.
Subscriptions: use or access goods or services
Merchandise: in addition to the main trading activity, some organisations sell their souvenirs or clothes to get extra revenues
Dividends: companies that own stock/shares within another business can also get dividends
Donations: charities and non-profit
Interest earnings: on cash deposits in banks
Subversions: Government subsidies- aimed at benefiting society
wholesale market
a market where a trader buys goods from a manufacturer in bulk and re-sells the goods to business houses or retailers to further sell the goods to end consumers
Venture Capital
Financial capital proved by investors to high-risk, high potential start ups or small businesses.
Business Angels
Highly affluent individuals who provide financial capital to small startups in return for ownership in their business.
High Geared
Large proportion of loan capital to share capital
Low Geared
Small proportion of loan capital to share capital
Cost
The total expenditure incurred by a business in order to run its operations
Revenue
Measure of the money generated from the sale of goods/services
Contribution
sum of money that remains after all direct and variable costs have been taken away from sales revenue
Contribution Per Unit
Refers to the difference between the selling price per unit and the variable costs
Margin of Safety
The difference between the firm’s sales and the break-even quantity
Target Profit Output (TPO)
The level of output that is needed to earn a specified amount of profit
Trading Account
Shows the difference between the sales revenue and the cost of goods sold
Profit and Loss Account
Second part of the income statement that shows the net profit before interest and tax, net profit before tax, and net profit after interest
Appropriation Account
final part of the profit/loss account that shows how the company's net profit after interest and tax is distributed
Gross Profit
profit made by a company (sales revenue - cost of goods sold)
how to improve gross profit
lower costs
increase sales
net profit
the profit after all expenses are subtracted from the total revenue
Dividends
A sum of the money paid to shareholders which is decided by the board of directors
Stock
unsold goods, raw materials or work-in-progress that the company has in hand at the end of the trading period
Opening Stock
the quantity of goods produced/owned by the business that are unsold in the previous accounting period
Closing Stock
the quantity of goods produced/owned by the business after sales at the close of the accounting period such as a year
Balance Sheet
a statement of the financial position of a business in terms of assets, liabilities and owner's equity at a particular point in time
Assets
all items of value that are owned by the firm, such as cash or buildings
Fixed Assets
Long-term assets that last in a business for more than 12 months (Ex. vehicles, buildings, and machinery)
Current Assets
Short-term assets that last in a business for up to 12 months (Ex. Cash, debtors, stock)
Liabilities
all funds owed by the company to financial and other institutions, such as banks and suppliers
Long-term liabilities
Long-term debts payable after 12 months by the business (Ex. Mortgages)
Current Liabilities
Short-term debts that are payable within 12 months (Ex. creditors, tax, overdraft)
Working Capital
(Net current assets) Helps establish whether a firm can pay its day-to-day running costs
Equity
shows the value of the business attributable to its owners
intangible assets
Non-physical fixed assets that have the ability to earn revenue for a business
Debtors
people who owe money
Creditors
People who lend money
Patents
exclusive rights to make or sell inventions
Goodwill
the value of all favorable attributes that relate to a company
Copyright Laws
laws that provide creators with the exclusive right to protect the production and sale of their artistic or literary work
Trademarks
Recognizable symbol, word, phrase, or design that is officially registered and identifies a product or business
Depreciation
the decline in the value of fixed assets over time mainly due to usage and newer models or better technologies being available
Obsolescence
state of being no longer useful or in fashion
Straight-line method
Spreads out the cost of an asset equally over its lifetime by deducting a given constant amount of depreciation
Reducing Balance Method
the value of the asset depreciates by a predetermined percentage for the duration of its life
more realistic
Residual Value
the estimated value of a fixed asset at the end of its useful life
Ratio Analysis
Financial management tool for analysing and judging the performance of a business
Profitability Ratios
show a company's overall efficiency, performance and financial position
liquidity ratio
ability of firm to pay its short-term liabilities
current ratio
looks at whether a company can pay/cover its short-term debts
current assets/current liabilities
acid test (quick) ratio
similar to current ratio but ignores stocks
cash
cash-
held by hand
deposited in bank account
role of cash-
business need cash to sustain itself
inability to pay suppliers, employees or creditors would a successful business into bankruptcy
profit
profit-
difference between total sales revenue and costs
any sales beyond- lead to a profit
purchases made can be through a cheque, cash, on credit (Buy now pay later)
credit option-
enables customers to buy right away
might result in cashflow problems for the business
short-term liquidity problems
occur due to-
poor credit control
expanding too quickly
hence cashflow management is key
working capital cycle
the delay between cash receipts from customers and cash payments to supplier
working capital cycle cont’d
working capital- The cash or liquid assets available for the daily running of a business
used to pay suppliers, employees, creditors
liquidity- how easily an asset available could be turned into cash
insolvency- working capital insufficient to meet current liabilities
liquidation- selling off of a business
creditors take legal action against the business to recover their money
working capital=current asset-current liabilities
current asset
the liquid resources, which could be converted into cash within a year
cash
Debtors
stock
current liabilities
money owed which needs to be repaid within a year
overdrafts
creditors
tax
cash flow
Financial document that shows expected movement of cash inside and outside of a business per time period
Cash inflows – usually from sales revenues when cash payment is received
Cash outflows – payment of bills, usually itemised expenses
Net cash flow – the differences between cash inflow and outflow
reasons for cashflow
business planning
is the business financially healthy
plan for and alleviate liquidity crisis
causes of cashflow problems
overtrading
over borrowing
overstocking
poor credit control
unforeseen changes
strategies to deal with cash flow problems
reducing cash outflows
improving cash inflows
seeking alternative sources of finance
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
Measures the financial performance of a firm compared with the amount of capital invested
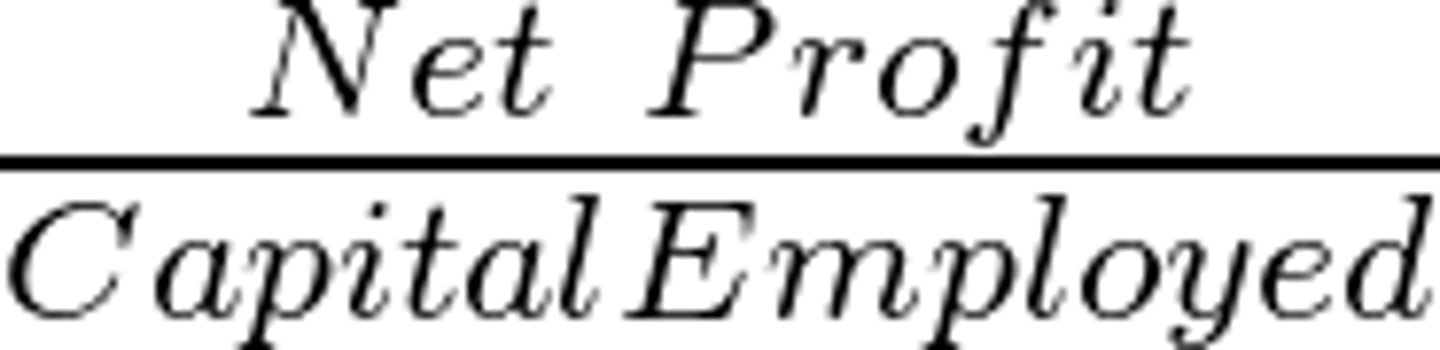
Stock Turnover Ratio
Measures how quickly a firm's stock is sold and replaced over a given period
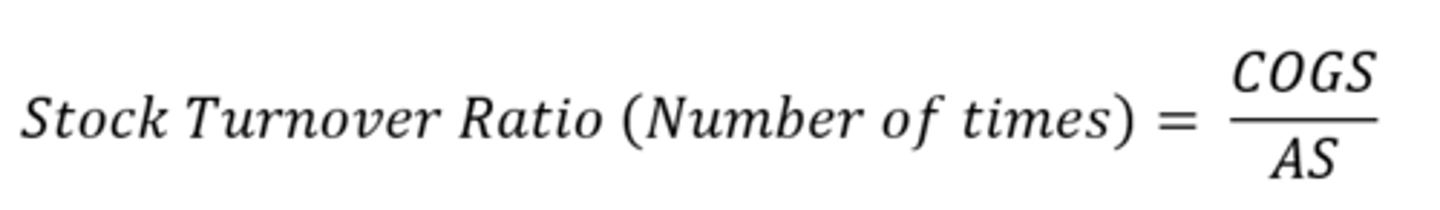
Debtor Days
Measures the number of days it takes on average for a firm to collect its debts from customers if it has sold goods to on credit.
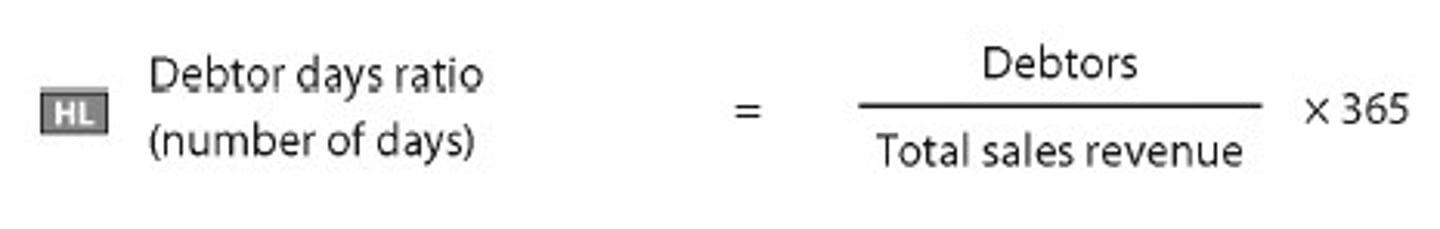
Creditor Days
measures the average number of days a firm takes to pay its creditors
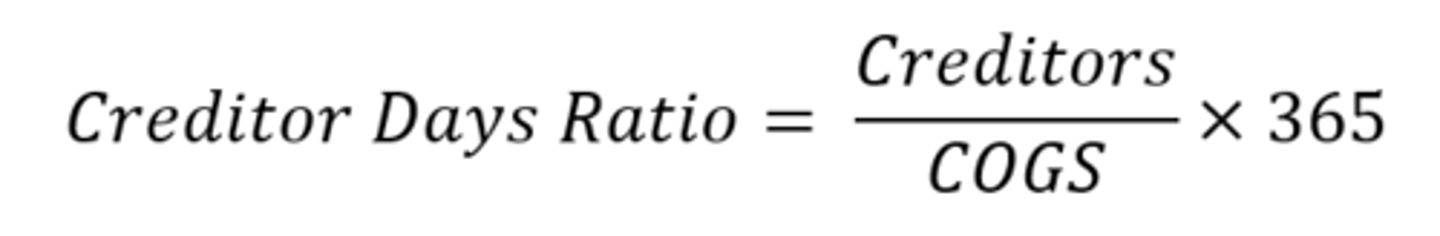
Gearing Ratio
Measures the extent to which capital employed by a firm is financed from loan capital
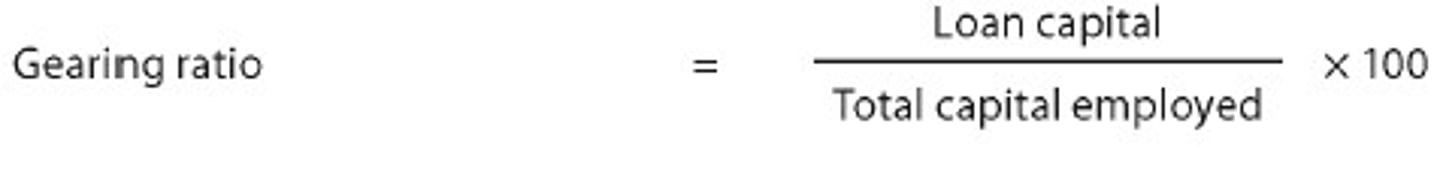
Opening Balance
The amount of money in a business at the start of the month
Closing Balance
The amount of money in a business at the end of the month
Investment
Purchase of asset with potential to yield a financial benefit in the future
Investment Appraisal
Quantitative techniques used to calculate the financial costs and benefits of an investment
Payback Period
Estimates the length of time required for an investment project to pay back its initial cost outlay

Average Rate of Return
Measures the annual net return on an investment as a percentage of its capital cost
Net Present Value
considers time value of money
Budget
A financial plan for expected revenue and expenditure for an organisation for a given time period
reasons-
planning and guidance
coordination
control
motivation
Cost Center
Department or unit of business that incurs costs
Doesn’t contribute to profit directly.
e.g. Marketing and HR departments
Departments must be made aware of their costs to help managers operate within the allocated budget
Profit Center
Branch of a company that is accounted for on a standalone basis for the purposes of profit calculation
Used to know which aspects of a business are the most and least profitable
Managers have to be responsible for costs and earnings of their profit center, and they should know how to best use resources to maximise profitability
variance analysis
variance- difference between budgets and actuals
favorable variance-
adverse variance- overspending and/or underselling
Benchmarking
a process by which a company compares its performance with that of high-performing organizations